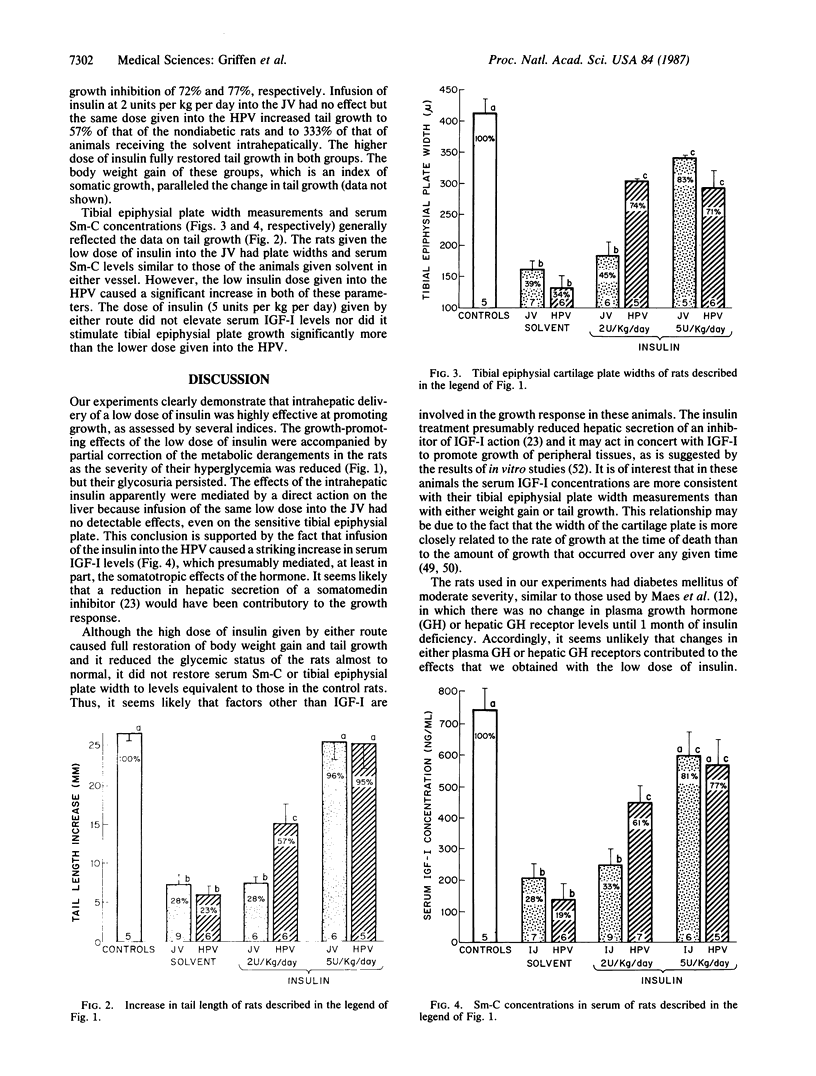
Abstract
The functional significance of the portal vascular link between the beta cells of the pancreatic islets and the liver has not been established. Previous studies indicated that insulin does not acutely regulate glucose metabolism by a direct hepatic effect. More recent observations suggest that the role of insulin in regulating body growth may be mediated, at least in part, by the liver. Our experiments were designed to test whether insulin can promote body growth and regulate glucose metabolism by a direct hepatic action in vivo. Rats were made diabetic by injections of streptozotocin, and insulin or solvent was infused into the jugular vein (JV) or the hepatic portal vein (HPV) for 14 days using catheters that were attached to osmotic minipumps. Infusion of a low dose of insulin (2 units per kg per day) into the JV had no effects on the hyperglycemia, body weight gain, tail growth, tibial epiphysial cartilage plate thickness, or serum levels of somatomedin C in the diabetic rats. However, the same dose given into the HPV caused a 30% reduction of blood glucose and stimulated a significant degree of growth, as determined by all indices. Infusion of a higher dose of insulin (5 units per kg per day) into either vein caused full restoration of body weight gain and tail growth and it restored the glycemic status almost to normal. However, it did not increase the tibial epiphysial plate width or serum somatomedin C levels above those of the rats given the low dose of the hormone into the HPV. These results indicate that insulin can act directly on the liver to promote body growth and to regulate glucose metabolism. The significance of direct delivery of insulin from the pancreatic beta cells to the liver may be as much for growth control as for glucose homeostasis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amiel S. A., Sherwin R. S., Hintz R. L., Gertner J. M., Press C. M., Tamborlane W. V. Effect of diabetes and its control on insulin-like growth factors in the young subject with type I diabetes. Diabetes. 1984 Dec;33(12):1175–1179. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.12.1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson I., Billig H., Fryklund L., Hansson H. A., Isaksson O., Isgaard J., Nilsson A., Rozell B., Skottner A., Stemme S. Localization of IGF-I in adult rats. Immunohistochemical studies. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Feb;126(2):311–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton I. K., Dornan T. L., Pocock A. E., Turner R. C., Bron A. J. Plasma somatomedin activity and diabetic retinopathy. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1983 Jul;19(1):105–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1983.tb00748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkison P. R., Hayden L. J., Bala R. M., Hollenberg M. D. Production of somatomedin-like activity by human adult tumor-derived, transformed, and normal cell cultures and by cultured rat hepatocytes: effects of culture conditions and of epidermal growth factor (urogastrone). Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;62(12):1343–1350. doi: 10.1139/o84-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkison P. R., Weidman E. R., Bhaumick B., Bala R. M. Release of somatomedin-like activity by cultured WI-38 human fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1980 Jun;106(6):2006–2012. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-6-2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binoux M., Lassarre C., Hardouin N. Somatomedin production by rat liver in organ culture. III. Studies on the release of insulin-like growth factor and its carrier protein measured by radioligand assays. Effects of growth hormone, insulin and cortisol. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1982 Mar;99(3):422–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botz C. K., Leibel B. S., Zingg W., Gander R. E., Albisser A. M. Comparison of peripheral and portal routes of insulin infusion by a computer-controlled insulin infusion system (artificial endocrine pancreas). Diabetes. 1976 Aug;25(8):691–700. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.8.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R. Multiple hormones stimulate the production of somatomedin by cultured human fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 May;58(5):850–856. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-5-850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J. Hormonal control of immunoreactive somatomedin production by cultured human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):10–19. doi: 10.1172/JCI110001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Van Wyk J. J. Evidence for a functional role of endogenously produced somatomedinlike peptides in the regulation of DNA synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts and porcine smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):1914–1918. doi: 10.1172/JCI111906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R. Variables controlling the secretion of a somatomedin-like peptide by cultured porcine smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1985 Mar;56(3):418–426. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.3.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. P., Jasti K., Rye D. L. Somatomedin on insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Aug;45(2):236–239. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-2-236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover C. A., Hintz R. L., Rosenfeld R. G. Comparative effects of somatomedin C and insulin on the metabolism and growth of cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jan;122(1):133–141. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041220120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Applewhite G. T., Underwood L. E. Evidence that somatomedin is synthesized by multiple tissues in the fetus. Dev Biol. 1980 Mar 15;75(2):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Stiles A. D., Underwood L. E. Tissue concentrations of somatomedin C: further evidence for multiple sites of synthesis and paracrine or autocrine mechanisms of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):935–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Mariz I. K., Blethen S. L. Inhibition of access of bound somatomedin to membrane receptor and immunobinding sites: a comparison of radioreceptor and radioimmunoassay of somatomedin in native and acid-ethanol-extracted serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Oct;51(4):781–788. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-4-781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Phillips L. S., Mueller M. C. The effects of insulin and growth hormone on the release of somatomedin by the isolated rat liver. Endocrinology. 1976 May;98(5):1214–1219. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-5-1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman S. D., Hirshberg G. E., Dodi G., Raizman M. E., Scharp D. W., Ballinger W. F., Lacy P. E. Intrasplenic islet isografts. Surgery. 1977 Sep;82(3):386–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch D. R., Wise P. H., Morris P. J. Successful intra-splenic transplantation of syngeneic and allogeneic isolated pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1977 May;13(3):195–199. doi: 10.1007/BF01219699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson L. I., Menander-Sellman K., Stenström A., Thorngren K. G. Rate of normal longitudinal bone growth in the rat. Calcif Tissue Res. 1972;10(3):238–251. doi: 10.1007/BF02012553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinze E., Ranke M., Manske E., Vetter U., Voigt K. H. The effect of glibenclamide on plasma insulin, plasma somatomedin bioactivity and skeletal growth in hypophysectomized rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1982 Oct;101(2):187–192. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1010187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Milner R. D. Insulin as a growth factor. Pediatr Res. 1985 Sep;19(9):879–886. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198509000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner J. M., Kemp S. F., Hintz R. L. Growth hormone and somatomedin in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Dec;53(6):1148–1153. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-6-1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp C. B., Knight M. J., Scharp D. W., Ballinger W. F., Lacy P. E. Effect of transplantation site on the results of pancreatic islet isografts in diabetic rats. Diabetologia. 1973 Dec;9(6):486–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00461694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogawa M., Takano K., Asakawa K., Hizuka N., Tsushima T., Shizume K. Insulin stimulation of somatomedin A production in monolayer cultures of rat hepatocytes. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1983 Jul;103(3):385–390. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1030385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogawa M., Takano K., Hizuka N., Asakawa K., Shizume K. Effect of GH and insulin on the generation of somatomedin by perfused rat liver. Endocrinol Jpn. 1982 Apr;29(2):141–147. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.29.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberton R. P., Goodman A. D., Kassoff A., Rubin C. L., Treble D. H., Saba T. M., Merimee T. J., Dodds W. J. Von Willebrand factor (VIII R:Ag), fibronectin, and insulin-like growth factors I and II in diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy. Diabetes. 1984 Feb;33(2):125–129. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z. Somatomedin, insulin, growth hormone and growth: a review. Isr J Med Sci. 1982 Aug;18(8):823–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADISON L. L., UNGER R. H. The physiologic significance of the secretion of endogenous insulin into the portal circulation. I. Comparison of the effects of glucagon-free insulin adminstered via the portal vein and via a peripheral vein on the magnitude of hypoglycemia and peripheral glucose utilization. J Clin Invest. 1958 May;37(5):631–639. doi: 10.1172/JCI103646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN F. I., LEONARDS J. R., MILLER M. A comparison of the effect of the intraportal and intravenous administration of I131-insulin on peripheral blood glucose and serum radioactivity. Metabolism. 1959 Jul 2;8(4 Pt 2):472–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maes M., Ketelslegers J. M., Underwood L. E. Low plasma somatomedin-C in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Correlation with changes in somatogenic and lactogenic liver binding sites. Diabetes. 1983 Nov;32(11):1060–1069. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.11.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merimee T. J., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors. Studies in diabetics with and without retinopathy. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 1;309(9):527–530. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309013090904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mick C. C., Nicoll C. S. Prolactin directly stimulates the liver in vivo to secrete a factor (synlactin) which acts synergistically with the hormone. Endocrinology. 1985 May;116(5):2049–2053. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-5-2049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. G. Rate of insulin infusion with a minipump required to maintain a normoglycemia in diabetic rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983 Jan;172(1):74–78. doi: 10.3181/00379727-172-41529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rerup C. C. Drugs producing diabetes through damage of the insulin secreting cells. Pharmacol Rev. 1970 Dec;22(4):485–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanus J. A., Rabinovitch A., Rechler M. M. Neonatal rat islet cell cultures synthesize insulin-like growth factor I. Diabetes. 1985 Jul;34(7):696–702. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.7.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolf M. C., Sherwin R. S., Markowitz R., Bates S. E., Genel M., Hochstadt J., Tamborlane W. V. Effect of intensive insulin treatment on linear growth in the young diabetic patient. J Pediatr. 1982 Sep;101(3):333–339. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOEMAKER W. C., MAHLER R., ASHMORE J. The effect of insulin on hepatic glucose metabolism in the unanesthetized dog. Metabolism. 1959 Jul 2;8(4 Pt 2):494–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARZL T. E., BUTZ G. W., Jr, MEYER W. H., Jr, TOROK E. E., DOLKART R. E. Effect in dogs of various portal vein shunts on response to insulin. Am J Physiol. 1962 Aug;203:275–277. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARZL T. E., SCANLAN W. A., YANOF H. M., THORNTON F. H., WENDEL R. M., STEARN B., LAZARUS R. E., MCALLISTER W., SHOEMAKER W. C. A COMPARISON OF THE HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF INSULIN WITH SYSTEMIC VENOUS AND PORTAL VENOUS ADMINISTRATION. J Surg Res. 1963 Aug;3:293–300. doi: 10.1016/s0022-4804(63)80009-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalch D. S., Heinrich U. E., Draznin B., Johnson C. J., Miller L. L. Role of the liver in regulating somatomedin activity: hormonal effects on the synthesis and release of insulin-like growth factor and its carrier protein by the isolated perfused rat liver. Endocrinology. 1979 Apr;104(4):1143–1151. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-4-1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheiwiller E., Guler H. P., Merryweather J., Scandella C., Maerki W., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Growth restoration of insulin-deficient diabetic rats by recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):169–171. doi: 10.1038/323169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlechter N. L., Russell S. M., Greenberg S., Spencer E. M., Nicoll C. S. A direct growth effect of growth hormone in rat hindlimb shown by arterial infusion. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):E231–E235. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.3.E231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. D., Baxter R. C. Production of insulin-like growth factor I and its binding protein in rat hepatocytes cultured from diabetic and insulin-treated diabetic rats. Endocrinology. 1986 Nov;119(5):2346–2352. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-5-2346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. D., Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Production of insulin-like growth factor I and its binding protein by adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Endocrinology. 1985 Mar;116(3):1094–1101. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-3-1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stracke H., Schulz A., Moeller D., Rossol S., Schatz H. Effect of growth hormone on osteoblasts and demonstration of somatomedin-C/IGF I in bone organ culture. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1984 Sep;107(1):16–24. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1070016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. S. Growth-stimulatory actions of insulin in vitro and in vivo. Endocr Rev. 1984 Spring;5(2):356–369. doi: 10.1210/edrv-5-2-356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Morell B., Walter H., Laron Z., Froesch E. R. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and its carrier protein in various metabolic disorders. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1980 Dec;95(4):505–517. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0950505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]