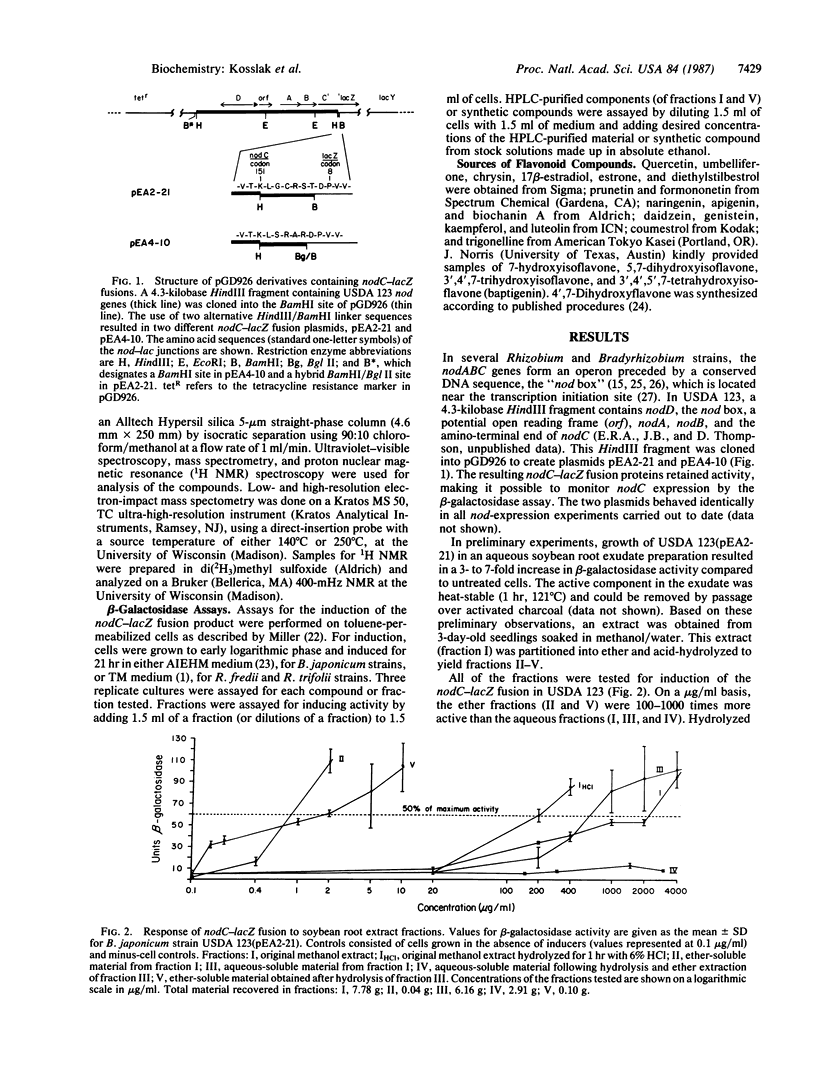
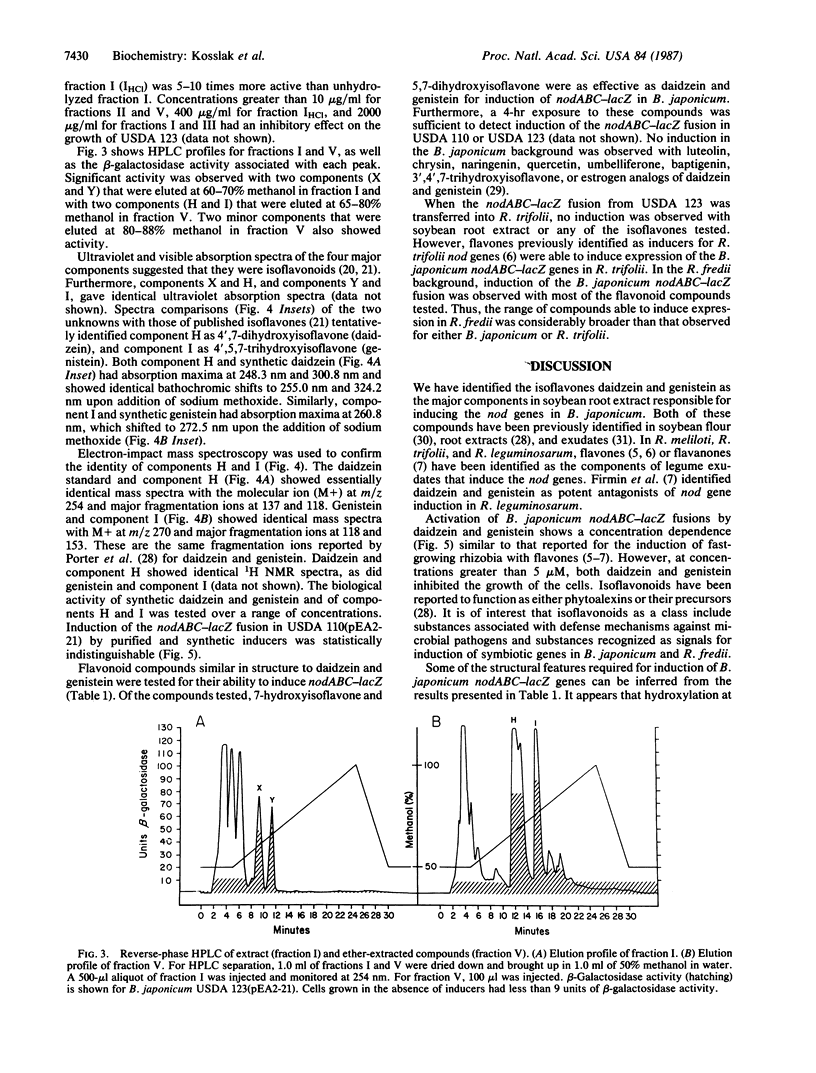
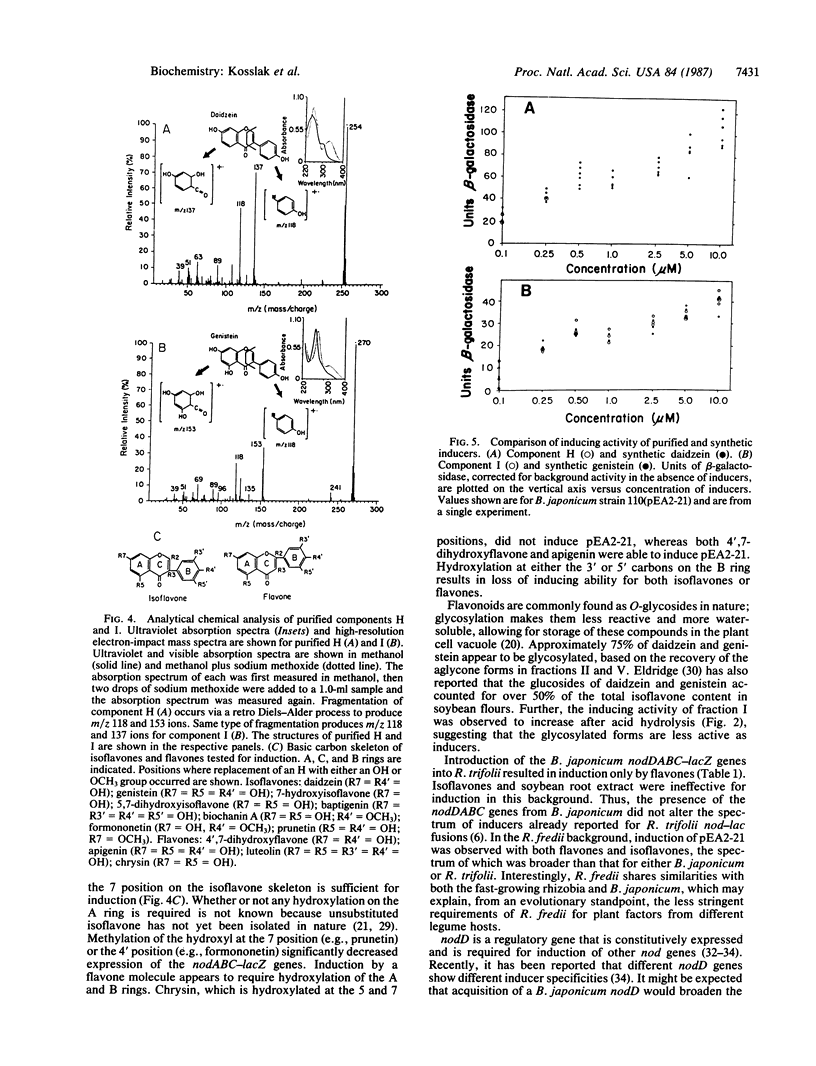
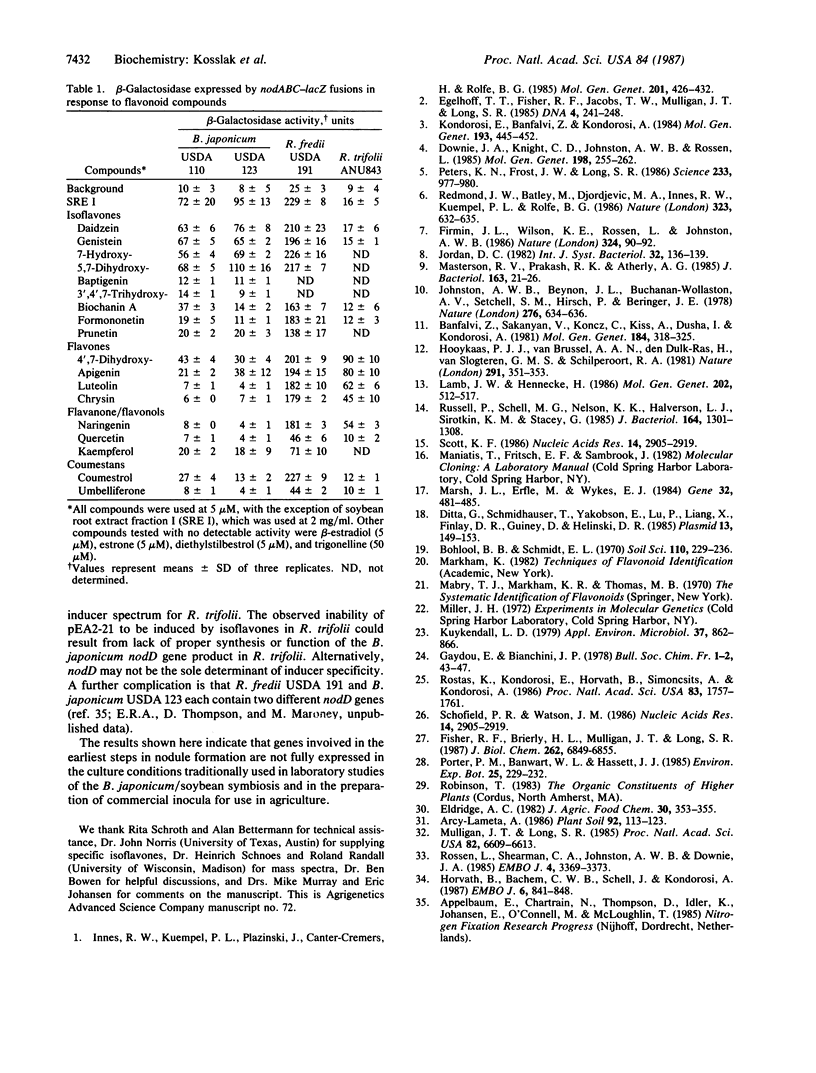
Abstract
The early events in legume nodulation by Rhizobium spp. involve a conserved gene cluster known as the common nod region. A broad-host-range plasmid (pEA2-21) containing a Bradyrhizobium japonicum nodDABC-lacZ translational fusion was constructed and used to monitor nod gene expression in response to soybean root extract. Two inducing compounds were isolated and identified. Analysis using ultraviolet absorption spectra, proton nuclear magnetic resonance, and mass spectrometry showed that the two inducers were 4′,7-dihydroxyisoflavone (daidzein) and 4′,5,7-trihydroxyisoflavone (genistein). Induction was also seen with some, but not all, of the flavonoid compounds that induce nod genes in fast-growing Rhizobium strains that nodulate clover, alfalfa, or peas. When pEA2-21 was introduced into Rhizobium trifolii, it was inducible by flavones but not by daidzein and genistein. In Rhizobium fredii, pEA2-21 was induced by isoflavones and flavones. Thus, the specificity of induction appears to be influenced by the host-strain genome.
Keywords: symbiosis, nodulation, nodC-lacZ fusion, soybeans
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bánfalvi Z., Sakanyan V., Koncz C., Kiss A., Dusha I., Kondorosi A. Location of nodulation and nitrogen fixation genes on a high molecular weight plasmid of R. meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):318–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00272925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Schmidhauser T., Yakobson E., Lu P., Liang X. W., Finlay D. R., Guiney D., Helinski D. R. Plasmids related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelhoff T. T., Fisher R. F., Jacobs T. W., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Nucleotide sequence of Rhizobium meliloti 1021 nodulation genes: nodD is read divergently from nodABC. DNA. 1985 Jun;4(3):241–248. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Brierley H. L., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Transcription of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Identification of a nodD transcription initiation site in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6849–6855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath B., Bachem C. W., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Host-specific regulation of nodulation genes in Rhizobium is mediated by a plant-signal, interacting with the nodD gene product. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):841–848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04829.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuykendall L. D. Transfer of R factors to and between genetically marked sublines of Rhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):862–866. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.862-866.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson R. V., Prakash R. K., Atherly A. G. Conservation of symbiotic nitrogen fixation gene sequences in Rhizobium japonicum and Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):21–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.21-26.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Induction of Rhizobium meliloti nodC expression by plant exudate requires nodD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6609–6613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Frost J. W., Long S. R. A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3738520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossen L., Shearman C. A., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. The nodD gene of Rhizobium leguminosarum is autoregulatory and in the presence of plant exudate induces the nodA,B,C genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3369–3373. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostas K., Kondorosi E., Horvath B., Simoncsits A., Kondorosi A. Conservation of extended promoter regions of nodulation genes in Rhizobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1757–1761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Schell M. G., Nelson K. K., Halverson L. J., Sirotkin K. M., Stacey G. Isolation and characterization of the DNA region encoding nodulation functions in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1301–1308. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1301-1308.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K. F. Conserved nodulation genes from the non-legume symbiont Bradyrhizobium sp. (Parasponia). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2905–2919. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K. F. Conserved nodulation genes from the non-legume symbiont Bradyrhizobium sp. (Parasponia). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2905–2919. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



