Abstract
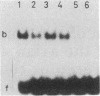
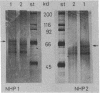
The DNA sequence corresponding to the estradiol response element has been synthesized and tested in vitro for the binding of specific proteins. Gel retardation experiments combined with dimethyl sulfate protection experiments revealed that this region binds two nonhistone proteins (NHPs). One of them, NHP-1, has a molecular weight of 70,000 and binds specifically to the dyad symmetry sequence GGTCAGCGTGACC. The NHP-1 can be separated from the estradiol receptor chromatographically; it does not bind estradiol and does not cross-react with an antibody directed against the estradiol receptor. A series of synthetic "mutant" oligonucleotides were tested in a protein-DNA binding competition assay. Deletion of the GCG in the center of the dyad symmetry sequence suppressed the binding of NHP-1 by 90%, and the conversion of any GC pair to an AT pair decreased the affinity of the binding site for NHP-1. Methylation of the two CpGs on both strands of the dyad symmetry sequence decreased the affinity of the binding site for NHP-1 by 60%, whereas hemimethylation of the same structure did not inhibit the binding of NHP-1. NHP-1 and NHP-2, the NHP binding to the DNA next to the dyad symmetry sequence, bind exclusively to double-stranded DNA. NHP-2 has a molecular weight of 60,000. NHP-1 and NHP-2 are neither tissue nor species specific. In vitro reconstitution experiments show that NHP-1 and NHP-2 increase the binding efficiency of the estradiol-receptor complex to the estradiol response element.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Best-Belpomme M., Mester J., Weintraub H., Baulieu E. E. Oestrogen receptors in chick oviduct. Characterization and subcellular distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):537–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürk R. R., Eschenbruch M., Leuthard P., Steck G. Sensitive detection of proteins and peptides in polyacrylamide gels after formaldehyde fixation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:247–254. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hora J., Horton M. J., Toft D. O., Spelsberg T. C. Nuclease resistance and the enrichment of native nuclear acceptor sites for the avian oviduct progesterone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8839–8843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Seldran M. Association of transcriptionally active vitellogenin II gene with the nuclear matrix of chicken liver. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2005–2008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02082.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Seldran M., Geiser M. Preferential binding of estrogen-receptor complex to a region containing the estrogen-dependent hypomethylation site preceding the chicken vitellogenin II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):429–433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Schorpp M., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5' flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Staub A., Chambon P. Localisation of the oestradiol-binding and putative DNA-binding domains of the human oestrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2231–2236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois A. J., Lapis K., Ishizaki R., Beard J. W., Bolognesi D. P. Isolation of a transplantable cell line induced by the MC29 avian leukosis virus. Cancer Res. 1974 Jun;34(6):1457–1464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinari A. M., Medici N., Moncharmont B., Puca G. A. Estradiol receptor of calf uterus: interactions with heparin-agarose and purification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4886–4890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncharmont B., Anderson W. L., Rosenberg B., Parikh I. Interaction of estrogen receptor of calf uterus with a monoclonal antibody: probing of various molecular forms. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3907–3912. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncharmont B., Su J. L., Parikh I. Monoclonal antibodies against estrogen receptor: interaction with different molecular forms and functions of the receptor. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6916–6921. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvihill E. R., LePennec J. P., Chambon P. Chicken oviduct progesterone receptor: location of specific regions of high-affinity binding in cloned DNA fragments of hormone-responsive genes. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):621–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., Gilbert W. An amino-terminal fragment of lac repressor binds specifically to lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5851–5854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Ohno T., Jost J. P. In vitro RNA synthesis and expression of vitellogenin gene in isolated chicken liver nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Apr;5(4):1353–1370. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puca G. A., Nola E., Hibner U., Cicala G., Sica V. Interaction of the estradiol receptor from calf uterus with its nuclear acceptor sites. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6452–6459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puca G. A., Sica V., Nola E. Identification of a high affinity nuclear acceptor site for estrogen receptor of calf uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):979–983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruh T. S., Ross P., Jr, Wood D. M., Keene J. L. The binding of [3H]oestradiol-receptor complexes to calf uterine chromatin. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 15;200(1):133–142. doi: 10.1042/bj2000133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruh T. S., Spelsberg T. C. Acceptor sites for the oestrogen receptor in hen oviduct chromatin. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):905–912. doi: 10.1042/bj2100905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saluz H. P., Jiricny J., Jost J. P. Genomic sequencing reveals a positive correlation between the kinetics of strand-specific DNA demethylation of the overlapping estradiol/glucocorticoid-receptor binding sites and the rate of avian vitellogenin mRNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7167–7171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Walker P., Martinez E., Mérillat A. M., Givel F., Wahli W. Identification of estrogen-responsive DNA sequences by transient expression experiments in a human breast cancer cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8755–8770. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Germond J. E., Brown-Luedi M., Givel F., Wahli W. Sequence homologies in the region preceding the transcription initiation site of the liver estrogen-responsive vitellogenin and apo-VLDLII genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8611–8626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Heggeler-Bordier B., Hipskind R., Seiler-Tuyns A., Martinez E., Corthésy B., Wahli W. Electron microscopic visualization of protein-DNA interactions at the estrogen responsive element and in the first intron of the Xenopus laevis vitellogenin gene. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1715–1720. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]