Abstract
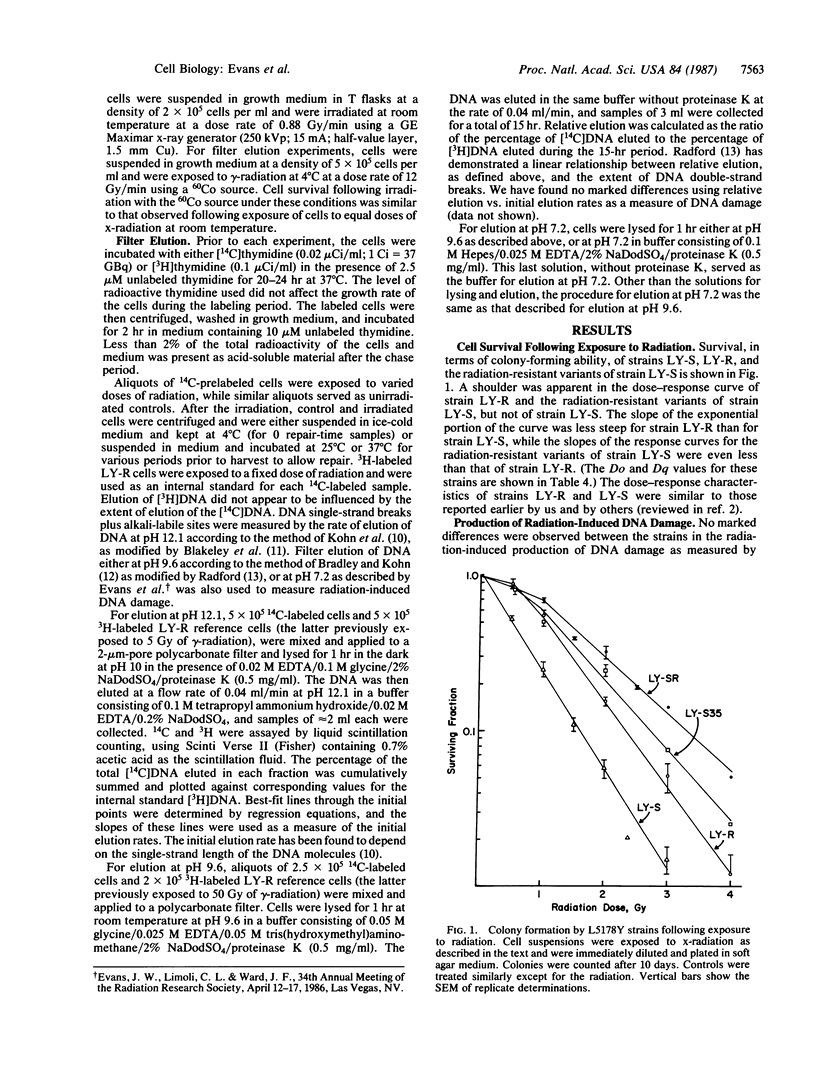
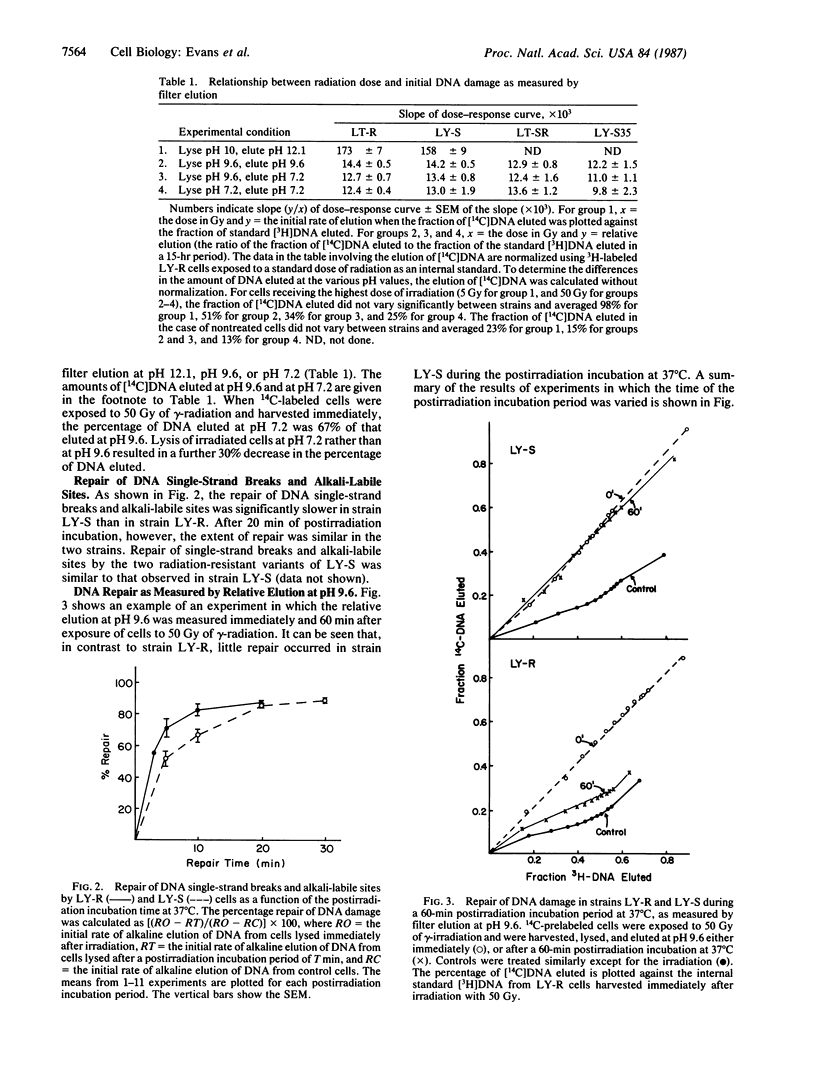
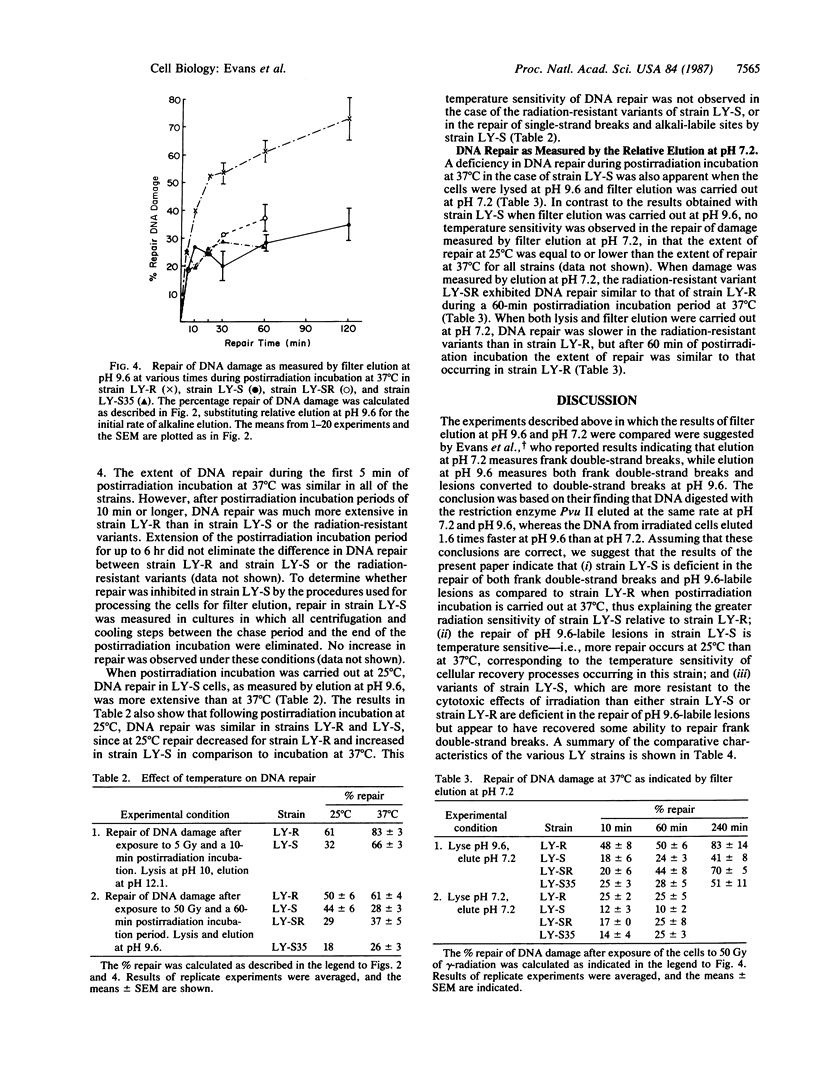
The production and repair of radiation-induced DNA damage were measured by filter elution in strains of mouse lymphoma L5178Y cells differing in their sensitivity to ionizing radiation. The induction of radiation-induced damage, as measured by filter elution at pH 12.1, 9.6, and 7.2, was similar in the resistant strain LY-R and the sensitive strain LY-S. The repair of single-strand breaks and alkali-labile sites, as measured by filter elution at pH 12.1 at various times after irradiation, was somewhat slower in strain LY-S than in strain LY-R, although after a 20-min repair period the extent of repair was equal in the two strains. However, when filter elution was performed at either pH 9.6 or pH 7.2, the repair of x-radiation-induced damage was much less extensive in strain LY-S than in strain LY-R. We have assumed that the extent of filter elution at pH 9.6 is a measure of the occurrence of frank double-strand breaks as well as closely opposing single-strand breaks and pH 9.6-labile sites (and combinations thereof), and that the extent of elution at pH 7.2 is a measure of the occurrence of frank double-strand breaks alone. If these assumptions are correct, the results suggest that the sensitivity of strain LY-S to the cytotoxic effects of ionizing radiation is caused by a deficiency in the ability of this strain to repair frank double-strand breaks and pH 9.6-labile lesions. The repair of pH 9.6-labile lesions was temperature sensitive in strain LY-S, as previously found for cellular recovery processes in this strain. Two independent radiation-resistant variants of strain LY-S, isolated after protracted exposure of LY-S cells to low-dose-rate radiation, showed a deficiency in the repair of pH 9.6-labile lesions similar to that observed in strain LY-S. However, the repair of frank double-strand breaks was more extensive in the radiation-resistant variants than in strain LY-S and was similar in extent to that occurring in strain LY-R after a 60-min postirradiation incubation. The results suggest that there is a difference in the nature of DNA damage measured by filter elution at pH 9.6 vs. pH 7.2 and that a deficiency in the repair of pH 9.6-labile lesions does not contribute to cell lethality in the case of the radiation-resistant variants. The radiation resistance of these variants in comparison to strain LY-S may be due at least in part to recovery of the ability to rejoin frank DNA double-strand breaks.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER P. Mouse lymphoma cells with different radiosensitivities. Nature. 1961 Nov 11;192:572–573. doi: 10.1038/192572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEER J. Z., LETT J. T., ALEXANDER P. INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE AND MEDIUM ON THE X-RAY SENSITIVITIES OF LEUKEMIA CELLS IN VITRO. Nature. 1963 Jul 13;199:193–194. doi: 10.1038/199193a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beer J. Z., Budzicka E., Niepokojczycka E., Rosiek O., Szumiel I., Walicka M. Loss of tumorigenicity with simultaneous changes in radiosensitivity and photosensitivity during in vitro growth of L5178Y murine lymphoma cells. Cancer Res. 1983 Oct;43(10):4736–4742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beer J. Z., Mencl J., Horng M. F., Gregg E. C., Evans H. H. Effects of low dose rate (0.003-0.025 Gy/h) chronic X-irradiation on radioresistant and radiosensitive L5178Y mouse lymphoma cells. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1985 Oct;48(4):609–619. doi: 10.1080/09553008514551671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakely W. F., Ward J. F., Joner E. I. A quantitative assay of deoxyribonucleic acid strand breaks and their repair in mammalian cells. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 15;124(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90229-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocian E., Bouzyk E., Rosiek O., Ziemba-Zótowska B. Chromosomal aberrations induced by x-rays in two mouse lymphoma (L5178Y) sublines of different radiosensitivity. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1982 Sep;42(3):347–351. doi: 10.1080/09553008214551261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. O., Kohn K. W. X-ray induced DNA double strand break production and repair in mammalian cells as measured by neutral filter elution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):793–804. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. H., Horng M. F., Mencl J., Glazier K. G., Beer J. Z. The influence of dose rate on the lethal and mutagenic effects of X-rays in proliferating L5178Y cells differing in radiation sensitivity. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1985 May;47(5):553–562. doi: 10.1080/09553008514550781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenberg D., Frankenberg-Schwager M., Harbich R. Split-dose recovery is due to the repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1984 Nov;46(5):541–553. doi: 10.1080/09553008414551751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaccia A., Weinstein R., Hu J., Stamato T. D. Cell cycle-dependent repair of double-strand DNA breaks in a gamma-ray-sensitive Chinese hamster cell. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Sep;11(5):485–491. doi: 10.1007/BF01534842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin E. M., Cox A. B., Lett J. T. Correlation of survival with the restoration of DNA structure in X-irradiated L5178Y S/S cells. Radiat Res. 1980 Sep;83(3):668–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeggo P. A., Kemp L. M. X-ray-sensitive mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Isolation and cross-sensitivity to other DNA-damaging agents. Mutat Res. 1983 Dec;112(6):313–327. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(83)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson K. J., Wlodek D., Szumiel I. DNA repair and replication in radiation-sensitive and -resistant mouse lymphoma cells gamma-irradiated under aerobic and hypoxic conditions. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1982 Mar;41(3):261–270. doi: 10.1080/09553008214551721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn K. W., Erickson L. C., Ewig R. A., Friedman C. A. Fractionation of DNA from mammalian cells by alkaline elution. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4629–4637. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radford I. R. The level of induced DNA double-strand breakage correlates with cell killing after X-irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1985 Jul;48(1):45–54. doi: 10.1080/09553008514551051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A., Martin P. The repair of double-strand breaks in the nuclear DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its genetic control. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jan 16;143(2):119–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00266917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. L., Stanbridge E. J., Epstein C. J. Incorporation of 3H-uridine and 3H-uracil into RNA: a simple technique for the detection of mycoplasma contamination of cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 15;84(1):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90411-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamato T. D., Weinstein R., Giaccia A., Mackenzie L. Isolation of cell cycle-dependent gamma ray-sensitive Chinese hamster ovary cell. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 Mar;9(2):165–173. doi: 10.1007/BF01543175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker J., Stretch A. Responses of 4 X-ray-sensitive CHO cell mutants to different radiations and to irradiation conditions promoting cellular recovery. Mutat Res. 1985 Jul;146(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(85)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno A. M., Goldin E. M., Cox A. B., Lett J. T. Deficient repair and degradation of DNA in X-irradiated L5178Y S/S cells: cell-cycle and temperature dependence. Radiat Res. 1979 Aug;79(2):377–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno A. M., Lett J. T. Deficient repair and degradation of DNA in L5178Y S/S cells. Radiat Res. 1979 Aug;79(2):424–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau T. M., Kim S. C., Gregg E. C., Nygaard O. F. Inverse X-irradiation split-dose effect in a murine lymphoma cell line. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1979 Jun;35(6):577–581. doi: 10.1080/09553007914550691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



