Abstract
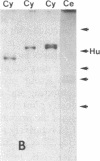
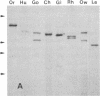
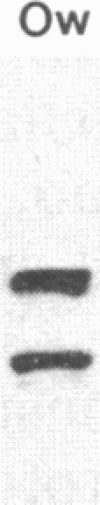
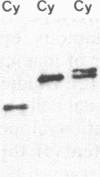
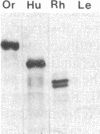
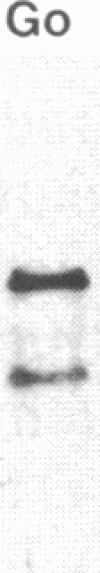
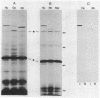
Hominoid apes (gorilla, chimpanzee, orangutan, gibbon), Old World monkeys (rhesus, cynomolgus), New World monkeys (owl, cebus), and a prosimian (lemur) express involucrin-like proteins in cultured keratinocytes. Primate involucrins can be precipitated with trichloroacetic acid, resolubilized at pH 8, and subsequently retain aqueous solubility in 67% ethanol. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of keratinocyte extracts after this rapid partial purification has revealed in each species tested one (chimpanzee, orangutan, gibbon) or two (gorilla, rhesus, owl, cebus) antigenically crossreactive proteins that migrate in the vicinity of human involucrin. In the species examined further (gorilla, chimpanzee, rhesus), poly(A)+ mRNA isolated from the cultures directed the cell-free translation of polypeptides with mobilities similar to those extracted from the cells. From five cynomolgus monkeys, three different electrophoretic profiles were obtained, suggesting the existence of different alleles. Quantitative comparisons by a sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay indicated that certain primate involucrins have a higher density of antigenic determinants than the human protein, whereas others lack some determinant(s). In contrast to those from other species, all of which showed substantial crossreactivity, the lemur protein was minimally immunoreactive by immunoblotting and not clearly detected by solid-phase assay. The electrophoretic and antigenic differences displayed throughout the primate order suggest that this protein has been subject to relatively rapid evolution.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks-Schlegel S., Green H. Formation of epidermis by serially cultivated human epidermal cells transplanted as an epithelium to athymic mice. Transplantation. 1980 Apr;29(4):308–313. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198004000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R. L., Green H. Structure and evolution of the human involucrin gene. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):583–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90884-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etoh Y., Simon M., Green H. Involucrin acts as a transglutaminase substrate at multiple sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90875-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H. Cyclic AMP in relation to proliferation of the epidermal cell: a new view. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):801–811. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H. The keratinocyte as differentiated cell type. Harvey Lect. 1980;74:101–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimann R., Rice R. H. Rat esophageal and epidermal keratinocytes: intrinsic differences in culture and derivation of continuous lines. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Dec;117(3):362–367. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041170311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Shirley J. E. Characterization of transglutaminase activity in rabbit tracheal epithelial cells. Regulation by retinoids. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15097–15101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichti U., Ben T., Yuspa S. H. Retinoic acid-induced transglutaminase in mouse epidermal cells is distinct from epidermal transglutaminase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1422–1426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parenteau N. L., Pilato A., Rice R. H. Induction of keratinocyte type-I transglutaminase in epithelial cells of the rat. Differentiation. 1986;33(2):130–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G. Serial cultivation of normal human epidermal keratinocytes. Methods Cell Biol. 1980;21A:229–254. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60769-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. H., Green H. Presence in human epidermal cells of a soluble protein precursor of the cross-linked envelope: activation of the cross-linking by calcium ions. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarich V. M., Wilson A. C. Immunological time scale for hominid evolution. Science. 1967 Dec 1;158(3805):1200–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3805.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Green H. Enzymatic cross-linking of involucrin and other proteins by keratinocyte particulates in vitro. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90216-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Green H. Differentiation of the epidermal keratinocyte in cell culture: formation of the cornified envelope. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 1):511–521. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacher S. M., Rice R. H. Keratinocyte-specific transglutaminase of cultured human epidermal cells: relation to cross-linked envelope formation and terminal differentiation. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):685–695. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]