Abstract
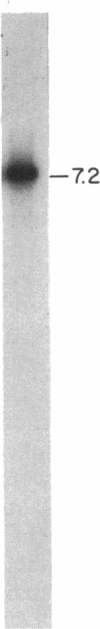
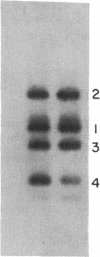
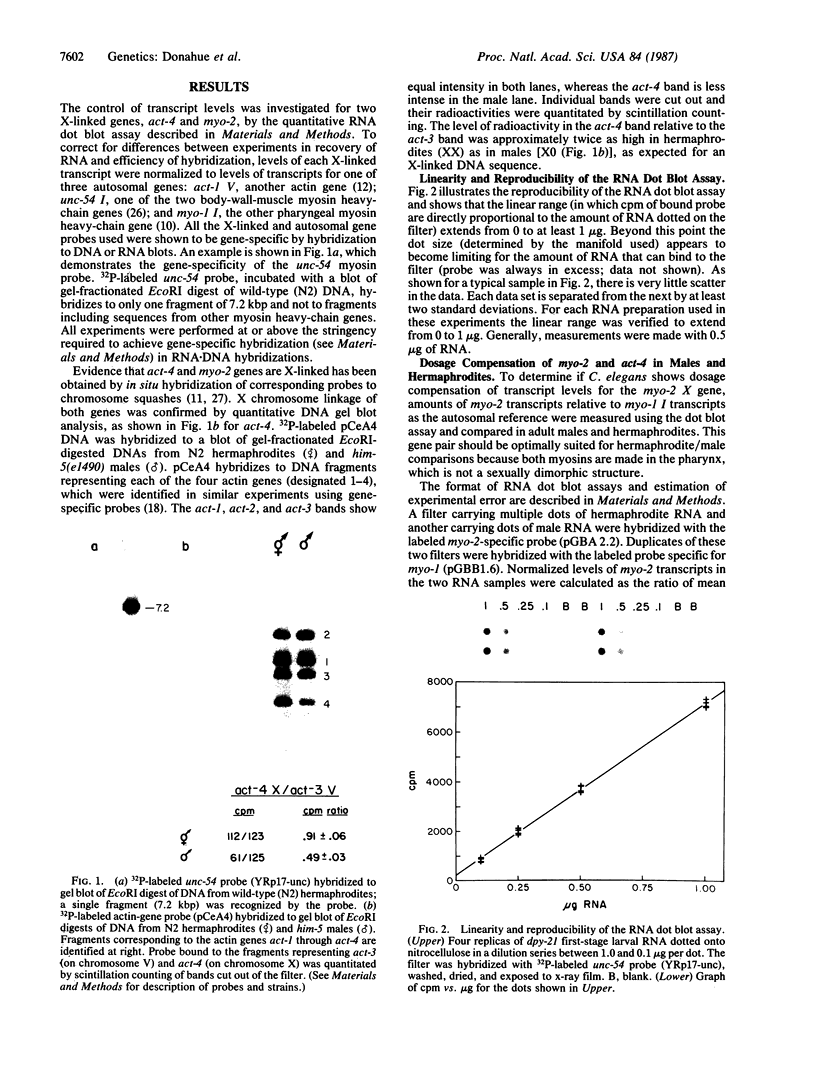
We used a convenient quantitative dot blot assay to measure transcript levels for two X chromosome-linked genes, myo-2 and act-4, in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. We show that there is dosage compensation of transcript levels for these two genes between XX hermaphrodites and X0 males and that a mutation in the dpy-21 gene, postulated from genetic analysis to be involved in control of X chromosome expression, can affect these transcript levels in the manner predicted. However, we observe the dpy-21 effects only at some stages of the life cycle and not at others. These results are generally consistent with earlier genetic and molecular evidence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertson D. G. Localization of the ribosomal genes in Caenorhabditis elegans chromosomes by in situ hybridization using biotin-labeled probes. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1227–1234. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albertson D. G. Mapping muscle protein genes by in situ hybridization using biotin-labeled probes. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2493–2498. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Belote J. M. Sex determination and dosage compensation in Drosophila melanogaster. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:345–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassada R. C., Russell R. L. The dauerlarva, a post-embryonic developmental variant of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1975 Oct;46(2):326–342. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Klass M. R., Hirsh D. Analysis of the constancy of DNA sequences during development and evolution of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1333–1337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson E. L., Sternberg P. W., Horvitz H. R. A genetic pathway for the specification of the vulval cell lineages of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):259–267. doi: 10.1038/326259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Files J. G., Carr S., Hirsh D. Actin gene family of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 5;164(3):355–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcea R. L., Schachat F., Epstein H. F. Coordinate synthesis of two myosins in wild-type and mutant nematode muscle during larval development. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Riggs A. D. Mammalian X-chromosome inactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:155–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. K., Madl J. E., Kari C. K. Duplications in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1979 Jun;92(2):419–435. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J., Horvitz H. R., Brenner S. Nondisjunction Mutants of the Nematode CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS. Genetics. 1979 Jan;91(1):67–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L. Protein structural domains in the Caenorhabditis elegans unc-54 myosin heavy chain gene are not separated by introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4253–4257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. M., Cox G. N., Hirsh D. Expression of the Caenorhabditis elegans collagen genes col-1 and col-2 is developmentally regulated. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1945–1951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod A. R., Waterston R. H., Fishpool R. M., Brenner S. Identification of the structural gene for a myosin heavy-chain in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madl J. E., Herman R. K. Polyploids and sex determination in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1979 Oct;93(2):393–402. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer B. J., Casson L. P. Caenorhabditis elegans compensates for the difference in X chromosome dosage between the sexes by regulating transcript levels. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):871–881. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90802-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. M., Stockdale F. E., Karn J. Immunological identification of the genes encoding the four myosin heavy chain isoforms of Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2305–2309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B., Hecht R., Carr S., Vanderslice R., Wolf N., Hirsh D. Parental effects and phenotypic characterization of mutations that affect early development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1980 Feb;74(2):446–469. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90445-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B., Meneely P., Schedin P., Donahue L. Aspects of dosage compensation and sex determination in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:575–583. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]