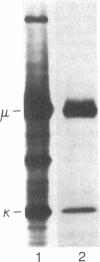
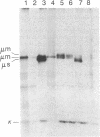
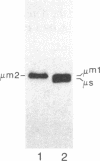
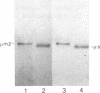
Abstract
Membrane immunoglobulin heavy chain in pre-B and in B cells is initially synthesized as a relatively hydrophilic protein that is nonetheless stably anchored in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. In B cells, but not in pre-B cells, the membrane immunoglobulin heavy chain is post-translationally converted to a relatively hydrophobic form that partitions into the oil phase when solubilized with the phase-separating detergent Triton X-114. Covalent myristoylation of the membrane and secretory forms of immunoglobulin heavy chains as well as of light chains was observed in B cells. Myristoylation of the membrane immunoglobulin heavy chain correlates with its transport to the cell surface and its post-translational conversion to a relatively hydrophobic form. This post-translational modification is hydroxylamine resistant and may be responsible for the assembly and transport of membrane immunoglobulin to the cell surface in B cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Cohen P., Santikarn S., Williams D. H., Calder A. G., Smith A., Klee C. B. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of calcineurin B as myristic acid. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F., Rosenberg N., Lewis S., Thomas E., Baltimore D. Organization and reorganization of immunoglobulin genes in A-MULV-transformed cells: rearrangement of heavy but not light chain genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90421-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid, a rare fatty acid, is the lipid attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus and its cellular homolog. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.7-12.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Newman J. F., Filman D., Hogle J. M., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Myristylation of picornavirus capsid protein VP4 and its structural significance. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):482–486. doi: 10.1038/327482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulis B. H., Kloppel T. M., Grey H. M., Kubo R. T. Regulation of catabolism of IgM heavy chains in a B lymphoma cell line. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4369–4374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Glycosyl-sn-1,2-dimyristylphosphatidylinositol is covalently linked to Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14547–14555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Hamblin T. J., Smith J. L., Stevenson F. K., Stevenson G. T. A human b-cell lymphoma synthesizing and expressing surface mu-chain in the absence of detectable light chain. Blood. 1981 Sep;58(3):552–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Dangl J. L., Hayakawa K., Jager G., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Frequent lambda light chain gene rearrangement and expression in a Ly-1 B lymphoma with a productive kappa chain allele. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1438–1442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedo J. A., Collier E., Watkinson A. Myristyl and palmityl acylation of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):954–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendershot L., Levitt D. Analysis of surface mu-chain expression in human lymphoblastoid cell lines that do not produce light chains. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):502–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Krutzsch H. C., Oroszlan S. Myristyl amino-terminal acylation of murine retrovirus proteins: an unusual post-translational proteins modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Krangel M. S., Strominger J. L. Cysteines in the transmembrane region of major histocompatibility complex antigens are fatty acylated via thioester bonds. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7230–7238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland M. E. The coming of age of the immunoglobulin J chain. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:425–453. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathey-Prevot B., Baltimore D. Specific transforming potential of oncogenes encoding protein-tyrosine kinases. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1769–1774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omary M. B., Trowbridge I. S. Covalent binding of fatty acid to the transferrin receptor in cultured human cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4715–4718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paige C. J., Kincade P. W., Ralph P. Independent control of immunoglobulin heavy and light chain expression in a murine pre-B-cell line. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):631–633. doi: 10.1038/292631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P. Functional subsets of murine and human B lymphocyte cell lines. Immunol Rev. 1979;48:107–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Early P., Carter C., Calame K., Bond M., Hood L., Wall R. Two mRNAs with different 3' ends encode membrane-bound and secreted forms of immunoglobulin mu chain. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90616-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Adams G. A., Gallione C. J. The presence of cysteine in the cytoplasmic domain of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is required for palmitate addition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2050–2054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sairam M. R., Porath J. Isolation of antibodies to protein hormones by bioaffinity chromatography on divinylsulfonyl sepharose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):190–196. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schekman R. Protein localization and membrane traffic in yeast. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:115–143. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F. Fatty acid binding: a new kind of posttranslational modification of membrane proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;102:101–129. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68906-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli C. H., Griffin B. E. Myristic acid is coupled to a structural protein of polyoma virus and SV40. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):619–622. doi: 10.1038/326619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Schulz M. F., Vassalli P. Bone marrow pre-B lymphocytes synthesize immunoglobulin mu chains of membrane type with different properties and intracellular pathways. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):361–368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B. M., Cowman A. F., Gerondakis S. D., Adams J. M., Bernard O. mRNA for surface immunoglobulin gamma chains encodes a highly conserved transmembrane sequence and a 28-residue intracellular domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2008–2012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D., Costantini F., Imanishi-Kari T., Baltimore D. A transgenic immunoglobulin mu gene prevents rearrangement of endogenous genes. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):117–127. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost C. S., Hedgpeth J., Lingappa V. R. A stop transfer sequence confers predictable transmembrane orientation to a previously secreted protein in cell-free systems. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):759–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90532-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]