Abstract
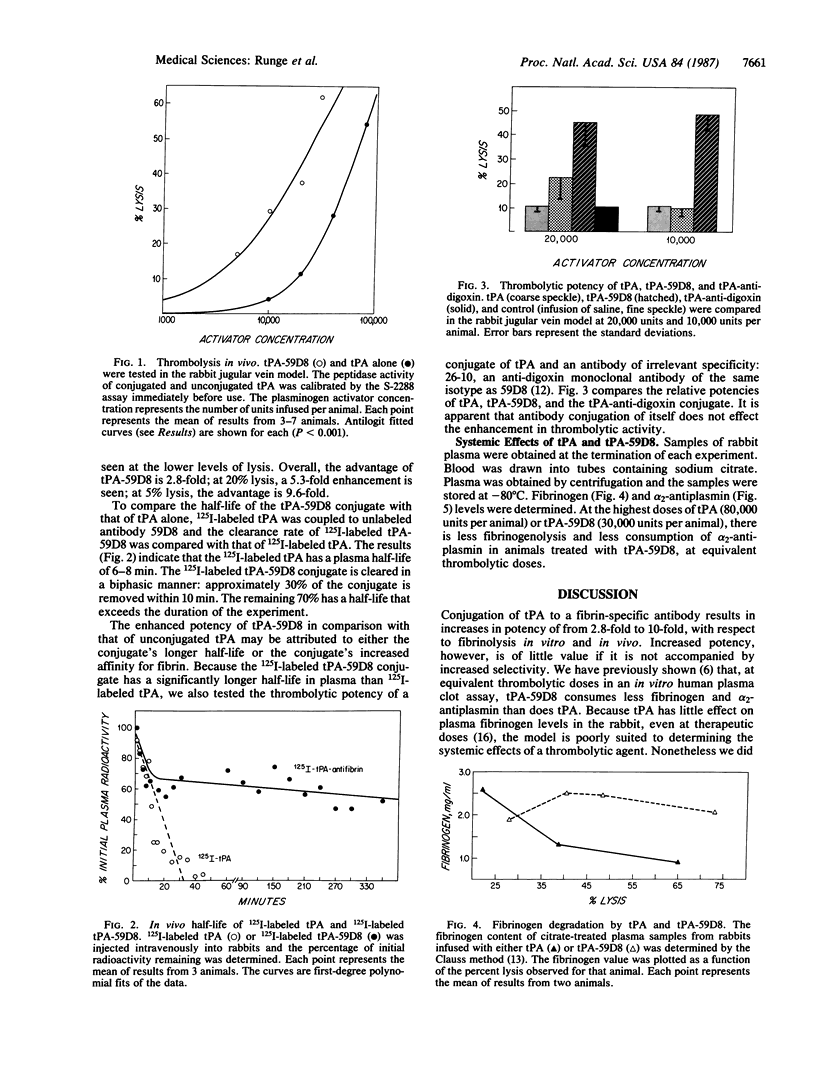
Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) was modified by the unidirectional crosslinking reagent N-succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate and coupled to iminothiolane-modified anti-fibrin antibody 59D8 by the formation of disulfide bonds at neutral pH. Purification by two affinity-chromatography steps yielded tPA-anti-fibrin antibody conjugate (tPA-59D8) possessing both tPA and anti-fibrin antibody activities. In a quantitative rabbit thrombolysis model, the activity of the purified conjugate was compared with that of tPA alone and that of a conjugate between tPA and a digoxin-specific monoclonal antibody. After correction for spontaneous lysis (10.9 +/- 2.5%), tPA-59D8 was shown to be 2.8-9.6 times more potent than tPA alone. Unconjugated tPA and tPA-digoxin were equipotent. At equivalent thrombolytic concentrations, tPA-59D8 degraded less fibrinogen and consumed less alpha 2-antiplasmin than did tPA alone. This suggests that tPA can be efficiently directed to the site of a thrombus by conjugation to an anti-fibrin monoclonal antibody, resulting in both more potent and more selective thrombolysis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bode C., Matsueda G. R., Hui K. Y., Haber E. Antibody-directed urokinase: a specific fibrinolytic agent. Science. 1985 Aug 23;229(4715):765–767. doi: 10.1126/science.4023710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode C., Runge M. S., Newell J. B., Matsueda G. R., Haber E. Thrombolysis by a fibrin-specific antibody Fab'-urokinase conjugate. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1987 Apr;19(4):335–341. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(87)80578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAUSS A. Gerinnungsphysiologische Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung des Fibrinogens. Acta Haematol. 1957 Apr;17(4):237–246. doi: 10.1159/000205234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Stassen J. M., Verstraete M. Thrombolysis with human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in rabbits with experimental jugular vein thrombosis. Effect of molecular form and dose of activator, age of the thrombus, and route of administration. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):368–376. doi: 10.1172/JCI110778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Topol E. J., Tiefenbrunn A. J., Gold H. K., Weisfeldt M. L., Sobel B. E., Leinbach R. C., Brinker J. A., Ludbrook P. A., Yasuda I. Coronary thrombolysis with recombinant human tissue-type plasminogen activator: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Circulation. 1984 Dec;70(6):1012–1017. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.70.6.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edy J., De Cock F., Collen D. Inhibition of plasmin by normal and antiplasmin-depleted human plasma. Thromb Res. 1976 Apr;8(4):513–518. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui K. Y., Haber E., Matsueda G. R. Monoclonal antibodies to a synthetic fibrin-like peptide bind to human fibrin but not fibrinogen. Science. 1983 Dec 9;222(4628):1129–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.6648524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudgett-Hunter M., Anderson W., Haber E., Margolies M. N. Binding and structural diversity among high-affinity monoclonal anti-digoxin antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1985 Apr;22(4):477–488. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampling M. W., Gaffney P. J. The sulphite precipitation method for fibrinogen measurement; its use on small samples in the presence of fibrinogen degradation products. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Feb 16;67(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90215-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



