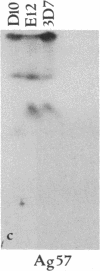
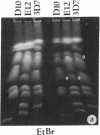
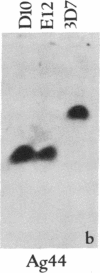
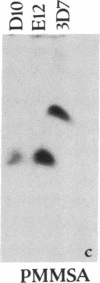
Abstract
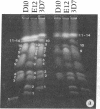
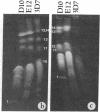
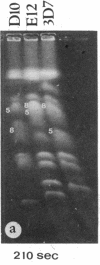
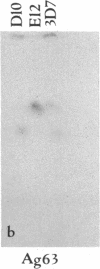
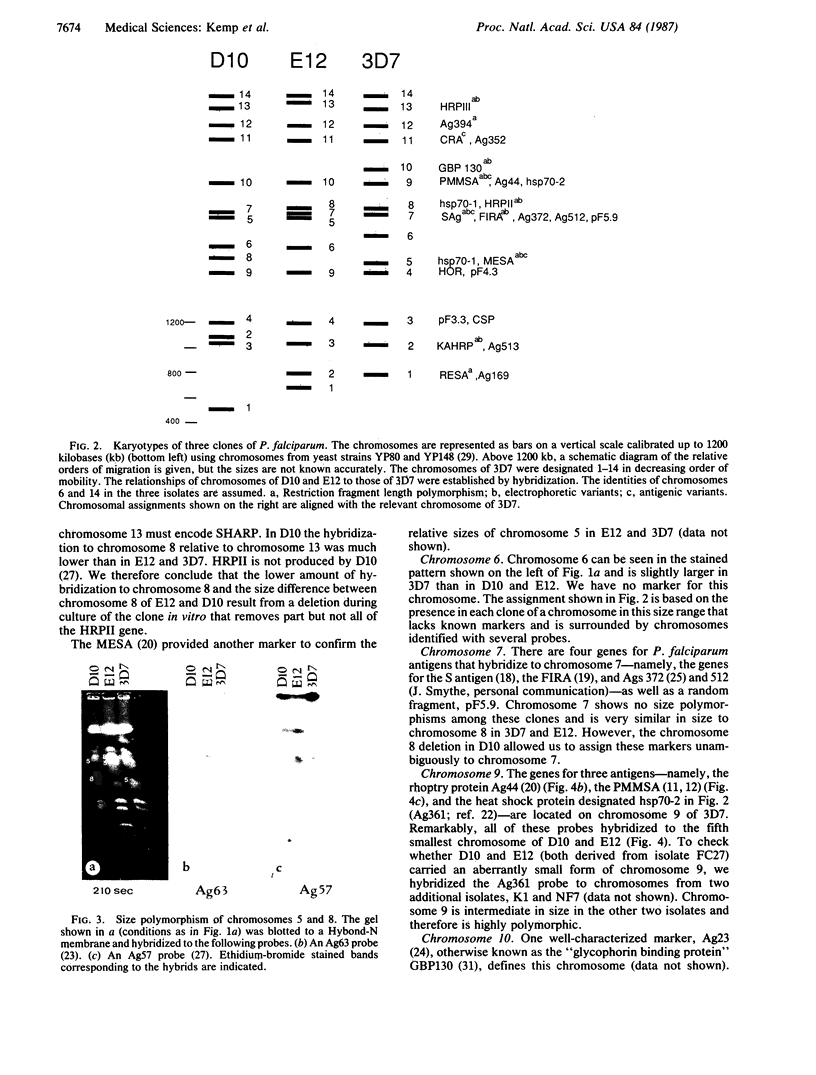
We describe fractionation of the Plasmodium falciparum genome into 14 chromosomal DNA molecules by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. This number agrees with the number of chromosomes observed by electron microscopic visualization of kinetochores. The assignment of 25 markers to 12 of the 14 chromosomes in three cloned parasite lines demonstrates that chromosomal size variation can greatly change the relative migration of genetically equivalent chromosomes. Deletions that include genes for three different histidine-rich proteins, located on chromosomes 2, 8, and 13, contribute to size differences in some clones. Other karyotypic differences result from chromosome segregation and/or recombination during meiosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianco A. E., Culvenor J. G., Coppel R. L., Crewther P. E., McIntyre P., Favaloro J. M., Brown G. V., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Putative glycophorin-binding protein is secreted from schizonts of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Feb;23(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco A. E., Favaloro J. M., Burkot T. R., Culvenor J. G., Crewther P. E., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Coppel R. L., Kemp D. J. A repetitive antigen of Plasmodium falciparum that is homologous to heat shock protein 70 of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8713–8717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Bianco A. E., Culvenor J. G., Crewther P. E., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. A cDNA clone expressing a rhoptry protein of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Aug;25(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Culvenor J. G., Bianco A. E., Crewther P. E., Stahl H. D., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Variable antigen associated with the surface of erythrocytes infected with mature stages of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Sep;20(3):265–277. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Favaloro J. M., Crewther P. E., Burkot T. R., Bianco A. E., Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F., Brown G. V. A blood stage antigen of Plasmodium falciparum shares determinants with the sporozoite coat protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5121–5125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Forsyth K. P., Bianco A. E., Brown G. V., Kemp D. J. Chromosome size polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum can involve deletions and are frequent in natural parasite populations. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90487-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Kemp D. J. Chromosomes of Plasmodium falciparum. P N G Med J. 1986 Mar;29(1):95–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Saint R. B., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Conserved sequences flank variable tandem repeats in two S-antigen genes of Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crewther P. E., Bianco A. E., Brown G. V., Coppel R. L., Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Affinity purification of human antibodies directed against cloned antigens of Plasmodium falciparum. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Feb 12;86(2):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culvenor J. G., Langford C. J., Crewther P. E., Saint R. B., Coppel R. L., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F., Brown G. V. Plasmodium falciparum: identification and localization of a knob protein antigen expressed by a cDNA clone. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Feb;63(1):58–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J. M., Coppel R. L., Corcoran L. M., Foote S. J., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Structure of the RESA gene of Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8265–8277. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
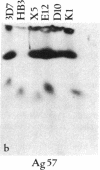
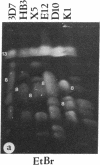
- Kemp D. J., Corcoran L. M., Coppel R. L., Stahl H. D., Bianco A. E., Brown G. V., Anders R. F. Size variation in chromosomes from independent cultured isolates of Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):347–350. doi: 10.1038/315347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan J., Perkins M., Ravetch J. V. A tandemly repeated sequence determines the binding domain for an erythrocyte receptor binding protein of P. falciparum. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90834-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langsley G., Sibilli L., Mattei D., Falanga P., Mercereau-Puijalon O. Karyotype comparison between P. chabaudi and P. falciparum: analysis of a P. chabaudi cDNA containing sequences highly repetitive in P. falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2203–2211. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pologe L. G., Ravetch J. V. A chromosomal rearrangement in a P. falciparum histidine-rich protein gene is associated with the knobless phenotype. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):474–477. doi: 10.1038/322474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prensier G., Slomianny C. The karyotype of Plasmodium falciparum determined by ultrastructural serial sectioning and 3D reconstruction. J Parasitol. 1986 Oct;72(5):731–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D., Woollett G., Bergin-Cartwright M., Kay D., Scaife J. A malaria protein exported into a new compartment within the host erythrocyte. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):485–491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spithill T. W., Samaras N. Genomic organization, chromosomal location and transcription of dispersed and repeated tubulin genes in Leishmania major. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 May;24(1):23–37. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H. D., Bianco A. E., Crewther P. E., Anders R. F., Kyne A. P., Coppel R. L., Mitchell G. F., Kemp D. J., Brown G. V. Sorting large numbers of clones expressing Plasmodium falciparum antigens in Escherichia coli by differential antibody screening. Mol Biol Med. 1986 Aug;3(4):351–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H. D., Bianco A. E., Crewther P. E., Burkot T., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. An asparagine-rich protein from blood stages of Plasmodium falciparum shares determinants with sporozoites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):3089–3102. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.3089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H. D., Crewther P. E., Anders R. F., Brown G. V., Coppel R. L., Bianco A. E., Mitchell G. F., Kemp D. J. Interspersed blocks of repetitive and charged amino acids in a dominant immunogen of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):543–547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Crewther P. E., Scanlon D. B., Woodrow G., Brown G. V., Bianco A. E., Anders R. F., Coppel R. L. Sequence of a cDNA encoding a small polymorphic histidine- and alanine-rich protein from Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7837–7846. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe K., Mackay M., Goman M., Scaife J. G. Allelic dimorphism in a surface antigen gene of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):273–287. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90649-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Smits M., Ponnudurai T., Vermeulen A., Meuwissen J. H., Langsley G. Chromosome-sized DNA molecules of Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1985 Aug 16;229(4714):658–661. doi: 10.1126/science.3895435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walliker D., Quakyi I. A., Wellems T. E., McCutchan T. F., Szarfman A., London W. T., Corcoran L. M., Burkot T. R., Carter R. Genetic analysis of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1987 Jun 26;236(4809):1661–1666. doi: 10.1126/science.3299700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellems T. E., Howard R. J. Homologous genes encode two distinct histidine-rich proteins in a cloned isolate of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6065–6069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellems T. E., Walliker D., Smith C. L., do Rosario V. E., Maloy W. L., Howard R. J., Carter R., McCutchan T. F. A histidine-rich protein gene marks a linkage group favored strongly in a genetic cross of Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):633–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90539-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]