In search of morphological determinants for the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC), we found that a concerted action of Arf1, Arf4, and PLA2G6-A controls the architecture of the ERGIC by regulating tubular carriers. This is predicted to impact the rate of transport and destination of cargos in the ERGIC.
Abstract
Organelle morphology of the endomembrane system is critical for optimal organelle function. ADP ribosylation factors (Arfs), a family of small GTPases, are required for maintaining the structure of the Golgi and endosomes. What determines the discontinuous nature of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)–Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC) as tubulovesicular clusters is unknown. In search of morphological determinants for the ERGIC, we found that a double knockdown of Arf1+Arf4 induced dynamic ERGIC tubules that connect ERGIC clusters, indicating that the tubules mediated lateral intraERGIC traffic. Tubule formation was inhibited by an antagonist of group VI calcium-independent phospholipase A2 (PLA2G6) and by silencing the A isoform of PLA2G6 (PLA2G6-A). Arf1+Arf4 depletion altered the expression of PLA2G6-A splice variants and relocalized PLA2G6-A from the cytosol to ERGIC clusters and tubules, suggesting that the enzyme became locally active. We show that changes in Arf1 can modulate the activity of PLA2G6-A. We propose that a concerted action of Arf1, Arf4, and PLA2G6-A controls the architecture of the ERGIC in a way that is predicted to impact the rate and possibly the destination of cargos. Our findings have identified key components in the molecular mechanism underlying the regulation of tubules in the ERGIC and uncover tubular carriers as tightly controlled machinery.
INTRODUCTION
The early secretory pathway is formed by the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the ER–Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC), and the Golgi, which have strikingly different structures (Palade, 1975; Bannykh et al., 1996; Appenzeller-Herzog and Hauri, 2006). The ERGIC consists of a constant average number of discontinuous long-lived stationary tubulovesicular clusters that stain positive for the type I transmembrane lectin ERGIC-53 and for the cytosolic coat protein (COP) I subunit β-COP (Schweizer et al., 1988; Klumperman et al., 1998; Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005). The ERGIC is equivalent to the site at which ER-to-Golgi transport of some cargo proteins and receptors is reversibly blocked at 15°C (Kuismanen and Saraste, 1989; Schweizer et al., 1990; Lotti et al., 1992; Klumperman et al., 1998; Blum et al., 2000; Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005; Simpson et al., 2006). ERGIC stationary clusters operate as sorting stations of anterograde cargo directed to the Golgi and retrograde cargo directed to the ER (Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005). In addition, the stationary clusters communicate by fusion and fission and by fast-moving carriers, the function of which is unknown (Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005). Recently, the ERGIC was found to be more complex than anticipated, including a centrosomal connection that was proposed to mediate traffic to the recycling endosomes (Marie et al., 2009; Saraste et al., 2009).
Various drugs affect the morphology of the ERGIC. For example, treating cells with the fungal metabolite brefeldin A (BFA) induces cycling proteins to accumulate in the ERGIC and increases the size of ERGIC clusters (Lippincott-Schwartz et al., 1990; Fullekrug et al., 1997; Scheel et al., 1997; Breuza et al., 2004). BFA prevents the activation of ADP ribosylation factor (Arf) 1 by guanine exchange factors, thus blocking Arf1 in its guanosine diphosphate-inactive form (Renault et al., 2003; Zeghouf et al., 2005). This prevents binding of COPI to membranes (Donaldson et al., 1990; Scheel et al., 1997). A phenotype similar but not identical to BFA arises in HeLa cells after Arf1 and Arf4 knockdown. The double knockdown but not single knockdowns of Arf1 and Arf4 causes ß-COP to disperse throughout the cytosol (Volpicelli-Daley et al., 2005). In that case, however, dispersal of β-COP was not reported to coincide with a change in the morphology of the ERGIC.
Temperature manipulations also can change the architecture of the ERGIC. In cells incubated at 15–16°C and rewarmed for short times to 37°C, tubules positive for the ERGIC marker ERGIC-53 are observed, indicating accentuated ERGIC-to-ER retrograde traffic (Lippincott-Schwartz et al., 1990; Schweizer et al., 1990; Klumperman et al., 1998; Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005; Simpson et al., 2006). ERGIC tubules are also observed in cells knocked down for guanine nucleotide exchange factor (Szul et al., 2007), in cells overexpressing some cargo proteins or cargo receptors (Blum et al., 2000; Mironov et al., 2003; Simpson et al., 2006) as well as in cells expressing Rab1A (Sannerud et al., 2006).
The determinants of ER morphology, as a reticular network (Vedrenne et al., 2005; Hu et al., 2009; Orso et al., 2009), and of the Golgi, as stacked cisternae (Glick and Nakano, 2009), have been investigated for several years and with substantial but incomplete success, but those dictating the discontinuous nature of the ERGIC as a few hundred tubulovesicular clusters are unknown. Here, we show that Arf1, Arf4, and PLA2G6-A activity are necessary to maintain the discontinuous morphology of the ERGIC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Recombinant pSUPER Vectors
Standard molecular biology protocols were used. Oligonucleotides were from the Microsynth (Balgach, Switzerland) and enzymes were from New England Biolabs (Ipswich, MA). Construction of nuclear (nuc)ECFP was done as follows: 1) introduction of EcoRI and BamHI sites by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of S6-NLS (Jones et al., 1999b), 2) ligation into pECFP-C1 (Clontech, Mountain View, CA), 3) addition of SpeI and SacII sites to the cytomegalovirus promoter-ECFP-NLS sequence, 4) ligation into TOPO-TA vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA), 5) ligation into pSUPER vectors in the antiparallel direction to the H1 promoter to avoid interferences with short hairpin RNA (shRNA) production, and 6) authentication by DNA sequencing.
Cell Culture, Transfection, and Knockdown
HeLa cells were grown as described previously (Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005). FuGENE 6 (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland) was used for transfections and knockdowns. Arf1+Arf4 double knockdowns were as described previously (Volpicelli-Daley et al., 2005). In double knockdown experiments where two pSUPER vectors were cotransfected, only one of the vectors carried nucECFP. PLA2G6-A shRNAs were from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). PLA2G6-A knockdowns were for 48 h. When needed, PLA2G6-A shRNAs were cotransfected with pDsRedT1 (red fluorescent protein [RFP]) as a transfection marker. This was the case in rewarming experiments because the endogenous signal of PLA2G6-A was affected by the block and the rewarming. Myc-tagged mArf1 cDNA was from GeneCopoeia (Rockville, MD). Of note, mArf1 is resistant to human Arf1 shRNA, although it is identical to human Arf1 at the protein level. PLA2G6-A long splice variant (L-iPLA2) transfection was as described previously (Larsson et al., 1998).
Immunofluorescence Microscopy
Immunofluorescence microscopy was as described previously (Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005). The antibodies used were as follows: mouse monoclonal antibodies against CLIMP-63 (Schweizer et al., 1993), α-tubulin (Kreis, 1987), myc (Itin et al., 1995), and GPP130 (Linstedt et al., 1997) and rabbit polyclonal antibodies against PLA2G6-A (H-120; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA), and Sec31 (Shugrue et al., 1999). H-120 antibody is predicted to detect an epitope at the N terminus of all PLA2G6-A splice variants. Phalloidin was from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). Bright field images were taken with a DM5000B (63 × 1.32 numerical aperture [NA] oil lens; Leica, Wetzlar, Germany), and confocal images were taken with an SPE (63 × 1.3 NA oil lens; Leica). Unbiased quantification of GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules was as follows: 1) selection of cells with nucECFP signal or with RFP signal, 2) scoring of cells with tubules if they have at least one long peripheral GFP-ERGIC-53 tubule, and 3) blind tests to minimize subjective analyses; 100% represents the total of counted cells. Unless stated otherwise, data are presented as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed with either a Student's t test or with a Wilcoxon rank sum test using MATLAB software (The MathWorks, Natick, MA).
Live Cell Imaging, Transport Blocks, and Drug Treatment
Imaging and processing were as described previously (Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005). Here, filters were applied to Supplemental Movies 2, 3, and 4. Block at 16°C and rewarming were as described previously (Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005). Nocodazole was from Fluka (Buchs, Switzerland); ONO-RS-082 was from BIOMOL International (Plymouth Meeting, PA); pyrrolidine-1 was from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA); and bromoenolactone (BEL) was from BIOMOL International. Egg l-α-lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) was from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). All the drugs were diluted in HEPES-buffered Ham's F12 medium (Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005). LPC was introduced into cells as follows. A 40 mM LPC stock solution diluted in chloroform was dried by blowing it with nitrogen gas. It was then mixed with 1 mg/ml fatty acid-free bovine serum albumin (Sigma-Aldrich) diluted in HEPES-buffered Ham's F12 medium to a final concentration of 25 μM LPC. Cells were treated with this mixture combined with 50 μM BEL for 20 min at 37°C.
Immunoblotting and Immunoprecipitation
Arf1 and Arf4 immunoblotting was described previously (Volpicelli-Daley et al., 2005). Quantification of knockdown efficiency was with the Odyssey program (Li-Cor Biosciences, Lincoln, NE). PLA2G6-A and myc immunoblotting was as follows. Cells were harvested at 4°C in lysis buffer (25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Na deoxycholate, and 1% NP40) supplemented with protease inhibitors. Lysates were then centrifuged 15 min at 14,000 × g at 4°C. Equal amounts of protein per lane were separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, immunoblotted, and visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence (Alpha Innotech, San Leandro, CA). PLA2G6-A was detected with P-19 antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), the myc tag with anti-myc antibody (Itin et al., 1995), Arf4 with R-891 (Cavenagh et al., 1996), and Arf1 with either R-1026 (Cavenagh et al., 1996) or with a peptide antibody (Skippen et al., 2002). Quantification was with Image Pro (Media Cybernetics, Bethesda, MD). For the immunoprecipitation, cells were transfected or not with mArf1, and supernatants of cell lysates were incubated with anti-PLA2G6-A (H-120) or anti-L-iPLA2 (T-14; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) coupled to protein G-Sepharose beads (Sigma-Aldrich). Beads were then washed with 1× phosphate-buffered saline and immunoblotted as described above.
RESULTS
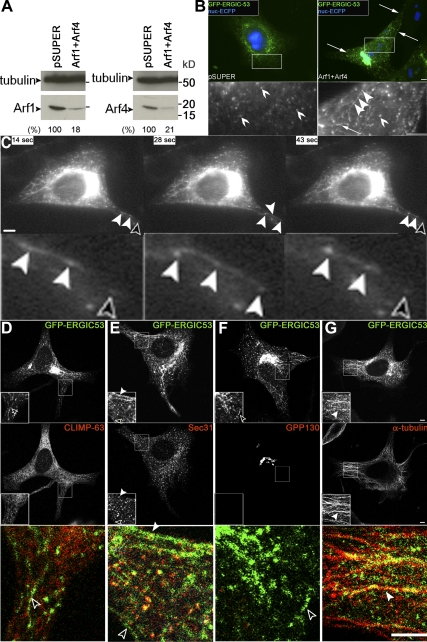
We studied the role of Arf1+Arf4 in controlling the ERGIC by using fluorescence microscopy and a knockdown approach. Because this method deals with single cells, proper detection of individual cells was required. To this end, we cloned into pSUPER vectors ECFP in frame with a nuclear localization signal (nucECFP). HeLa cells stably expressing GFP-ERGIC-53 transfected with Arf1+Arf4 shRNAs exhibited ∼80% reduction of both Arf1 and Arf4 (Figure 1A) similarly to shRNAs not carrying the nuclear indicator (Volpicelli-Daley et al., 2005), suggesting that nucECFP did not impair the knockdown efficiency. As predicted, nucECFP localized to the nucleus and to structures reminiscent of nucleoli (Figure 1B). nucECFP expression did not affect the localization of GFP-ERGIC-53 in control pSUPER-transfected cells, suggesting that this indicator was appropriate to identify single transfected cells.
Figure 1.
Arf1+Arf4 double knockdown induces ERGIC tubules. (A) The protein level of both Arf1 and Arf4 (lower arrowheads) was reduced to ∼20% in HeLa cells stably expressing GFP-ERGIC-53 and cotransfected with Arf1+Arf4 shRNAs. Lysates were blotted with anti-Arf1, anti-Arf4, or as a loading control with anti-tubulin. (B) Arf1+Arf4 knockdown induces GFP-ERGIC-53-positive tubules (arrows), which connect ERGIC clusters (bottom panel, filled arrowheads). Such connections are restricted to some ERGIC clusters in knockdown cells and are absent in control cells (bottom panel, empty arrowheads). Bottom panels are magnifications of the highlighted regions. (C) Time series of live cells imaged every ∼3 s (from Supplemental Movie S1) where stationary ERGIC clusters connected (filled arrowheads) or not (empty arrowheads) by tubules are observed. The bottom panel is a magnification. (D–G) Confocal sections of knockdown cells as described in B stained for CLIMP-63 (D), Sec31 (E), GPP130 (F), or α-tubulin (G). GFP-ERGIC-53 do not colocalize with CLIMP-63, Sec31, or GPP130 (empty arrowheads in D-F). In some instances GFP-ERGIC-53-positive tubules colocalize with Sec31 spots or α-tubulin tubules (filled arrowheads in E and G). Insets and bottom panels are a magnification of the highlighted regions. pSUPER and Arf1 shRNA vectors carry nucECFP. Transfected cells were identified by nucECFP signal. Bars, 5 μm.
Arf1+Arf4 Silencing Induces Tubulation of the ERGIC
Fixed Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells exhibited extensive GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules (Figure 1B). A tubule was defined as a membrane structure ≥5 μm in length. Tubules seemed to connect peripheral ERGIC clusters. More than 80% of double knockdown cells showed GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules. On average, only 19% of control cells, 27% of Arf1 knockdown cells and 14% of Arf4 knockdown cells exhibited tubules (Supplemental Figure S1A), consistent with the previous findings that single knockdowns of Arf1 or Arf4 have no noticeable phenotype (Volpicelli-Daley et al., 2005). Upon Arf1+Arf4 depletion, tubules were observed in two HeLa cell lines stably expressing GFP-ERGIC-53 as well as in parental HeLa cells stained for endogenous ERGIC-53 (Supplemental Figure S1B), indicating that the stable cells and parental HeLa cells behave indistinguishably. Thus, we think that tubulation of the ERGIC is a normal process that is highly accentuated in cells depleted of Arf1+Arf4.
Video microscopy of double knockdown cells showed that GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules were continuously elongating and shrinking (Figure 1C and Supplemental Movie 1), suggesting that a tubule was a continuous entity rather than a string of vesicles. Occasionally, tubules elongated toward peripheral spots (Figure 1C), confirming our observation with fixed cells that they connect ERGIC clusters. Tracking peripheral ERGIC spots revealed that Arf1+Arf4 knockdown did not alter the fission and fusion activity of GFP-ERGIC-53 stationary clusters (Supplemental Movie 2), and fast-moving carriers were still observed (Supplemental Movie 3). We conclude that Arf1+Arf4 act synergistically in cells to regulate the formation of ERGIC tubules.
To further characterize the tubules, we double labeled GFP-ERGIC-53 with markers of the secretory pathway. Arf1+Arf4 knockdown did not affect the morphology of ER or ER export sites (ERESs; Figure 1, D and E). GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules did not colocalize with the ER marker CLIMP-63 (Figure 1D), suggesting that these tubules were not ER-derived. ERESs, revealed by Sec31 staining, occasionally localized to GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules (Figure 1E). This overlap was fortuitous because localization of Sec31 spots on a tubule was random, and tubules with no Sec31 staining were observed. A previous study of Arf1+Arf4 knockdown reported cis-Golgi GM130-positive tubules (Volpicelli-Daley et al., 2005). However, GM130 can rapidly cycle between cis-Golgi and ERGIC (Marra et al., 2001), compromising the value of GM130 as a specific cis-Golgi marker. As a genuine cis-Golgi marker, we thus used the membrane protein GPP130 (Linstedt et al., 1997). In Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells, GPP130 showed an unchanged Golgi pattern, and no colocalization with GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules was observed (Figure 1F). Because the Golgi and the juxtanuclear accumulation of ERGIC clusters cannot be resolved by light microscopy, we focused our further analysis on peripheral ERGIC tubules at considerable distance from the Golgi.
In living cells, tubules were dynamic, suggesting that they moved along the cytoskeleton. To test this, we stained Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells for tubulin and actin. The distribution of microtubules (Figure 1G and Supplemental Figure S1C) and the actin cytoskeleton (Supplemental Figure S1D) was unchanged in these cells. GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules aligned with tubulin (Figure 1G and Supplemental Figure S1C) but not with actin (Supplemental Figure S1D). Treatment with nocodazole, a microtubule-disruptive drug, inhibited GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules, whereas no inhibition was observed with the actin-disrupting chemical latrunculin B (Supplemental Figure S1, C and D). These results are most consistent with the conclusion that the ERGIC tubules that arise in cells depleted of Arf1+Arf4 move along microtubules.
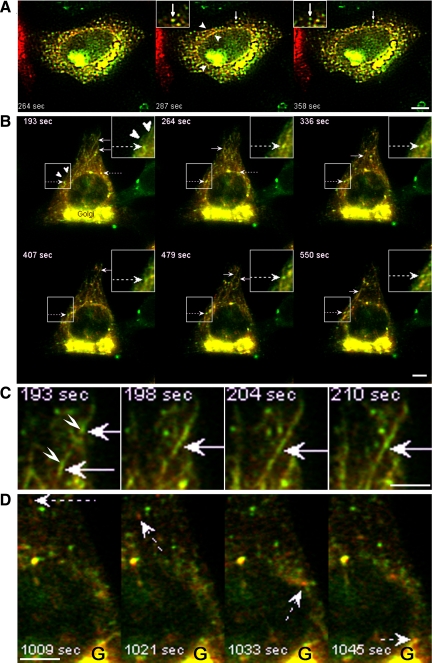
To understand the role of ERGIC tubules upon Arf1+Arf4 knockdown, we studied a marker of the secretory pathway, ssDsRed, in which an N-terminal signal sequence was added to DsRed (Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005). ssDsRed accumulates in the ER and ERGIC when cells are cooled to 16°C and is sorted into anterograde transport carriers directed to the Golgi upon rewarming to 37°C (Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005). This is clearly the result of a sorting event and not fusion of ERGIC with other organelles as the ERGIC clusters persist upon rewarming. In control pSUPER-transfected cells (Figure 2A and Supplemental Movie 4) or Arf1+Arf4-depleted cells (Figure 2B and Supplemental Movie 5) briefly rewarmed to 37°C, ssDsRed localized to ER and ERGIC clusters. Occasionally in control cells, dual-labeled dynamic tubules connecting peripheral ERGIC clusters were observed (Figure 2A). As the rewarming progressed, ERGIC clusters segregated ssDsRed without being consumed by the sorting event. In Arf1+Arf4-depleted cells, ssDsRed localized to tubules virtually all positive for GFP-ERGIC-53 (Figure 2B). Conversely, not all GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules were positive for ssDsRed. We assume that the ssDsRed-negative tubules represent ERGIC-to-ER retrograde traffic (Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005). Double-labeled tubules emerging from a peripheral ERGIC cluster were often directed toward another ERGIC cluster with which they seemed to fuse (Figure 2C). These tubules showed no substantial movement to the juxtanuclear Golgi region (Supplemental Movie 5). At later rewarming times, ERGIC clusters segregated ssDsRed carriers that moved to the Golgi (Figure 2D). Like in control cells, the sorting event did not consume ERGIC stationary clusters (Figure 2B and Supplemental Movie 5). Together, these observations indicate that cargo in the ERGIC can move between ERGIC clusters via tubules that are more numerous and persistent in Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells.
Figure 2.
Arf1+Arf4 mediate traffic between ERGIC peripheral clusters. Time series of live cells extracted from Supplemental Movies S4 and S5. Control and knockdown cells were as described in Figure 1B. They were in addition transfected with ssDsRed and incubated 3 h at 16°C followed by a shift to 37°C. Images were acquired every 3 s. (A) Arrows point to sorting ERGIC clusters. Arrowheads point to dual-labeled tubules. Insets are magnifications. (B) Arrows, dual-labeled tubules; dashed arrows, ERGIC clusters sorting ssDsRed without being consumed; arrowheads, ERGIC tubules devoid of ssDsRed. Insets, magnification of the highlighted region. (C) Arrows point to dual-labeled tubules connecting ERGIC clusters. Arrowheads point to ERGIC clusters. (D) Dashed arrows point to ssDsRed-positive anterograde carrier moving to the Golgi (G). Bars, 5 μm.
Role of Phospholipase A2 in ERGIC Tubulation
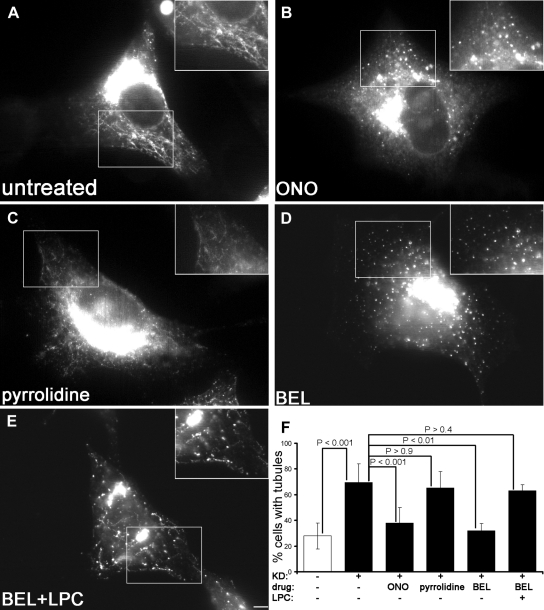
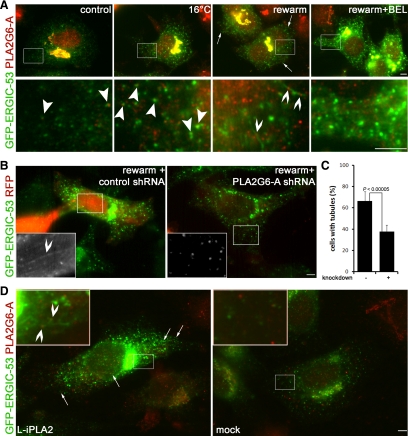
Tubulation in the early secretory pathway is controlled by PLA2 activity (de Figueiredo et al., 2000), probably due to the generation of lysophospholipids, fusogenic inverted cone-shaped lipids produced by PLA2, on the outer leaflet of the lipid bilayer (Brown et al., 2003). To date two PLA2 groups were suggested to function in the early secretory pathway: group IV calcium Ca2+-dependent PLA2 (PLA2G4, also named cPLA2) and group VI Ca2+-independent PLA2 (PLA2G6, also named iPLA2) (Brown et al., 2003; Ghosh et al., 2006). To explore whether the tubules observed in response to Arf1+Arf4 silencing were due to these PLA2, we treated knockdown cells with ONO-RS-082, an inhibitor of these activities. ONO-RS-082 reduced the number of ERGIC tubules (Figure 3B) as well as the percentage of cells with ERGIC tubules (Figure 3F), suggesting that tubules were due to PLA2. PLA2G4 has six members named A–E. Only PLA2G4-A (also named cytosolic PLA2α) can associate with the Golgi (Evans et al., 2001) and was shown to control Golgi morphology and intracellular traffic (Choukroun et al., 2000; San Pietro et al., 2009). To determine whether the tubules were due to PLA2G4-A activity, we treated Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells with pyrrolidine (Seno et al., 2000), which inhibits the activity of some PLA2G4 members without affecting the activity of PLA2G6 (Ghomashchi et al., 2001). Clearly, 20 μM pyrrolidine did not inhibit ERGIC tubules (Figure 3C) and did not decrease the percentage of cells with GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules (Figure 3F). Because HeLa cells have high levels of PLA2G4-A (Grewal et al., 2005), we increased the concentration of pyrrolidine up to 160 μM. Even at this high concentration, no effect on ERGIC tubules was observed (Supplemental Figure S2), suggesting that PLA2G4-A activity is not controlling ERGIC tubulation in Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells.
Figure 3.
ERGIC tubules induced by Arf1+Arf4 double knockdown are sensitive to some PLA2 antagonists. Cells were processed as described in Figure 1D and were either untreated (A) or treated for 20 min with ONO-RS-082 (B), pyrrolidine (C), BEL (D), or BEL supplemented with LPC (E). Bar, 5 μm. Insets are magnifications of the highlighted regions. (F) 100% represents the total number of cells counted. Results are shown as mean ± SD of three to nine independent experiments. p values were calculated with a Wilcoxon rank test. The white bar represents pSUPER-transfected cells. Black bars represent Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells.
BEL, a membrane permeable antagonist with a >1000-fold selectivity for PLA2G6 over PLA2G4 (Ackermann et al., 1995), inhibits tubules in the early secretory pathway (de Figueiredo et al., 2000). Treatment of Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells with 50 μM BEL inhibited ERGIC tubules (Figure 3D) and reduced the percentage of cells with GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules down to ∼32% (Figure 3F). This percentage was similar to that of pSUPER-transfected cells (∼28%), suggesting that tubules induced by Arf1+Arf4 depletion were dependent upon PLA2G6 activity.
LPC, a product of PLA2G6, bypasses the inhibition by BEL (Fensome-Green et al., 2007). To test whether this is also the case in Arf1+Arf4-depleted cells, we supplemented BEL-treated cells with LPC. BEL+LPC treatment restored GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules (Figure 3E), and 63% of Arf1+Arf4 depleted cells treated with BEL+LPC showed GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules (Figure 3F). This percentage was similar to untreated knockdown cells (69%), indicating that upon Arf1+Arf4 silencing, a product of PLA2G6 is necessary to induce ERGIC tubulation.
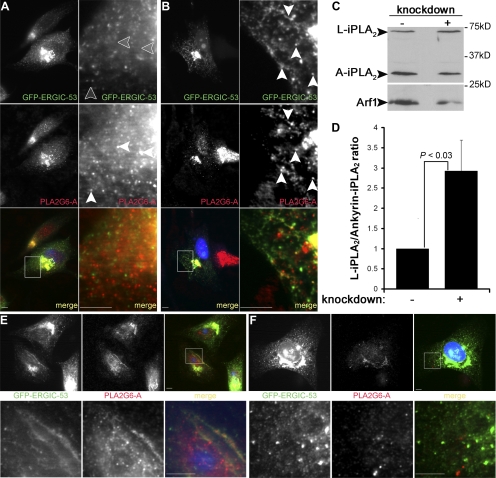
To pinpoint the PLA2G6 enzyme controlling ERGIC tubulation in vivo, we localized the endogenous A isoform of PLA2G6 (PLA2G6-A, also named iPLA2β). The B isoform (also named iPLA2γ) localizes to peroxisomes (Yang et al., 2003), ER, and mitochondria and responds to oxidative stress (Kinsey et al., 2007), rendering it less likely to control ERGIC tubulation upon Arf1+Arf4 depletion. In control cells, PLA2G6-A localized to peripheral puncta and to the Golgi region where it colocalized with juxtanuclear GFP-ERGIC-53 (Figure 4A). In these cells, peripheral PLA2G6-A puncta were largely distinct from ERGIC clusters. In Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells, PLA2G6-A accumulated in the juxtanuclear region and also localized to puncta (Figure 4B). Strikingly, in these cells PLA2G6-A puncta colocalized with GFP-ERGIC-53 clusters. In addition, PLA2G6-A associated with extensions that partially overlapped with GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules, suggesting that PLA2G6-A acts at these sites.
Figure 4.
Arf1+Arf4 depletion affects PLA2G6-A localization, and PLAG6-A silencing inhibits ERGIC tubules. (A) Control cells were treated as described in Figure 1B and stained with anti-PLA2G6-A. Arrowheads point to PLA2G6-A spots not colocalizing with ERGIC clusters. (B) Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells were treated as described in Figure 1D. Arrowheads point to PLA2G6-A spots and tubules colocalizing with ERGIC clusters and tubules. Right panels are magnifications of the highlighted regions. (C) Equal amounts of proteins from cell lysates were blotted with anti-PLA2G6-A (top) or with anti-Arf1 (bottom). (D) Quantification of the ratio L-iPLA2 to ankyrin-iPLA2. Values from Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells were normalized to pSUPER-transfected cells, the values of which were set to 1. Results are shown as mean ± SD from four independent experiments. p values were calculated using a Wilcoxon rank test. (E and F) Knockdown cells as described in B were transfected with control (E) or L-iPLA2 (F) shRNAs. Bottom panels are magnifications of the highlighted regions. Bars, 5 μm.
PLA2G6A has multiple splice variants: long variants (L-iPLA2) and short variants (ankyrin-iPLA2) (Larsson et al., 1998). If PLA2G6-A activity is high, ankyrin-iPLA2 protein levels are reduced. Thus, the L-iPLA2/ankyrin-iPLA2 ratio is proportional to PLA2G6-A activity (Manguikian and Barbour, 2004; Poulsen et al., 2007). We visualized L-iPLA2 and ankyrin-iPLA2 expression by Western blotting. Figure 4C shows that ankyrin-iPLA2 was reduced in Arf1+Arf4-depleted cells. The L-iPLA2/ankyrin-iPLA2 ratio was, on average, approximately threefold higher in knockdown cells (Figure 4D), indicating that PLA2G6-A activity was increased upon Arf1+Arf4 silencing.
L-iPLA2 overexpression induces PLA2G6-A activity (Larsson et al., 1998). We hypothesized that L-iPLA2 knockdown would decrease PLA2G6-A activity, and we tested whether L-iPLA2 controls ERGIC tubules. In cells depleted for L-iPLA2 and stained with an antibody recognizing all PLA2G6-A splice variants, PLA2G6-A fluorescence was reduced (Figure 4F). Triple transfection with Arf1+Arf4 shRNAs and control shRNA did not affect ERGIC tubules (Figure 4E). L-iPLA2 depletion inhibited ERGIC tubules in Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells (Figure 4F and Supplemental S3) and significantly reduced the percentage of cells with GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules (Supplemental Figure S3B), indicating that tubules are controlled by PLA2G6-A activity.
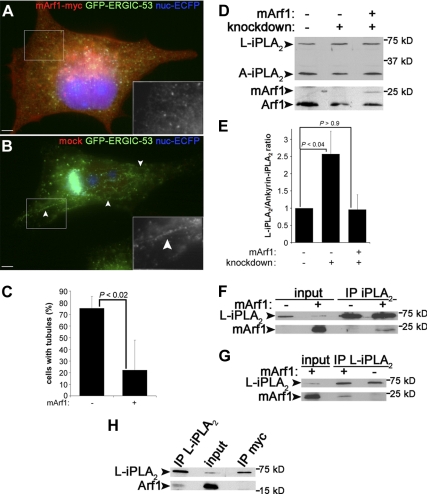
To explore the link between Arf1+Arf4 and PLA2G6-A, we attempted to rescue normal ERGIC morphology after Arf1+Arf4 depletion. Overexpression of mouse Arf1 (mArf1) in Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells decreased ERGIC tubules threefold (Figure 5, A–C), indicating that mArf1 rescues Arf1+Arf4 knockdown and thus mirrors an Arf4 single knockdown, which has no tubulation phenotype (Supplemental Figure S1A) (Volpicelli-Daley et al., 2005). We also tested whether mArf1 expression restores PLA2G6-A activity, which would be expected if Arf1+Arf4 and PLA2G6-A were linked. Figure 5D shows that ankyrin-iPLA2 level was increased in these cells. Quantification showed that expression of mArf1 reduces the L-iPLA2/ankyrin-iPLA2 ratio back to control levels (Figure 5E), suggesting that mArf1 restores PLA2G6-A activity that in turn decreases ERGIC tubules. We hypothesized that Arf1 regulates PLA2G6-A activity by binding to it and tested whether Arf1 interacts with PLA2G6-A. Coimmunoprecipitation indeed showed that endogenous PLA2G6-A (Figure 5F) and particularly endogenous L-iPLA2 can pull down a fraction of both mArf1 (Figure 5G) and endogenous Arf1 (Figure 5H).
Figure 5.
mArf1 rescues Arf1+Arf4 knockdown and interacts with PLA2G6-A. (A) Arf1+Arf4 knockdown cells as described in Figure 1D were transfected with mArf1 and stained with anti-myc. (B) Cells as described in A mock transfected. Insets are magnifications of GFP-ERGIC-53 channel in the highlighted regions. Arrowheads point to tubules. Bar, 5 μm. (C) Knockdown cells were counted as described in Figure 3F. Data are represented as mean ± SD from four to five independent experiments. The p value was calculated with a Wilcoxon rank test. (D) Same immunoblots as shown in Figure 4C with the rescue condition in addition. (E) Quantification of the ratio L-iPLA2 to ankyrin-iPLA2 as described in Figure 4D. Results are shown as mean ± SEM from four to eight independent experiments. p values were calculated using a Student's t test. (F) Cells transfected (+) or not (−) with mArf1 were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-PLA2G6-A (IP iPLA2) and blotted with anti-PLA2G6-A (top) or anti-myc (bottom). The total lysate (1%) is shown as a loading control. (G) Cells were processed as described in F and immunoprecipitated with anti-L-iPLA2 antibody (IP L-iPLA2). They were then immunoblotted as described in F. (H) Cells as described in F were immunoprecipitated with anti-L-iPLA2 antibody or as a negative control with anti-myc antibody. They were then immunoblotted with anti-PLA2G6-A (top) or anti-Arf1 (bottom).
Tubule formation at the ERGIC is not restricted to cells depleted of Arf1+Arf4. We and others have shown previously that in cells blocked at 15–16°C for a few hours and rewarmed briefly to 37°C, ERGIC tubules are generated (Lippincott-Schwartz et al., 1990; Schweizer et al., 1990; Klumperman et al., 1998; Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005; Simpson et al., 2006). These tubules move between ERGIC clusters and mediate recycling from the ERGIC to the ER (Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005). To test whether these tubules also depend on PLA2G6, we stained cells blocked at 16°C and rewarmed to 37°C for 5 min with anti-PLA2G6-A antibody. As shown in Figure 6A, in cells blocked at 16°C PLA2G6-A localized more often to ERGIC clusters than in control cells. Importantly, PLA2G6-A spots were observed on ERGIC tubules in cells rewarmed to 37°C. When cells were treated with BEL during the rewarming, no GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules were detected, in line with what was reported previously (de Figueiredo et al., 2000) and suggesting that traffic out of the ERGIC is mediated by PLA2G6-A activity. To corroborate this suggestion, we performed a 16°C/rewarming experiment in cells knocked down for PLA2G6-A. Figure 6B shows that, contrary to control cells that exhibit long tubules, PLA2G6-A knockdown inhibits ERGIC tubules in cells rewarmed from 16°C. Quantification confirmed these observations and revealed that upon PLA2G6-A depletion, the percentage of cells with ERGIC tubules was significantly decreased (Figure 6C). If appearance of ERGIC tubules is indeed controlled by PLA2G6-A, as our data indicate, then overexpression of L-iPLA2should induce at least some tubulation of the ERGIC. Figure 6D shows that cells overexpressing L-iPLA2 indeed exhibit GFP-ERGIC-53 positive tubules that are positive for PLA2G6-A spots.
Figure 6.
PLA2G6-A controls tubulation of the ERGIC under conditions where Arf1+Arf4 are not depleted. (A) HeLa cells stably expressing GFP-ERGIC-53 were incubated or not at 16°C for 3 h and rewarmed or not in the presence or absence of BEL. Cells were then stained with anti-PLA2G6-A. Arrows point to GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules. Filled arrowheads point to PLA2G6-A spots colocalizing with ERGIC clusters. Empty arrowheads indicate PLA2G6-A spots connected to ERGIC tubules. Bottom panels are magnifications of the highlighted regions. (B) Cells were cotransfected with pDsRedT1 (RFP) and either a control shRNA or a shRNA targeting PLA2G6-A. Cells were then rewarmed from 16°C as described above. PLA2G6-A knockdown cells were identified by RFP signal. The arrowhead points to ERGIC tubules. Insets are magnifications of GFP-ERGIC-53 channel in the highlighted regions. (C) PLA2G6-A knockdown cells treated as described in B were counted as described in Figure 3F. Data are represented as mean ± SD from five to six experiments. The p value was calculated using a Student's t test. (D) Cells were either mock transfected or transfected with L-iPLA2. Arrows point to GFP-ERGIC-53 tubules. Arrowheads point to PLA2G6-A spots localizing to ERGIC clusters and connected to ERGIC tubules. Insets are magnifications of the highlighted regions. Bars, 5 μm.
DISCUSSION
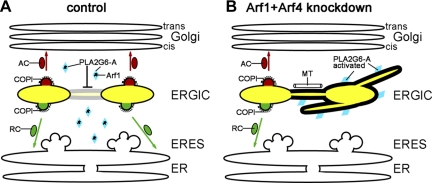
These and previous findings (Ben-Tekaya et al., 2005) show that ERGIC clusters are relatively stable entities that communicate by means of dynamic tubules (Figure 7). These ERGIC tubules are transient, and their formation is under regulation by both PLA2G6-A and Arf family GTPases. An increase in PLA2G6-A activity at ERGIC membranes leads to local changes in lipid composition, probably including increases in LPC. This leads to the formation of tubules that connect ERGIC clusters and through which cargo can move (Figure 7B). The ERGIC tubules were found to align with microtubules and depend upon microtubules for their formation. We propose that the role of these tubules is to direct cargo, quickly and efficiently, to ERGIC clusters where cargo sorting can still occur. This could serve either to help equilibrate the composition of ERGIC clusters and their cargos throughout the cell or perhaps to more efficiently move cargos to clusters that are more actively engaged in sorting of cargos. Such a model suggests that under normal conditions, Arf1+Arf4 together regulate PLA2G6-A activity, thereby promoting the more discontinuous nature of ERGIC clusters (Figure 7A). Arf1 and Arf4 were reported to localize to the ERGIC (Chun et al., 2008), consistent with the notion that they function in this compartment, although until now it was widely assumed that their function there was primarily to recruit COPI. Indeed, because Arf1+Arf4 silencing was shown to alter COPI recruitment to the early secretory pathway (Volpicelli-Daley et al., 2005), it will probably prove interesting in future studies to determine whether COPI plays any role in the regulation of ERGIC tubulation. Such a role may be difficult to dissect or reconcile with its role in ERGIC to cis-Golgi traffic. However, because Arfs have been found to regulate both adaptor recruitment and changes in lipid-metabolizing enzymes at other sites, one could speculate that tubulation is a viable cellular alternative to carrier biogenesis that is controlled by Arf activities. Our data do not give a clear explanation of which forms of Arf1 and Arf4 control PLA2G6-A activity and how they would do so. Because active PLA2G6-A is thought to be a homotetramer (Ackermann et al., 1994), one could speculate that Arf1+Arf4 inhibit PLA2G6-A tetramerization by sequestering L-iPLA2 monomers. We think that this function is independent of the GTPase activity of Arf1 and/or Arf4 as was shown for the interaction of Arf1 with phospholipase D (Jones et al., 1999a).
Figure 7.
Model of how Arf1, Arf4, and PLA2G6-A control ERGIC morphology. (A) Under steady-state conditions, ERGIC clusters (yellow) sort anterograde cargo (red) into anterograde carriers (AC) directed to the Golgi (red arrows) from retrograde cargo (green) into retrograde carriers (RC) directed to the ER (green arrows). Arf1 binds to PLA2G6-A, thus suppressing generation of ERGIC tubules. (B) Upon Arf1+Arf4 knockdown (or during rewarming from a 16°C block), PLA2G6-A becomes activated and changes the lipid composition of ERGIC membranes leading to tubules connecting ERGIC clusters. Cargo is transported via these tubules to ERGIC clusters that are still sorting-competent. ERGIC tubules move along microtubules (MT).
Effects of phospholipases on the secretory pathway were long believed to be indirect because the products of phospholipases stimulate various signal transduction pathways. However, recent findings point to direct effects of PLA2 and PLA1 (Morikawa et al., 2009; San Pietro et al., 2009; Schmidt and Brown, 2009), suggesting that different phospholipases control specific transport steps in the early secretory pathway. Here, we provide novel evidence for the involvement of PLA2G6-A in controlling the architecture of the ERGIC. Our findings indicate that in the ERGIC, a tight regulation of tubules is achieved through the interplay between Arf GTPases and PLA2G6-A. Such regulation might be an efficient way to flexibly cope with changes in the demands of membrane traffic.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Franck Gorelick (Yale University School of Medicine) for anti-Sec 31 antibodies; Laura Volpicelli-Daley for knockdown protocols; Pascal Escher (Biozentrum, University of Basel) for nucEGFP; Brian P. Kennedy (Merck Frosst Centre for Therapeutic Research) for L-iPLA2 cDNA; Benjamin S. Glick (University of Chicago) for pDsRedT1 vector; Jean Pieters (Biozentrum, University of Basel) for PLA2G6-A antibody; Eva Kögler, Käthy Bucher, Sandra Mitrovic, and Carine Bonnon for technical advice; Shamshad Cockroft (University College London) for valuable input and for reagents; and members of the Hauri group for suggestions. We also thank Christoph Dehio and his group members for support during the revision of this manuscript. The study was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation and the University of Basel (to H.B.-T. and H.-P.H.) and by the National Institutes of Health grant GM-67226 (to R.A.K.).
Abbreviations used:
- Arf
ADP ribosylation factor
- BEL
bromoenolactone
- BFA
brefeldin A
- ERGIC
endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment
- L-iPLA2
PLA2G6-A long splice variant
- LPC
lysophosphatidylcholine
- mArf1
mouse Arf1
- nucECFP
nuclear localized ECFP
- PLA2
phospholipase A2
- PLA2G4
group IV calcium Ca2+-dependent PLA2
- PLA2G6
group VI calcium independent phospholipase A2.
Footnotes
This article was published online ahead of print in MBoC in Press (http://www.molbiolcell.org/cgi/doi/10.1091/mbc.E10-01-0022) on September 29, 2010.
REFERENCES
- Ackermann E. J., Conde-Frieboes K., Dennis E. A. Inhibition of macrophage Ca(2+)-independent phospholipase A2 by bromoenol lactone and trifluoromethyl ketones. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:445–450. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.1.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann E. J., Kempner E. S., Dennis E. A. Ca(2+)-independent cytosolic phospholipase A2 from macrophage-like P388D1 cells. Isolation and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:9227–9233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appenzeller-Herzog C., Hauri H. P. The ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC): in search of its identity and function. J. Cell Sci. 2006;119:2173–2183. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannykh S. I., Rowe T., Balch W. E. The organization of endoplasmic reticulum export complexes. J. Cell Biol. 1996;135:19–35. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Tekaya H., Miura K., Pepperkok R., Hauri H. P. Live imaging of bidirectional traffic from the ERGIC. J. Cell Sci. 2005;118:357–367. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum R., Stephens D. J., Schulz I. Lumenal targeted GFP, used as a marker of soluble cargo, visualises rapid ERGIC to Golgi traffic by a tubulo-vesicular network. J. Cell Sci. 2000;113:3151–3159. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.18.3151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuza L., Halbeisen R., Jeno P., Otte S., Barlowe C., Hong W., Hauri H. P. Proteomics of endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC) membranes from brefeldin A-treated HepG2 cells identifies ERGIC-32, a new cycling protein that interacts with human Erv46. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:47242–47253. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406644200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Chambers K., Doody A. Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) enzymes in membrane trafficking: mediators of membrane shape and function. Traffic. 2003;4:214–221. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2003.00078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenagh M. M., Whitney J. A., Carroll K., Zhang C., Boman A. L., Rosenwald A. G., Mellman I., Kahn R. A. Intracellular distribution of Arf proteins in mammalian cells. Arf6 is uniquely localized to the plasma membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:21767–21774. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.36.21767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choukroun G. J., Marshansky V., Gustafson C. E., McKee M., Hajjar R. J., Rosenzweig A., Brown D., Bonventre J. V. Cytosolic phospholipase A(2) regulates Golgi structure and modulates intracellular trafficking of membrane proteins. J. Clin. Invest. 2000;106:983–993. doi: 10.1172/JCI8914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun J., Shapovalova Z., Dejgaard S. Y., Presley J. F., Melancon P. Characterization of class I and II ADP-ribosylation factors (Arfs) in live cells: GDP-bound class II Arfs associate with the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment independently of GBF1. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2008;19:3488–3500. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E08-04-0373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Figueiredo P., Drecktrah D., Polizotto R. S., Cole N. B., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Brown W. J. Phospholipase A2 antagonists inhibit constitutive retrograde membrane traffic to the endoplasmic reticulum. Traffic. 2000;1:504–511. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2000.010608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bloom G. S., Kreis T. E., Klausner R. D. Dissociation of a 110-kD peripheral membrane protein from the Golgi apparatus is an early event in brefeldin A action. J. Cell Biol. 1990;111:2295–2306. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. H., Spencer D. M., Zweifach A., Leslie C. C. Intracellular calcium signals regulating cytosolic phospholipase A2 translocation to internal membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:30150–30160. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100943200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fensome-Green A., Stannard N., Li M., Bolsover S., Cockcroft S. Bromoenol lactone, an inhibitor of Group V1A calcium-independent phospholipase A2 inhibits antigen-stimulated mast cell exocytosis without blocking Ca2+ influx. Cell Calcium. 2007;41:145–153. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2006.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullekrug J., Sonnichsen B., Schafer U., Nguyen Van P., Soling H. D., Mieskes G. Characterization of brefeldin A induced vesicular structures containing cycling proteins of the intermediate compartment/cis-Golgi network. FEBS Lett. 1997;404:75–81. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(97)00097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghomashchi F., Stewart A., Hefner Y., Ramanadham S., Turk J., Leslie C. C., Gelb M. H. A pyrrolidine-based specific inhibitor of cytosolic phospholipase A(2)alpha blocks arachidonic acid release in a variety of mammalian cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2001;1513:160–166. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(01)00349-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh M., Tucker D. E., Burchett S. A., Leslie C. C. Properties of the Group IV phospholipase A2 family. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006;45:487–510. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2006.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. S., Nakano A. Membrane traffic within the Golgi apparatus. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009;25:113–132. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.24.110707.175421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewal S., Herbert S. P., Ponnambalam S., Walker J. H. Cytosolic phospholipase A2-alpha and cyclooxygenase-2 localize to intracellular membranes of EA.hy. 926 endothelial cells that are distinct from the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. FEBS J. 2005;272:1278–1290. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J., Shibata Y., Zhu P. P., Voss C., Rismanchi N., Prinz W. A., Rapoport T. A., Blackstone C. A class of dynamin-like GTPases involved in the generation of the tubular ER network. Cell. 2009;138:549–561. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itin C., Schindler R., Hauri H. P. Targeting of protein ERGIC-53 to the ER/ERGIC/cis-Golgi recycling pathway. J. Cell Biol. 1995;131:57–67. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Bax B., Fensome A., Cockcroft S. ADP ribosylation factor 1 mutants identify a phospholipase D effector region and reveal that phospholipase D participates in lysosomal secretion but is not sufficient for recruitment of coatomer I. Biochem. J. 1999a;341:185–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G., Moore C., Hashemolhosseini S., Brenner H. R. Constitutively active MuSK is clustered in the absence of agrin and induces ectopic postsynaptic-like membranes in skeletal muscle fibers. J. Neurosci. 1999b;19:3376–3383. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-09-03376.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsey G. R., McHowat J., Beckett C. S., Schnellmann R. G. Identification of calcium-independent phospholipase A2gamma in mitochondria and its role in mitochondrial oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2007;292:F853–F860. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00318.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klumperman J., Schweizer A., Clausen H., Tang B. L., Hong W., Oorschot V., Hauri H. P. The recycling pathway of protein ERGIC-53 and dynamics of the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment. J. Cell Sci. 1998;111:3411–3425. doi: 10.1242/jcs.111.22.3411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E. Microtubules containing detyrosinated tubulin are less dynamic. EMBO J. 1987;6:2597–2606. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuismanen E., Saraste J. Low temperature-induced transport blocks as tools to manipulate membrane traffic. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;32:257–274. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson P. K., Claesson H. E., Kennedy B. P. Multiple splice variants of the human calcium-independent phospholipase A2 and their effect on enzyme activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:207–214. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.1.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linstedt A. D., Mehta A., Suhan J., Reggio H., Hauri H. P. Sequence and overexpression of GPP130/GIMPc: evidence for saturable pH-sensitive targeting of a type II early Golgi membrane protein. Mol. Biol. Cell. 1997;8:1073–1087. doi: 10.1091/mbc.8.6.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Donaldson J. G., Schweizer A., Berger E. G., Hauri H. P., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Microtubule-dependent retrograde transport of proteins into the ER in the presence of brefeldin A suggests an ER recycling pathway. Cell. 1990;60:821–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90096-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotti L. V., Torrisi M. R., Pascale M. C., Bonatti S. Immunocytochemical analysis of the transfer of vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein from the intermediate compartment to the Golgi complex. J. Cell Biol. 1992;118:43–50. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manguikian A. D., Barbour S. E. Cell cycle dependence of group VIA calcium-independent phospholipase A2 activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:52881–52892. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410659200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marie M., Dale H. A., Sannerud R., Saraste J. The function of the intermediate compartment in pre-Golgi trafficking involves its stable connection with the centrosome. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2009;20:4458–4470. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E08-12-1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra P., Maffucci T., Daniele T., Tullio G. D., Ikehara Y., Chan E. K., Luini A., Beznoussenko G., Mironov A., De Matteis M. A. The GM130 and GRASP65 Golgi proteins cycle through and define a subdomain of the intermediate compartment. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001;3:1101–1113. doi: 10.1038/ncb1201-1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mironov A. A., et al. ER-to-Golgi carriers arise through direct en bloc protrusion and multistage maturation of specialized ER exit domains. Dev. Cell. 2003;5:583–594. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00294-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa R. K., Aoki J., Kano F., Murata M., Yamamoto A., Tsujimoto M., Arai H. Intracellular phospholipase A1gamma (iPLA1gamma) is a novel factor involved in coat protein complex I- and Rab6-independent retrograde transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2009;284:26620–26630. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.038869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orso G., Pendin D., Liu S., Tosetto J., Moss T. J., Faust J. E., Micaroni M., Egorova A., Martinuzzi A., McNew J. A., Daga A. Homotypic fusion of ER membranes requires the dynamin-like GTPase Atlastin. Nature. 2009;460:978–983. doi: 10.1038/nature08280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein transport. Science. 1975;189:347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen K. A., Pedersen S. F., Kolko M., Lambert I. H. Induction of group VIA phospholipase A2 activity during in vitro ischemia in C2C12 myotubes is associated with changes in the level of its splice variants. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007;293:C1605–C1615. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00012.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renault L., Guibert B., Cherfils J. Structural snapshots of the mechanism and inhibition of a guanine nucleotide exchange factor. Nature. 2003;426:525–530. doi: 10.1038/nature02197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Pietro E., et al. Group IV phospholipase A(2)alpha controls the formation of inter-cisternal continuities involved in intra-Golgi transport. PLoS Biol. 2009;7:e1000194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sannerud R., Marie M., Nizak C., Dale H. A., Pernet-Gallay K., Perez F., Goud B., Saraste J. Rab1 defines a novel pathway connecting the pre-Golgi intermediate compartment with the cell periphery. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2006;17:1514–1526. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E05-08-0792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Dale H. A., Bazzocco S., Marie M. Emerging new roles of the pre-Golgi intermediate compartment in biosynthetic-secretory trafficking. FEBS Lett. 2009;583:3804–3810. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheel J., Pepperkok R., Lowe M., Griffiths G., Kreis T. E. Dissociation of coatomer from membranes is required for brefeldin A-induced transfer of Golgi enzymes to the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 1997;137:319–333. doi: 10.1083/jcb.137.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A., Brown W. J. Lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase 3 regulates Golgi complex structure and function. J. Cell Biol. 2009;186:211–218. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200904147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer A., Ericsson M., Bachi T., Griffiths G., Hauri H. P. Characterization of a novel 63 kDa membrane protein. Implications for the organization of the ER-to-Golgi pathway. J. Cell Sci. 1993;104:671–683. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.3.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer A., Fransen J. A., Bachi T., Ginsel L., Hauri H. P. Identification, by a monoclonal antibody, of a 53-kD protein associated with a tubulo-vesicular compartment at the cis-side of the Golgi apparatus. J. Cell Biol. 1988;107:1643–1653. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer A., Fransen J. A., Matter K., Kreis T. E., Ginsel L., Hauri H. P. Identification of an intermediate compartment involved in protein transport from endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi apparatus. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1990;53:185–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seno K., et al. Pyrrolidine inhibitors of human cytosolic phospholipase A(2) J. Med. Chem. 2000;43:1041–1044. doi: 10.1021/jm9905155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shugrue C. A., Kolen E. R., Peters H., Czernik A., Kaiser C., Matovcik L., Hubbard A. L., Gorelick F. Identification of the putative mammalian orthologue of Sec31P, a component of the COPII coat. J. Cell Sci. 1999;112:4547–4556. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.24.4547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J. C., Nilsson T., Pepperkok R. Biogenesis of tubular ER-to-Golgi transport intermediates. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2006;17:723–737. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E05-06-0580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skippen A., Jones D. H., Morgan C. P., Li M., Cockcroft S. Mechanism of ADP ribosylation factor-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate synthesis in HL60 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:5823–5831. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110274200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szul T., Grabski R., Lyons S., Morohashi Y., Shestopal S., Lowe M., Sztul E. Dissecting the role of the ARF guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1 in Golgi biogenesis and protein trafficking. J. Cell Sci. 2007;120:3929–3940. doi: 10.1242/jcs.010769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedrenne C., Klopfenstein D. R., Hauri H. P. Phosphorylation controls CLIMP-63-mediated anchoring of the endoplasmic reticulum to microtubules. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2005;16:1928–1937. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E04-07-0554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpicelli-Daley L. A., Li Y., Zhang C. J., Kahn R. A. Isoform-selective effects of the depletion of ADP-ribosylation factors 1–5 on membrane traffic. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2005;16:4495–4508. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E04-12-1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Han X., Gross R. W. Identification of hepatic peroxisomal phospholipase A(2) and characterization of arachidonic acid-containing choline glycerophospholipids in hepatic peroxisomes. FEBS Lett. 2003;546:247–250. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00581-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeghouf M., Guibert B., Zeeh J. C., Cherfils J. Arf, Sec7 and Brefeldin A: a model towards the therapeutic inhibition of guanine nucleotide-exchange factors. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005;33:1265–1268. doi: 10.1042/BST0331265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.