Abstract
Vitamin D is a pleiotropic secosteroid hormone important for health and disease prevention. The actions of vitamin D are mediated by the vitamin D receptor that binds the active form of vitamin D [1,25(OH)2D] to induce both transcriptional and non-genomic responses. Vitamin D has well known classical functions in calcium uptake and bone metabolism, but more recent work highlights the importance of the nonclassical actions of vitamin D in a variety of cell types. These actions include modulation of the innate and adaptive immune systems and regulation of cell proliferation. Adequate vitamin D intake is essential for maternal and fetal health during pregnancy, and epidemiological data indicate that many pregnant women have sub-optimal vitamin D levels. Notably, vitamin D deficiency correlates with preeclampsia, gestational diabetes mellitus, and bacterial vaginosis, and an increased risk for C-section delivery. Recent work emphasizes the importance of nonclassical roles of vitamin D in pregnancy and the placenta. The placenta produces and responds to vitamin D where vitamin D functions as a modulator of implantation, cytokine production and the immune response to infection. We describe vitamin D metabolism and the cellular responses to vitamin D, and then summarize the role of vitamin D in placental trophoblast, pregnancy and the fetus.
Keywords: Vitamin D, Vitamin D receptor, Placenta, Pregnancy, Trophoblast
1. Introduction
The vitamin D endocrine system is pivotal for calcium homeostasis, bone mineralization, immune function, cell proliferation, and disease prevention [1]. Vitamin D is not a true vitamin because there are sources other than diet. Instead, this key nutrient is a pro-hormone, which can be synthesized from a steroid precursor if not obtained from diet. Vitamin D was discovered as a preventive treatment for rickets, a disease of children that yields bone softening, fractures, and deformity [2]. The classical actions of this hormone were first described in kidney and bone. We now know that vitamin D is also involved in many nonclassical processes [3]. Vitamin D itself is devoid of biological activity, but enzymatic conversion to 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D] generates the hormonal form with diverse biological activities [4]. The actions of 1,25(OH)2D are mediated through specific, high affinity binding to the vitamin D receptor (VDR), which is present in multiple tissues [5,6]. Target organs for the nonclassical actions of the vitamin D endocrine system include the adaptive and innate immune systems, pancreatic β-cells, the heart and cardiovascular system, and the brain [6]. Tissue responses include effects on hormone secretion, modulation of immune responses, and control of cellular proliferation and differentiation [3]. Vitamin D analogs may prove useful to prevent some human diseases and to treat autoimmune diseases and cancer [7,8].
Recent work suggests important roles for the VDR and VDR signaling pathways in the placenta. Human placental trophoblasts express the VDR, and the P450 cytochromes encoded by the CYP27B1 and CYP24A1 genes. Trophoblasts both produce and respond to 1,25(OH)2D. 1,25(OH)2D regulates synthesis of hormones involved in pregnancy and influences the trophoblast anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial responses [9–13]. In early pregnancy, 1,25(OH)2D induces decidualization, which is key to implantation [14, 15]. Moreover, CYP27B1 modulates immune function during early gestation [16] and vitamin D deficiency associates with bacterial vaginosis, impaired calcium metabolism and fetal growth, preeclampsia, insulin resistance, gestational diabetes mellitus and primary cesarean section [17–21]. This review summarizes vitamin D metabolism and action, with a focus on the function of vitamin D during human pregnancy and on human placental villi and cultures of placental trophoblasts.
2. Biochemistry of vitamin D and the vitamin D receptor
2.1. Metabolism and transport of vitamin D
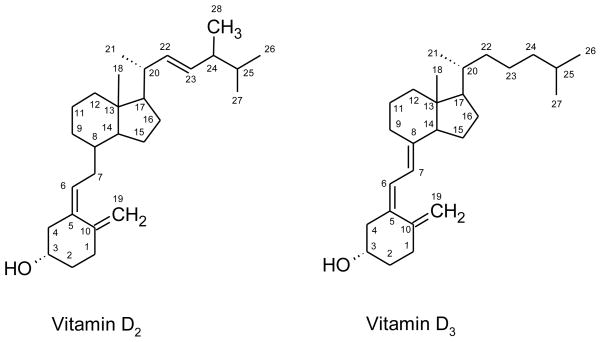
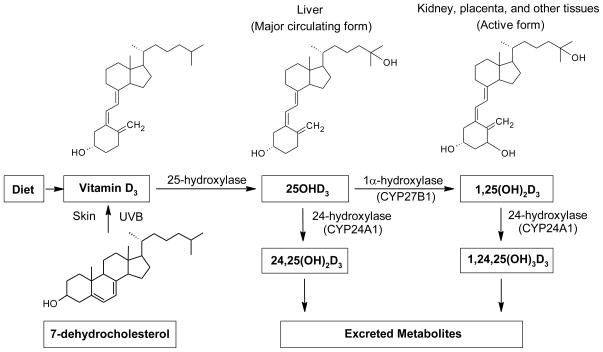
Vitamin D is a general term for a chemically related family of secosteroid hormones. Vitamin D2 is produced in plants and vitamin D3 is produced in mammals (Fig. 1). In humans, vitamin D2, also called ergocholecalciferol, is one-third as potent as vitamin D3, which is also called cholecalciferol [22]. Vitamin D can be obtained from dietary sources but can also be synthesized. Ultraviolet B light induces cleavage of the B-ring of 7-dehydrocholesterol in skin to yield the secosteroid vitamin D3 [1, 23] (Fig. 2). Hereafter, “vitamin D” is used to represent either vitamin D2 or vitamin D3.
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of vitamins D2 and D3.
Figure 2. Synthesis and metabolism of vitamin D.
Vitamin D2 and D3 can be obtained by diet. Vitamin D2 is metabolized similarly to vitamin D3, but with only one third of the biological activity (see text). Vitamin D3 is synthesized photochemically in the skin from 7-dehydrocholesterol by ultraviolet B exposure and converted to 25OHD3 by a 25-hydroxylase in the liver. The major circulating form of vitamin D, 25OHD3, is hydroxylated in the kidney, placenta, and other tissues by the enzyme, 1α– hydroxylase (encoded by the CYP27B1 gene), to the bioactive form, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25(OH)2D3]. The enzyme, 24-hydroxylase (encoded by the CYP24A1 gene), catabolizes both 25OHD3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 to inactive metabolites 24,25(OH)2D3 and 1,24,25(OH)3D3, respectively, which are then excreted.
Vitamin D and metabolites are hydrophobic, and >99% are transported in the blood bound to vitamin D binding protein (DBP, also known as Gc-globulin) which binds with high affinity in the order 25OHD=24,25(OH)2D>1,25(OH)2D>vitamin D2 or D3. A small fraction (<1%) of these metabolites are also carried by albumin and lipoprotein [2,24]. DBP-bound vitamin D2 and D3 are internalized in the liver and hydroxylation by a mitochondrial P450 enzyme generates 25OHD, which is the predominant vitamin D compound in the circulation. In the renal proximal tubules of the kidney, DBP-25OHD binds to and is internalized by megalin/cubilin, a heterodimeric endocytic receptor pair [25,26]. The 25OHD is released and is hydroxylated by 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1α-hydroxylase, the product of the CYP27B1 gene, to yield 1,25(OH)2D. This kidney generated 1,25(OH)2D is key in mediating the classical functions of vitamin D in calcium homeostasis and bone mineralization [4,27,28]. The production of 1,25(OH)2D in the kidney is stimulated by parathyroid hormone and inhibited by fibroblast growth factor 23 and by elevated calcium and phosphate concentrations [29]. Extra-renal expression of CYP27B1 and 1,25(OH)2D production from 25OHD occurs in immune cells, the skin, the placenta and other tissues [1,13,30] and may contribute to health in both non-pregnant and pregnant women [13,31,32].
Importantly, both 1,25(OH)2D and 25OHD are inactivated by CYP24A1, a 24-hydroxylase mitochondrial cytochrome p450 enzyme. This hydroxylase converts both substrates into inactive end products, including 1,24,25-trihydroxyvitamin D and 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [27,33]. As CYP24A1 transcription is induced by 1,25(OH)2D [34], 1,25(OH)2D provides a negative feedback control on 1,25(OH)2D levels.
The mechanisms of 25OHD and 1,25(OH)2D import into most non-kidney tissues are poorly understood. DBP-bound vitamin D compounds have limited effect on most target cells and biological activity often correlates with the free hormone concentration [2,36,37]. This is in agreement with the “free hormone hypothesis” which postulates the active form for most target cells is unbound 1,25(OH)2D that diffuses across the plasma membrane and binds the VDR to effect either non-genomic, transcriptional, or both, responses [35]. However, megalin/cubilin mediates the import of DBP-bound 25OHD into mammary cells, which express CYP27B1 and can therefore produce 1,25(OH)2D intracellularly [38]. Megalin/cubilin-mediated endocytosis may be involved in import of DBP-25OHD into other CYP27B1-expressing target cells [39]. One such candidate is the placenta, which expresses megalin and cubilin [40–45]. What has not been studies is whether or not vitamin D compounds enter placental cells by endocytosis of DBP-25OHD, by diffusion of free hormone, or by both mechanisms. Polymorphisms and allelic variants of the vitamin D system have been correlated with disease. Notably, polymorphisms in the VDR and DBP genes associate with several forms of cancer, multiple sclerosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and polymorphisms in the VDR, CYP27B1 and cubilin genes are associated with type I diabetes [46–50]. Some of these polymorphisms yield altered levels of circulating 25OHD, while others may affect the vitamin D pathway at other levels [46].
2.2. Vitamin D receptor and response pathways
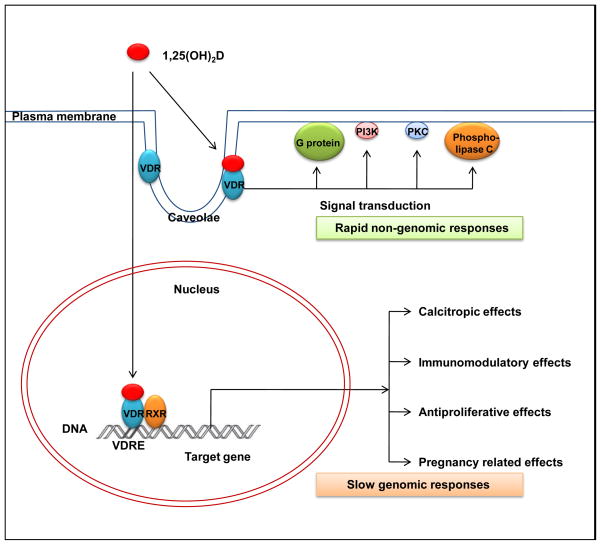
The biological activity of vitamin D occurs via two pathways, a slow genomic response and a rapid, non-genomic response [6] (Fig. 3). Both involve binding of 1,25(OH)2D with the VDR, a member of the super family of nuclear receptors for steroid hormones [51–53]. In the genomic response pathway, ligand-bound VDR then binds a partner receptor, typically the retinoid X receptor (RXR), and the heterodimer regulates the transcription of vitamin D target genes by binding with high affinity to vitamin D response elements (VDREs) in the promoter region of the gene [2,52]. The VDR contains two globular domains, a DNA-binding domain (DBD) and a ligand-binding domain (LBD) [52,53]. The DBD has two zinc-finger motifs responsible for recognition and binding to the VDREs. The LBD binds to 1,25(OH)2D with high affinity and is involved in dimerization and transcriptional activation. Coactivators and corepressors also affect VDR molecular action [3,54,55]. The steroid receptor coactivator complex (SRC) 1–3 and vitamin D receptor interacting complex (DRIP) act as coactivators to enhance gene transcription. Corepressors, such as those encoded by the hairless gene, bind to VDR in the absence of ligand and block VDR-mediated transcription but the corepressors rapidly detach from the VDR in the presence of 1,25(OH)2D. In the non-genomic response pathway, 1,25(OH)2D binds to VDR associated with caveolae of the plasma membrane and the ligand-bound VDR then activates one or more signaling cascades, including protein kinase C, mitogen-activated protein kinases, phospholipase A2, and phospholipase C [6,56].
Figure 3.
Genomic and non-genomic responses of vitamin D receptor binding to 1,25(OH)2D.
In the genomic response, 1,25(OH)2D binds to the nuclear vitamin D receptor (VDR). Heterodimerization of the VDR with the retinoid X receptor (RXR) and binding to vitamin D response elements (VDREs) in the promoters of target genes affects transcription, usually by increasing transcription, and generating downstream biological responses. In the non-genomic response pathway, binding of 1,25(OH)2D to VDR associated with caveolae of the plasma membrane activates one or more second messenger systems to elicit rapid responses. PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C
3. Nonclassical actions of vitamin D
The classical functions of vitamin D are in the kidney, liver and intestine to regulate calcium and phosphate absorption and bone synthesis and metabolism. Recent data indicate vitamin D functions in nonclassical ways as well. Over 30 human tissues express the vitamin D receptor and are thus equipped to respond to 1,25(OH)2D [6]. Vitamin D and the VDR play a role in immune function, cell proliferation, cellular differentiation and hormone secretion.
3.1. Regulation of immune function
Vitamin D affects the function of both the adaptive and innate immune systems. In general, 1,25(OH)2D reduces the activity of the adaptive immune system and enhances the activity of the innate immune system [3,57,58].
In the adaptive immune system, 1,25(OH)2D inhibits IgG production, proliferation and differentiation of B lymphocytes and inhibits proliferation of T lymphocytes [58–61]. 1,25(OH)2D also inhibits proliferation of T helper 1 (Th1) cells and thus limits the cytokines produced by these cells. Conversely, 1,25(OH)2D induces the cytokines of T helper 2 (Th2) and regulatory T cells (Treg) [58,62]. Th1 cells produce interferon gamma (IFN-γ), interleukin-2 (IL-2), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and Th2 cells produce IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-10, and IL-13 [63]. Perhaps because of its ability to inhibit the adaptive immune response and inflammation, vitamin D and vitamin D agonists are effective in suppression of autoimmune disorders in several animal models. Among these disorders are rheumatoid arthritis, type I diabetes, experimental allergic encephalitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and systemic lupus erythematosus [7]. Vitamin D analogs are currently being investigated for treatment of autoimmune diseases in humans [64,65]. Recommendations for treatment however must await clinical studies of safety as suppression of the adaptive immune system may compromise resistance to infection.
The innate immune system acts immediately when confronted with microbial infection. This process involves vitamin D and myeloid and epithelial cells that express Toll-like receptors (TLRs), CYP27B1, and the VDR [66–68]. There are ten TLRs in humans and they are activated by binding ligands of microbial origin. Antimicrobial peptides, including α- and β-defensins and cathelicidins, kill organisms in the macrophage and are secreted by epithelial cells [69]. A typical antimicrobial secreted by epithelium is cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP), which is also called LL-37/FALL-39 in the cleaved, active form [67,70,71]. TLR activation induces LL-37 secretion in multiple epithelial lined tissues exposed to microbial agents, from salivary glands to reproductive tissues [70]. TLR activation also increases CYP27B1 transcription, 1,25(OH)2D levels, and CAMP transcription [66,67,70,71]. CAMP activation and the response capability is limited if VDR is blocked, CYP24A1 is inhibited, or 25OHD is deficient. These data show that vitamin D clearly affects multiple arms of the body’s immune response.
3.2. Regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation
1,25(OH)2D can regulate cell cycle progression, cell differentiation and induce apoptosis [8,72–76]. Over the last several decades, 1,25(OH)2D has been shown to have anti-proliferative and pro-differentiation activity in a variety of cell types, including keratinocytes, osteoblasts, mesenchymal, neural, vascular endothelial, chondrocytes and immune cells. The proliferation effects are mediated, at least in part, by the induction of cell-cycle inhibitors that prevent the transition from the G1 to the S phase of the cell cycle, and the differentiation effects by changes in the expression of growth factors and cytokines. 1,25(OH)2D does not always inhibit proliferation and promote differentiation: in dendritic cells 1,25(OH)2D promotes a persistent state of immaturity [77]. Thus, the effects of vitamin D on cell proliferation and differentiation are complex and vary between cell types.
Vitamin D and its analogs have clinical importance in the treatment of psoriasis, a skin condition characterized by keratinocyte hyperproliferation, abnormal differentiation, and immune-cell infiltration into the epidermis and dermis [74]. Topical administration of calcipotriene, a vitamin D analog, and corticosteroids are an effective treatment [78]. The anti-psoriatic activity of calcipotriene and other vitamin D analogs likely involves increased differentiation and decreased proliferation of keratinocytes, and reduced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and of several genes, including keratin 16 which is abnormally expressed in psoriatic epidermal cells [74,78]. The anti-proliferative and pro-differentiation effects of vitamin D has recently suggested a role for this hormone in cancer evolution and in the suppression of tumor growth. Vdr−/− mutant mice display hyperproliferation of cells in the kidney and mammary gland and develop cancer at elevated rates when challenged with carcinogens [79]. Parathyroid hyperplasia is a serious secondary complication in patients with kidney failure, and recent studies indicate vitamin D or its analogs may have clinical relevance. In a uremic rat model of kidney disease, parathyroid hyperplasia is associated with an increase in expression of transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF-α) and its receptor (epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR), are increased [80]. Treatment with 1,25(OH)2D diminished TGF-α expression and increased expression of p21WAF with a concomitant reduction in parathyroid cell proliferation [81]. In a recent clinical trial with dialysis patients, intravenous treatment with 1,25(OH)2D reduced the progression of parathyroid enlargement [82].
Breast, colon, prostate and other cancers are associated with vitamin D deficiency [29,53,83]. Importantly, postmenopausal women who received four years of 1,100 IU vitamin D per day and 1500 mg calcium per day had substantially lower risks of many forms of cancer compared to control [84]. Vitamin D and its analogs show promise in the treatment of breast, colon and prostate cancers in animal and cell culture models [8,53,85], likely because of the anti-proliferative, pro-differentiation and pro-apoptotic activities of this hormone. Because the hypercalcemic effects of vitamin D limit its therapeutic application, non-hypercalcemic analogs are more likely to have clinical value. Collectively, these studies show that vitamin D has wide ranging effects on normal and dysregulated cellular growth.
4. Vitamin D effects during pregnancy
4.1. Effects of vitamin D on the placenta and trophoblast cells
The human placenta expresses all components for vitamin D signaling, including the VDR, RXR, CYP27B1 and CYP24A1. Weisman et al. [86] found that human decidual and placental tissues synthesize 1,25(OH)2D and 24,25(OH)2D. In agreement with these findings, cultured primary human syncytiotrophoblasts and decidual cells produce 1,25(OH)2D and secrete the active form into the culture medium [86–89]. Increased levels of 1,25(OH)2D reduces transcription of CYP27B1 in primary human cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts [13,34] but transcription of CYP24A1 increases [34]. Antagonists of VDR can block the 1,25(OH)2D induced increase in CYP24A1 levels, suggesting the effect is mediated by ligand-bound VDR [34]. Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), a key regulator of fetal growth, stimulates hydroxylation of 25OHD in a dose-dependent manner in cultured placental cells [90]. In the 3A human trophoblast cell line, unlike in macrophages, CYP27A1 expression is not increased by TLR2 binding ligand [13,91]. 1,25(OH)2D inhibits expression of cytokines, such as granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor 2 (GMCSF-2), TNF-α, IL-6, and increases expression of CAMP in primary cultured human decidual cells and cytotrophoblasts [12,13,89]. Importantly, when the 3A trophoblast cell line was exposed to E. coli, vitamin D treatment resulted in a lower rate of infection and reduced cell death, likely because of the increased CAMP levels [13]. This finding suggests vitamin D supplementation may reduce infection during pregnancy.
4.2. Vitamin D functions during pregnancy
Important changes occur in the maternal concentration of vitamin D and in calcium metabolism during pregnancy. Calcium is transported from the mother to the fetus through the placenta. In rats, the placenta transports 25(OH)2D and 24,25(OH)2D but not 1,25(OH)2D [92]. Although transplacental transport has not been studied in humans, vitamin D passage from the mother to the fetus would be facilitated by serum concentrations of 1,25(OH)2D being higher in the maternal compared to the fetal cirulations [93]. Synthesis in the kidney of 1,25(OH)2D increases during pregnancy. In addition, the decidua and placenta generate a large amount of 1,25(OH)2D by CYP27B1 enzyme activity [86]. Moreover, specific methylation of the placental CYP24A1 represses transcription of this gene [94]. Production thus exceeds clearance and 1,25(OH)2D levels increase, being two-fold higher in serum of women in the third trimester of pregnancy than in non-pregnant or post-partum women [93,95].
The synthesis, metabolism and function of vitamin D compounds during pregnancy are complex. The human endometrial decidua makes 1,25(OH)2D and 24,25(OH)2D and the placenta synthesizes 24,25OH2D [86]. Notably, the 24,25(OH)2D synthesized by the placenta accumulates in bone [92] and may be involved in ossification of the fetal skeleton [86]. Although the sheep fetus can synthesize 24,25(OH)D from 25OH and the 24 hydroxylase enzyme is expressed in the fetal kidney [96] the sheep fetus cannot produce 1,25(OH)2D, as renal 1 hydroxylase activity is suppressed in this relatively hypercalcemic and hyperphosphatemic environment. 24,25(OH)2D is the major form of vitamin D in the fetal lamb [96] and this metabolite, instead of 1,25(OH)2D, may promote calcium absorption by the placenta and enhance skeletal ossification, without increasing fetal blood calcium concentrations or urinary excretion of calcium. If the sheep placenta produces 1,25(OH)2D, as does the human placenta, increased calcium absorption by the maternal gut may be enhanced to meet the increasing demands of the fetus for calcium through gestation.
1,25(OH)2D and CYP27B1 play a role in the autocrine and paracrine immunomodulatory networks prominent during gestation [16]. 1,25(OH)2D affects decidual dendritic cells and macrophages, which in turn interact in the maternal-fetal interface to stimulate T-regulatory cells [97,98]. 1,25(OH)2D also inhibits the release of Th1 cytokines and increases release of Th2 cytokines, as discussed in section 3.1, and Th2 cytokines thus dominate at implantation [16,63]. This modulation of the immune system may prevent rejection of the implanted embryo. 1,25(OH)2D also aids in the transformation of endometrial cells into decidual cells [14,97] and increases expression of HOXA10 [15] a gene important for embryo implantation and myeloid differentiation in early pregnancy [14,15,97].
Established as the chorioallantoic placenta at the end of the first trimester, villous tissues secrete multiple hormones that maintain pregnancy and regulate placental physiology. In human syncytiotrophoblasts, the VDR, CYP27B1, CYP24A1 and 1,25(OH)2D, in an autocrine manner, combine to regulate the expression of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), human placental lactogen (hPL), estradiol and progesterone [9–11]. Collectively, the data suggest that 1,25(OH)2D aids implantation and maintains normal pregnancy, supports fetal growth through delivery of calcium, controls secretion of multiple placental hormones, and limits production of proinflammatory cytokines.
4.3. Vitamin D effects on the mother and child
Vitamin D intake is essential for maternal health and prevention of adverse outcomes. Circulating 25OHD concentrations reflect vitamin D status, and the normal range is between ~32ng/mL and ~80ng/mL, with values below ~32 ng/mL defined as deficient [29,99] (Table 1). Pregnancy does not exacerbate hypocalcaemia and secondary hyperparathyroidism in people with pre-existing vitamin D deficiency [100]. However, vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy is associated with the nonclassical actions of this hormone, being linked with preeclampsia insulin resistance, and gestational diabetes mellitus [18,32,98,101,102]. Notably, vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy is of epidemic proportions, present in ~20–85% of women, depending on country of residence and other factors [99,103].
Table 1.
Risks of vitamin D deficiency (serum 25OHD <32ng/mL) during pregancy mothers and offspring
| Mother | Fetus and newborn | Child |
|---|---|---|
| Preeclampsia [18] | Low birth weight [70] | Bone weakening [120,121] |
| Gestational diabetes [20] | Craniotabes [115] | Type I diabetes [125] |
| Cesarean section [21] | Acute lower respiratory tract infection [119] | Schizophrenia [124] |
| Bacterial vaginosis [17] | Hypocalcemic seizure [116] Reduced femur growth in utero [117] Infant heart failure [118] |
Asthma [122,123] |
Preeclampsia, as identified by new onset hypertension and proteinuria during pregnancy, is a serious disorder affecting 5–8% of pregnancies, and is alleviated only by delivery of the placenta. Preeclampsia rates are elevated during winter months, when sunlight-dependent 25OHD production is reduced [104], and vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of preeclampsia [18, 102]. Vitamin D supplementation reduces preeclampsia risk, compared to unsupplemented controls [101]. Preeclampsia is associated with low circulating levels of IGF-I and 1,25(OH)2D [102] and, in vitro, IGF-1 increases 1,25(OH)2D production by primary human syncytiotrophoblasts from placentas from normal pregnancies [90] but not from preeclamptic pregnancies [105]. Furthermore, trophoblasts isolated from the placentas of preeclamptic women have only one-tenth the CYP27B1 enzyme activity of trophoblasts from uncomplicated pregnancies [68]. Although the role of vitamin D in preeclampsia is unclear [32,102,106], one hypothesis is that low vitamin D levels impair the normal Th1 to Th2 cytokine balance, with higher Th1 cytokine expression adversely affecting the immunological tolerance of embryo implantation [107].
Insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, and diabetes are correlated with deficits in vitamin D. 1,25(OH)2D regulates insulin secretion by pancreatic β-cells and thereby affects circulating glucose levels [32,108,109]. As expected, low concentration of 25OHD is a risk factor for glucose intolerance while higher serum concentrations of 25OHD correlate with improved insulin sensitivity [108]. Vitamin D deficiency during early pregnancy significantly increases the risk for gestational diabetes in later pregnancy [20].
Vitamin D may influence the course of infectious diseases during pregnancy. In limited studies, low vitamin D levels in HIV-positive pregnant women were correlated with increased mortality and mother-to-child HIV transmission [110,111] and a polymorphism in the VDR gene is correlated with the frequency of HIV-to-AIDS progression [112]. Low 25OHD levels are correlated with increased bacterial vaginosis in the first trimester [17] and bacterial vaginosis is more prevalent in black women. Indeed, black women typically have lower serum 25OHD concentrations and have a six-fold higher chance of vitamin D deficiency, compared with white women [17,103]. Vitamin D effects on the immune system, cytokines, and antibacterial peptides likely regulate the bacterial flora.
Serum 25OHD levels are inversely related to primary cesarean section in nulliparous women, an unexpected and unexplained maternal outcome recently identified [21]. The risk was four-fold higher in women with serum 25OHD level below 37.5 nM/L (15ng/mL) controlling for multiple confounding factors. VDR and 1,25(OH)2D normally increase skeletal muscle function. Conversely, vitamin D deficiency results in proximal muscle weakness and decreased lower extremity muscle function [113], perhaps contributing to the risk for cesarean section [21].
Adequate maternal vitamin D levels are also important for fetal and child health (Table 1). Inadequate vitamin D intake during pregnancy is associated with low infant birth weight in populations at risk for adverse outcomes [70]. Maternal vitamin D deficiency also has been associated with craniotabes [115], a softening of skull bones that is one of the earliest signs of vitamin D deficiency, in a case study with neonatal seizures of a hypocalcemic infant [116] and with impaired skeletal development in utero [117]. Recent retrospective studies found a significant and previously undetected association of maternal vitamin D deficiency with rickets-associated infant heart failure [118] and with acute lower respiratory tract infection [119], a serious complication often associated with sepsis without clinical signs of rickets. Interestingly, vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy is also associated with risks of health problems later in childhood, including improper bone development at 9 yrs of age [120,121], asthma [122,123], schizophrenia [124], and type I diabetes [125].
5. Conclusions
We have described the multiple effects of vitamin D in human health. The classical and nonclassical pathways of this hormone affect calcium metabolism, the immune system, cell proliferation and differentiation, infection, and cancer. The enzymes encoded by the CYP27B1 and CYP24A1 genes are local regulators of levels of 1,25(OH)2D, which binds the VDR to induce both the genomic and non-genomic responses. Importantly, vitamin D analogs offer new potentials for treatments of a variety of diseases and disorders. What is clear is that adequate vitamin D intake in pregnancy is optimal for maternal, fetal and child health. However, vitamin D deficiency is prevalent and this potentially has negative consequences for both mother and child. Clearly, further investigation into the effects of vitamin D, of vitamin D supplementation, and of vitamin D analogs will contribute to an improvement in human health generally and mothers and children specifically.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant RO1-HD29190 to D.M.N. CHA University provided financial support for J.S. We thank Baosheng Chen for helpful discussions.
Abbreviations
- 1,25(OH)2D
1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D
- 25OHD
25-hydroxyvitamin D
- CYP24A1
24-hydroxylase
- CYP27B1
1α-hydroxylase
- CAMP
cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide
- DBD
DNA-binding domain
- EGFR
epidermal growth factor receptor
- hCG
human chorionic gonadotropin
- hPL
human placental lactogen
- IFN-γ
interferon-gamma
- IGF
insulin-like growth factor
- IL
interleukin
- LBD
ligand-binding domain
- RXR
retinoid X receptor
- Th1
T helper 1
- Th2
T helper 2
- TLR
toll-like receptor
- TGF-α
tumor growth factor-alpha
- TNF-α
tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- Treg
regulatory T cell
- DBP
vitamin D binding protein (Gc-globulin)
- VDR
vitamin D receptor
- VDRE
vitamin D response element
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Norman AW. From vitamin D to hormone D: fundamentals of the vitamin D endocrine system essential for good health. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;88:491S–9S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/88.2.491S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brown AJ, Dusso A, Slatopolsky E. Vitamin D. Am J Physiol. 1999;277:F157–75. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1999.277.2.F157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bikle D. Nonclassic actions of vitamin D. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:26–34. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jones G, Strugnell SA, DeLuca HF. Current understanding of the molecular actions of vitamin D. Physiol Rev. 1998;78:1193–231. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1998.78.4.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zittermann A. Vitamin D in preventive medicine: are we ignoring the evidence? Br J Nutr. 2003;89:552–72. doi: 10.1079/BJN2003837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mizwicki MT, Norman AW. The vitamin D sterol vitamin D receptor ensemble model offers unique insights into both genomic and rapid-response signaling. Sci Signal. 2009;2:re4. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.275re4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Adorini L. Intervention in autoimmunity: The potential of vitamin D receptor agonists. Cell Immunol. 2005;233:115–24. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2005.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Masuda S, Jones G. Promise of vitamin D analogues in the treatment of hyperproliferative conditions. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5:797–808. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Barrera D, Avila E, Hernández G, Méndez I, González L, Halhali A, et al. Calcitriol affects hCG gene transcription in cultured human syncytiotrophoblasts. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2008;6:3. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-6-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stephanou A, Ross R, Handwerger S. Regulation of human placental lactogen expression by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Endocrinology. 1994;135:2651–6. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.6.7988455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Barrera D, Avila E, Hernández G, Halhali A, Biruete B, Larrea F, et al. Estradiol and progesterone synthesis in human placenta is stimulated by calcitriol. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007;103:529–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.12.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Díaz L, Noyola-Martínez N, Barrera D, Hernández G, Avila E, Halhali A, et al. Calcitriol inhibits TNF-alpha-induced inflammatory cytokines in human trophoblasts. J Reprod Immunol. 2009;81:17–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2009.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Liu N, Kaplan AT, Low J, Nguyen L, Liu GY, Equils O, et al. Vitamin D induces innate antibacterial responses in human trophoblasts via an intracrine pathway. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:3517–22. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.108.073577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Halhali A, Acker GM, Garabédian M. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 induces in vivo the decidualization of rat endometrial cells. J Reprod Fertil. 1991;91:59–64. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0910059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Du H, Daftary GS, Lalwani SI, Taylor HS. Direct regulation of HOXA10 by 1,25-(OH)2D3 in human myelomonocytic cells and human endometrial stromal cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2005;19:2222–33. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zehnder D, Evans KN, Kilby MD, Bulmer JN, Innes BA, Stewart PM, et al. The ontogeny of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase expression in human placenta and decidua. Am J Pathol. 2002;161:105–14. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64162-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bodnar LM, Krohn MA, Simhan HN. Maternal vitamin D deficiency is associated with bacterial vaginosis in the first trimester of pregnancy. J Nutr. 2009;139:1157–61. doi: 10.3945/jn.108.103168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bodnar LM, Catov JM, Simhan HN, Holick MF, Powers RW, Roberts JM. Maternal vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of preeclampsia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:3517–22. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-0718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mannion CA, Gray-Donald K, Koski KG. Association of low intake of milk and vitamin D during pregnancy with decreased birth weight. CMAJ. 2006;174:1287–90. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.1041388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhang C, Qiu C, Hu FB, David RM, van Dam RM, Bralley A, et al. Maternal plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and the risk for gestational diabetes mellitus. PLoS One. 2008;3:e3753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Merewood A, Mehta SD, Chen TC, Bauchner H, Holick MF. Association between vitamin D deficiency and primary cesarean section. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:940–5. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Armas LA, Hollis BW, Heaney RP. Vitamin D2 is much less effective than vitamin D3 in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:5387–91. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-0360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Holick MF, Frommer JE, McNeill SC, Richtand NM, Henley JW, Potts JT., Jr Photometabolism of 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3 in skin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977;76:107–14. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91674-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cooke NE, Haddad JG. Vitamin D binding protein (Gcglobulin) Endocr Rev. 1989;10:294–307. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-3-294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Christensen EI, Birn H. Megalin and cubilin: multifunctional endocytic receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:256–66. doi: 10.1038/nrm778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Christensen EI, Verroust PJ, Nielsen R. Receptor-mediated endocytosis in renal proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 2009;458:1039–48. doi: 10.1007/s00424-009-0685-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Omdahl JL, Morris HA, May BK. Hydroxylase enzymes of the vitamin D pathway: expression, function, and regulation. Annu Rev Nutr. 2002;22:139–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.22.120501.150216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shinki T, Shimada H, Wakino S, Anazawa H, Hayashi M, Saruta T, et al. Cloning and expression of rat 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1alpha-hydroxylase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:12920–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.24.12920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:266–81. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra070553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zehnder D, Bland R, Williams MC, McNinch RW, Howie AJ, Stewart PM, et al. Extrarenal expression of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1 alpha-hydroxylase. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:888–94. doi: 10.1210/jcem.86.2.7220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hewison M, Burke F, Evans KN, Lammas DA, Sansom DM, Liu P, et al. Extra-renal 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1alpha-hydroxylase in human health and disease. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007;103:316–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.12.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lapillonne A. Vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy may impair maternal and fetal outcomes. Med Hypotheses. 2010;74:71–5. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2009.07.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Henry HL. The 25(OH)D3/1alpha,25(OH)2D3-24R-hydroxylase: a catabolic or biosynthetic enzyme? Steroids. 2001;66:391–8. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(00)00158-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Avila E, Díaz L, Barrera D, Halhali A, Méndez I, González L, et al. Regulation of vitamin D hydroxylases gene expression by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and cyclic AMP in cultured human syncytiotrophoblasts. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007;103:90–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mendel CM. The free hormone hypothesis: a physiologically based mathematical model. Endocr Rev. 1989;10:232–74. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-3-232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chun RF, Lauridsen AL, Suon L, Zella LA, Pike JW, Modlin RL, et al. Vitamin D-Binding Protein Directs Monocyte Responses to 25-Hydroxy- and 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:3368–76. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Speeckaert M, Huang G, Delanghe JR, Taes YE. Biological and clinical aspects of the vitamin D binding protein (Gc-globulin) and its polymorphism. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;372:33–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2006.03.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rowling MJ, Kemmis CM, Taffany DA, Welsh J. Megalin-mediated endocytosis of vitamin D binding protein correlates with 25-hydroxycholecalciferol actions in human mammary cells. J Nutr. 2006;136:2754–9. doi: 10.1093/jn/136.11.2754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jones G. Pharmacokinetics of vitamin D toxicity. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;88:582S–6S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/88.2.582S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cox B, Kotlyar M, Evangelou AI, Ignatchenko V, Ignatchenko A, Whiteley K, et al. Comparative systems biology of human and mouse as a tool to guide the modeling of human placental pathology. Mol Syst Biol. 2009;5:279. doi: 10.1038/msb.2009.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Juhlin C, Lundgren S, Johansson H, Lorentzen J, Rask L, Larsson E, et al. 500-Kilodalton calcium sensor regulating cytoplasmic Ca2+ in cytotrophoblast cells of human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:8275–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sahali D, Mulliez N, Chatelet F, Laurent-Winter C, Citadelle D, Roux C, et al. Coexpression in humans by kidney and fetal envelopes of a 280 kDa-coated pit-restricted protein. Similarity with the murine target of teratogenic antibodies. Am J Pathol. 1992;140:33–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Crider-Pirkle S, Billingsley P, Faust C, Hardy DM, Lee V, Weitlauf H. Cubilin, a binding partner for galectin-3 in the murine utero-placental complex. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:15904–12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200331200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Viola-Villegas N, Rabideau AE, Bartholomä M, Zubieta J, Doyle RP. Targeting the cubilin receptor through the vitamin B12 uptake pathway: cytotoxicity and mechanistic insight through fluorescent Re(I) delivery. J Med Chem. 2009;52:5253–61. doi: 10.1021/jm900777v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lambot N, Lybaert P, Boom A, Delogne-Desnoeck J, Vanbellinghen AM, Graff G, et al. Evidence for a clathrin-mediated recycling of albumin in human term placenta. Biol Reprod. 2006;75:90–7. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.105.050021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.McGrath JJ, Saha S, Burne TH, Eyles DW. A systematic review of the association between common single nucleotide polymorphisms and 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2010;121:471–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.03.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Köstner K, Denzer N, Müller CS, Klein R, Tilgen W, Reichrath J. The relevance of vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphisms for cancer: a review of the literature. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:3511–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chishimba L, Thickett DR, Stockley RA, Wood AM. The vitamin D axis in the lung: a key role for vitamin D-binding protein. Thorax. 2010;65:456–62. doi: 10.1136/thx.2009.128793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Smolders J, Peelen E, Thewissen M, Menheere P, Cohen Tervaert JW, Hupperts R, et al. The relevance of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms for vitamin D research in multiple sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;8:621–6. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2009.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ramos-Lopez E, Lange B, Penna-Martinez M, Brück P, Swiech K, Mauf S, et al. The role of cubilin gene polymorphisms and their influence on 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 plasma levels in type 1 diabetes patients. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2010;121:442–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.03.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Baker AR, McDonnell DP, Hughes M, Crisp TM, Mangelsdorf DJ, Haussler MR, et al. Cloning and expression of full-length cDNA encoding human vitamin D receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:3294–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Dusso AS, Brown AJ, Slatopolsky E. Vitamin D. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;289:F8–28. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00336.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Deeb KK, Trump DL, Johnson CS. Vitamin D signalling pathways in cancer: potential for anticancer therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:684–700. doi: 10.1038/nrc2196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sutton AL, MacDonald PN. Vitamin D: More than a “Bone-a-Fide” hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17:777–91. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Rachez C, Freedman LP. Mechanisms of gene regulation by vitamin D3 receptor: a network of coactivator interactions. Gene. 2000;246:9–21. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(00)00052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Huhtakangas JA, Olivera CJ, Bishop JE, Zanello LP, Norman AW. The vitamin D receptor is present in caveolae-enriched plasma membranes and binds 1 alpha,25(OH)2-vitamin D3 in vivo and in vitro. Mol Endocrinol. 2004;18:2660–71. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Adams JS, Liu PT, Chun R, Modlin RL, Hewison M. Vitamin D in defense of the human immune response. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2007;1117:94–105. doi: 10.1196/annals.1402.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Adams JS, Hewison M. Unexpected actions of vitamin D: new perspectives on the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2008;4:80–90. doi: 10.1038/ncpendmet0716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Rigby WF, Stacy T, Fanger MW. Inhibition of T lymphocyte mitogenesis by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) J Clin Invest. 1984;74:1451–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI111557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Chen S, Sims GP, Chen XX, Gu YY, Chen S, Lipsky PE. Modulatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on human B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 2007;179:1634–47. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.3.1634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lemire JM, Adams JS, Sakai R, Jordan SC. 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses proliferation and immunoglobulin production by normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Clin Invest. 1984;74:657–61. doi: 10.1172/JCI111465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Lemire JM, Archer DC, Beck L, Spiegelberg HL. Immunosuppressive actions of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: preferential inhibition of Th1 functions. J Nutr. 1995;125(6 Suppl):1704S–8S. doi: 10.1093/jn/125.suppl_6.1704S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Piccinni MP, Scaletti C, Maggi E, Romagnani S. Role of hormone-controlled Th1- and Th2-type cytokines in successful pregnancy. J Neuroimmunol. 2000;109:30–3. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(00)00299-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Laverny G, Penna G, Vetrano S, Correale C, Nebuloni M, Danese S, et al. Efficacy of a potent and safe vitamin D receptor agonist for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Immunol Lett. 2010;131:49–58. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2010.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Cutolo M. Hormone therapy in rheumatic diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010;22:257–63. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e328336ec24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Liu PT, Schenk M, Walker VP, Dempsey PW, Kanchanapoomi M, Wheelwright M, et al. Convergence of IL-1b and VDR activation pathways in human TLR2/1-induced antimicrobial responses. PLoS One. 2009;4:e5810. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Wang TT, Nestel FP, Bourdeau V, Nagai Y, Wang Q, Liao J, et al. Cutting edge: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression. J Immunol. 2004;173:2909–12. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.5.2909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Liu PT, Stenger S, Tang DH, Modlin RL. Cutting Edge: Vitamin D mediated human antimicrobial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis is dependent on the induction of cathelicidin. J Immunol. 2007;179:2060–3. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.4.2060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Zasloff M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature. 2002;415:389–95. doi: 10.1038/415389a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Gombart AF, Borregaard N, Koeffler HP. Human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor and is strongly up-regulated in myeloid cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. FASEB J. 2005;19:1067–77. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-3284com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Martineau AR, Wilkinson KA, Newton SM, Floto RA, Norman AW, Skolimowska K, et al. IFN-gamma- and TNF-independent vitamin D-inducible human suppression of mycobacteria: the role of cathelicidin LL-37. J Immunol. 2007;178:7190–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.11.7190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Banerjee P, Chatterjee M. Antiproliferative role of vitamin D and its analogs- a brief overview. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003;253:247–54. doi: 10.1023/a:1026072118217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Samuel S, Sitrin MD. Vitamin D’s role in cell proliferation and differentiation. Nutr Rev. 2008;66(10 Suppl 2):S116–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2008.00094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Nagpal S, Na S, Rathnachalam R. Noncalcemic actions of vitamin D receptor ligands. Endocr Rev. 2005;26:662–87. doi: 10.1210/er.2004-0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Gurlek A, Pittelkow MR, Kumar R. Modulation of growth factor/cytokine synthesis and signaling by 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: implications in cell growth and differentiation. Endocr Rev. 2002;23:763–86. doi: 10.1210/er.2001-0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Verstuyf A, Carmeliet G, Bouillon R, Mathieu C. Vitamin D: a pleiotropic hormone. Kidney Int. 2010;78:140–5. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Griffin MD, Lutz W, Phan VA, Bachman LA, McKean DJ, Kumar R. Dendritic cell modulation by 1alpha,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its analogs: a vitamin D receptor-dependent pathway that promotes a persistent state of immaturity in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:6800–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.121172198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Saraceno R, Gramiccia T, Frascione P, Chimenti S. Calcipotriene/betamethasone in the treatment of psoriasis: a review article. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009;10:2357–65. doi: 10.1517/14656560903198960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Bouillon R, Carmeliet G, Verlinden L, van Etten E, Verstuyf A, Luderer HF, et al. Vitamin D and human health: lessons from vitamin D receptor null mice. Endocr Rev. 2008;29:726–76. doi: 10.1210/er.2008-0004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Cozzolino M, Lu Y, Sato T, Yang J, Suarez IG, Brancaccio D, et al. A critical role for enhanced TGF-alpha and EGFR expression in the initiation of parathyroid hyperplasia in experimental kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;289:F1096–102. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00167.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Cozzolino M, Lu Y, Finch J, Slatopolsky E, Dusso AS. p21WAF1 and TGF-alpha mediate parathyroid growth arrest by vitamin D and high calcium. Kidney Int. 2001;60:2109–17. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Taniguchi M, Tokumoto M, Tsuruya K, Hirakata H, Iida M. Intravenous calcitriol therapy in an early stage prevents parathyroid gland growth. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:3662–9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Guyton KZ, Kensler TW, Posner GH. Cancer chemoprevention using natural vitamin D and synthetic analogs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001;41:421–42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.41.1.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lappe JM, Travers-Gustafson D, Davies KM, Recker RR, Heaney RP. Vitamin D and calcium supplementation reduces cancer risk: results of a randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 85:1586–91. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/85.6.1586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Choi M, Makishima M. Therapeutic applications for novel non-hypercalcemic vitamin D receptor ligands. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2009;19:593–606. doi: 10.1517/13543770902877717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Weisman Y, Harell A, Edelstein S, David M, Spirer Z, Golander A. 1 alpha, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in vitro synthesis by human decidua and placenta. Nature. 1979;281:317–9. doi: 10.1038/281317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Díaz L, Sánchez I, Avila E, Halhali A, Vilchis F, Larrea F. Identification of a 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase gene transcription product in cultures of human syncytiotrophoblast cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:2543–9. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.7.6693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Pospechova K, Rozehnal V, Stejskalova L, Vrzal R, Pospisilova N, Jamborova G, et al. Expression and activity of vitamin D receptor in the human placenta and in choriocarcinoma BeWo and JEG-3 cell lines. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009;299:178–87. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Evans KN, Nguyen L, Chan J, Innes BA, Bulmer JN, Kilby MD, et al. Effects of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on cytokine production by human decidual cells. Biol Reprod. 2006;75:816–22. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.106.054056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Halhali A, Díaz L, Sánchez I, Garabédian M, Bourges H, Larrea F. Effects of IGF-I on 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 synthesis by human placenta in culture. Mol Hum Reprod. 1999;5:771–6. doi: 10.1093/molehr/5.8.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Liu PT, Stenger S, Li H, Wenzel L, Tan BH, Krutzik SR, et al. Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response. Science. 2006;311:1770–3. doi: 10.1126/science.1123933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Noff D, Edelstein S. Vitamin D and its hydroxylated metabolites in the rat. Placental and lacteal transport, subsequent metabolic pathways and tissue distribution. Horm Res. 1978;9:292–300. doi: 10.1159/000178924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Kovacs CS, Kronenberg HM. Maternal-fetal calcium and bone metabolism during pregnancy, puerperium, and lactation. Endocr Rev. 1997;18:832–72. doi: 10.1210/edrv.18.6.0319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Novakovic B, Sibson M, Ng HK, Manuelpillai U, Rakyan V, Down T, et al. Placenta-specific methylation of the vitamin D 24-hydroxylase gene: Implications for feedback autoregulation of active vitamin D levels at the fetomaternal interface. J Biol Chem. 2009;28:14838–48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809542200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Cross NA, Hillman LS, Allen SH, Krause GF, Vieira NE. Calcium homeostasis and bone metabolism during pregnancy, lactation, and postweaning: a longitudinal study. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995;61:514–23. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/61.3.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Kooh SW, Vieth R. 25-hydroxyvitamin D metabolism in the sheep fetus and lamb. Pediatric Res. 1980;14:360. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198004000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Evans KN, Bulmer JN, Kilby MD, Hewison M. Vitamin D and placental-decidual function. J Soc Gynecol Investig. 2004;11:263–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jsgi.2004.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Gregori S, Casorati M, Amuchastegui S, Smiroldo S, Davalli AM, Adorini L. Regulatory T cells induced by 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and mycophenolate mofetil treatment mediate transplantation tolerance. J Immunol. 2001;167:1945–53. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.4.1945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Mulligan ML, Felton SK, Riek AE, Bernal-Mizrachi C. Implications of vitamin D deficiency in pregnancy and lactation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;202:429.e1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2009.09.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Kovacs CS. Vitamin D in pregnancy and lactation: maternal, fetal, and neonatal outcomes from human and animal studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;88:520S–8S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/88.2.520S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Haugen M, Brantsaeter AL, Trogstad L, Alexander J, Roth C, Magnus P, et al. Vitamin D supplementation and reduced risk of preeclampsia in nulliparous women. Epidemiology. 2009;20:720–6. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181a70f08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Halhali A, Tovar AR, Torres N, Bourges H, Garabedian M, Larrea F. Preeclampsia is associated with low circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor I and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D in maternal and umbilical cord compartments. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:1828–33. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.5.6528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Bodnar LM, Simhan HN, Powers RW, Frank MP, Cooperstein E, Roberts JM. High prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in black and white pregnant women residing in the northern United States and their neonates. J Nutr. 2007;137:447–52. doi: 10.1093/jn/137.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Magnu P, Eskild A. Seasonal variation in the occurrence of pre-eclampsia. BJOG. 2001;108:1116–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2003.00273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Díaz L, Arranz C, Avila E, Halhali A, Vilchis F, Larrea F. Expression and activity of 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1 alpha-hydroxylase are restricted in cultures of human syncytiotrophoblast cells from preeclamptic pregnancies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:3876–82. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.8.8730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Darmochwal-Kolarz D, Leszczynska-Gorzelak B, Rolinski J, Oleszczuk J. T helper 1- and T helper 2-type cytokine imbalance in pregnant women with pre-eclampsia. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1999;86:165–70. doi: 10.1016/s0301-2115(99)00065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Hyppönen E. Vitamin D for the prevention of preeclampsia? A hypothesis. Nutr Rev. 2005;63:225–32. doi: 10.1301/nr.2005.jul.225-232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Maghbooli Z, Hossein-Nezhad A, Karimi F, Shafaei AR, Larijani B. Correlation between vitamin D3 deficiency and insulin resistance in pregnancy. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2008;24:27–32. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Peechakara SV, Pittas AG. Vitamin D as a potential modifier of diabetes risk. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2008;4:182–3. doi: 10.1038/ncpendmet0762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Mehta S, Giovannucci E, Mugusi FM, Spiegelman D, Aboud S, Hertzmark E, et al. Vitamin D status of HIV-infected women and its association with HIV disease progression, anemia, and mortality. PLoS One. 2010;5:e8770. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Mehta S, Hunter DJ, Mugusi FM, Spiegelman D, Manji KP, Giovannucci EL, et al. Perinatal outcomes, including mother-to-child transmission of HIV, and child mortality and their association with maternal vitamin D status in Tanzania. J Infect Dis. 2009;200:1022–30. doi: 10.1086/605699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Nieto G, Barber Y, Rubio MC, Rubio M, Fibla J. Association between AIDS disease progression rates and the Fok-I polymorphism of the VDR gene in a cohort of HIV-1 seropositive patients. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2004;89–90:199–207. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.03.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Giovannucci E, Willett WC, Dietrich T, Dawson-Hughes B. Estimation of optimal serum concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D for multiple health outcomes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;84:18–28. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/84.1.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Scholl TO, Chen X. Vitamin D intake during pregnancy: association with maternal characteristics and infant birth weight. Early Hum Dev. 2009;85:231–4. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2008.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Yorifuji J, Yorifuji T, Tachibana K, Nagai S, Kawai M, Momoi T, et al. Craniotabes in normal newborns: the earliest sign of subclinical vitamin D deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:1784–8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-2254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Camadoo L, Tibbott R, Isaza F. Maternal vitamin D deficiency associated with neonatal hypocalcaemic convulsions. Nutr J. 2007;6:23. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-6-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Mahon P, Harvey N, Crozier S, Inskip H, Robinson S, Arden N, et al. Low maternal vitamin D status and fetal bone development: cohort study. J Bone Min Res. 2010;25:14–19. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.090701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Maiya S, Sullivan I, Allgrove J, Yates R, Malone M, Brain C, et al. Hypocalcaemia and vitamin D deficiency: an important, but preventable, cause of life-threatening infant heart failure. Heart. 2008;94:581–4. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2007.119792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Karatekin G, Kaya A, Salihoğlu O, Balci H, Nuhoğlu A. Association of subclinical vitamin D deficiency in newborns with acute lower respiratory infection and their mothers. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2009;63:473–7. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Javaid MK, Crozier SR, Harvey NC, Gale CR, Dennison EM, Boucher BJ, et al. Maternal vitamin D status during pregnancy and childhood bone mass at age 9 years: a longitudinal study. Lancet. 2006;367:36–43. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)67922-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Sayers A, Tobias JH. Estimated maternal ultraviolet B exposure levels in pregnancy influence skeletal development of the child. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:765–71. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Litonjua AA, Weiss ST. Is vitamin D deficiency to blame for the asthma epidemic? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:1031–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.08.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Brehm JM, Celedón JC, Soto-Quiros ME, Avila L, Hunninghake GπM, Forno E, et al. Serum vitamin D levels and markers of severity of childhood asthma in Costa Rica. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179:765–71. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200808-1361OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Kinney DK, Teixeira P, Hsu D, Napoleon SC, Crowley DJ, Miller A, et al. Relation of schizophrenia prevalence to latitude, climate, fish consumption, infant mortality, and skin color: a role for prenatal vitamin d deficiency and infections? Schizophr Bull. 2009;35:582–95. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbp023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Stene LC, Ulriksen J, Magnus P, Joner G. Use of cod liver oil during pregnancy associated with lower risk of Type I diabetes in the offspring. Diabetologia. 2000;43:1093–8. doi: 10.1007/s001250051499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]