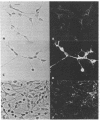
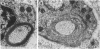
Abstract
Schwann cells derived from neonatal rat sciatic nerve are quiescent in culture unless treated with specific mitogens. The use of glial growth factor (GGF) and forskolin has been found to be an effective method for stimulating proliferation of Schwann cells on a poly(L-lysine) substratum while maintaining their ability to myelinate axons in vitro. We find that repetitive passaging of Schwann cells with GGF and forskolin results in the loss of normal growth control; the cells are able to proliferate without added mitogens. The immortalized cells grow continuously in the absence of added growth factor and in the presence or absence of serum yet continue to express distinctive Schwann cell-surface antigens. The cells can associate with axons in culture, deposit a basal lamina, and ensheath axons, but they gradually lose their capacity to myelinate axons. The immortalized cells release growth-promoting activity into their culture medium. The released activity is effective in stimulating proliferation of primary Schwann cells that retain normal growth properties. Extracellular matrix molecules (laminin and fibronectin) augment the response of primary Schwann cells to the secreted mitogen. Quiescent primary Schwann cells also secrete a growth factor into their culture medium, but its activity is detectable only in the presence of added laminin or fibronectin. The results suggest that both normal and immortalized Schwann cells secrete an autocrine growth factor. Response to the autocrine factor appears to entail a multicomponent mechanism. Unlike primary cells, immortalized Schwann cells have the capacity to secrete all of the necessary components and to respond to them constitutively.
Full text
PDF

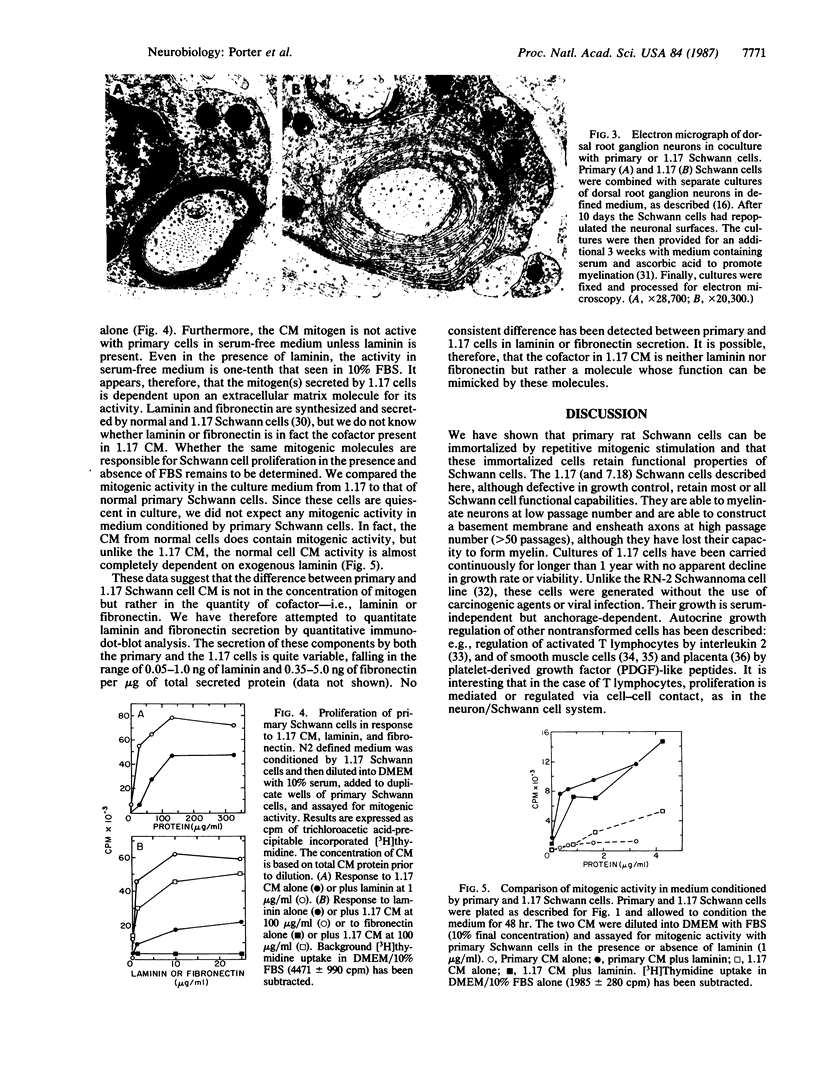

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron-Van Evercooren A., Kleinman H. K., Seppä H. E., Rentier B., Dubois-Dalcq M. Fibronectin promotes rat Schwann cell growth and motility. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):211–216. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch E. P., Assouline J. G., Miller J. F., Lim R. Glia maturation factor promotes proliferation and morphologic expression of rat Schwann cells. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 25;304(2):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90335-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Fields K. L., Raff M. C. Studies on cultured rat Schwann cells. I. Establishment of purified populations from cultures of peripheral nerve. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 6;165(1):105–118. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Lemke G. E., Balzer D. R., Jr Purification and preliminary characterization of a glial growth factor from the bovine pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8374–8377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunge M. B., Williams A. K., Wood P. M., Uitto J., Jeffrey J. J. Comparison of nerve cell and nerve cell plus Schwann cell cultures, with particular emphasis on basal lamina and collagen formation. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):184–202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunge R. P., Bunge M. B., Eldridge C. F. Linkage between axonal ensheathment and basal lamina production by Schwann cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:305–328. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.001513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey D. J., Bunge R. P. Factors influencing the release of proteins by cultured Schwann cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):666–672. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Wood P. M., Bunge R. P., Glaser L. Mitogenicity of brain axolemma membranes and soluble factors for dorsal root ganglion Schwann cells. J Cell Biochem. 1982;18(4):433–445. doi: 10.1002/jcb.1982.240180405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornbrooks C. J., Carey D. J., McDonald J. A., Timpl R., Bunge R. P. In vivo and in vitro observations on laminin production by Schwann cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3850–3854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVries G. H., Salzer J. L., Bunge R. P. Axolemma-enriched fractions isolated from PNS and CNS are mitogenic for cultured Schwann cells. Brain Res. 1982 Feb;255(2):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(82)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Dammerman M. A monoclonal antibody equivalent to anti-rat neural antigen-1 as a marker for Schwann cells. Neuroscience. 1985 Jul;15(3):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Gosling C., Megson M., Stern P. L. New cell surface antigens in rat defined by tumors of the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1296–1300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goustin A. S., Betsholtz C., Pfeifer-Ohlsson S., Persson H., Rydnert J., Bywater M., Holmgren G., Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Ohlsson R. Coexpression of the sis and myc proto-oncogenes in developing human placenta suggests autocrine control of trophoblast growth. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke G. E., Brockes J. P. Identification and purification of glial growth factor. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):75–83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00075.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim R., Miller J. F., Hicklin D. J., Andresen A. A. Purification of bovine glia maturation factor and characterization with monoclonal antibody. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):8070–8074. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarvey M. L., Baron-Van Evercooren A., Kleinman H. K., Dubois-Dalcq M. Synthesis and effects of basement membrane components in cultured rat Schwann cells. Dev Biol. 1984 Sep;105(1):18–28. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meador-Woodruff J. H., Lewis B. L., DeVries G. H. Cyclic AMP and calcium as potential mediators of stimulation of cultured Schwann cell proliferation by axolemma-enriched and myelin-enriched membrane fractions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):373–380. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90485-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moya F., Bunge M. B., Bunge R. P. Schwann cells proliferate but fail to differentiate in defined medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6902–6906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng W. W., Bressler J. P., Tiffany-Castiglioni E., de Vellis J. Development of a monoclonal antibody against a tumor-associated antigen. Science. 1982 Feb 26;215(4536):1102–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.7063842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer S. E., Wechsler W. Biochemically differentiated neoplastic clone of Schwann cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2885–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter S., Clark M. B., Glaser L., Bunge R. P. Schwann cells stimulated to proliferate in the absence of neurons retain full functional capability. J Neurosci. 1986 Oct;6(10):3070–3078. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-10-03070.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Abney E., Brockes J. P., Hornby-Smith A. Schwann cell growth factors. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):813–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Hornby-Smith A., Brockes J. P. Cyclic AMP as a mitogenic signal for cultured rat Schwann cells. Nature. 1978 Jun 22;273(5664):672–673. doi: 10.1038/273672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner N., Bunge R. P., Glaser L. A neuronal cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan is required for dorsal root ganglion neuron stimulation of Schwann cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):744–754. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner N., Elbein A., Bunge M. B., Porter S., Bunge R. P., Glaser L. Specific asparagine-linked oligosaccharides are not required for certain neuron-neuron and neuron-Schwann cell interactions. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):159–170. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner N., Glaser L., Bunge R. P. PC12 cells as a source of neurite-derived cell surface mitogen, which stimulates Schwann cell division. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1150–1155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzer J. L., Bunge R. P., Glaser L. Studies of Schwann cell proliferation. III. Evidence for the surface localization of the neurite mitogen. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):767–778. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzer J. L., Bunge R. P. Studies of Schwann cell proliferation. I. An analysis in tissue culture of proliferation during development, Wallerian degeneration, and direct injury. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):739–752. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzer J. L., Williams A. K., Glaser L., Bunge R. P. Studies of Schwann cell proliferation. II. Characterization of the stimulation and specificity of the response to a neurite membrane fraction. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):753–766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Daly J. W. Forskolin: a unique diterpene activator of cyclic AMP-generating systems. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;7(4):201–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R. A., Schwartz S. M., Bowen-Pope D. F. Developmentally regulated production of platelet-derived growth factor-like molecules. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):669–671. doi: 10.1038/311669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobue G., Kreider B., Asbury A., Pleasure D. Specific and potent mitogenic effect of axolemmal fraction on Schwann cells from rat sciatic nerves in serum-containing and defined media. Brain Res. 1983 Dec 5;280(2):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Autocrine growth factors and cancer. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):745–747. doi: 10.1038/313745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. N., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R., Reidy M. A. Production of platelet-derived growth factor-like molecules by cultured arterial smooth muscle cells accompanies proliferation after arterial injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7311–7315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. M. Separation of functional Schwann cells and neurons from normal peripheral nerve tissue. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 22;115(3):361–375. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90355-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]