Abstract
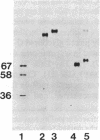
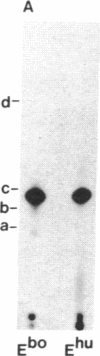
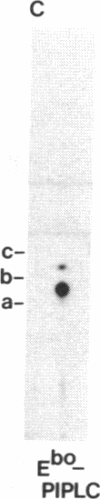
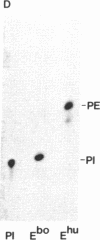
Acetylcholinesterases (AcChoEases; EC 3.1.1.7) from bovine (Ebo) and human (Ehu) erythrocytes were purified to apparent homogeneity by affinity chromatography. The hydrophobic portion of the glycolipid membrane anchor of each enzyme was radiolabeled with the photoactivated reagent 3-(trifluoromethyl)-3-(m-[125I]iodophenyl)diazirine. Several cleavage procedures demonstrated that this radiolabel was highly selective for the fatty acid portion of the anchor in both enzymes. The labeled enzymes were digested with phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns)-specific phospholipase C (EC 3.1.4.10), and label release was assessed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. About 85% of the radiolabel was cleaved from Ebo AcChoEase, whereas only 5% was released from Ehu AcChoEase. This finding agrees with a report that Ebo AcChoEase was quantitatively released from intact erythrocytes by PtdIns-specific phospholipase C but Ehu AcChoEase was not [Low, M. G. & Finean, J. B. (1977) FEBS Lett. 82, 143-146]. The two AcChoEases contained comparable amounts of the anchor components ethanolamine, glucosamine, and myo-inositol, but qualitative and quantitative differences were found in the fatty acids. Thin-layer chromatography of radiolabeled fragments generated from Ebo and Ehu AcChoEases by nitrous acid deamination revealed a major difference in the membrane anchors of the two enzymes. The fragment released from Ebo AcChoEase by this procedure comigrated with PtdIns, whereas the corresponding fragment from Ehu AcChoEase had a mobility much greater than that of PtdIns even though it contained myo-inositol and fatty acids. These studies show that 3-(trifluoromethyl)-3-(m-[125I]iodophenyl)diazirine is useful for analysis of lipid-containing compounds and indicate that, whereas Ebo AcChoEase contains PtdIns in its glycolipid anchor, Ehu AcChoEase has a different anchor structure, which is resistant to PtdIns-specific phospholipase C. This observation suggests the existence of a class of glycolipid-anchored membrane proteins resistant to this phospholipase.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brennan P. J. Phosphoinositides of Corynebacterium xerosis. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;109(1):158–160. doi: 10.1042/bj1090158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner J., Semenza G. Selective labeling of the hydrophobic core of membranes with 3-(trifluoromethyl)-3-(m-[125I]iodophenyl)diazirine, a carbene-generating reagent. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 8;20(25):7174–7182. doi: 10.1021/bi00528a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Low M. G., Nussenzweig V. Release of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) from the cell membrane by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PIPLC). Selective modification of a complement regulatory protein. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1150–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta-Choudhury T. A., Rosenberry T. L. Human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase is an amphipathic protein whose short membrane-binding domain is removed by papain digestion. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5653–5660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fatemi S. H., Haas R., Jentoft N., Rosenberry T. L., Tartakoff A. M. The glycophospholipid anchor of Thy-1. Biosynthetic labeling experiments with wild-type and class E Thy-1 negative lymphomas. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4728–4732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Cross G. A. Myristylation of the membrane form of a Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3011–3015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Glycosyl-sn-1,2-dimyristylphosphatidylinositol is covalently linked to Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14547–14555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futerman A. H., Fiorini R. M., Roth E., Low M. G., Silman I. Physicochemical behaviour and structural characteristics of membrane-bound acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo electric organ. Effect of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):369–377. doi: 10.1042/bj2260369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnagey A. L., Forte M., Rosenberry T. L. Isolation and characterization of acetylcholinesterase from Drosophila. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13290–13298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas R., Brandt P. T., Knight J., Rosenberry T. L. Identification of amine components in a glycolipid membrane-binding domain at the C-terminus of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3098–3105. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakow J. L., Hereld D., Bangs J. D., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Identification of a glycolipid precursor of the Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12147–12153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Biochemistry of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane protein anchors. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2440001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Finean J. B. Non-lytic release of acetylcholinesterase from erythrocytes by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80905-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik A. S., Low M. G. Conversion of human placental alkaline phosphatase from a high Mr form to a low Mr form during butanol extraction. An investigation of the role of endogenous phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):519–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2400519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Bon S. The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:57–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Kelly K. L., Abler A., Jarett L. Identification of a novel insulin-sensitive glycophospholipid from H35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2131–2137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Roberts W. L., Haas R., Rosenberry T. L. Decay accelerating factor of complement is anchored to cells by a C-terminal glycolipid. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6740–6747. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi T., Ikezawa H. Alkaline phosphodiesterase I release from eucaryotic plasma membranes by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. I. The release from rat organs. J Biochem. 1986 Mar;99(3):703–712. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Rosenberry T. L. Identification of covalently attached fatty acids in the hydrophobic membrane-binding domain of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):621–627. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90950-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Rosenberry T. L. Selective radiolabeling and isolation of the hydrophobic membrane-binding domain of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3091–3098. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L., Scoggin D. M. Structure of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Characterization of intersubunit disulfide bonding and detergent interaction. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5643–5652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Fox J. A., Sherline P., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin-stimulated hydrolysis of a novel glycolipid generates modulators of cAMP phosphodiesterase. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):967–972. doi: 10.1126/science.3016898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E., Conrad H. E. Formation of anhydrosugars in the chemical depolymerization of heparin. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):3932–3942. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takesue Y., Yokota K., Nishi Y., Taguchi R., Ikezawa H. Solubilization of trehalase from rabbit renal and intestinal brush-border membranes by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 26;201(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80560-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse A. G., Barclay A. N., Watts A., Williams A. F. A glycophospholipid tail at the carboxyl terminus of the Thy-1 glycoprotein of neurons and thymocytes. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1003–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.2865810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]