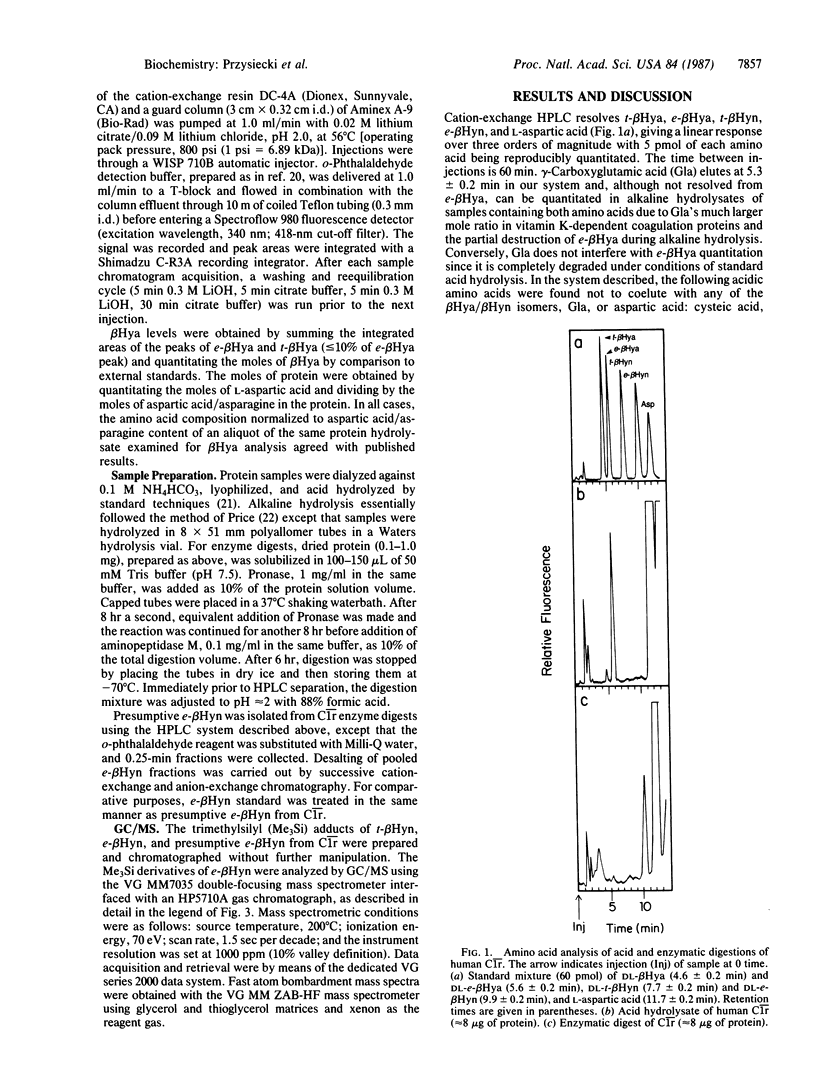
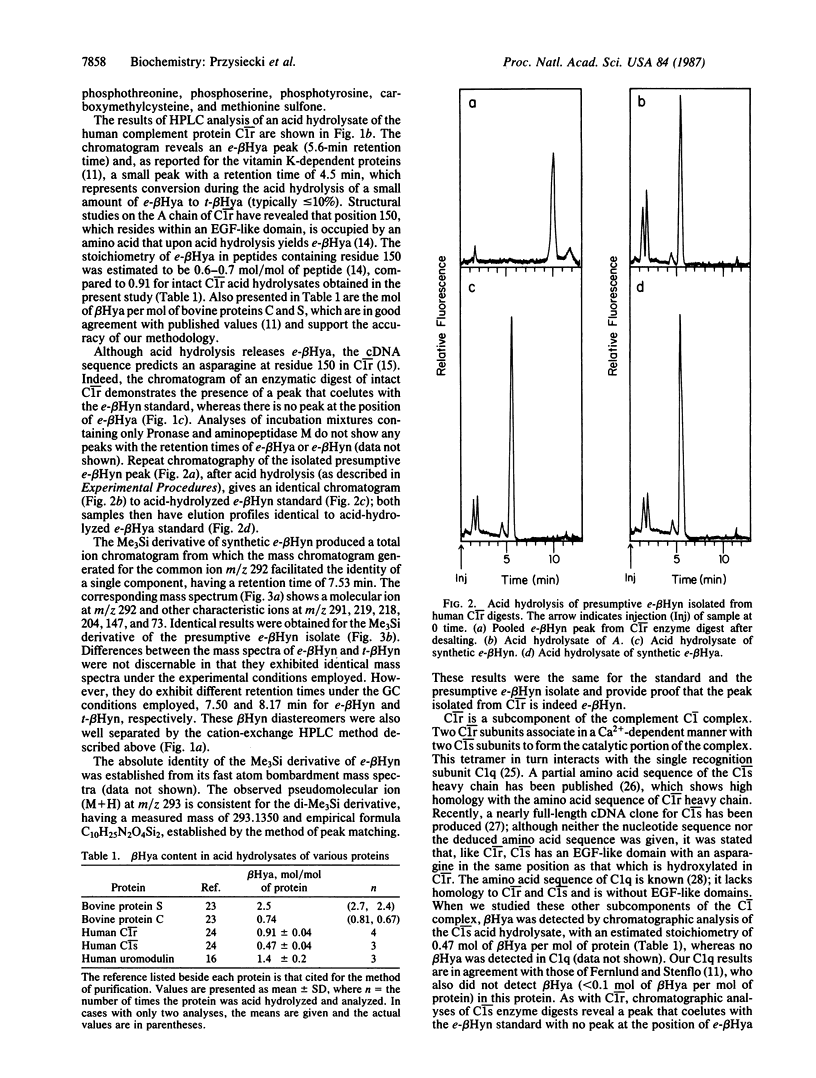
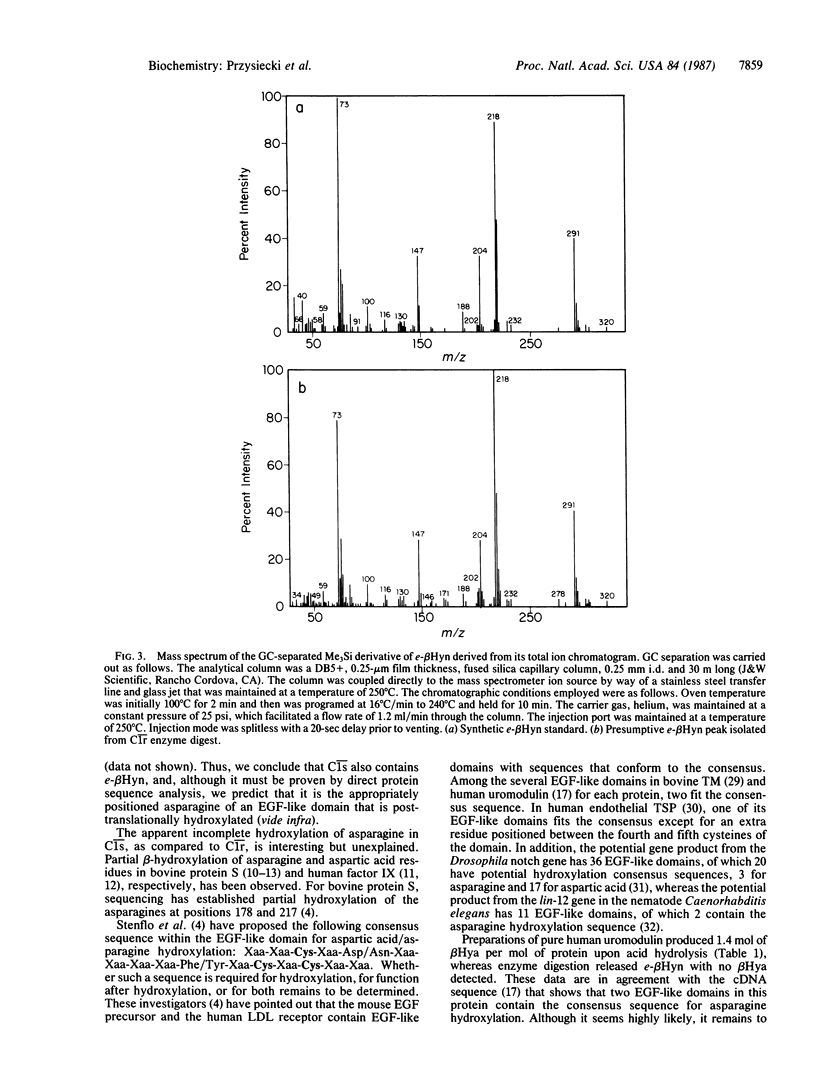
Abstract
Vitamin K-dependent bovine protein S has been shown to contain a posttranslationally hydroxylated asparagine within a conserved sequence in three of its epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains. In a review of amino acid sequences deduced from cDNA data, we have observed that a conserved sequence containing a potential asparagine hydroxylation site exists within EGF-like domains of a variety of functionally diverse proteins. We have studied a number of these and report the presence of erythro-beta-hydroxyasparagine (e-beta Hyn) in three non-vitamin K-dependent proteins: the plasma complement proteins C1r and C1s (where overbar indicates activated form) and the urinary protein uromodulin. For each protein, e-beta Hyn was identified in enzyme digests following the initial observation of erythro-beta-hydroxyaspartic acid (e-beta Hya) in acid hydrolysates of the proteins. e beta Hya and e-beta Hyn residues are detected by a postcolumn derivatization cation-exchange HPLC method herein described. HPLC isolation of the presumptive e-beta Hyn residue from enzyme digests of intact C1r allowed confirmation of its structure by GC/MS. Based upon available cDNA sequence data and observation of e-beta Hya in acid hydrolysates, we suggest other proteins in which e-beta Hyn may occur.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appella E., Robinson E. A., Ullrich S. J., Stoppelli M. P., Corti A., Cassani G., Blasi F. The receptor-binding sequence of urokinase. A biological function for the growth-factor module of proteases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4437–4440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlaud G. J., Willis A. C., Gagnon J. Complete amino acid sequence of the A chain of human complement-classical-pathway enzyme C1r. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):711–720. doi: 10.1042/bj2410711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. D., Rodkey J. A., Sondey J. M., Hirschmann R. Dihydrofolate reductase: the amino acid sequence of the enzyme from a methotrexate-resistant mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1328–1337. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing D. H., Andrews J. M., Morris K. M., Cole E., Irish V. Purification of subcomponents Clq, Cl(-)r and Cl(-)s of the first component of complement from Cohn Fraction I by affinity chromatography. Prep Biochem. 1980;10(3):269–296. doi: 10.1080/10826068009412829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colomb M. G., Arlaud G. J., Villiers C. L. Structure and activation of C1: current concepts. Complement. 1984;1(2):69–80. doi: 10.1159/000467818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Lundwall A., Stenflo J. Primary structure of bovine vitamin K-dependent protein S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4199–4203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernlund P., Stenflo J. Beta-hydroxyaspartic acid in vitamin K-dependent proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12509–12512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler S. A., Paulson D., Owen B. A., Owen W. G. Binding of iron by factor IX. Possible role for beta-hydroxyaspartic acid. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4371–4372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald I. lin-12, a nematode homeotic gene, is homologous to a set of mammalian proteins that includes epidermal growth factor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):583–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90230-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto N., Morita T., Iwanaga S. A method for systematic purification from bovine plasma of six vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors: prothrombin, factor X, factor IX, protein S, protein C, and protein Z. J Biochem. 1985 May;97(5):1347–1355. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Højrup P., Jensen M. S., Petersen T. E. Amino acid sequence of bovine protein Z: a vitamin K-dependent serine protease homolog. FEBS Lett. 1985 May 20;184(2):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80633-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackman R. W., Beeler D. L., VanDeWater L., Rosenberg R. D. Characterization of a thrombomodulin cDNA reveals structural similarity to the low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8834–8838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNGUTH M. L., SALLACH H. J. beta-Hydroxyaspartic acid: synthesis and separation of its diastereoisomers. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Nov;91:39–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Hynes R. O. The structure of human thrombospondin, an adhesive glycoprotein with multiple calcium-binding sites and homologies with several different proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1635–1648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leytus S. P., Kurachi K., Sakariassen K. S., Davie E. W. Nucleotide sequence of the cDNA coding for human complement C1r. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 26;25(17):4855–4863. doi: 10.1021/bi00365a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundwall A., Dackowski W., Cohen E., Shaffer M., Mahr A., Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J., Wydro R. Isolation and sequence of the cDNA for human protein S, a regulator of blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6716–6720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Isaacs B. S., Esmon C. T., Johnson A. E. Derivatives of blood coagulation factor IX contain a high affinity Ca2+-binding site that lacks gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5698–5704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Kisiel W. Calcium binding to a human factor IXa derivative lacking gamma-carboxyglutamic acid: evidence for two high-affinity sites that do not involve beta-hydroxyaspartic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):841–847. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90493-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchmore A. V., Decker J. M. Uromodulin: a unique 85-kilodalton immunosuppressive glycoprotein isolated from urine of pregnant women. Science. 1985 Aug 2;229(4712):479–481. doi: 10.1126/science.2409603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L. Evolution of the proteases of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis by assembly from modules. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):657–663. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Kohr W. J., Kuang W. J., Glaister D., Aggarwal B. B., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. Identification of human uromodulin as the Tamm-Horsfall urinary glycoprotein. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):83–88. doi: 10.1126/science.3453112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J., Villiers C. L., Arlaud G. J., Boyd J., Burton D. R., Colomb M. G., Dwek R. A. Neutron scattering studies of subcomponent C1q of first component C1 of human complement and its association with subunit C1r2C1s2 within C1. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 5;179(3):547–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A. Analysis for gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:13–17. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Hash J. H., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Location of disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7669–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singerman A., Liwschitz Y. Threo- and erythro-beta-hydroxyl-l-asparagines. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968 Sep;(46):4733–4734. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(00)75943-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spycher S. E., Nick H., Rickli E. E. Human complement component C1s. Partial sequence determination of the heavy chain and identification of the peptide bond cleaved during activation. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):49–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Page M., Campbell A. K., Luzio J. P. A mechanism for the insertion of complement component C9 into target membranes. Mol Immunol. 1986 May;23(5):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Lundwall A., Dahlbäck B. beta-Hydroxyasparagine in domains homologous to the epidermal growth factor precursor in vitamin K-dependent protein S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):368–372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugo T., Björk I., Holmgren A., Stenflo J. Calcium-binding properties of bovine factor X lacking the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing region. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5705–5710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugo T., Dahlbäck B., Holmgren A., Stenflo J. Calcium binding of bovine protein S. Effect of thrombin cleavage and removal of the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing region. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5116–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of activated protein C by protein S. The role of phospholipid in factor Va inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11128–11131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Johansen K. M., Xu T., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nucleotide sequence from the neurogenic locus notch implies a gene product that shares homology with proteins containing EGF-like repeats. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):567–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



