Abstract
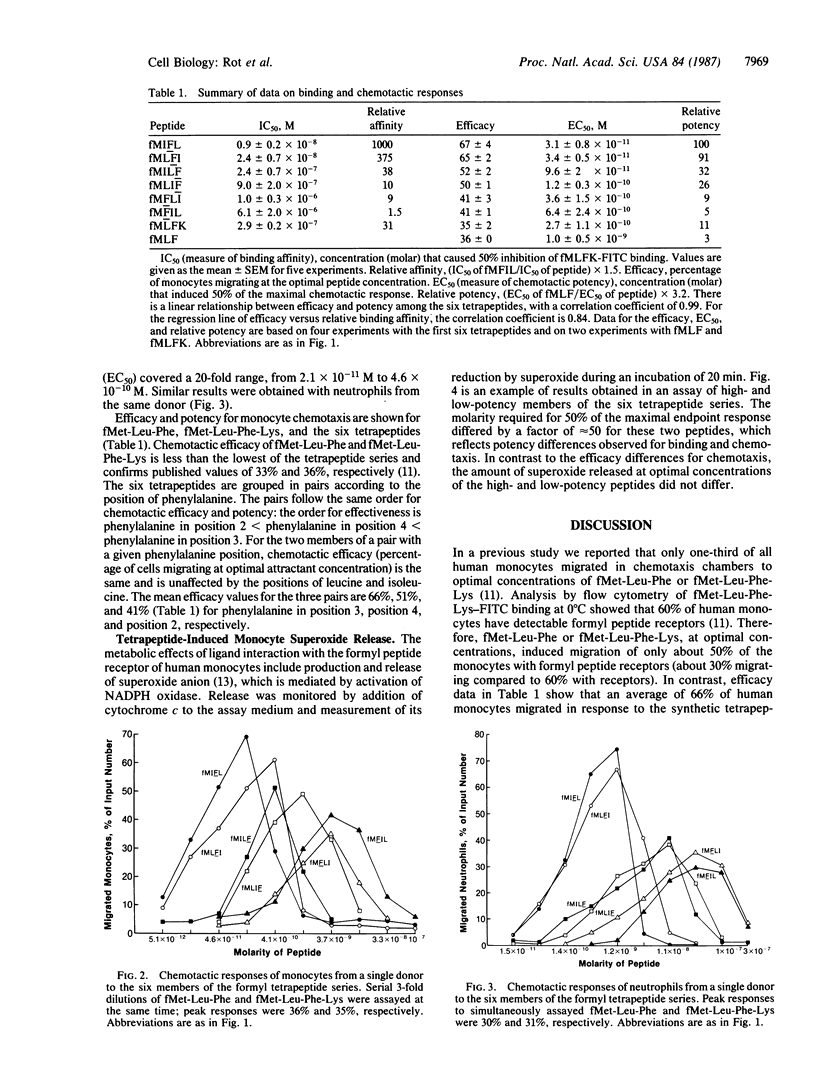
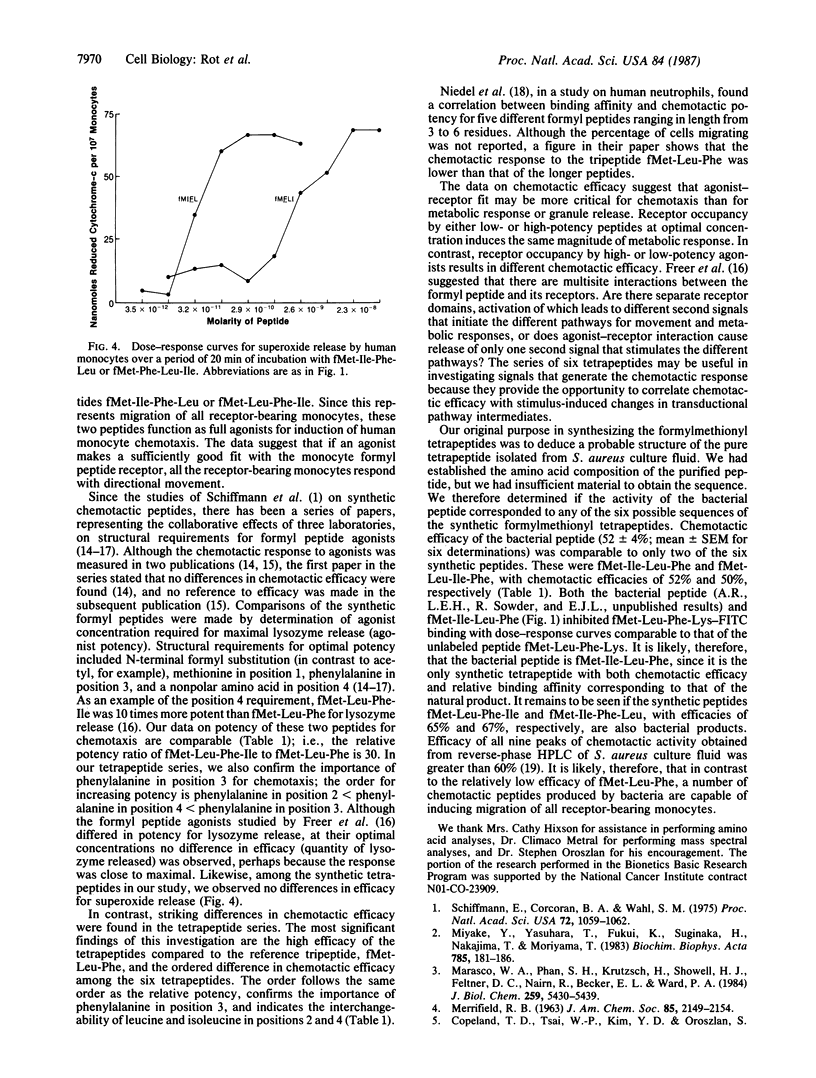
We recently isolated, from culture fluids of Staphylococcus aureus, a chemotactic peptide that comprised equimolar quantities of methionine, leucine, phenylalanine, and isoleucine. It interacted with the formylmethionyl peptide receptor of human leukocytes and had considerably higher potency and efficacy than the widely studied tripeptide agonist fMet-Leu-Phe. On the assumption that the attractant was a formylmethionyl tetrapeptide, we synthesized the six possible sequences and tested the products for chemotactic potency and efficacy, as well as their capacity to inhibit binding of fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled fMet-Leu-Phe-Lys to human monocytes. The concentrations required for inhibition of fluorescein-labeled fMet-Leu-Phe-Lys binding by the six peptides covered three orders of magnitude. Chemotactic potency (concentration that caused 50% of the maximum chemotactic response) ranged from 3.1 X 10(-11) M to 6.4 X 10(-10) M; efficacy (percentage of monocytes migrating at optimal attractant concentration) ranged from 41% to 66%. When the six synthetic tetrapeptides were ranked for chemotactic efficacy, they paired according to the position of phenylalanine. The average percentage migration was 66% for the two peptides with phenylalanine in position 3, 51% for phenylalanine in position 4, and 41% for phenylalanine in position 2. Since the published value for the percentage of human monocytes with detectable formyl peptide receptors is 60%, it is apparent that the two tetrapeptides with phenylalanine in position 3 (fMet-Ile-Phe-Leu and fMet-Leu-Phe-Ile) are full chemotactic agonists, which are capable of inducing migration of all the receptor-bearing cells. This is in contrast to the tripeptide fMet-Leu-Phe, which induces migration of only 50% of monocytes with receptors (efficacy of 33%). Since the chemotactic efficacy of the six tetrapeptides covers a wide range, the series may be useful to investigate signals that lead to directed movement after occupancy of receptors by chemoattractants.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen H. J., Chovaniec M. E. Superoxide generation by digitonin-stimulated guinea pig granulocytes. A basis for a continuous assay for monitoring superoxide production and for the study of the activation of the generating system. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1081–1087. doi: 10.1172/JCI109007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk W., Goodwin R. H., Jr, Leonard E. J. A 48-well micro chemotaxis assembly for rapid and accurate measurement of leukocyte migration. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer R. J., Day A. R., Muthukumaraswamy N., Pinon D., Wu A., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Formyl peptide chemoattractants: a model of the receptor on rabbit neutrophils. Biochemistry. 1982 Jan 19;21(2):257–263. doi: 10.1021/bi00531a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer R. J., Day A. R., Radding J. A., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Further studies on the structural requirements for synthetic peptide chemoattractants. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2404–2410. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvath L., Falk W., Leonard E. J. Rapid quantitation of neutrophil chemotaxis: use of a polyvinylpyrrolidone-free polycarbonate membrane in a multiwell assembly. J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvath L., Lazdins J. K., Alteri E., Leonard E. J. Differences in superoxide production by nonmigrating and migrating human monocyte subpopulations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 16;108(1):392–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91879-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J., Noer K., Skeel A. Analysis of human monocyte chemoattractant binding by flow cytometry. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Sep;38(3):403–413. doi: 10.1002/jlb.38.3.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J., Skeel A. Effects of cell concentration on chemotactic responsiveness of mouse resident peritoneal macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Oct;30(4):271–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Phan S. H., Krutzsch H., Showell H. J., Feltner D. E., Nairn R., Becker E. L., Ward P. A. Purification and identification of formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine as the major peptide neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5430–5439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake Y., Yasuhara T., Fukui K., Suginaka H., Nakajima T., Moriyama T. Purification and characterization of neutrophil chemotactic factors of Streptococcus sanguis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 29;758(2):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J., Wilkinson S., Cuatrecasas P. Receptor-mediated uptake and degradation of 125I-chemotactic peptide by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10700–10706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rot A., Henderson L. E., Leonard E. J. Staphylococcus aureus-derived chemoattractant activity for human monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1986 Jul;40(1):43–53. doi: 10.1002/jlb.40.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo C., Bonora G. M., Showell H., Freer R. J., Becker E. L. Structural requirements for formyl homooligopeptide chemoattractants. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 14;23(4):698–704. doi: 10.1021/bi00299a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



