Abstract
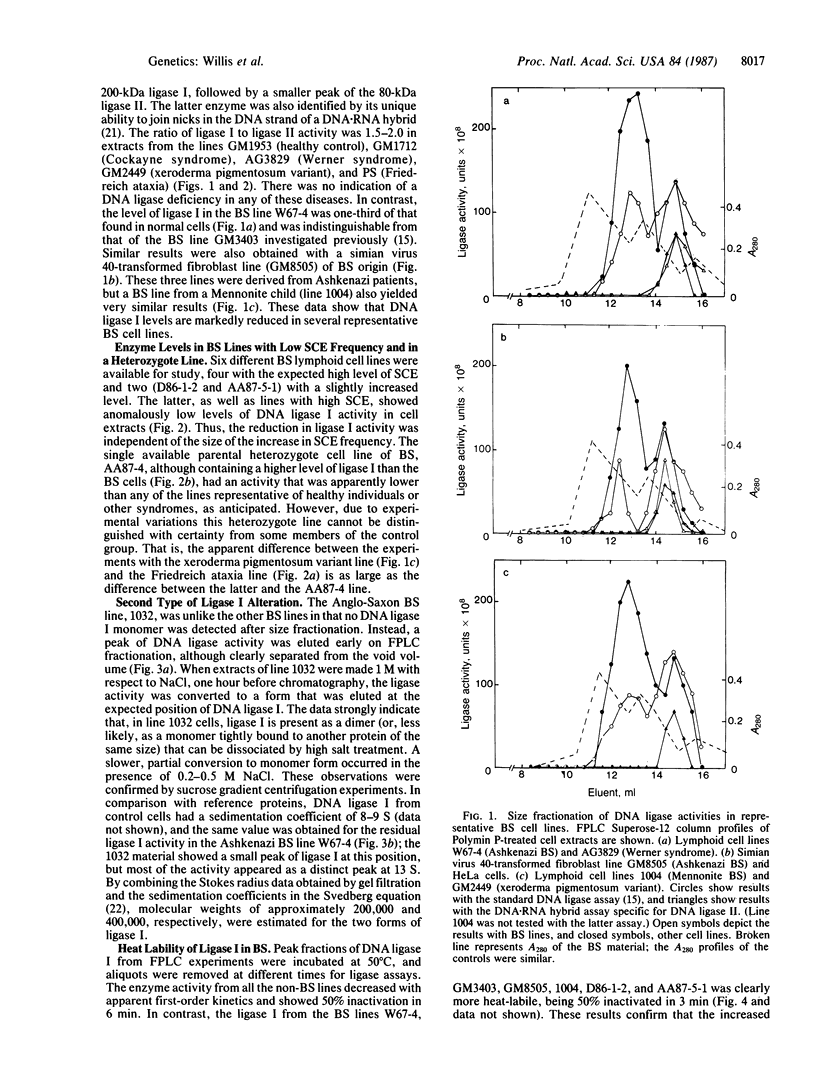
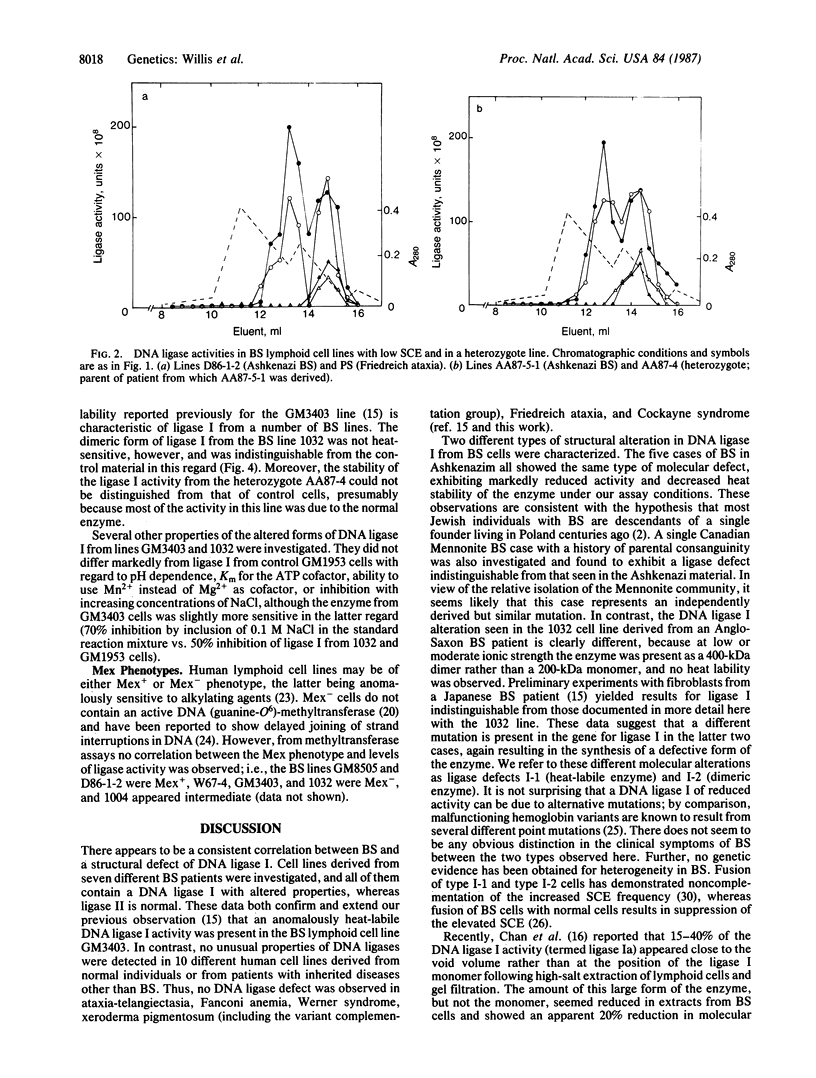
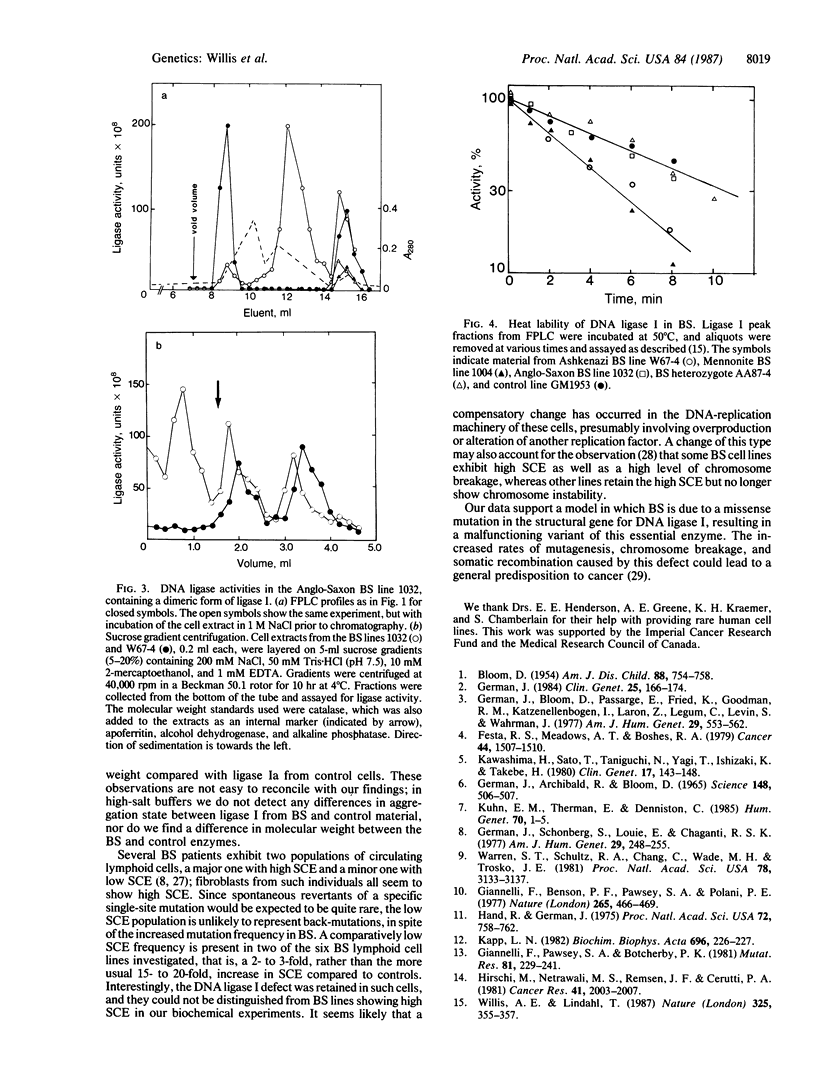
Cell lines derived from seven patients with Bloom syndrome all contain a DNA ligase I with unusual properties. Six lines were shown to have a reduced level of this enzyme activity and the residual enzyme was anomalously heat-labile. The seventh line contained a dimeric rather than monomeric form of ligase I. Several cell lines representative of other inherited human syndromes have apparently normal DNA ligases. The data indicate that Bloom syndrome is due to a defect in the structure of DNA ligase I caused by a "leaky" point mutation occurring at one of at least two alternative sites.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrand J. E., Willis A. E., Goldsmith I., Lindahl T. Different substrate specificities of the two DNA ligases of mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9079–9082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOOM D. Congenital telangiectatic erythema resembling lupus erythematosus in dwarfs; probably a syndrome entity. AMA Am J Dis Child. 1954 Dec;88(6):754–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant E. M., Hoehn H., Martin G. M. Normalisation of sister chromatid exchange frequencies in Bloom's syndrome by euploid cell hybridisation. Nature. 1979 Jun 28;279(5716):795–796. doi: 10.1038/279795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. Y., Becker F. F., German J., Ray J. H. Altered DNA ligase I activity in Bloom's syndrome cells. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):357–359. doi: 10.1038/325357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Festa R. S., Meadows A. T., Boshes R. A. Leukemia in a black child with Bloom's syndrome: somatic recombination as a possible mechanism for neoplasia. Cancer. 1979 Oct;44(4):1507–1510. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197910)44:4<1507::aid-cncr2820440448>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German J., Bloom D., Passarge E. Bloom's syndrome XI. Progress report for 1983. Clin Genet. 1984 Feb;25(2):166–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb00480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German J., Bloom D., Passarge E., Fried K., Goodman R. M., Katzenellenbogen I., Laron Z., Legum C., Levin S., Wahrman Bloom's syndrome. VI. The disorder in Israel and an estimation of the gene frequency in the Ashkenazim. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Nov;29(6):553–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German J., Schonberg S., Louie E., Chaganti R. S. Bloom's syndrome. IV. Sister-chromatid exchanges in lymphocytes. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 May;29(3):248–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianneli F., Benson P. F., Pawsey S. A., Polani P. E. Ultraviolet light sensitivity and delayed DNA-chain maturation in Bloom's syndrome fibroblasts. Nature. 1977 Feb 3;265(5593):466–469. doi: 10.1038/265466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannelli F., Pawsey S. A., Botcherby P. K. Tendency to high levels of UVR-induced unscheduled DNA synthesis in Bloom syndrome. Mutat Res. 1981 Apr;81(2):229–241. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(81)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R., German J. A retarded rate of DNA chain growth in Bloom's syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):758–762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L., Karran P., Lindahl T. O6-Methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase of human lymphoid cells: structural and kinetic properties and absence in repair-deficient cells. Cancer Res. 1983 Jul;43(7):3247–3252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Gamo S., Furuyama J., Chiyo H. Loss of high frequency of sister chromatid exchanges in Epstein-Barr virus-established lymphoblastoid cell lines from two patients with Bloom's syndrome. Hum Genet. 1983;63(1):75–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00285403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. E., Ribecky R. DNA repair in lymphoblastoid cell lines established from human genetic disorders. Chem Biol Interact. 1980 Dec;33(1):63–81. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(80)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschi M., Netrawali M. S., Remsen J. F., Cerutti P. A. Formation of DNA single-strand breaks by near-ultraviolet and gamma-rays in normal and Bloom's syndrome skin fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1981 May;41(5):2003–2007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp L. N. DNA fork displacement rates in Bloom's syndrome fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 26;696(2):226–227. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima H., Sato T., Taniguchi N., Yagi T., Ishizaki K., Takebe H. Bloom's syndrome in a Japanese girl. Clin Genet. 1980 Feb;17(2):143–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb00123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson A. G., Jr Genetics of human cancer. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:231–251. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E. M., Therman E., Denniston C. Mitotic chiasmata, gene density, and oncogenes. Hum Genet. 1985;70(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00389448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern M. R., Paone R. F., Day R. S., 3rd Human tumor strains defective in the repair of alkylated DNA fail to regenerate rapidly-sedimenting nucleoids after N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine treatment. Carcinogenesis. 1981;2(11):1215–1218. doi: 10.1093/carcin/2.11.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry P., Wolff S. New Giemsa method for the differential staining of sister chromatids. Nature. 1974 Sep 13;251(5471):156–158. doi: 10.1038/251156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi Y., Yosida T. H., Sandberg A. A. Malignant transformation of Bloom syndrome B-lymphoblastoid cell lines by carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5102–5106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar R., Strauss B. Removal of O6-methylguanine from DNA of normal and xeroderma pigmentosum-derived lymphoblastoid lines. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):417–420. doi: 10.1038/289417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. T., Schultz R. A., Chang C. C., Wade M. H., Trosko J. E. Elevated spontaneous mutation rate in Bloom syndrome fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3133–3137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis A. E., Lindahl T. DNA ligase I deficiency in Bloom's syndrome. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):355–357. doi: 10.1038/325355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


