Abstract
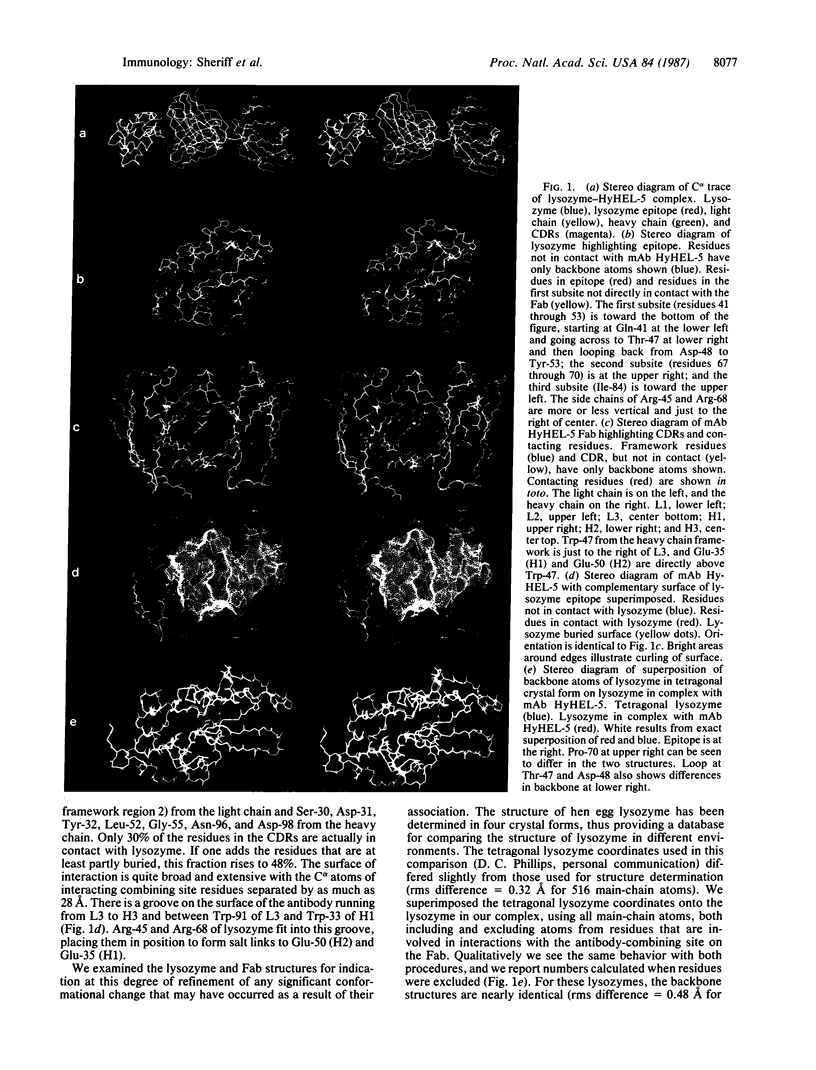
We have determined the three-dimensional structure of two crystal forms of an antilysozyme Fab-lysozyme complex by x-ray crystallography. The epitope on lysozyme consists of three sequentially separated subsites, including one long, nearly continuous, site from Gln-41 through Tyr-53 and one from Gly-67 through Pro-70. Antibody residues interacting with lysozyme occur in each of the six complementarity-determining regions and also include one framework residue. Arg-45 and Arg-68 form a ridge on the surface of lysozyme, which binds in a groove on the antibody surface. Otherwise the surface of interaction between the two proteins is relatively flat, although it curls at the edges. The surface of interaction is approximately 26 X 19 A. No water molecules are found in the interface. The positive charge on the two arginines is complemented by the negative charge of Glu-35 and Glu-50 from the heavy chain of the antibody. The backbone structure of the antigen, lysozyme, is mostly unperturbed, although there are some changes in the epitope region, most notably Pro-70. One side chain not in the epitope, Trp-63, undergoes a rotation of approximately 180 degrees about the C beta--C gamma bond. The Fab elbow bends in the two crystal forms differ by 7 degrees.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amit A. G., Mariuzza R. A., Phillips S. E., Poljak R. J. Three-dimensional structure of an antigen-antibody complex at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):747–753. doi: 10.1126/science.2426778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amzel L. M., Poljak R. J., Saul F., Varga J. M., Richards F. F. The three dimensional structure of a combining region-ligand complex of immunoglobulin NEW at 3.5-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1427–1430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artymiuk P. J., Blake C. C., Grace D. E., Oatley S. J., Phillips D. C., Sternberg M. J. Crystallographic studies of the dynamic properties of lysozyme. Nature. 1979 Aug 16;280(5723):563–568. doi: 10.1038/280563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Koenig D. F., Mair G. A., North A. C., Phillips D. C., Sarma V. R. Structure of hen egg-white lysozyme. A three-dimensional Fourier synthesis at 2 Angstrom resolution. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):757–761. doi: 10.1038/206757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case D. A., Karplus M. Dynamics of ligand binding to heme proteins. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):343–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90265-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M., Laver W. G., Varghese J. N., Baker A. T., Tulloch P. A., Air G. M., Webster R. G. Three-dimensional structure of a complex of antibody with influenza virus neuraminidase. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):358–363. doi: 10.1038/326358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cygler M., Boodhoo A., Lee J. S., Anderson W. F. Crystallization and structure determination of an autoimmune anti-poly(dT) immunoglobulin Fab fragment at 3.0 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):643–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard A. J., Nielsen C., Xuong N. H. Software for a diffractometer with multiwire area detector. Methods Enzymol. 1985;114:452–472. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)14030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Deisenhofer J., Colman P. M., Matsushima M., Palm W. Crystallographic structure studies of an IgG molecule and an Fc fragment. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):415–420. doi: 10.1038/264415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquart M., Deisenhofer J., Huber R., Palm W. Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of the intact immunoglobulin molecule Kol and its antigen-binding fragment at 3.0 A and 1.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1980 Aug 25;141(4):369–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satow Y., Cohen G. H., Padlan E. A., Davies D. R. Phosphocholine binding immunoglobulin Fab McPC603. An X-ray diffraction study at 2.7 A. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 20;190(4):593–604. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90245-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul F. A., Amzel L. M., Poljak R. J. Preliminary refinement and structural analysis of the Fab fragment from human immunoglobulin new at 2.0 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):585–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverton E. W., Padlan E. A., Davies D. R., Smith-Gill S., Potter M. Crystalline monoclonal antibody Fabs complexed to hen egg white lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):761–765. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Gill S. J., Hamel P. A., Klein M. H., Rudikoff S., Dorrington K. J. Contribution of the VK4 light chain to antibody specificity for lysozyme and beta (1,6)D-galactan. Mol Immunol. 1986 Sep;23(9):919–926. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Gill S. J., Wilson A. C., Potter M., Prager E. M., Feldmann R. J., Mainhart C. R. Mapping the antigenic epitope for a monoclonal antibody against lysozyme. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):314–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh S. W., Bhat T. N., Navia M. A., Cohen G. H., Rao D. N., Rudikoff S., Davies D. R. The galactan-binding immunoglobulin Fab J539: an X-ray diffraction study at 2.6-A resolution. Proteins. 1986 Sep;1(1):74–80. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman J. L. Constrained-restrained least-squares (CORELS) refinement of proteins and nucleic acids. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:271–303. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tainer J. A., Getzoff E. D., Alexander H., Houghten R. A., Olson A. J., Lerner R. A., Hendrickson W. A. The reactivity of anti-peptide antibodies is a function of the atomic mobility of sites in a protein. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):127–134. doi: 10.1038/312127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Altschuh D., Moras D., Bloomer A. C., Mondragon A., Klug A., Van Regenmortel M. H. Correlation between segmental mobility and the location of antigenic determinants in proteins. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):123–126. doi: 10.1038/311123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]