Abstract
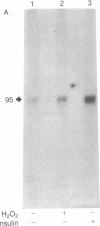
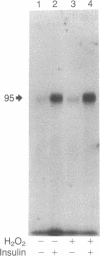
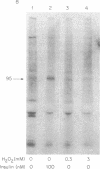
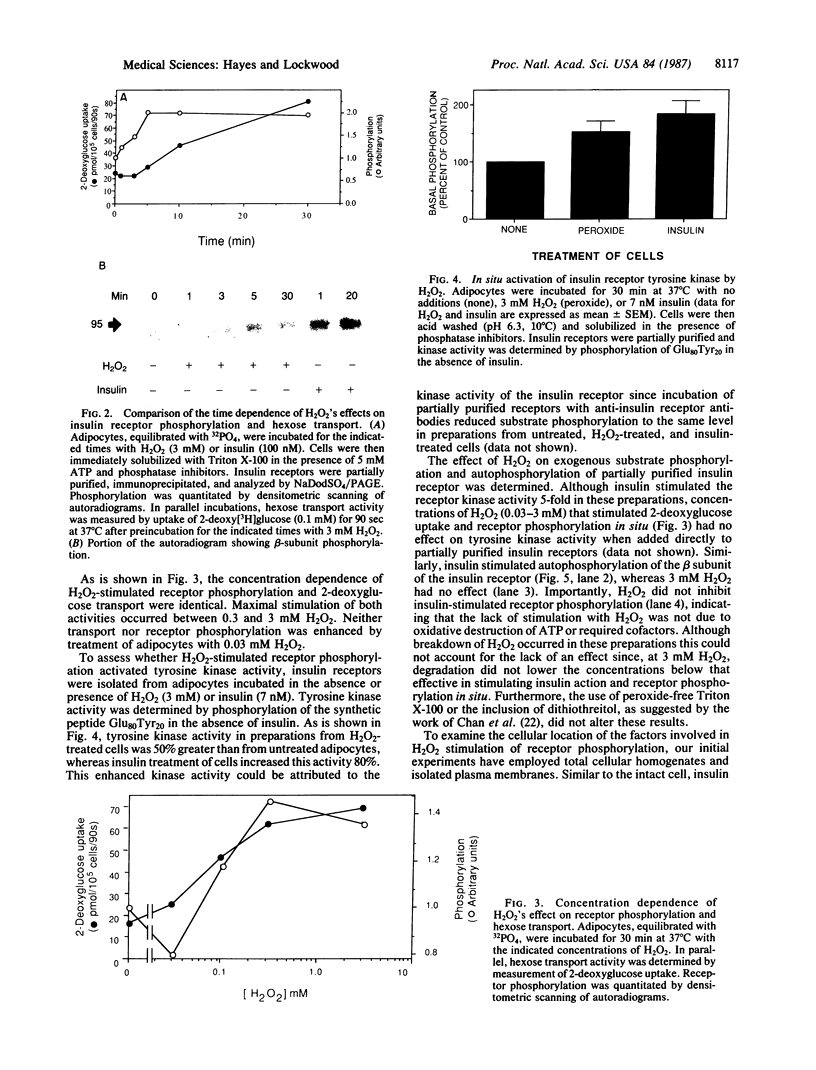
The oxidant H2O2 has many insulin-like effects in rat adipocytes. To determine whether these effects could be mediated by the tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor, the ability of H2O2 to stimulate receptor phosphorylation in intact adipocytes and partially purified insulin receptors has been examined. Phosphorylation of the beta subunit of the insulin receptor was increased approximately 2-fold by treatment of intact cells with 3 mM H2O2, a concentration that maximally stimulates 2-deoxyglucose uptake. Stimulation of receptor phosphorylation was rapid, reaching maximal levels within 5 min, and preceded activation of glucose transport. Phosphoamino acid analysis of insulin receptors from H2O2-treated adipocytes showed that 32P incorporation into phosphotyrosine and phosphoserine residues of the beta subunit was enhanced. Furthermore, partially purified receptors from H2O2-treated cells exhibit increased tyrosine kinase activity, as measured by phosphorylation of the peptide Glu80Tyr20. In contrast, the direct addition of H2O2 to partially purified insulin receptors did not stimulate tyrosine kinase activity or insulin receptor autophosphorylation. This was not due to breakdown of H2O2 or oxidation of ATP or the required divalent cations. To define the factors involved in H2O2's effect, we have examined receptor phosphorylation in fat cell homogenates and purified plasma membranes. Although insulin stimulated receptor phosphorylation in both of these systems, H2O2 was only effective in the cell homogenates. These data demonstrate that, under certain conditions, H2O2 stimulates insulin receptor phosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity, suggesting that the insulin-like effects of H2O2 may be mediated by stimulation of insulin receptor phosphorylation. This does not appear to be a direct effect of H2O2 on the insulin receptor and requires nonplasma membrane cellular constituents.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avruch J., Nemenoff R. A., Blackshear P. J., Pierce M. W., Osathanondh R. Insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in detergent extracts of human placental membranes. Comparison to epidermal growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15162–15166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier M., Laird D. M., Lane M. D. Insulin-activated tyrosine phosphorylation of a 15-kilodalton protein in intact 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1844–1848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun S., Raymond W. E., Racker E. Synthetic tyrosine polymers as substrates and inhibitors of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2051–2054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. M., Chen E., Tatoyan A., Shargill N. S., Pleta M., Hochstein P. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation in the rat liver plasma membrane by oxygen radicals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):439–445. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Fain J. N. Insulin protection against fat cell receptor inactivation by trypsin. Endocrinology. 1970 Jul;87(1):191–194. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Lawrence J. C., Jr, Lynn W. S. Evidence for the involvement of sulfhydryl oxidation in the regulation of fat cell hexose transport by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4173–4177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Araki E., Taira M., Shimada F., Mori M., Craik C. S., Siddle K., Pierce S. B., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of lysine residue 1030 in the putative ATP-binding region of the insulin receptor abolishes insulin- and antibody-stimulated glucose uptake and receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):704–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes G. R., Lockwood D. H. The role of cell surface sialic acid in insulin receptor function and insulin action. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2791–2798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann C., Crettaz M., Bruns P., Hessel P., Hadawi G. Cellular responses elicited by insulin mimickers in cells lacking detectable plasma membrane insulin receptors. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(4):401–414. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häring H. U., Kasuga M., Kahn C. R. Insulin receptor phosphorylation in intact adipocytes and in a cell-free system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 29;108(4):1538–1545. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blith D. L., Karlsson F. A., Häring H. U., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulation of phosphorylation of the beta subunit of the insulin receptor. Formation of both phosphoserine and phosphotyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):9891–9894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blithe D. L., Crettaz M., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in a cell-free system. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):667–669. doi: 10.1038/298667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight A. B., Rechler M. M., Romanus J. A., Van Obberghen-Schilling E. E., Nissley S. P. Stimulation of glucose incorporation and amino acid transport by insulin and an insulin-like growth factor in fibroblasts with defective insulin receptors cultured from a patient with leprechaunism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohanski R. A., Frost S. C., Lane M. D. Insulin-dependent phosphorylation of the insulin receptor-protein kinase and activation of glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12272–12281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M. N., Livingston J. N. Insulin binding to solubilized material from fat cell membranes: evidence for two binding species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. A., de Haën C. Effects of hydrogen peroxide on basal and hormone-stimulated lipolysis in perifused rat fat cells in relation to the mechanism of action of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10888–10895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. N., Amatruda J. M., Lockwood D. H. Studies of glucose transport system of fat cells: effects of insulin and insulin mimickers. Am J Physiol. 1978 May;234(5):E484–E488. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.5.E484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. N., Gurny P. A., Lockwood D. H. Insulin-like effects of polyamines in fat cells. Mediation by H2O2 formation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):560–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. N., Purvis B. J. Effects of wheat germ agglutinin on insulin binding and insulin sensitivity of fat cells. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):E267–E275. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.3.E267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood D. H., East L. E. Studies of the insulin-like actions of polyamines on lipid and glucose metabolism in adipose tissue cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7717–7722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloff B. L., Drake L., Riedy D. K., Lockwood D. H. Effects of sulfonylureas on the actions of insulin and insulin-mimickers: potentiation of stimulated hexose transport in adipocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 17;104(3-4):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90408-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May J. M., de Haën C. The insulin-like effect of hydrogen peroxide on pathways of lipid synthesis in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9017–9021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeel D. W., Jarett L. Preparation and characterization of a plasma membrane fraction from isolated fat cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 Feb;44(2):417–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Ho L., Korn L. J., Roth R. A. Insulin action is blocked by a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the insulin receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):328–332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Herrera R., Olowe Y., Petruzzelli L. M., Cobb M. H. Phosphorylation activates the insulin receptor tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3237–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Cassell D. J. Insulin receptor: evidence that it is a protein kinase. Science. 1983 Jan 21;219(4582):299–301. doi: 10.1126/science.6849137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Cassell D. J., Maddux B. A., Goldfine I. D. Regulation of insulin receptor kinase activity by insulin mimickers and an insulin antagonist. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90996-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Brown T. A., Dubler R. E., Larner J. Insulin-like effect of vanadate on adipocyte glycogen synthase and on phosphorylation of 95,000 dalton subunit of insulin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 31;113(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90434-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Larner J. Insulin-like effect of trypsin on the phosphorylation of rat adipocyte insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14749–14752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Czech M. P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor beta subunit activates the receptor tyrosine kinase in intact H-35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4715–4722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]