Abstract
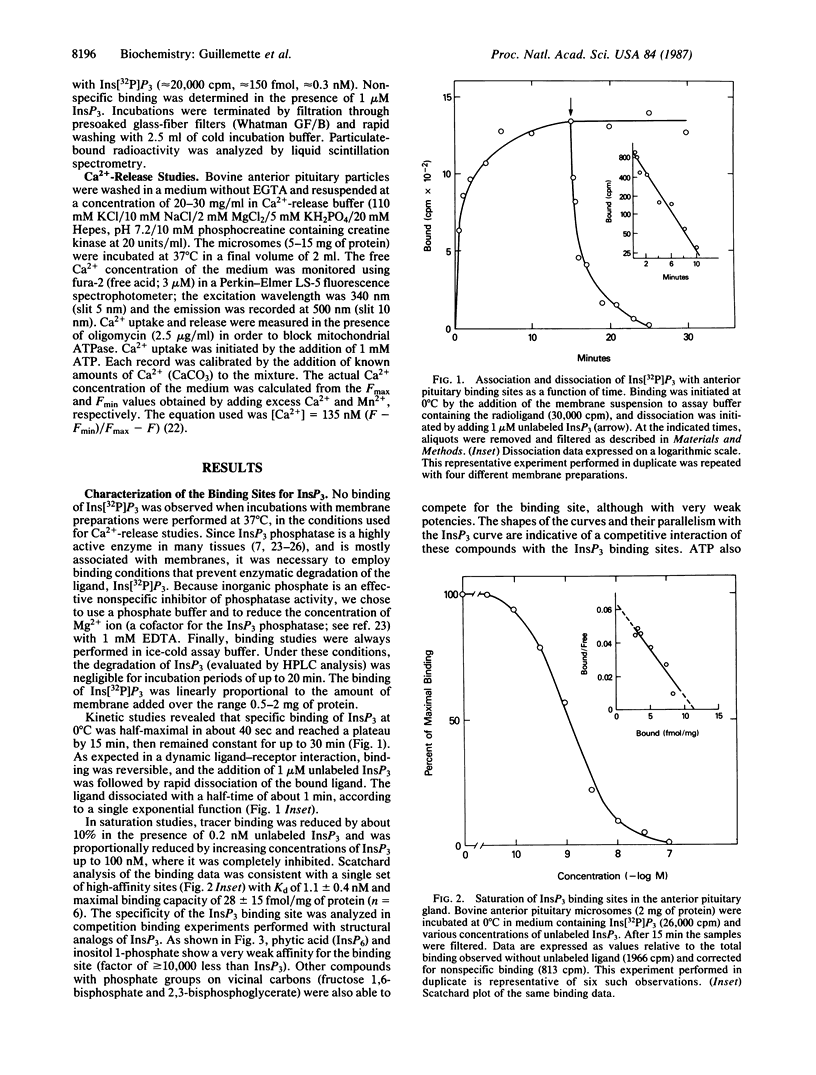
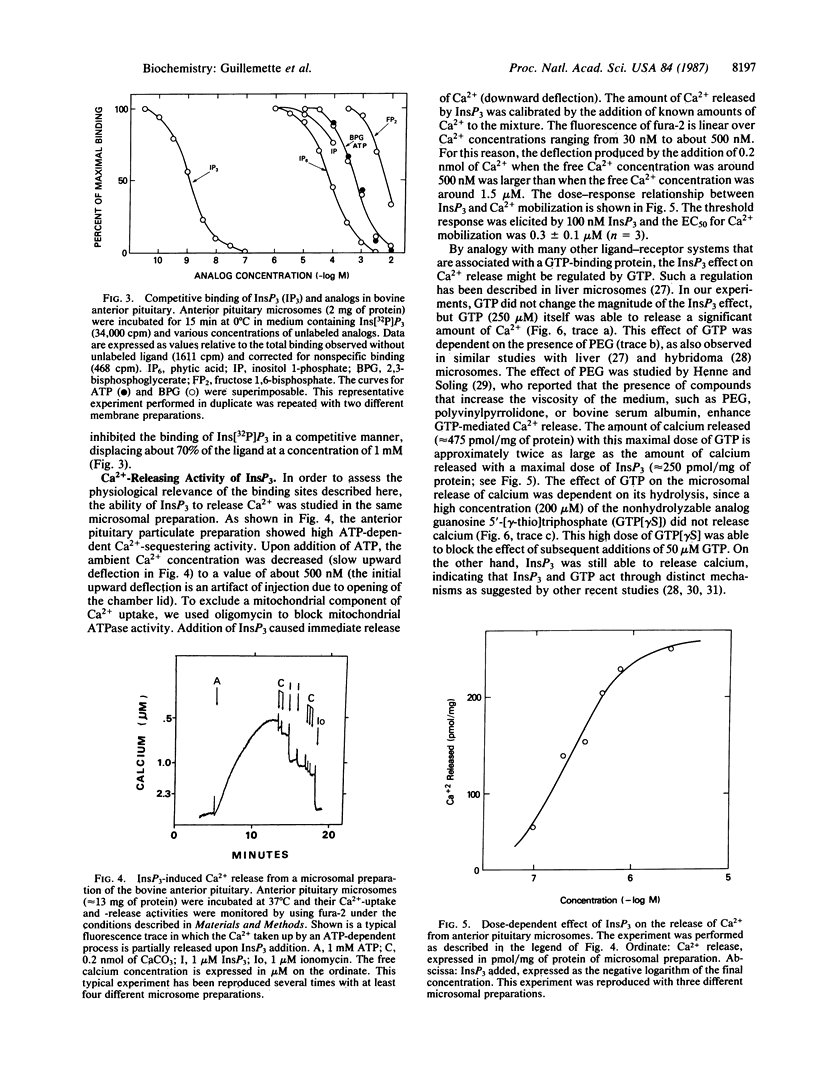
The properties of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) receptor sites in the anterior pituitary were evaluated by binding studies with InsP3 labeled with 32P to high specific radioactivity. Specific binding of Ins[32P]P3 was demonstrable in pituitary membrane preparations and was linearly proportional to the amount of membrane added over the range 0.5-2 mg of protein. Kinetic studies showed that specific InsP3 binding was half-maximal in about 40 sec and reached a plateau after 15 min at 0 degree C. Addition of 1 microM unlabeled InsP3 was followed by rapid dissociation of the bound ligand, according to a single exponential function with half-time of about 1 min. Scatchard analysis of the binding data was consistent with a single set of high-affinity sites with Kd of 1.1 +/- 0.4 nM and maximal binding capacity of 28 +/- 15 fmol/mg of protein (n = 6). The specificity of Ins[32P]P3 binding to these sites was illustrated by the much weaker affinity for structural analogs such as inositol 1-phosphate, phytic acid, 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate, and fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. To assess the functional relevance of the InsP3 binding sites, the Ca2+-releasing activity of InsP3 was measured in pituitary membrane preparations. In the presence of oligomycin (2.5 micrograms/ml), Ca2+ movements were monitored with the fluorescent indicator fura-2 (free acid). Under these conditions, 1 mM ATP caused rapid uptake of Ca2+ by a vesicular component of the membrane fraction. Addition of InsP3 (50-2000 nM) caused a dose-dependent release of Ca2+ with a half-maximal effect at 240 nM. In the presence of 3% polyethylene glycol, GTP also stimulated calcium release. However, a nonhydrolyzable GTP analog, guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate, did not release calcium and completely blocked the effect of GTP. Under physiological conditions within the cytosol, the high-affinity InsP3 binding sites characterized in pituitary membranes could serve as the putative receptors through which InsP3 triggers Ca2+ mobilization in the anterior pituitary gland.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aub D. L., Frey E. A., Sekura R. D., Cote T. E. Coupling of the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor to phospholipase C by a GTP-binding protein distinct from the inhibitory or stimulatory GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9333–9340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baukal A. J., Guillemette G., Rubin R., Spät A., Catt K. J. Binding sites for inositol trisphosphate in the bovine adrenal cortex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):532–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90939-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. L., MacLeod R. M. Angiotensin peptides stimulate phosphoinositide breakdown and prolactin release in anterior pituitary cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1986 Jan;118(1):233–238. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-1-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K. J., Loumaye E., Wynn P. C., Iwashita M., Hirota K., Morgan R. O., Chang J. P. GnRH receptors and actions in the control of reproductive function. J Steroid Biochem. 1985 Nov;23(5B):677–689. doi: 10.1016/s0022-4731(85)80003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chueh S. H., Gill D. L. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and guanine nucleotides activate calcium release from endoplasmic reticulum via distinct mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13883–13886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T. M., Bross T. E., Majerus P. W. Isolation of a phosphomonoesterase from human platelets that specifically hydrolyzes the 5-phosphate of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7868–7874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Irvine R. F. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and not phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate is the probable precursor of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in agonist-stimulated parotid gland. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):501–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2380501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Mussat M. C., Michell R. H. The inositol trisphosphate phosphomonoesterase of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):169–177. doi: 10.1042/bj2030169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drust D. S., Martin T. F. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rapidly activates protein phosphorylation in GH3 pituitary cells by a lipid-linked, protein kinase C-mediated pathway. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14520–14530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C., Geras E., Purrello V. S., Rebecchi M. J. Inositol trisphosphate mediates thyrotropin-releasing hormone mobilization of nonmitochondrial calcium in rat mammotropic pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10675–10681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. L., Ueda T., Chueh S. H., Noel M. W. Ca2+ release from endoplasmic reticulum is mediated by a guanine nucleotide regulatory mechanism. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):461–464. doi: 10.1038/320461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Balla T., Baukal A. J., Spät A., Catt K. J. Intracellular receptors for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in angiotensin II target tissues. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1010–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Baukal A. J., Balla T., Catt K. J. Angiotensin-induced formation and metabolism of inositol polyphosphates in bovine adrenal glomerulosa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 15;142(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90445-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Downes C. P. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands may both result indirectly from receptor-stimulated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj2380507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henne V., Söling H. D. Guanosine 5'-triphosphate releases calcium from rat liver and guinea pig parotid gland endoplasmic reticulum independently of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 7;202(2):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80699-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Sasaguri T., Hamachi T., Hashimoto T., Kukita M., Koga T. Irreversible inhibition of Ca2+ release in saponin-treated macrophages by the photoaffinity derivative of inositol-1, 4, 5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):723–725. doi: 10.1038/317723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai A., Gershengorn M. C. Evidence for tight coupling of thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptors to stimulated inositol trisphosphate formation in rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10536–10540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean T., Klee C. B. Calcium modulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release from neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid (NG108-15) microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16414–16420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiesel L., Bertges K., Rabe T., Runnebaum B. Gonadotropin releasing hormone enhances polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat pituitary cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):861–867. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80499-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A., Martin T. F. Direct stimulation by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) of polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in GH3 cell membranes by a guanine nucleotide-modulated mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 30;132(2):721–728. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone activates a Ca2+-dependent polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in permeable GH3 cells. GTP gamma S potentiation by a cholera and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2918–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsdell J. S., Tashjian A. H., Jr Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) elevation of inositol trisphosphate and cytosolic free calcium is dependent on receptor number. Evidence for multiple rapid interactions between TRH and its receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5301–5306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rana R. S., Sekar M. C., Hokin L. E., MacDonald M. J. A possible role for glucose metabolites in the regulation of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphomonoesterase activity in pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5237–5240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfred M. A., Farrell L. E., Wells W. W. Characterization of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate phosphatase in rat liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13204–13208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfred M. A., Farrell L. E., Wells W. W. Characterization of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate phosphatase in rat liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13204–13208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spät A., Bradford P. G., McKinney J. S., Rubin R. P., Putney J. W., Jr A saturable receptor for 32P-inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate in hepatocytes and neutrophils. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):514–516. doi: 10.1038/319514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spät A., Fabiato A., Rubin R. P. Binding of inositol trisphosphate by a liver microsomal fraction. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):929–932. doi: 10.1042/bj2330929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. J., Shears S. B., Kirk C. J., Michell R. H. Stepwise enzymatic dephosphorylation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to inositol in liver. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):374–376. doi: 10.1038/312374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., Gershengorn M. C. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone and GTP activate inositol trisphosphate formation in membranes isolated from rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2712–2717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Cooper R. H., Joseph S. K., Thomas A. P. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as intracellular second messengers in liver. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):C203–C216. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.3.C203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



