Abstract
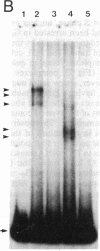
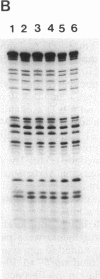
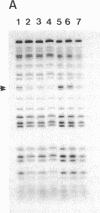
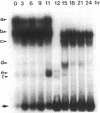
Induction of thymidine kinase parallels the onset of DNA synthesis. To investigate the transcriptional regulation of the thymidine kinase gene, we have examined whether specific nuclear factors interact in a cell-cycle-dependent manner with sequences upstream of this gene. Two inverted CCAAT boxes near the transcriptional initiation sites were observed to form complexes with nuclear DNA-binding proteins. The nature of the complexes changes dramatically as the cells approach DNA synthesis and correlates well with the previously reported transcriptional increase of the thymidine kinase gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bienz M. A CCAAT box confers cell-type-specific regulation on the Xenopus hsp70 gene in oocytes. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1037–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90703-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Heat shock regulatory elements function as an inducible enhancer in the Xenopus hsp70 gene and when linked to a heterologous promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):753–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90789-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw H. D., Jr Molecular cloning and cell cycle-specific regulation of a functional human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5588–5591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks R. F. Continuous protein synthesis is required to maintain the probability of entry into S phase. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Irminger J. C., Birnstiel M. L. Ubiquitous and gene-specific regulatory 5' sequences in a sea urchin histone DNA clone coding for histone protein variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):957–977. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Medrano E. E., Morreo G., Pardee A. B. Restriction point control of cell growth by a labile protein: evidence for increased stability in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):436–440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claycomb W. C. DNA synthesis and DNA enzymes in terminally differentiating cardiac muscle cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jan;118(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90588-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. B., Sheffery M., Kim C. G. Partial purification of a nuclear protein that binds to the CCAAT box of the mouse alpha 1-globin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):821–832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppock D. L., Pardee A. B. Control of thymidine kinase mRNA during the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2925–2932. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppock D. L., Pardee A. B. Regulation of thymidine kinase activity in the cell cycle by a labile protein. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Aug;124(2):269–274. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041240215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Hanly S. M., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Distinct transcription factors bind specifically to two regions of the human histone H4 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7241–7245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Sazer S., Tjian R., Schimke R. T. Transcription factor Sp1 recognizes a DNA sequence in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):246–248. doi: 10.1038/319246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
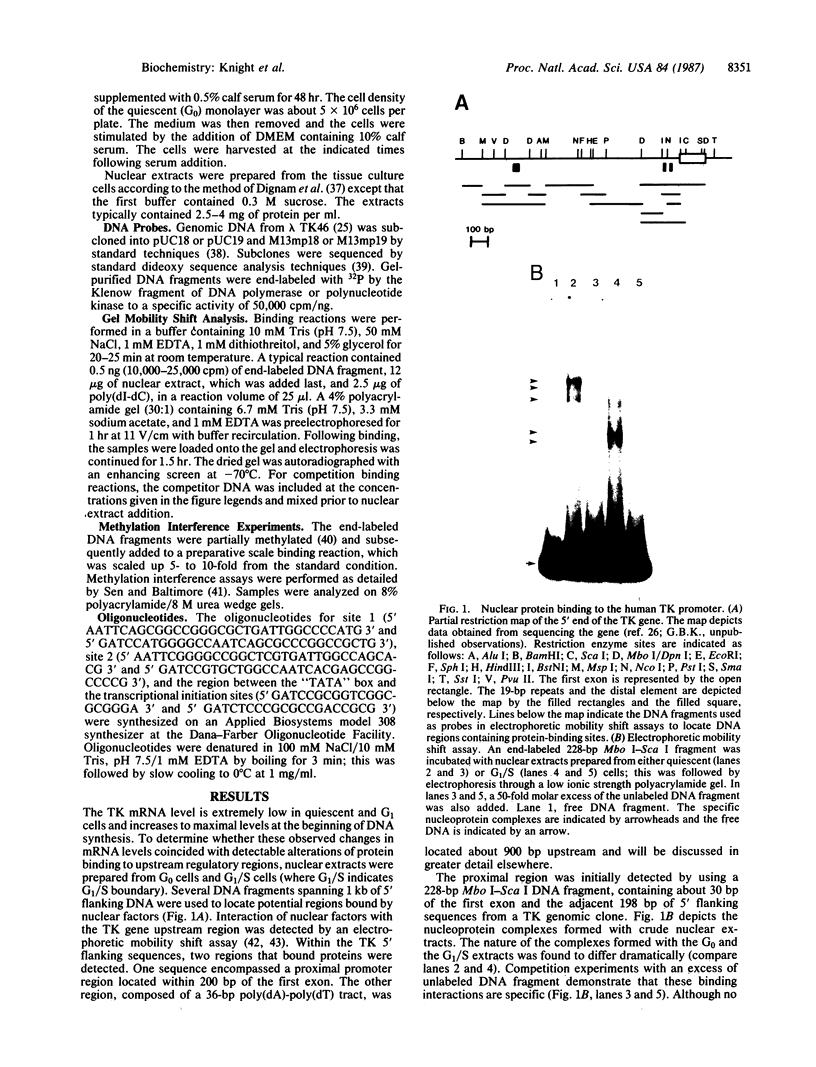
- Flemington E., Bradshaw H. D., Jr, Traina-Dorge V., Slagel V., Deininger P. L. Sequence, structure and promoter characterization of the human thymidine kinase gene. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Siegfried Z., Ziff E. B. Mutation of the c-fos gene dyad symmetry element inhibits serum inducibility of transcription in vivo and the nuclear regulatory factor binding in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1217–1225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Robins A. J., Wells J. R. Independently evolving chicken histone H2B genes: identification of a ubiquitous H2B-specific 5' element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7851–7863. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Kitchen A. M., Cochran B. H. Inducible binding of a factor to the c-fos regulatory region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1272–1276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson S. L., Wu J. S., Johnson L. F. Cell cycle regulation of dihydrofolate reductase mRNA metabolism in mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5140–5144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Fuhrman C. L., Wiedemann L. M. Regulation of dihydrofolate reductase gene expression in mouse fibroblasts during the transition from the resting to growing state. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Dec;97(3 Pt 2 Suppl 1):397–306. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040970314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Rao L. G., Muench A. J. Regulation of thymidine kinase enzyme level in serum-stimulated mouse 3T6 fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Mar;138(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreidberg J. A., Kelly T. J. Genetic analysis of the human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2903–2909. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeger P., Stewart C., Schaap T., van Wijnen A., Hirshman J., Helms S., Stein G., Stein J. Proximal and distal regulatory elements that influence in vivo expression of a cell cycle-dependent human H4 histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):3982–3986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A., Matkovich D. A. Genetic determinants of growth phase-dependent and adenovirus 5-responsive expression of the Chinese hamster thymidine kinase gene are contained within thymidine kinase mRNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2262–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A. Structure and expression of the Chinese hamster thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1998–2010. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leys E. J., Kellems R. E. Control of dihydrofolate reductase messenger ribonucleic acid production. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):961–971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. C., Spence A., Smith M. The distal transcription signals of the herpesvirus tk gene share a common hexanucleotide control sequence. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. D., Williams G. T., Morimoto R. I., Greene J., Kingston R. E., Tjian R. Two transcriptional activators, CCAAT-box-binding transcription factor and heat shock transcription factor, interact with a human hsp70 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1129–1138. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navalgund L. G., Rossana C., Muench A. J., Johnson L. F. Cell cycle regulation of thymidylate synthetase gene expression in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7386–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Prem veer Reddy G., Pardee A. B. Rapid incorporation of label from ribonucleoside disphosphates into DNA by a cell-free high molecular weight fraction from animal cell nuclei. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):443–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90464-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B., Dubrow R., Hamlin J. L., Kletzien R. F. Animal cell cycle. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:715–750. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli U., Chrysogelos S., Stein G., Stein J., Nick H. Protein-DNA interactions in vivo upstream of a cell cycle-regulated human H4 histone gene. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1308–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.3035717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prem veer Reddy G., Pardee A. B. Multienzyme complex for metabolic channeling in mammalian DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Roeder R. G. Inducible binding of a factor to the c-fos enhancer. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):777–784. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90520-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossow P. W., Riddle V. G., Pardee A. B. Synthesis of labile, serum-dependent protein in early G1 controls animal cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4446–4450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra F., Stein G., Stein J. Structure and in vitro transcription of a human H4 histone gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7069–7086. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. J., Ito M., Conrad S. E. Evidence for transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of the cellular thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1156–1163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart P., Ito M., Stewart C., Conrad S. E. Induction of cellular thymidine kinase occurs at the mRNA level. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1490–1497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubblefield E., Mueller G. C. Thymidine kinase activity in synchronized HeLa cell cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Aug 16;20(4):535–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Distinct factors bind to apparently homologous sequences in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):846–848. doi: 10.1038/322846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. C., Pardee A. B. Insulin-like growth factor I regulation of transcription and replicating enzyme induction necessary for DNA synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jun;127(3):410–416. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041270309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen A., Pardee A. B. Exponential 3T3 cells escape in mid-G1 from their high serum requirement. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 1;116(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]