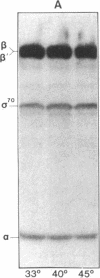
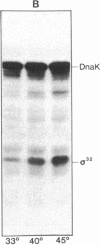
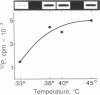
Abstract
S-30 extracts from Escherichia coli cells were used to express heat shock (HS) and non-HS genes in vitro in a DNA-directed protein synthesis system. The S-30 extracts prepared from cells that have been shifted to 45 degrees C express HS genes in vitro approximately 8 times better than extracts from cells at 33 degrees C. In contrast, the expression of non-HS genes in extracts from heat-induced cells is only 40% of that seen in extracts from cells at 33 degrees C. These results correlate well with the levels of HS sigma factor and normal sigma factor bound to RNA polymerase. Thus, there was an 8-fold increase in the HS sigma factor and a 60% decrease in the normal sigma factor associated with RNA polymerase at the higher temperature. Part of the increase in the level of the HS sigma factor could be accounted for by a 3-fold increase in the level of HS sigma factor mRNA during heat induction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahl H., Echols H., Straus D. B., Court D., Crowl R., Georgopoulos C. P. Induction of the heat shock response of E. coli through stabilization of sigma 32 by the phage lambda cIII protein. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):57–64. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M., Skelly S., VanBogelen R., Neidhardt F., Brot N., Weissbach H. In vitro effect of the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory protein on expression of heat shock genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):380–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.380-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowing D. W., Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A., Woolford C., Hendrix R. W., Gross C. A. Consensus sequence for Escherichia coli heat shock gene promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita N., Nomura T., Ishihama A. Promoter selectivity of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Purification and properties of holoenzyme containing the heat-shock sigma subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1855–1859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Goldberg A. L. Production of abnormal proteins in E. coli stimulates transcription of lon and other heat shock genes. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):587–595. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross C. A., Grossman A. D., Liebke H., Walter W., Burgess R. R. Effects of the mutant sigma allele rpoD800 on the synthesis of specific macromolecular components of the Escherichia coli K12 cell. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 25;172(3):283–300. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. The htpR gene product of E. coli is a sigma factor for heat-shock promoters. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Sigma 32 synthesis can regulate the synthesis of heat shock proteins in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):179–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt M. A., Knight D. M., Das A., Miller H. I., Echols H. Control of phage lambda development by stability and synthesis of cII protein: role of the viral cIII and host hflA, himA and himD genes. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landick R., Vaughn V., Lau E. T., VanBogelen R. A., Erickson J. W., Neidhardt F. C. Nucleotide sequence of the heat shock regulatory gene of E. coli suggests its protein product may be a transcription factor. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90538-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesley S. A., Thompson N. E., Burgess R. R. Studies of the role of the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory protein sigma 32 by the use of monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5404–5407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Lau E. T. Molecular cloning and expression of a gene that controls the high-temperature regulon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):597–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.597-603.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A. Positive regulatory gene for temperature-controlled proteins in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):894–900. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa T., Yura T. Effects of reduced amount of RNA polymerase sigma factor on gene expression and growth of Escherichia coli: studies of the rpoD450 (amber) mutation. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):166–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00272900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid translation. Comparable rates of polypeptide initiation and elongation on ovalbumin and globin messenger ribonucleic acid in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2095–2106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. The heat shock response of E. coli is regulated by changes in the concentration of sigma 32. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):348–351. doi: 10.1038/329348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. E., Straus D. B., Grossman A. D., Burton Z. F., Gross C. A., Burgess R. R. Transcription from a heat-inducible promoter causes heat shock regulation of the sigma subunit of E. coli RNA polymerase. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):371–381. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90492-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., Erickson J., Sharma S., Georgopoulos C. Heat shock regulatory gene rpoH mRNA level increases after heat shock in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1155–1158. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1155-1158.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Yura T. Genetic control of heat-shock protein synthesis and its bearing on growth and thermal resistance in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):860–864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarucki-Schulz T., Jerez C., Goldberg G., Kung H. F., Huang K. H., Brot N., Weissbach H. DNA-directed in vitro synthesis of proteins involved in bacterial transcription and translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6115–6119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]