Abstract
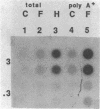
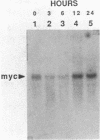
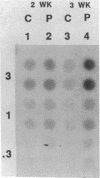
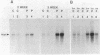
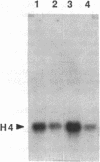
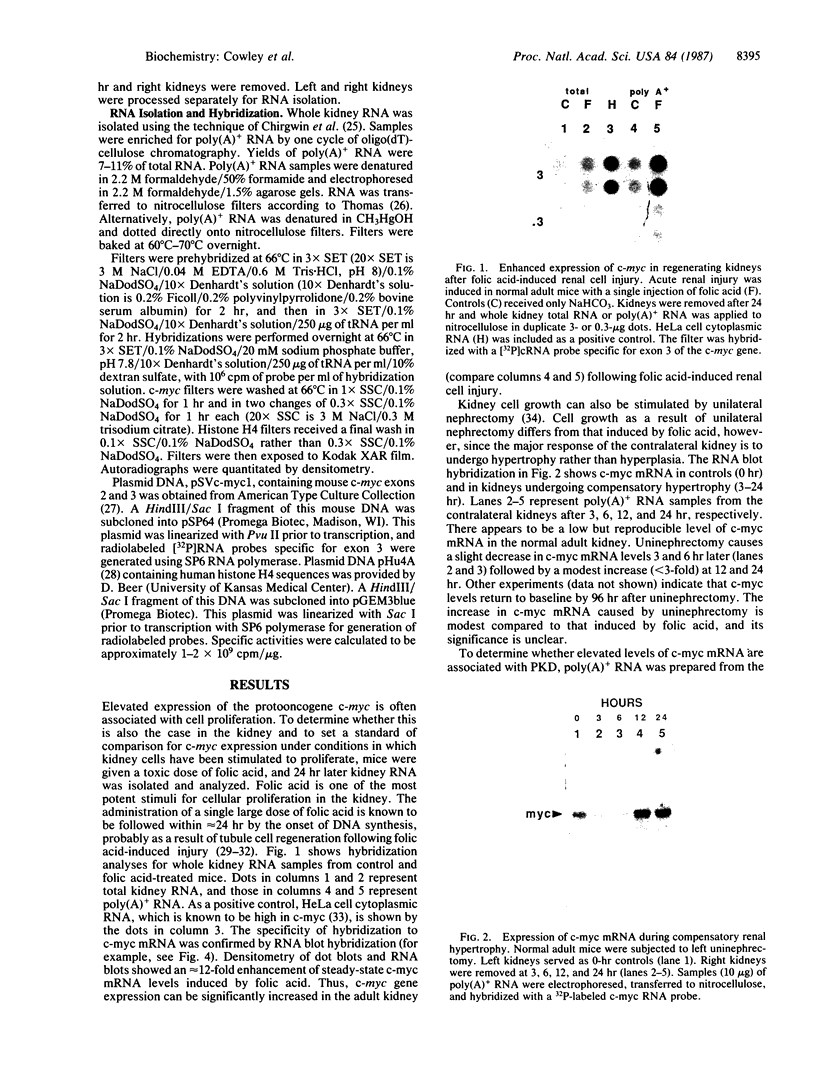
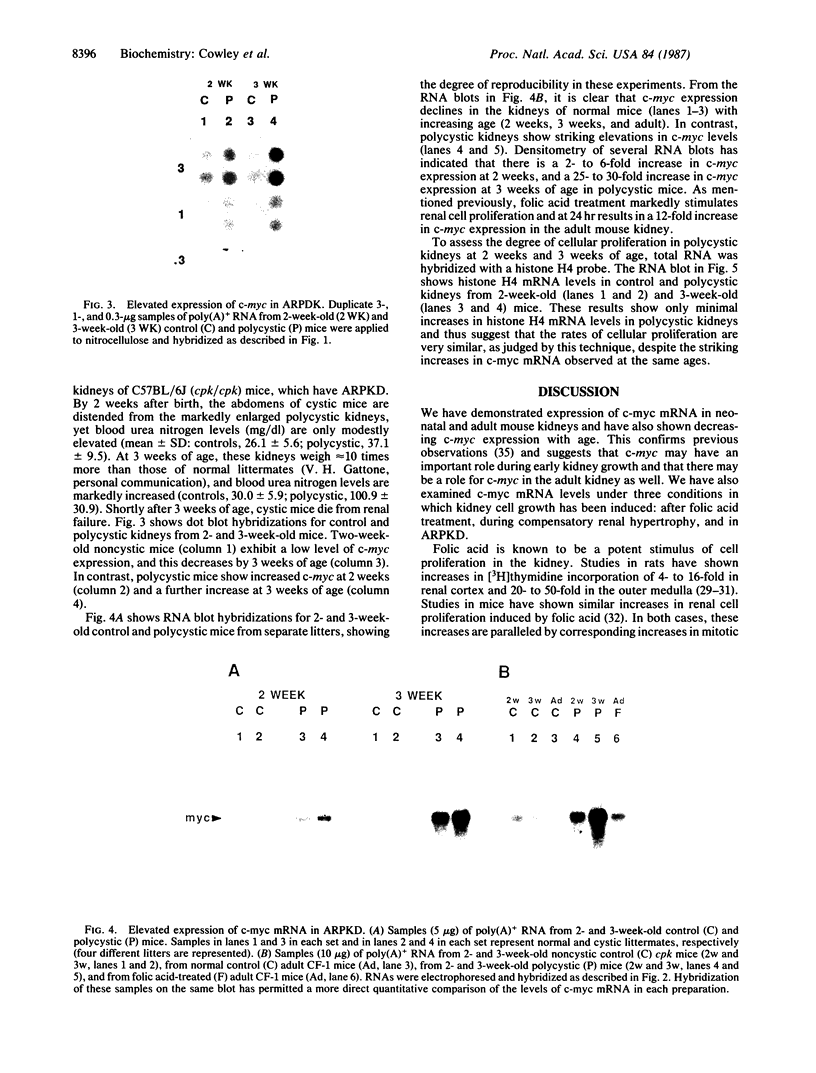
The polycystic kidney diseases (PKDs) are a group of disorders characterized by the growth of epithelial cysts from the nephrons and collecting ducts of kidney tubules. The diseases can be inherited or can be provoked by environmental factors. To investigate the molecular basis of the abnormal cell growth associated with PKD, c-myc protooncogene expression was studied in a mouse model for autosomal recessive PKD. Homozygous recessive C57BL/6J (cpk/cpk) mice develop massively enlarged cystic kidneys and die from renal failure shortly after 3 weeks of age. Quantitative dot blot and RNA blot hybridization experiments in which whole kidney poly(A)+ RNA was hybridized with a c-myc RNA probe showed a 2- to 6-fold increase in c-myc mRNA at 2 weeks, and a 25- to 30-fold increase in c-myc mRNA at 3 weeks of age in polycystic mice, as compared to normal littermates. c-myc expression was also examined under two conditions in which kidney cell growth was experimentally induced in normal adult mice: compensatory renal hypertrophy and tubule regeneration following folic acid-induced renal cell injury. While compensatory hypertrophy resulted in only a small (less than 3-fold) increase in c-myc, folic acid treatment gave rise after 24 hr to a 12-fold increase in c-myc mRNA. The induction of c-myc by folic acid is consistent with increased cellular proliferation in regenerating tubules. In contrast, polycystic kidneys show only a minimal increase in cellular proliferation over that seen in normal kidneys, while c-myc levels were found to be markedly elevated. Thus, the level of c-myc expression in cystic kidneys appears to be out of proportion to the rate of cell division, suggesting that elevated and potentially abnormal c-myc expression may be involved in the pathogenesis of PKD.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baserga R., Thatcher D., Marzi D. Cell proliferation in mouse kidney after a single injection of folic acid. Lab Invest. 1968 Jul;19(1):92–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beer D. G., Zweifel K. A., Simpson D. P., Pitot H. C. Specific gene expression during compensatory renal hypertrophy in the rat. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Apr;131(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. The molecular genetics of cancer. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):305–311. doi: 10.1126/science.3541204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carone F. A., Rowland R. G., Perlman S. G., Ganote C. E. The pathogenesis of drug-induced renal cystic disease. Kidney Int. 1974 Jun;5(6):411–421. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuppage F. E., Huseman R. A., Chapman A., Grantham J. J. Ultrastructure and function of cysts from human adult polycystic kidneys. Kidney Int. 1980 Mar;17(3):372–381. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., El Sabouty S., Marty L., Jeanteur P. Extreme instability of myc mRNA in normal and transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einat M., Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Close link between reduction of c-myc expression by interferon and, G0/G1 arrest. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):597–600. doi: 10.1038/313597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan A. P., Gardner K. D., Jr, Bernstein J. Polypoid and papillary epithelial hyperplasia: a potential cause of ductal obstruction in adult polycystic disease. Kidney Int. 1979 Dec;16(6):743–750. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan A. P., Gardner K. D., Jr Comparison of human polycystic and medullary cystic kidney disease with diphenylamine-induced cystic disease. Lab Invest. 1976 Jul;35(1):93–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine L. The biology of renal hypertrophy. Kidney Int. 1986 Mar;29(3):619–634. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyette M., Petropoulos C. J., Shank P. R., Fausto N. Regulated transcription of c-Ki-ras and c-myc during compensatory growth of rat liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1493–1498. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Levine E. Acquired cystic disease: replacing one kidney disease with another. Kidney Int. 1985 Aug;28(2):99–105. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J. Polycystic kidney disease: a predominance of giant nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):F3–10. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.1.F3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoire J. R., Torres V. E., Holley K. E., Farrow G. M. Renal epithelial hyperplastic and neoplastic proliferation in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1987 Jan;9(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(87)80158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression: kinetics of accumulation and changes in the rate of synthesis and in the half-lives of individual histone mRNAs during the HeLa cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):539–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh W., Rostorfer H. H. Chemically induced renal hypertrophy in the rat. Lab Invest. 1973 Nov;29(5):547–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Siebenlist U. The regulation and expression of c-myc in normal and malignant cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:317–338. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Klein E. Evolution of tumours and the impact of molecular oncology. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):190–195. doi: 10.1038/315190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingler E. L., Jr, Evan A. P., Anderson R. E. Folic acid-induced renal injury and repair. Correlation of structural and functional abnormalities. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1980 Feb;104(2):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino R., Hayashi K., Sugimura T. C-myc transcript is induced in rat liver at a very early stage of regeneration or by cycloheximide treatment. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):697–698. doi: 10.1038/310697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell J., Koch W. K., Nidess R., Preminger G. M., McFarland E. Congenital polycystic kidney disease. Genetically transmitted infantile polycystic kidney disease in C57BL/6J mice. Am J Pathol. 1983 Oct;113(1):112–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Slamon D. J., Tremblay J. M., Cline M. J., Verma I. M. Differential expression of cellular oncogenes during pre- and postnatal development of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):640–644. doi: 10.1038/299640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeders S. T., Breuning M. H., Davies K. E., Nicholls R. D., Jarman A. P., Higgs D. R., Pearson P. L., Weatherall D. J. A highly polymorphic DNA marker linked to adult polycystic kidney disease on chromosome 16. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):542–544. doi: 10.1038/317542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studzinski G. P., Brelvi Z. S., Feldman S. C., Watt R. A. Participation of c-myc protein in DNA synthesis of human cells. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.3532322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman K. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Collum R. G., Smith R. K., Kohl N. E., Denis K. A., Nau M. M., Witte O. N., Toran-Allerand D., Gee C. E. Differential expression of myc family genes during murine development. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):780–783. doi: 10.1038/319780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]