Abstract
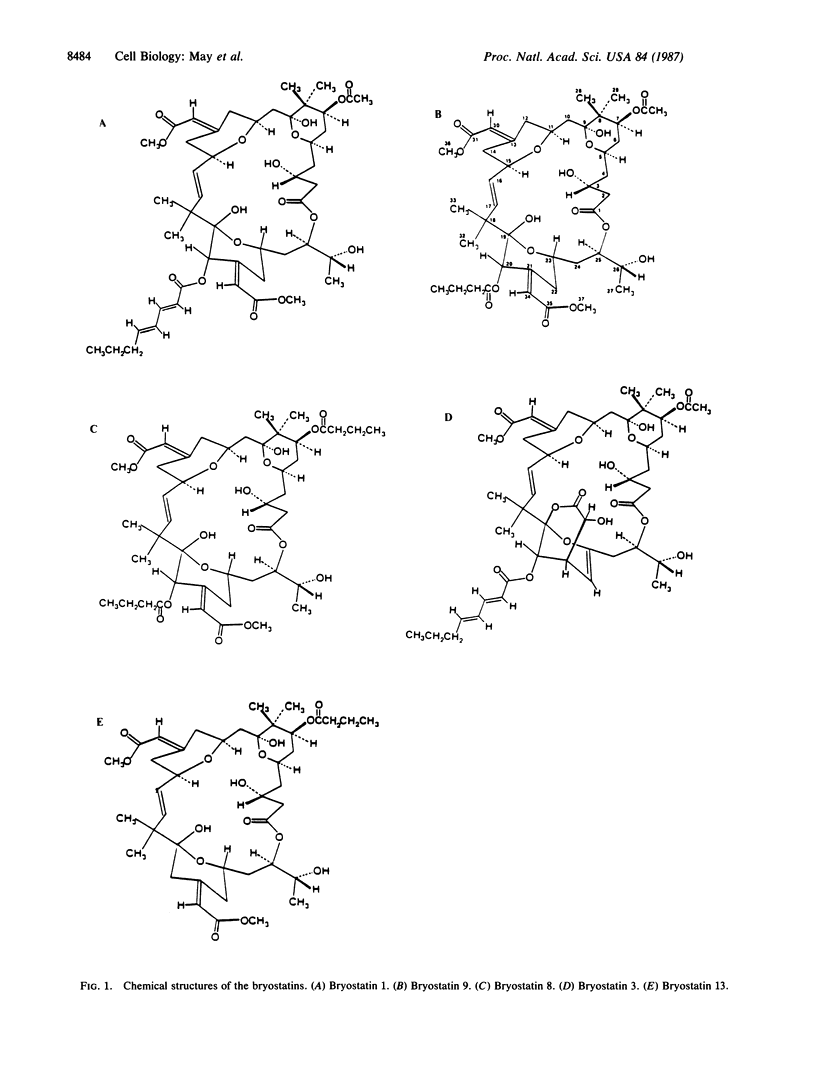
The bryostatins are macrocyclic lactones, extracted from the marine bryozoan Bugula neritina, and have been reported to be potent antineoplastic agents. Results described here demonstrate that the bryostatins may also be useful as stimulators of normal human hematopoietic cells since they can (i) directly stimulate bone marrow progenitor cells to form colonies in vitro and (ii) functionally activate neutrophils. Structure-activity studies with bryostatin congeners indicate that these stimulatory properties may be dependent on the chain length and the unsaturated nature of the acylated group at carbons 20 and 7 of the bryostatin molecule. These stimulatory properties demonstrate that the naturally occurring bryostatins can mimic many of the biological effects of multipotential granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Thus, the coupling of antineoplastic activity with stimulatory growth properties for normal hematopoietic cells makes this agent an excellent probe to dissect the mechanism(s) of normal hematopoiesis. In addition, bryostatin may represent a clinically attractive agent useful for treating bone marrow failure states.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Loose L. D. Phagocytic activation of a luminol-dependent chemiluminescence in rabbit alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkow R. L., Kraft A. S. Bryostatin, a non-phorbol macrocyclic lactone, activates intact human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and binds to the phorbol ester receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Sep 30;131(3):1109–1116. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90205-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Lukens J. N. Regulation of neutrophil inflammatory mediator release: chemotactic peptide activation of stimulus-dependent cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):850–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Baker V. V., May W. S. Bryostatin induces changes in protein kinase C location and activity without altering c-myc gene expression in human promyelocytic leukemia cells (HL-60). Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):111–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Smith J. B., Berkow R. L. Bryostatin, an activator of the calcium phospholipid-dependent protein kinase, blocks phorbol ester-induced differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells HL-60. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1334–1338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod D. L., Shreeve M. M., Axelrad A. A. Improved plasma culture system for production of erythrocytic colonies in vitro: quantitative assay method for CFU-E. Blood. 1974 Oct;44(4):517–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Begley C. G., Johnson G. R., Nicola N. A., Vadas M. A., Lopez A. F., Williamson D. J., Wong G. G., Clark S. C., Wang E. A. Biologic properties in vitro of a recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):37–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):16–22. doi: 10.1126/science.2990035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike B. L., Robinson W. A. Human bone marrow colony growth in agar-gel. J Cell Physiol. 1970 Aug;76(1):77–84. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040760111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsdell J. S., Pettit G. R., Tashjian A. H., Jr Three activators of protein kinase C, bryostatins, dioleins, and phorbol esters, show differing specificities of action on GH4 pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):17073–17080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomonaga M., Golde D. W., Gasson J. C. Biosynthetic (recombinant) human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: effect on normal bone marrow and leukemia cell lines. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F., Nicola N. A., Metcalf D., Burgess A. W. Hierarchical down-modulation of hemopoietic growth factor receptors. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Golde D. W., Clark S. C., Wong G. G., Gasson J. C. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a neutrophil activator. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):361–363. doi: 10.1038/314361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



