Abstract
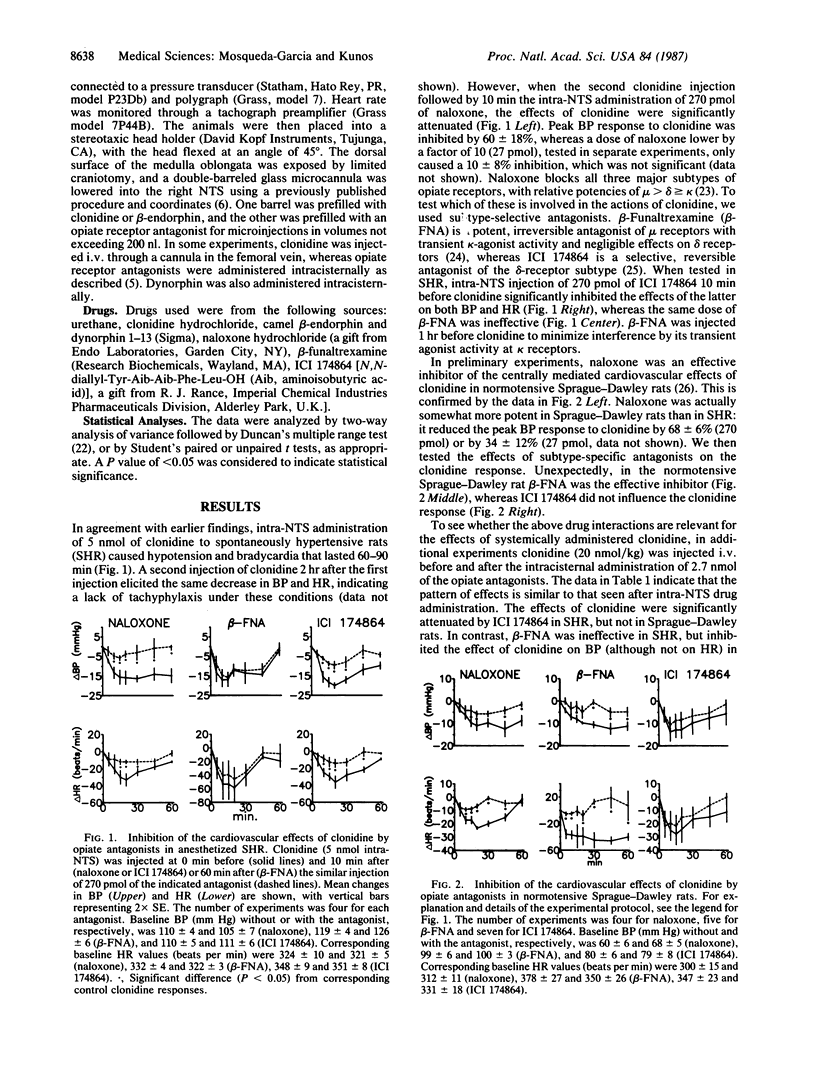
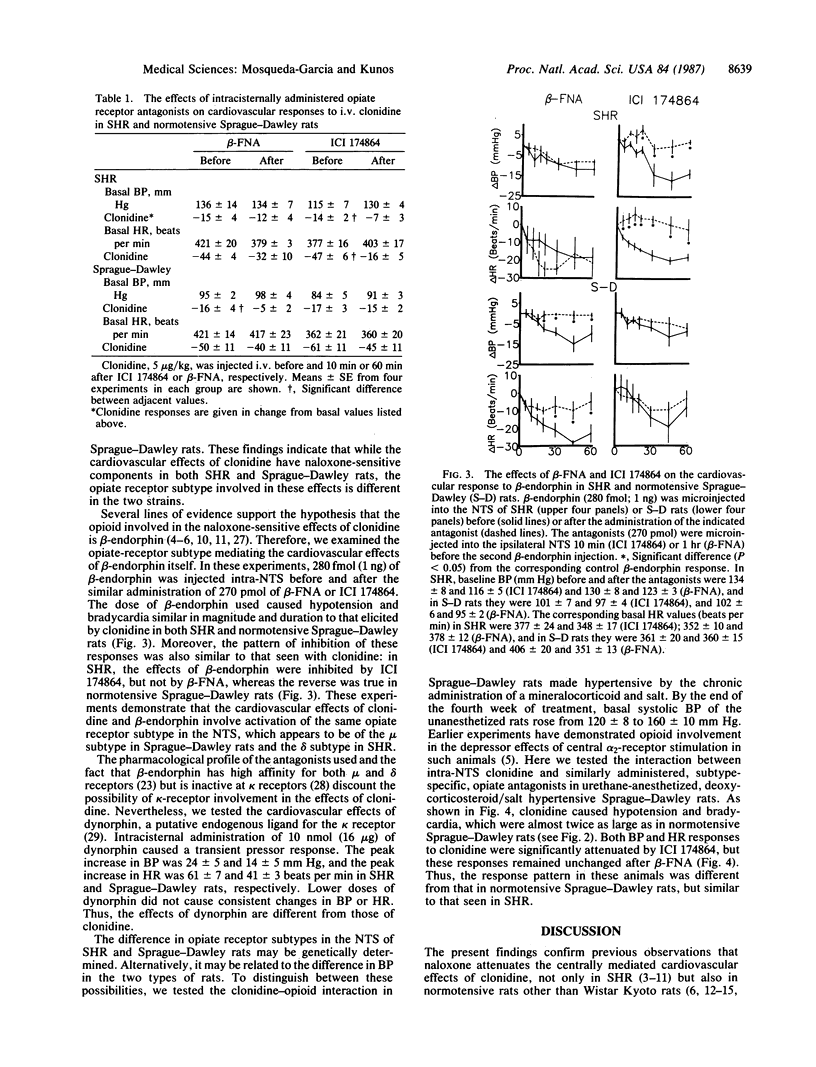
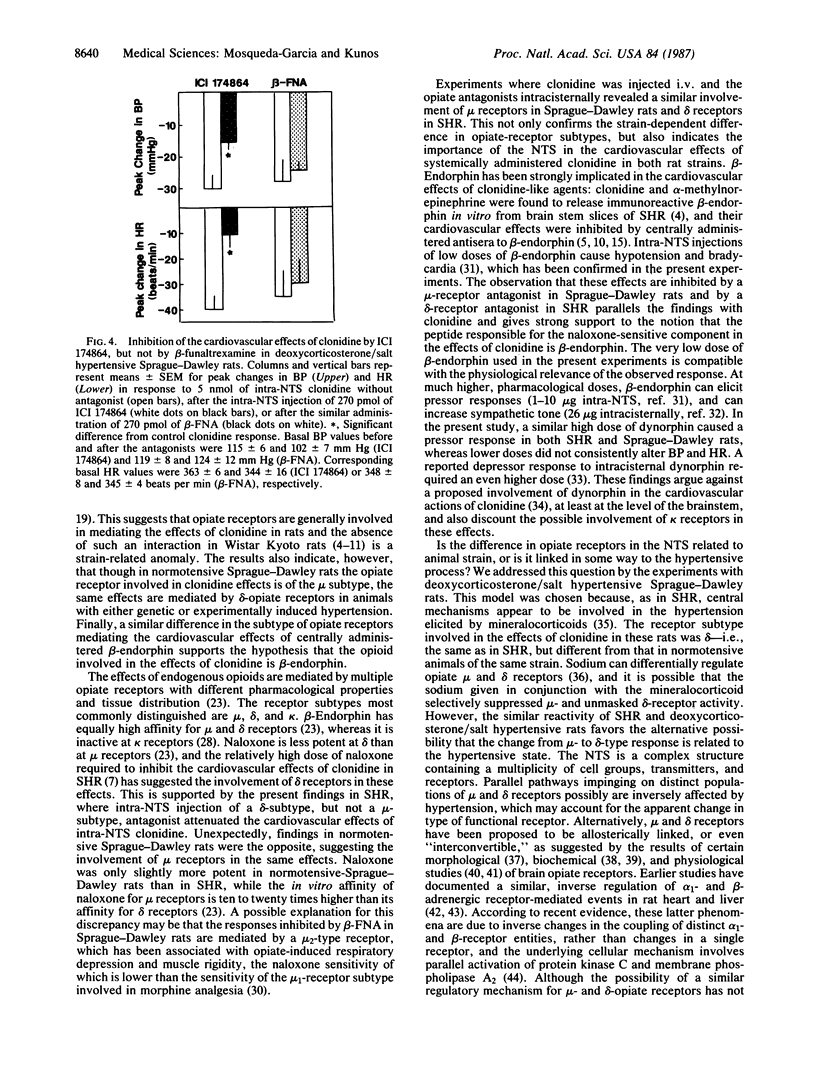
Effects of opiate receptor antagonists on centrally mediated cardiovascular responses to clonidine and beta-endorphin were studied in urethane-anesthetized spontaneously hypertensive Okamoto-Aoki rats (SHR), normotensive Sprague-Dawley rats, and Sprague-Dawley rats made hypertensive with deoxycorticosterone pivalate/salt. Microinjection of 270 pmol of naloxone into the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) significantly inhibited the hypotensive and bradycardic response to 5 nmol of similarly administered clonidine in both SHR and normotensive Sprague-Dawley rats. In SHR, a similar inhibition was observed after the delta-opiate receptor antagonist ICI 174864, but not after the mu-receptor antagonist beta-funaltrexamine (both at 270 pmol, intra-NTS), whereas in normotensive Sprague-Dawley rats, beta-funaltrexamine, but not ICI 174864, was an effective inhibitor. The same pattern of differential inhibition was seen when clonidine was given i.v. and the opiate antagonists were given intracisternally in SHR and Sprague-Dawley rats. Intra-NTS microinjection of 280 fmol of beta-endorphin caused hypotension and bradycardia, and these effects were similarly inhibited by ICI 174864 in SHR and by beta-funaltrexamine in Sprague-Dawley rats. In Sprague-Dawley rats made hypertensive by chronic administration of deoxycorticosterone pivalate and salt, the hypotensive and bradycardic effects of intra-NTS clonidine were inhibited by ICI 174864, but not by beta-funaltrexamine, a pattern similar to that in SHR, but different from that in normotensive Sprague-Dawley rats. These results support the hypothesis that beta-endorphin release and subsequent stimulation of opiate receptors in the NTS are involved in the cardiovascular effects of clonidine in rats. These results further suggest, however, that hypertension regulates the subtype of opiate receptors mediating these effects.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel N. M., Kiritsy-Roy J. A., van Loon G. R. Mu receptors at discrete hypothalamic and brainstem sites mediate opioid peptide-induced increases in central sympathetic outflow. Brain Res. 1986 Jul 16;378(1):8–20. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90281-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen W. D., Gentleman S., Herkenham M., Pert C. B. Interconverting mu and delta forms of the opiate receptor in rat striatal patches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4818–4822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelain P., Claeys M., van Dorsser W., Roba J. Antihypertensive activity of tibalosine (CP 804 S) in the rat. Possible involvement of a central alpha 1-adrenergic receptor blockade. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1984 Apr;268(2):271–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., James I. F., Goldstein A. Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.6120570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amato R., Holaday J. W. Multiple opioid receptors in endotoxic shock: evidence for delta involvement and mu-delta interactions in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2898–2901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray A., Nunan L. Selective delta-opioid receptor antagonism by ICI 174,864 in the central nervous system. Peptides. 1984 Sep-Oct;5(5):1015–1016. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson L., Tuomisto L. Effect of naloxone on the hypotensive action of clonidine in the conscious, normotensive goat. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1983 Apr;52(4):241–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1983.tb01094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farsang C., Kunos G. Naloxone reverses the antihypertensive effect of clonidine. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;67(2):161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08661.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farsang C., Ramirez-Gonzalez M. D., Mucci L., Kunos G. Possible role of an endogenous opiate in the cardiovascular effects of central alpha adrenoceptor stimulation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Jul;214(1):203–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Wei E. Analysis of cardiovascular effects of morphine in the cat. Neuroscience. 1986 Feb;17(2):495–506. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Sanchez E. P. Intracerebroventricular infusion of aldosterone induces hypertension in rats. Endocrinology. 1986 Feb;118(2):819–823. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-2-819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. C., Longman S. D. A comparison of the cardiovascular and sedative actions of the alpha-adrenoceptor agonists, FLA-136 and clonidine, in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):13–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Farsang C., Ramirez-Gonzales M. D. beta-Endorphin: possible involvement in the antihypertensive effect of central alpha-receptor activation. Science. 1981 Jan 2;211(4477):82–84. doi: 10.1126/science.6108611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Hirata F., Ishac E. J., Tchakarov L. Time-dependent conversion of alpha 1- to beta-adrenoceptor-mediated glycogenolysis in isolated rat liver cells: role of membrane phospholipase A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6178–6182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Ishac E. J. Mechanism of inverse regulation of alpha 1- and beta-adrenergic receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 15;36(8):1185–1191. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Mosqueda-Garcia R., Mastrianni J. A., Abbott F. V. Endorphinergic mechanism in the central cardiovascular and analgesic effects of clonidine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;65(8):1624–1632. doi: 10.1139/y87-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Robertson B., Kan W. H., Preiksaitis H., Mucci L. Adrenergic reactivity of the myocardium in hypertension. Life Sci. 1978 Mar;22(10):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90608-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Szentivanyi M. Evidence favouring the existence of a single adrenergic receptor. Nature. 1968 Mar 16;217(5133):1077–1078. doi: 10.1038/2171077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laubie M., Schmitt H. Sites of action of clonidine: centrally mediated increase in vagal tone, centrally mediated hypotensive and sympatho-inhibitory effects. Prog Brain Res. 1977;47:337–348. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)62738-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent S., Schmitt H. Central cardiovascular effects of kappa agonists dynorphin-(1-13) and ethylketocyclazocine in the anaesthetized rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec 9;96(1-2):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N. M., Smith A. P. A protein-lipid model of the opiate receptor. Life Sci. 1980 May 5;26(18):1459–1464. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Meli A. Suitability of urethane anesthesia for physiopharmacological investigations in various systems. Part 1: General considerations. Experientia. 1986 Feb 15;42(2):109–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01952426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrianni J. A., Ingenito A. J. On the relationship between clonidine hypotension and brain beta-endorphin in the spontaneously hypertensive rat: studies with alpha adrenergic and opiate blockers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jul;242(1):378–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosqueda-Garcia R., Eskay R., Zamir N., Palkovits M., Kunos G. Opioid-mediated cardiovascular effects of clonidine in spontaneously hypertensive rats: elimination by neonatal treatment with monosodium glutamate. Endocrinology. 1986 May;118(5):1814–1822. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-5-1814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Negishi K., Suda M., Matsumiya T., Inazu T., Ueki M. Rabbit vas deferens: a specific bioassay for opioid kappa-receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(2-3):235–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Wood P. J. Multiple mu opiate receptors. Life Sci. 1986 May 26;38(21):1889–1898. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90217-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty M. A., De Jong W. Cardiovascular effects of beta-endorphin after microinjection into the nucleus tractus solitarii of the anaesthetised rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 16;81(3):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty M. A., De Jong W. Endorphins and the hypotensive response to stimulation of alpha-receptors in the brainstem by alpha-methylnoradrenaline. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Jun;23(6):643–648. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Gonzalez M. D., Tchakarov L., Mosqueda Garcia R., Kunos G. beta-endorphin acting on the brainstem is involved in the antihypertensive action of clonidine and alpha-methyldopa in rats. Circ Res. 1983 Aug;53(2):150–157. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman R. B., Westfall T. C. Allosteric modulation by leucine-enkephalin of [3H]naloxone binding in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90577-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. J., Portoghese P. S., Takemori A. E. Pharmacological characterization in vivo of the novel opiate, beta-funaltrexamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Mar;220(3):494–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werling L. L., Brown S., Cox B. M. The sensitivity of opioid receptor types to regulation by sodium and GTP. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. A. Effect of clonidine and naloxone on the pressor response during contraction of cat hind-limb muscles. Cardiovasc Res. 1985 Aug;19(8):474–482. doi: 10.1093/cvr/19.8.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie C. W., Tang J., Han J. S. Clonidine stimulated the release of dynorphin in the spinal cord of the rat: a possible mechanism for its depressor effects. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Apr 11;65(2):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90309-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



