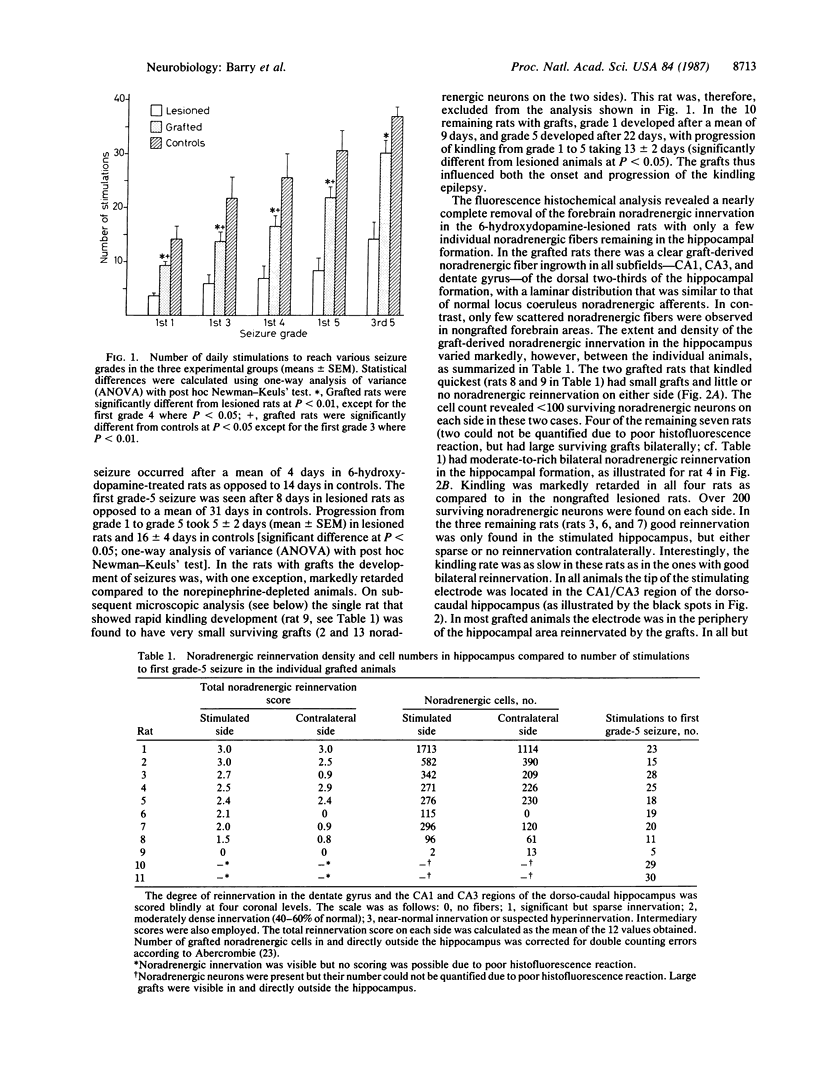
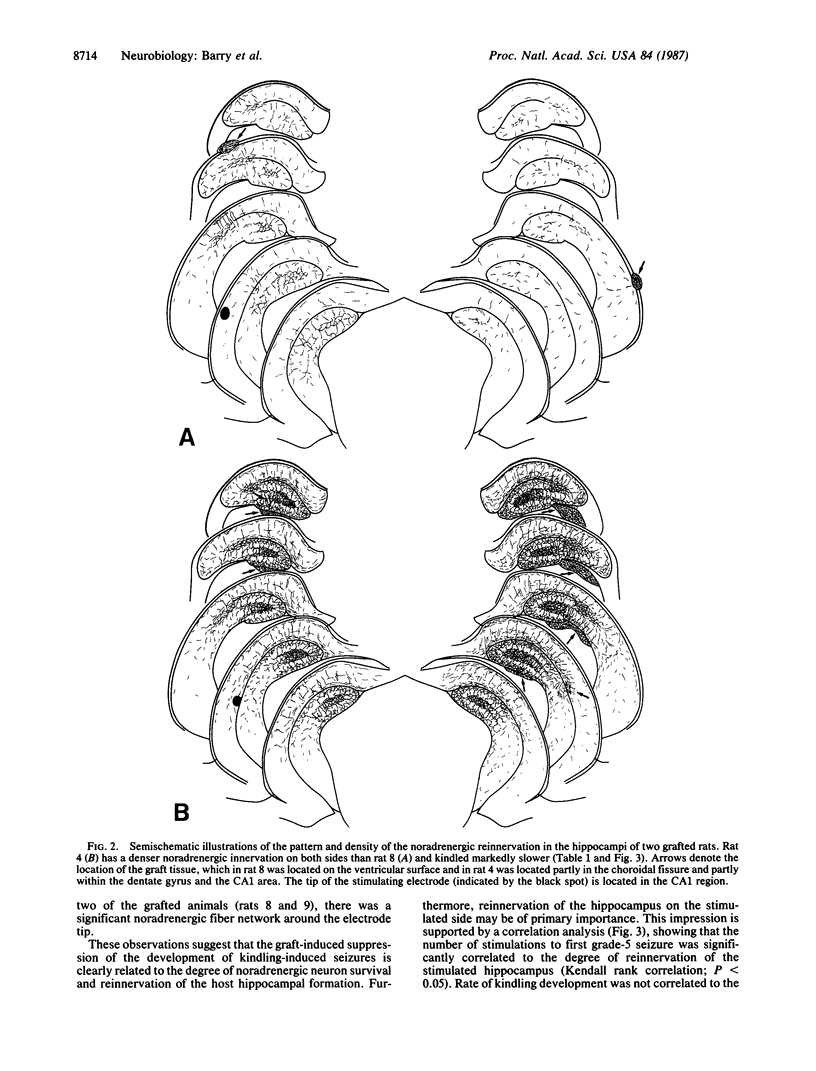
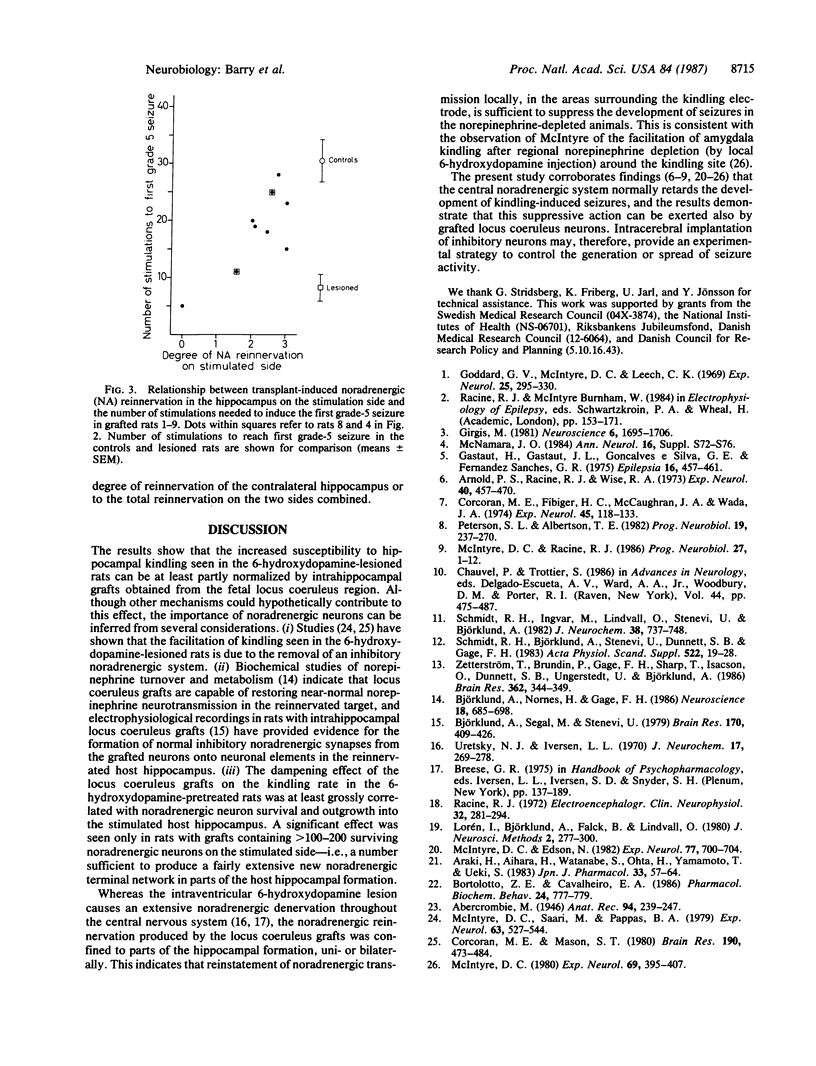
Abstract
Norepinephrine-rich cell suspensions, prepared from the locus coeruleus region of rat fetuses, were grafted bilaterally into the hippocampus of rats made hypersensitive to hippocampal kindling by a neurotoxic lesion of the central catecholamine system. The animals with grafts showed a marked suppression of the onset and progression of kindling-induced epilepsy, and this effect was correlated with the degree of graft-derived noradrenergic innervation of the host hippocampal formation. We conclude that grafted neurons can modulate the excitability of epileptic brain regions.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki H., Aihara H., Watanabe S., Ohta H., Yamamoto T., Ueki S. The role of noradrenergic and serotonergic systems in the hippocampal kindling effect. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1983 Feb;33(1):57–64. doi: 10.1254/jjp.33.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold P. S., Racine R. J., Wise R. A. Effects of atropine, reserpine, 6-hydroxydopamine, and handling on seizure development in the rat. Exp Neurol. 1973 Aug;40(2):457–470. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(73)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björklund A., Nornes H., Gage F. H. Cell suspension grafts of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons in rat hippocampus and spinal cord: reinnervation and transmitter turnover. Neuroscience. 1986 Jul;18(3):685–698. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90063-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björklund A., Segal M., Stenevi U. Functional reinnervation of rat hippocampus by locus coeruleus implants. Brain Res. 1979 Jul 20;170(3):409–426. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90961-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolotto Z. A., Cavalheiro E. A. Effect of DSP4 on hippocampal kindling in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1986 Mar;24(3):777–779. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(86)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran M. E., Fibiger H. C., McCaughran J. A., Jr, Wada J. A. Potentiation of amygdaloid kindling and metrazol-induced seizures by 6-hydroxydopamine in rats. Exp Neurol. 1974 Oct;45(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(74)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran M. E., Mason S. T. Role of forebrain catecholamines in amygdaloid kindling. Brain Res. 1980 May 26;190(2):473–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90289-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gastaut H., Gastaut J. L., Gonçalves e Silva G. E., Fernandez Sanchez G. R. Relative frequency of different types of epilepsy: a study employing the classification of the International League Against Epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1975 Sep;16(3):457–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1975.tb06073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girgis M. Commentary kindling as a model for limbic epilepsy. Neuroscience. 1981;6(9):1695–1706. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90205-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard G. V., McIntyre D. C., Leech C. K. A permanent change in brain function resulting from daily electrical stimulation. Exp Neurol. 1969 Nov;25(3):295–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorén I., Björklund A., Falck B., Lindvall O. The aluminum-formaldehyde (ALFA) histofluorescence method for improved visualization of catecholamines and indoleamines. I. A detailed account of the methodology for central nervous tissue using paraffin, cryostat or Vibratome sections. J Neurosci Methods. 1980 Jun;2(3):277–300. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(80)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre D. C. Amygdala kindling in rats: facilitation after local amygdala norepinephrine depletion with 6-hydroxydopamine. Exp Neurol. 1980 Aug;69(2):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(80)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre D. C., Edson N. Effect of norepinephrine depletion on dorsal hippocampus kindling in rats. Exp Neurol. 1982 Sep;77(3):700–704. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(82)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre D. C., Racine R. J. Kindling mechanisms: current progress on an experimental epilepsy model. Prog Neurobiol. 1986;27(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(86)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre D. C., Saari M., Pappas B. A. Potentiation of amygdala kindling in adult or infants rats by injections of 6-hydroxydopamine. Exp Neurol. 1979 Mar;63(3):527–544. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(79)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara J. O. Kindling: an animal model of complex partial epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1984;16 (Suppl):S72–S76. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson S. L., Albertson T. E. Neurotransmitter and neuromodulator function in the kindled seizure and state. Prog Neurobiol. 1982;19(4):237–270. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(82)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racine R. J. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1972 Mar;32(3):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(72)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. H., Björklund A., Stenevi U., Dunnett S. B., Gage F. H. Intracerebral grafting of neuronal cell suspensions. III. Activity of intrastriatal nigral suspension implants as assessed by measurements of dopamine synthesis and metabolism. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1983;522:19–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. H., Ingvar M., Lindvall O., Stenevi U., Björklund A. Functional activity of substantia nigra grafts reinnervating the striatum: neurotransmitter metabolism and [14C]2-deoxy-D-glucose autoradiography. J Neurochem. 1982 Mar;38(3):737–748. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uretsky N. J., Iversen L. L. Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on catecholamine containing neurones in the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1970 Feb;17(2):269–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb02210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterström T., Brundin P., Gage F. H., Sharp T., Isacson O., Dunnett S. B., Ungerstedt U., Björklund A. In vivo measurement of spontaneous release and metabolism of dopamine from intrastriatal nigral grafts using intracerebral dialysis. Brain Res. 1986 Jan 8;362(2):344–349. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




