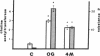Abstract
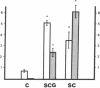
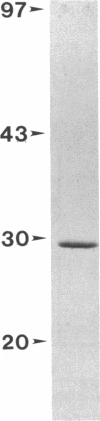
The choice of which neurotransmitters will be produced by a developing neuron is influenced by the microenvironment of the neuron. In this study we show that neuronal contact with membrane-associated molecules promotes expression of peptidergic and cholinergic traits. Treatment of cultured neonatal rat sympathetic neurons with plasma membranes derived from adult rat spinal cord or sympathetic ganglia induced expression of the peptide transmitter substance P and increased levels of the cholinergic biosynthetic enzyme choline acetyltransferase. The transmitter-stimulating activity could be solubilized from spinal cord membranes by the detergent octyl glucoside but not by Triton X-100. The choline acetyltransferase- and substance P-stimulating activity also could be extracted from spinal cord membranes by 4 M sodium chloride, suggesting that the active material is membrane associated rather than an intrinsic structural membrane molecule. Trypsin or heat treatment of the extract destroyed the transmitter-stimulating activity, indicating that the factor contains a protein. Activity also was destroyed by hyaluronidase treatment, suggesting that the active material may contain a glycosaminoglycan. The choline acetyltransferase-stimulating activity in the 4 M NaCl extract was eluted in a single peak from a calibrated Sephadex G-75 column with a retention time slightly less than that of a 25-kDa standard. NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the active peak revealed a predominant band at 29 kDa. Thus, contact-mediated stimulation of substance P and choline acetyltransferase activity in sympathetic neurons results from neuronal exposure to a 29-kDa membrane-associated factor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson A. L., Thoenen H. Cell contact-mediated regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase synthesis in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):925–928. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. E., Black I. B. Sympathetic neuron density differentially regulates transmitter phenotypic expression in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4296–4300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black I. B. Stages of neurotransmitter development in autonomic neurons. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1198–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4537.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunge R., Glaser L., Lieberman M., Raben D., Salzer J., Whittenberger B., Woolsey T. Growth control by cell to cell contact. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(2):175–187. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Modulation of cell adhesion during induction, histogenesis, and perinatal development of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1984;7:339–377. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.07.030184.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D. H., Thoenen H. Selective enzyme induction in a nerve growth factor-responsive pheochromocytoma cell line (PC 12). Brain Res. 1978 Oct 6;154(1):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Radiochemical micro assays for the determination of choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase activities. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):465–472. doi: 10.1042/bj1150465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier W., Glaser L. Surface components and cell recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:491–523. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada K. Purification and partial characterization of a cholinergic neuronal differentiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8795–8799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D., Rothman T. P., Joh T. H., Teitelman G. N. Transient and differential expression of aspects of the catecholaminergic phenotype during development of the fetal bowel of rats and mice. J Neurosci. 1984 Sep;4(9):2269–2280. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-09-02269.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Rein G. Synthesis, storage and release of acetylcholine by a noradrenergic pheochromocytoma cell line. Nature. 1977 Jul 28;268(5618):349–351. doi: 10.1038/268349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawrot E. Cultured sympathetic neurons: effects of cell-derived and synthetic substrata on survival and development. Dev Biol. 1980 Jan;74(1):136–151. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F., Hartikka J., Eckenstein F., Gnahn H., Heumann R., Schwab M. Nerve growth factor increases choline acetyltransferase but not survival or fiber outgrowth of cultured fetal septal cholinergic neurons. Neuroscience. 1985 Jan;14(1):55–68. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshishian H., Bentley D. Embryogenesis of peripheral nerve pathways in grasshopper legs. I. The initial nerve pathway to the CNS. Dev Biol. 1983 Mar;96(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90314-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. A., Conn G., Hatcher V. B. Isolated plasma membranes regulate neurotransmitter expression and facilitate effects of a soluble brain cholinergic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3528–3532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. A. Differential regulation of cholinergic and peptidergic development in the rat striatum in culture. Dev Biol. 1986 Jan;113(1):77–89. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. A. Differential regulation of peptide and catecholamine characters in cultured sympathetic neurons. Neuroscience. 1985 Jul;15(3):827–839. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. A. Environmental co-regulation of substance P, somatostatin and neurotransmitter synthesizing enzymes in cultured sympathetic neurons. Brain Res. 1984 Oct 29;321(1):155–159. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90693-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. A. Non-neuronal cell conditioned medium stimulates peptidergic expression in sympathetic and sensory neurons in vitro. Dev Biol. 1984 Nov;106(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. M. The ontogeny of the neural crest in avian embryo chimaeras. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):663–669. doi: 10.1038/286663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Schenker A., Shooter E. M. Characterization and isolation of proteolytically modified nerve growth factor. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 14;15(25):5543–5552. doi: 10.1021/bi00670a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson P. H., Chun L. L. The induction of acetylcholine synthesis in primary cultures of dissociated rat sympathetic neurons. I. Effects of conditioned medium. Dev Biol. 1977 Apr;56(2):263–280. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90269-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochiantz A., Daguet M. C., Herbet A., Glowinski J. Specific stimulation of in vitro maturation of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurones by striatal membranes. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):570–572. doi: 10.1038/293570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U. Molecular and biological properties of a neural cell adhesion molecule. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):501–514. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saadat S., Thoenen H. Selective induction of tyrosine hydroxylase by cell-cell contact in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells is mimicked by plasma membranes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1991–1997. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosney K. W. The early migration of neural crest cells in the trunk region of the avian embryo: an electron microscopic study. Dev Biol. 1978 Feb;62(2):317–333. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. J. A diffusible factor responsible for the determination of cholinergic functions in cultured sympathetic neurons. Partial purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3447–3453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]