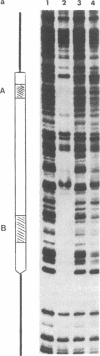
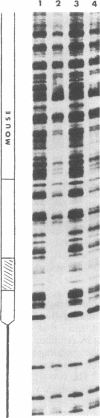
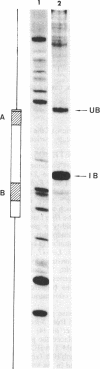
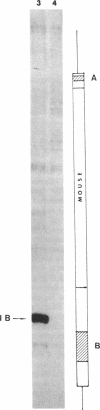
Abstract
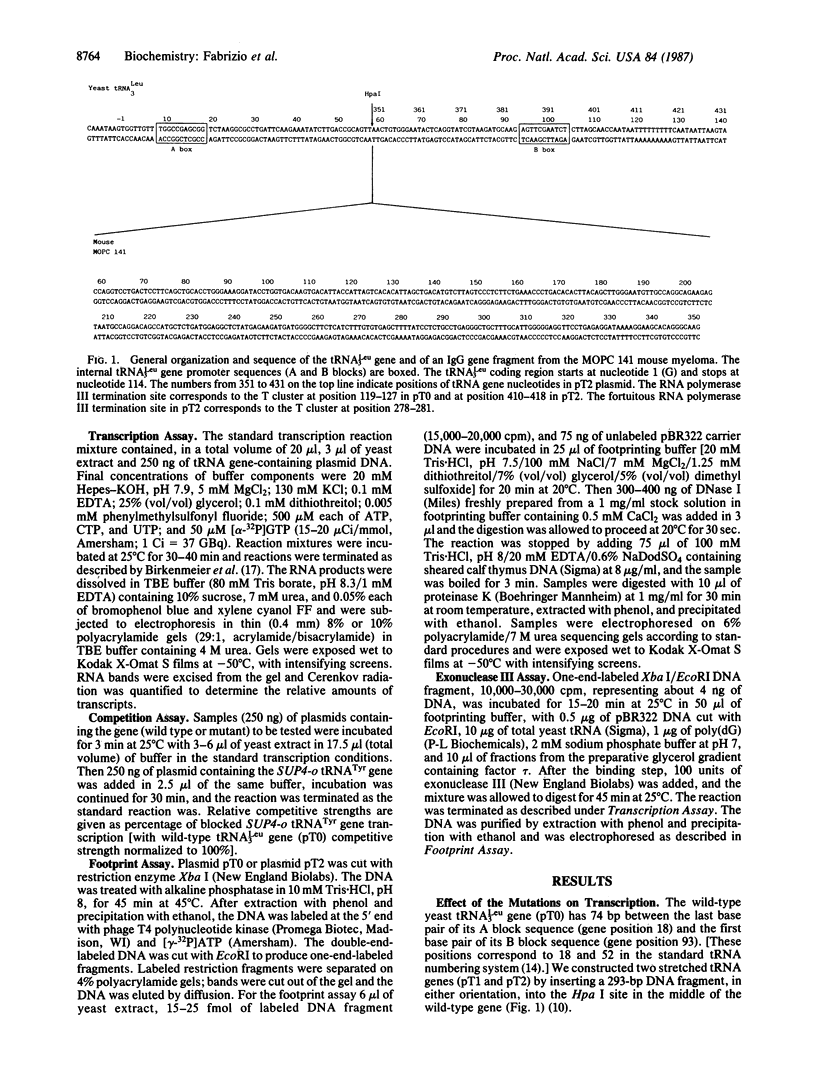
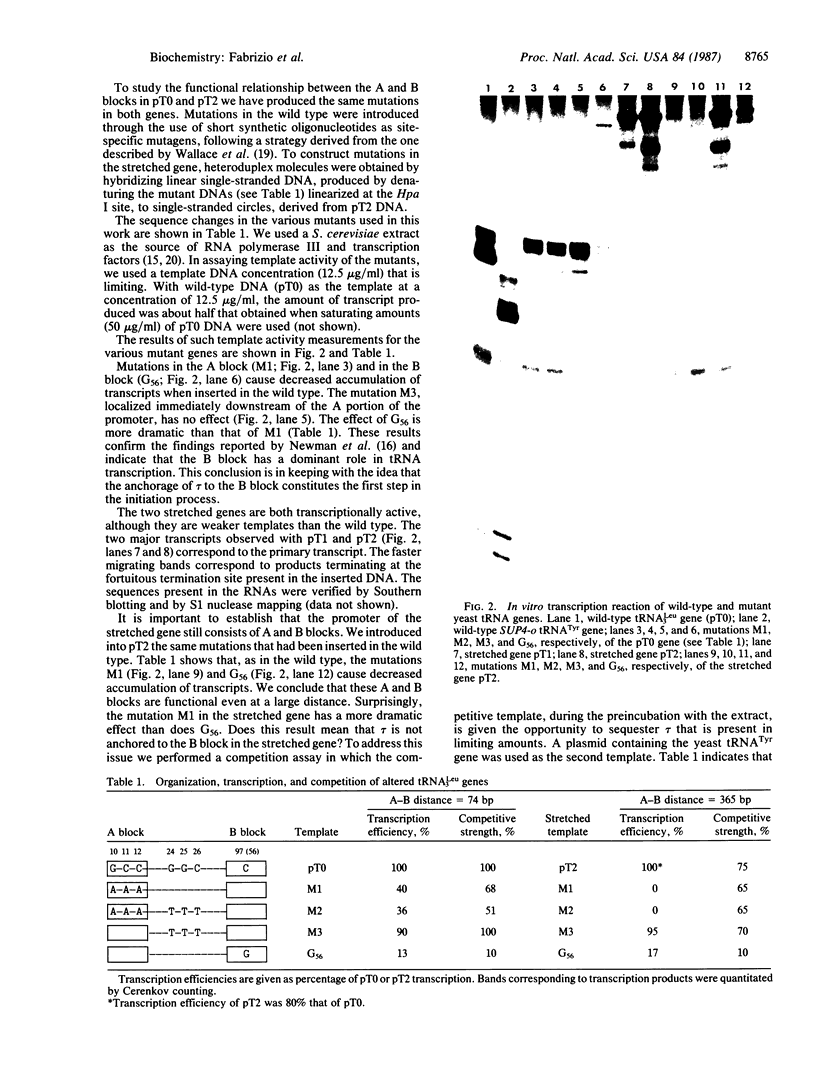
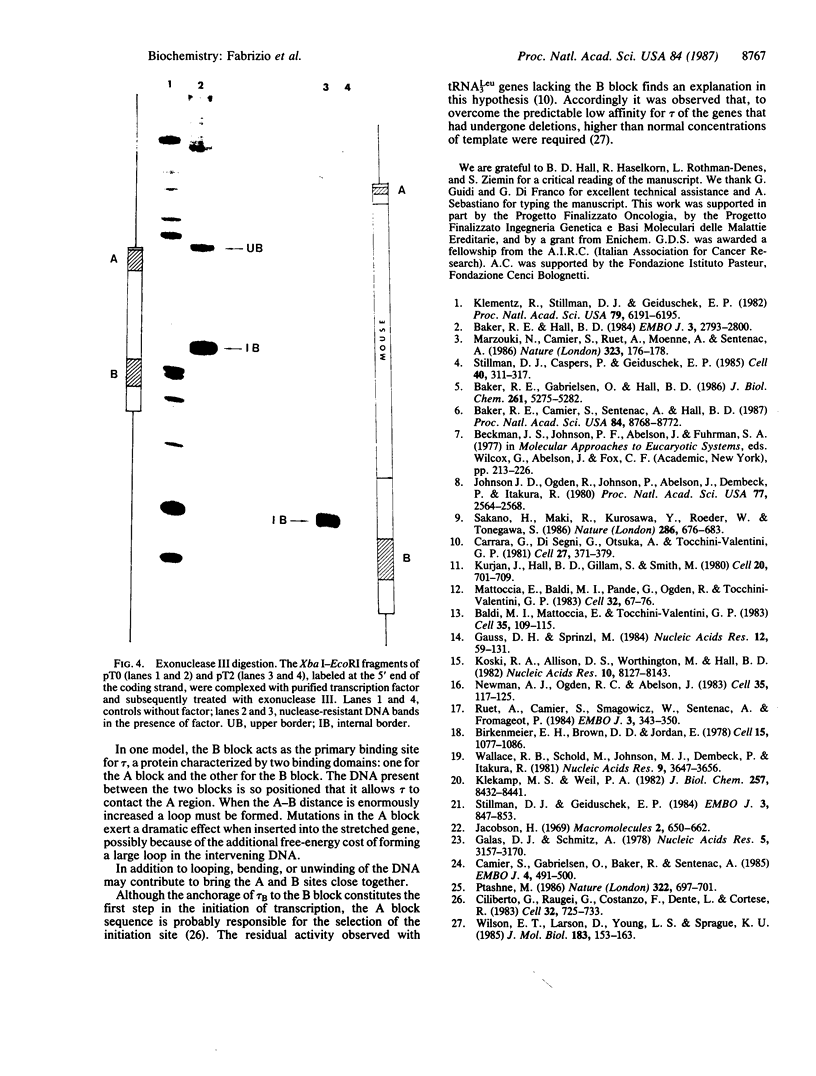
We demonstrate that, when the yeast tRNA(3Leu) gene is stretched so that the distance between the two portions of the intragenic promoter is increased to 365 base pairs, the A and B blocks remain functional. Mutations in the A block, which show a weak phenotype when inserted in the wild type, exert a dramatic effect when inserted into the stretched gene. Experiments with extensively purified transcription factor tau indicate that the tau B-B block interaction is not influenced by A-B distance; only the ability of tau A to interact with A block sequences is affected, possibly because of the additional free-energy cost of forming a large loop of the intervening DNA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker R. E., Camier S., Sentenac A., Hall B. D. Gene size differentially affects the binding of yeast transcription factor tau to two intragenic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8768–8772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. E., Gabrielsen O., Hall B. D. Effects of tRNATyr point mutations on the binding of yeast RNA polymerase III transcription factor C. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5275–5282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. E., Hall B. D. Structural features of yeast tRNA genes which affect transcription factor binding. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2793–2800. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldi M. I., Mattoccia E., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Role of RNA structure in splicing: excision of the intervening sequence in yeast tRNA3leu is dependent on the formation of a D stem. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):109–115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90213-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Brown D. D., Jordan E. A nuclear extract of Xenopus laevis oocytes that accurately transcribes 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1077–1086. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camier S., Gabrielsen O., Baker R., Sentenac A. A split binding site for transcription factor tau on the tRNA3Glu gene. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):491–500. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrara G., Di Segni G., Otsuka A., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Deletion of the 3' half of the yeast tRNA-Leu3 gene does not abolish promotor function in vitro. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90420-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Raugei G., Costanzo F., Dente L., Cortese R. Common and interchangeable elements in the promoters of genes transcribed by RNA polymerase iii. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):725–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Ogden R., Johnson P., Abelson J., Dembeck P., Itakura K. Transcription and processing of a yeast tRNA gene containing a modified intervening sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2564–2568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klekamp M. S., Weil P. A. Specific transcription of homologous class III genes in yeast-soluble cell-free extracts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8432–8441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Stillman D. J., Geiduschek E. P. Specific interactions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins with a promoter region of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6191–6195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski R. A., Allison D. S., Worthington M., Hall B. D. An in vitro RNA polymerase III system from S. cerevisiae: effects of deletions and point mutations upon SUP4 gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8127–8143. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Hall B. D., Gillam S., Smith M. Mutations at the yeast SUP4 tRNATyr locus: DNA sequence changes in mutants lacking suppressor activity. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzouki N., Camier S., Ruet A., Moenne A., Sentenac A. Selective proteolysis defines two DNA binding domains in yeast transcription factor tau. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):176–178. doi: 10.1038/323176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoccia E., Baldi M. I., Pande G., Ogden R., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Mutation in the a block of the yeast tRNAleu3 gene that allows transcription but abolishes splicing and 5'-end maturation. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):67–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90497-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Ogden R. C., Abelson J. tRNA gene transcription in yeast: effects of specified base substitutions in the intragenic promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruet A., Camier S., Smagowicz W., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Isolation of a class C transcription factor which forms a stable complex with tRNA genes. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):343–350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Maki R., Kurosawa Y., Roeder W., Tonegawa S. Two types of somatic recombination are necessary for the generation of complete immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):676–683. doi: 10.1038/286676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Gauss D. H. Compilation of sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984;12 (Suppl):r59–131. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.suppl.r59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman D. J., Caspers P., Geiduschek E. P. Effects of temperature and single-stranded DNA on the interaction of an RNA polymerase III transcription factor with a tRNA gene. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman D. J., Geiduschek E. P. Differential binding of a S. cerevisiae RNA polymerase III transcription factor to two promoter segments of a tRNA gene. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):847–853. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Schold M., Johnson M. J., Dembek P., Itakura K. Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis of the human beta-globin gene: a general method for producing specific point mutations in cloned DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3647–3656. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. T., Larson D., Young L. S., Sprague K. U. A large region controls tRNA gene transcription. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]