Abstract
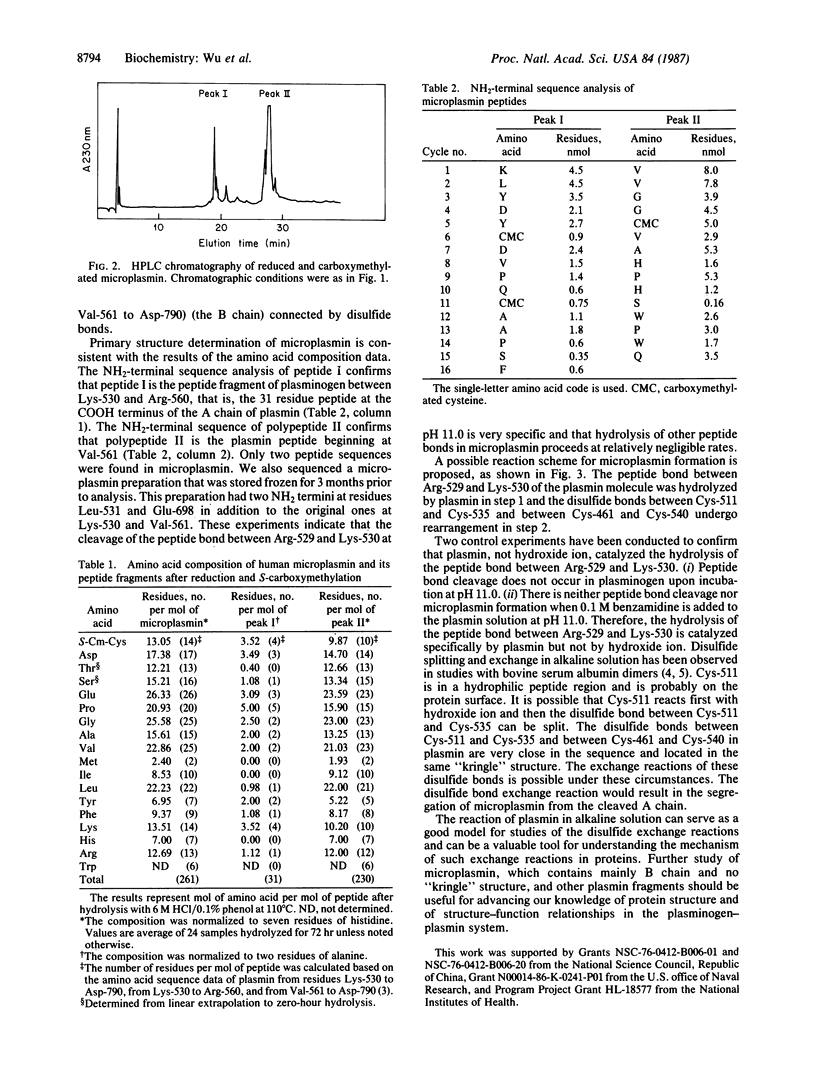
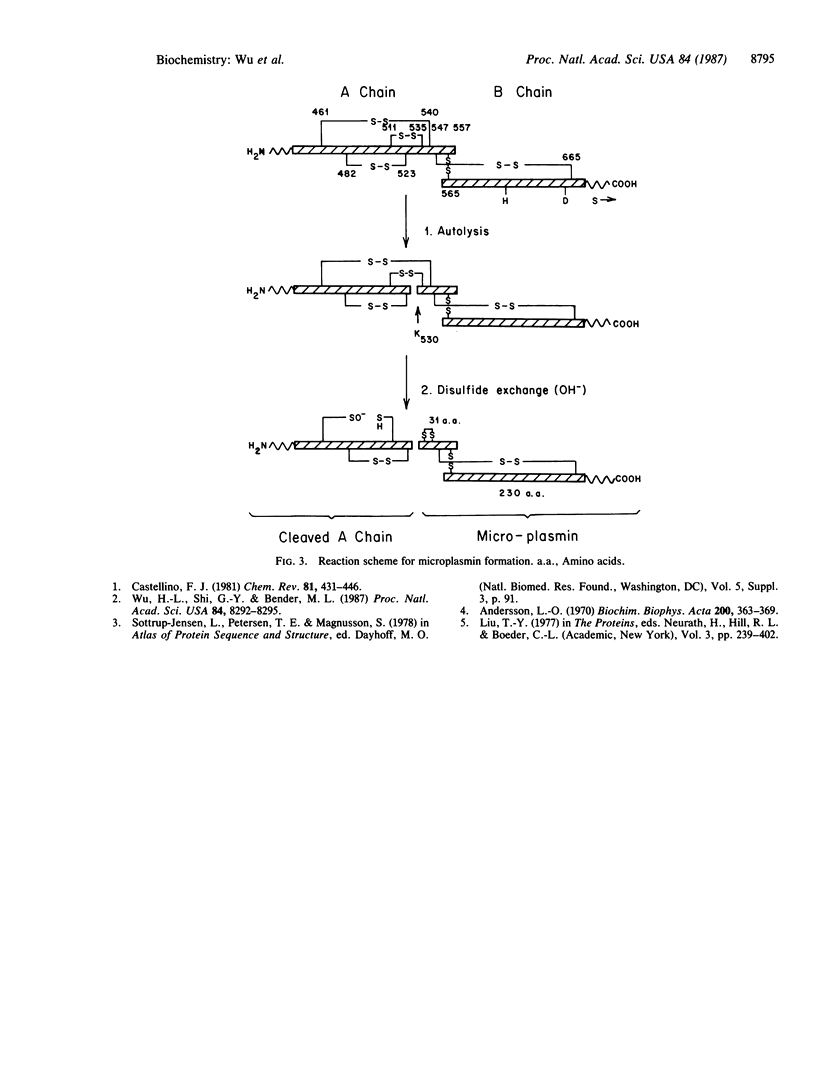
The structure of human microplasmin, prepared from plasmin in alkaline solution, has been studied. Microplasmin consists of two polypeptide chains connected by disulfide bonds. One polypeptide is the B chain of plasmin consisting of 230 amino acids, and the other peptide is the COOH-terminal portion of the A chain of plasmin consisting of 31 amino acid residues. Microplasmin has a molecular weight of 28,635, calculated from its primary sequence. It is slightly more positively charged than plasminogen and is a more hydrophobic molecule. The proposed scheme for the formation of microplasmin involves autolysis at specific peptide bonds and scrambling of especially sensitive disulfide bonds in alkaline solution.
Full text
PDF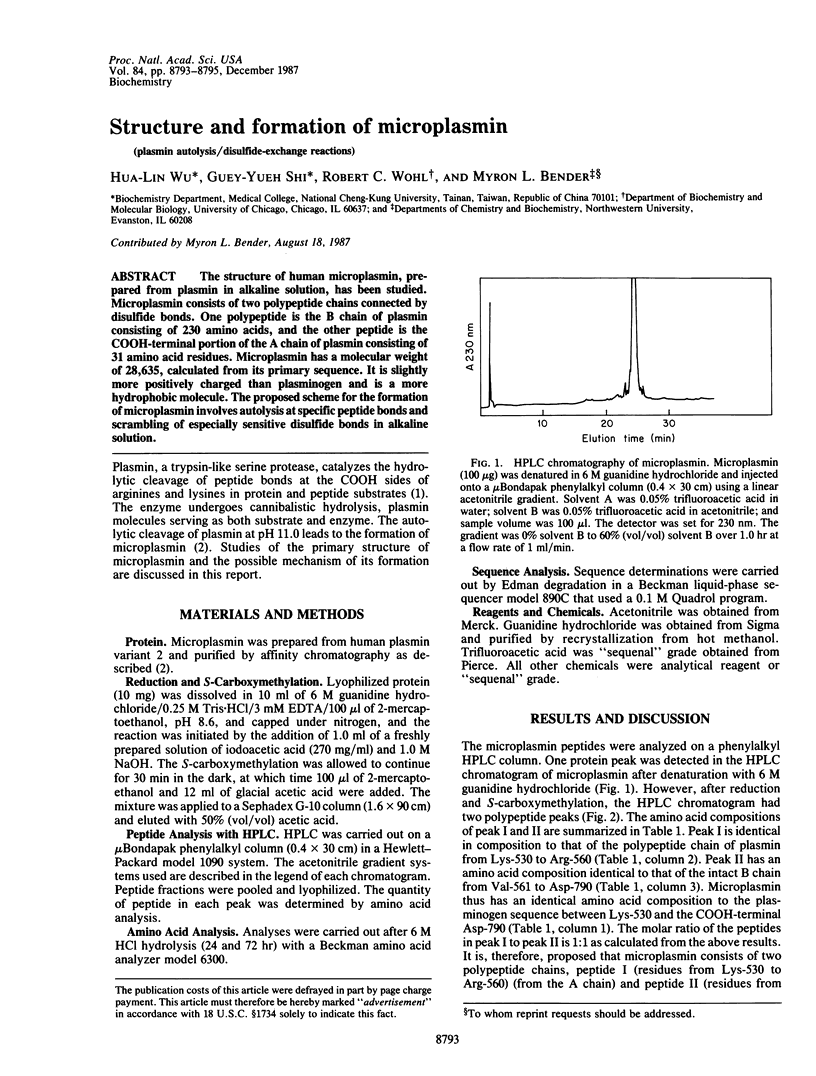
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. O. Hydrolysis of disulfide bonds in weakly alkaline media. II. Bovine serum albumin dimer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. L., Shi G. Y., Bender M. L. Preparation and purification of microplasmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8292–8295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


