Abstract
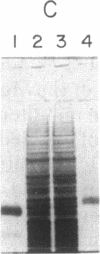
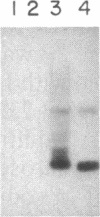
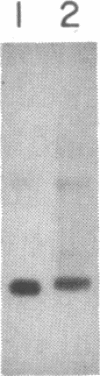
We report here the high-level expression of a synthetic gene for bovine rhodopsin in transfected monkey kidney COS-1 cells. Rhodopsin is produced in these cells to a level of 0.3% of the cell protein, and it binds exogenously added 11-cis-retinal to generate the characteristic rhodopsin absorption spectrum. We describe a one-step immunoaffinity procedure for purification of the rhodopsin essentially to homogeneity. The COS-1 cell rhodopsin activates the GTPase activity of bovine transducin in a light-dependent manner with the same specific activity as that of purified bovine rhodopsin. Electron microscopy of immunogold-stained cells indicates that rhodopsin is located in the plasma membrane of the transfected cells and is oriented with the amino terminus on the extracellular side of the membrane. This orientation is analogous to that of rhodopsin in the disk membranes of photoreceptor cells in the bovine retina.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges C. D. A method for preparing stable digitonin solutions for visual pigment extraction. Vision Res. 1977 Feb;17(2):301–302. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(77)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Protein purification by affinity chromatography. Derivatizations of agarose and polyacrylamide beads. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3059–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti L., Karnik S. S., Khorana H. G., Nassal M., Oprian D. D. Total synthesis of a gene for bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):599–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Flow of information in the light-triggered cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godchaux W., 3rd, Zimmerman W. F. Membrane-dependent guanine nucleotide binding and GTPase activities of soluble protein from bovine rod cell outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7874–7884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks D., Molday R. S. Differential immunogold-dextran labeling of bovine and frog rod and cone cells using monoclonal antibodies against bovine rhodopsin. Exp Eye Res. 1986 Jan;42(1):55–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(86)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Hubbell W. L. Lipid requirements for Rhodopsin regenerability. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4517–4523. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Knudsen P. J., Hubbell W. L. Purification of rhodopsin on hydroxyapatite columns, detergent exchange, and recombination with phospholipids. Methods Enzymol. 1982;81:144–150. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)81024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A. Expression of chimeric genes in the early region of SV40. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(2):147–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J. Identification of the components necessary for adenovirus translational control and their utilization in cDNA expression vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):689–693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Murtha P. Translational control mediated by eucaryotic initiation factor-2 is restricted to specific mRNAs in transfected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1568–1571. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman B. J. Purification of rhodopsin by concanavalin A affinity chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1982;81:150–153. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)81025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie D., Arendt A., Hargrave P., McDowell J. H., Molday R. S. Localization of binding sites for carboxyl terminal specific anti-rhodopsin monoclonal antibodies using synthetic peptides. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6544–6549. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molday R. S., Hicks D., Molday L. Peripherin. A rim-specific membrane protein of rod outer segment discs. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Jan;28(1):50–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molday R. S., MacKenzie D. Monoclonal antibodies to rhodopsin: characterization, cross-reactivity, and application as structural probes. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):653–660. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. Isolation, sequence analysis, and intron-exon arrangement of the gene encoding bovine rhodopsin. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld A. H., Levy H. M. A second ouabain-sensitive sodium-dependent adenosine triphosphate in brain microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6493–6497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]