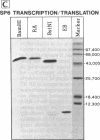
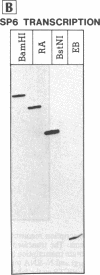
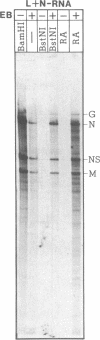
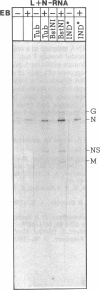
Abstract
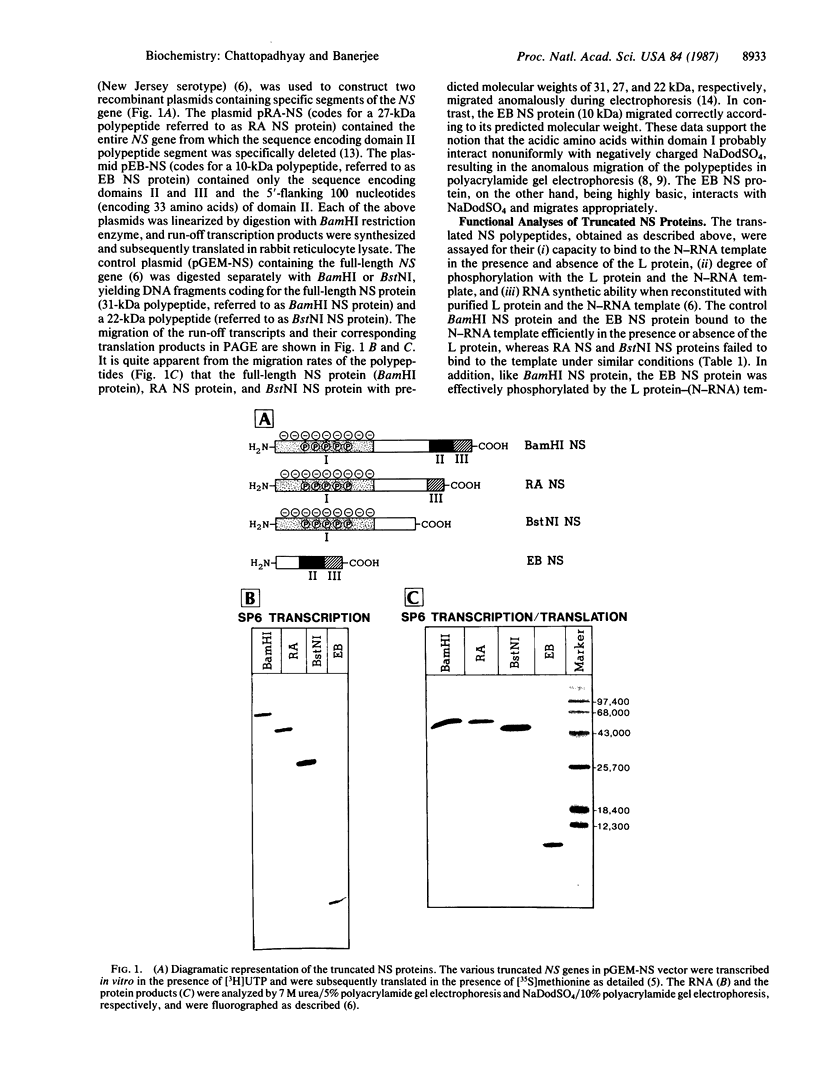
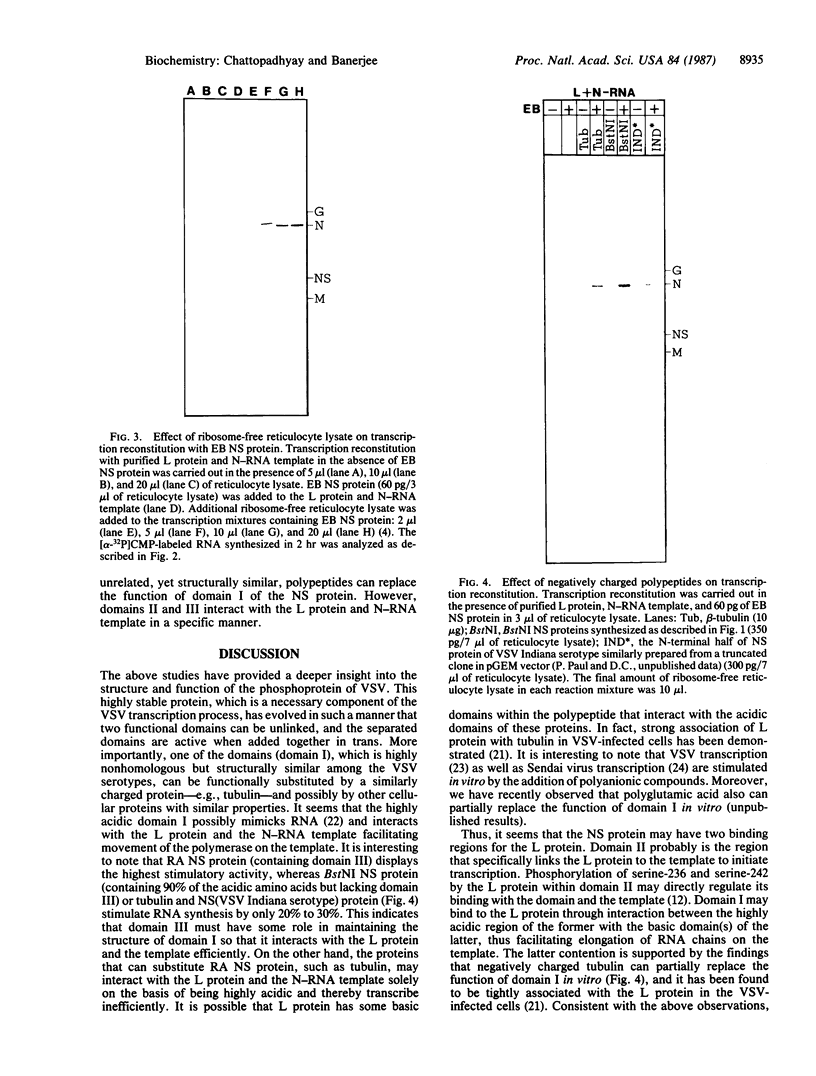
The structural phosphoprotein NS of vesicular stomatitis virus, in association with the virion-associated RNA polymerase L protein, transcribes the genome ribonucleoprotein template in vitro. It contains an acidic N-terminal domain and two distinct domains at the C-terminal end that are involved in binding to the polymerase protein and the template RNA enwrapped with the nucleocapsid protein. In the present study, the portions of the NS gene that encode the N- and C-terminal domains of the protein were cloned in pGEM vectors and expressed by in vitro transcription and translation. It was shown that two polypeptides obtained by translation of the encoded mRNAs support RNA synthesis in vitro in a reconstitution reaction when they are added together in trans. Moreover, the N-terminal domain can be functionally substituted by structurally similar polypeptides.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball L. A., White C. N. Coupled transcription and translation in mammalian and avian cell-free systems. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):479–495. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K. The transcription complex of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):363–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K. Transcription and replication of rhabdoviruses. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):66–87. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.66-87.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. C., Prevec L. Phosphorylation sites on phosphoprotein NS of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):697–702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.697-702.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Rozenblatt S., Arnheiter H., Richardson C. D. Measles virus P gene codes for two proteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):908–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.908-919.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll A. R., Wagner R. R. Reversal by certain polyanions of an endogenous inhibitor of the vesicular stomatitis virus-associated transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3361–3363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay D., Banerjee A. K. Phosphorylation within a specific domain of the phosphoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus regulates transcription in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90293-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. P., Banerjee A. K. Requirements and functions of vesicular stomatitis virus L and NS proteins in the transcription process in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):40–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90568-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. S., Banerjee A. K. Vesicular stomatitis virus NS proteins: structural similarity without extensive sequence homology. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):60–66. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.60-66.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. S., Chattopadhyay D., Banerjee A. K. Identification of a domain within the phosphoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus that is essential for transcription in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8873–8877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi C., Blumberg B. M., Kolakofsky D. Sendai virus contains overlapping genes expressed from a single mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill V. M., Harmon S. A., Summers D. F. Stimulation of vesicular stomatitis virus in vitro RNA synthesis by microtubule-associated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5410–5413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. H., Kingsbury D. W. Constitutively phosphorylated residues in the NS protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8990–8995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L. D., Condra C., Lazzarini R. A. Cloning and expression of a viral phosphoprotein: structure suggests vesicular stomatitis virus NS may function by mimicking an RNA template. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1571–1579. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luduena R. F., Woodward D. O. Isolation and partial characterization of alpha and beta-tubulin from outer doublets of sea-urchin sperm and microtubules of chick-embryo brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luk D., Sánchez A., Banerjee A. K. Messenger RNA encoding the phosphoprotein (P) gene of human parainfluenza virus 3 is bicistronic. Virology. 1986 Sep;153(2):318–325. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marnell L. L., Summers D. F. Characterization of the phosphorylated small enzyme subunit, NS, of the vesicular stomatitis virus RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13518–13524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters P. S., Banerjee A. K. Phosphoprotein NS of vesicular stomatitis virus: phosphorylated states and transcriptional activities of intracellular and virion forms. Virology. 1986 Oct 30;154(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90452-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters P. S., Banerjee A. K. Sequences of Chandipura virus N and NS genes: evidence for high mutability of the NS gene within vesiculoviruses. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):298–306. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer S. A., Baker S. C., Lessard J. L. Tubulin: a factor necessary for the synthesis of both Sendai virus and vesicular stomatitis virus RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5405–5409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae B. P., Elliott R. M. Conservation of potential phosphorylation sites in the NS proteins of the New Jersey and Indiana serotypes of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1351–1360. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Lodish H. F., Brock M. L. Giant heterogeneous polyadenylic acid on vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA synthesized in vitro in the presence of S-adenosylhomocysteine. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):683–693. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.683-693.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol F., Clark H. F., Wiktor T. J., McFalls M. L., Bishop D. H., Obijeski J. F. Structural phosphoproteins associated with ten rhabdoviruses. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):433–445. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. O., Kingsbury D. W. Stimulation of Sendai virion transcriptase by polyanions. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):243–249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.243-249.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez A., De B. P., Banerjee A. K. In vitro phosphorylation of NS protein by the L protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 May;66(Pt 5):1025–1036. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-5-1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Villasante A., Lewis S. A., Cowan N. J. The mammalian beta-tubulin repertoire: hematopoietic expression of a novel, heterologous beta-tubulin isotype. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1903–1910. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]