Abstract
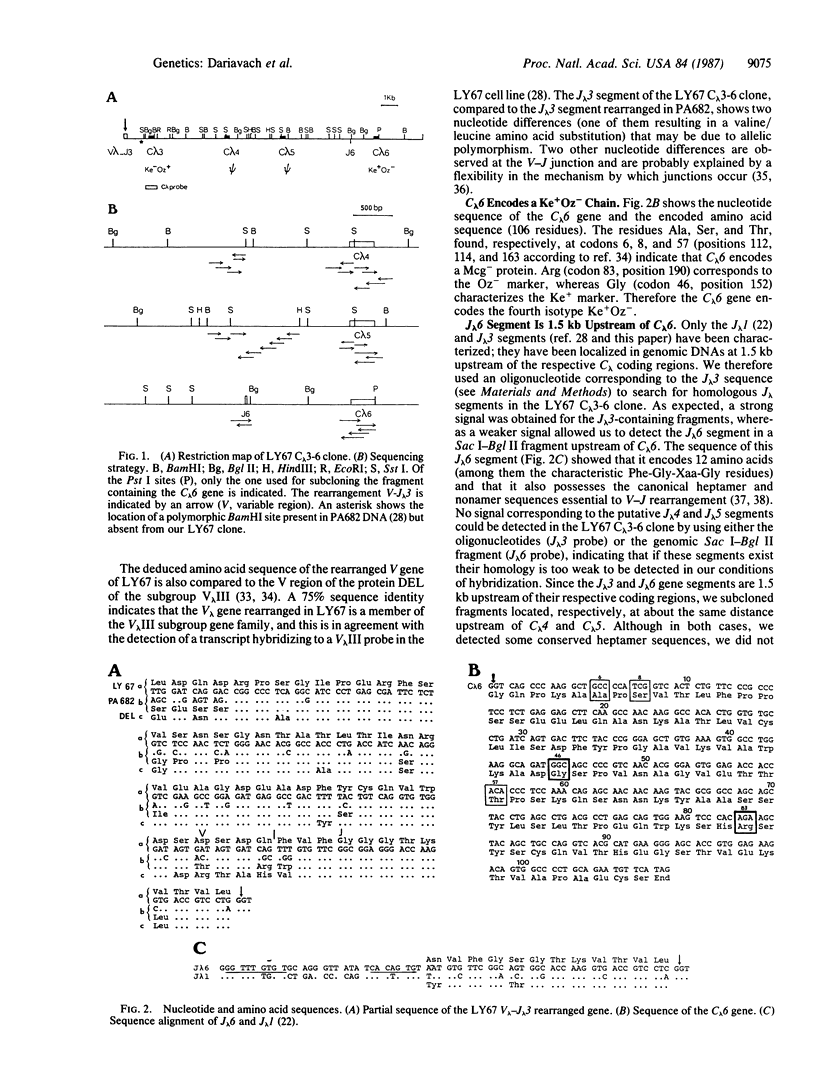
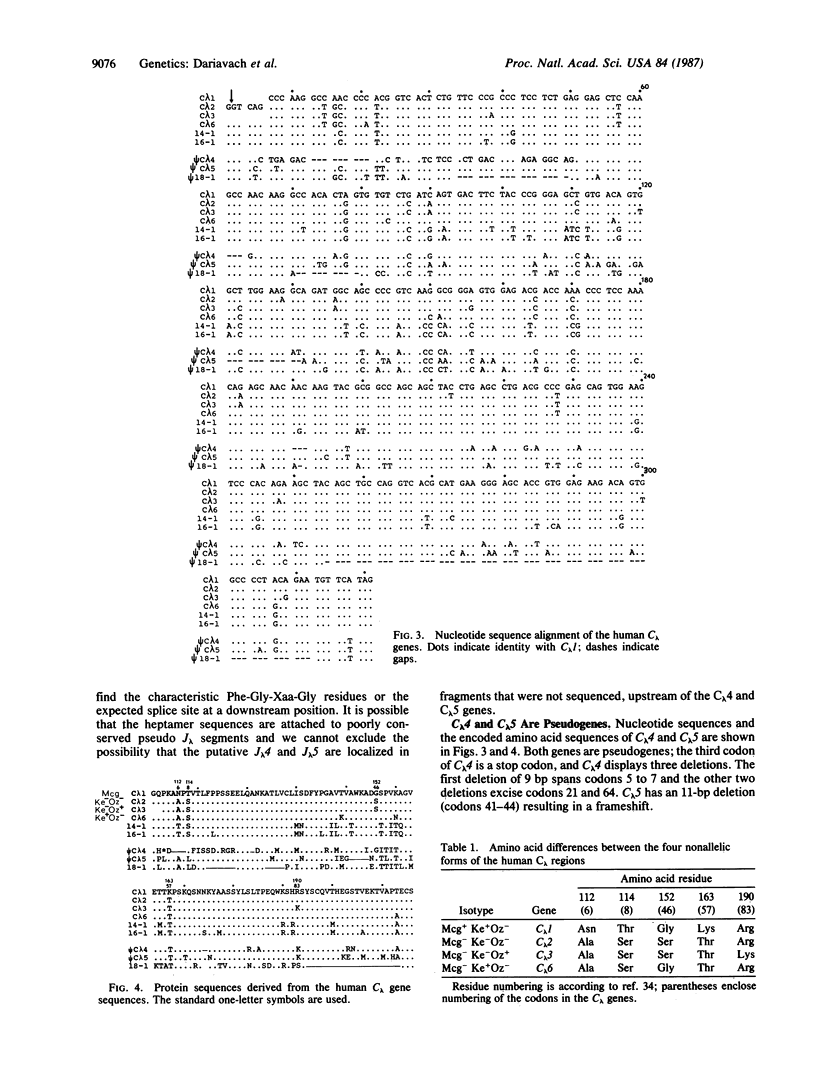
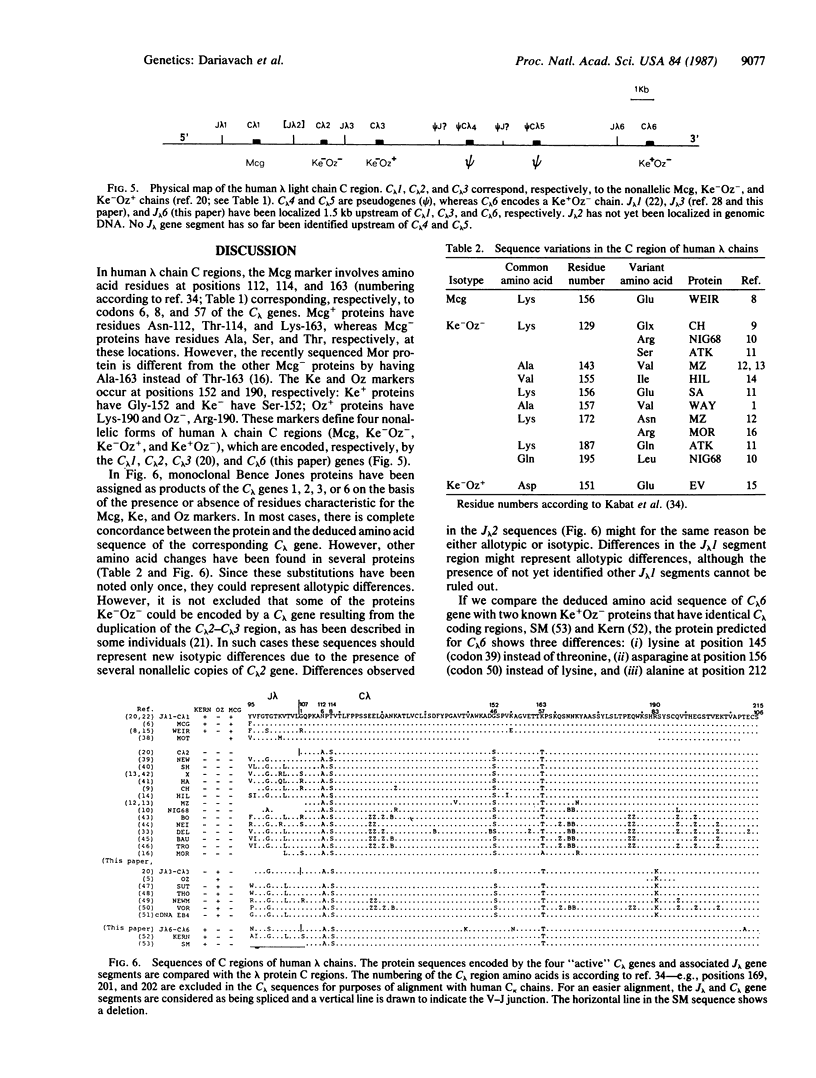
Six nonallelic immunoglobulin lambda constant region genes have been previously characterized on a 40-kilobase stretch of DNA. The nucleotide sequences of the three upstream genes of this cluster (C lambda 1, C lambda 2, C lambda 3) have been determined by other workers and shown to encode, respectively, the isotypic Mcg, Kern-Oz-, and Kern-Oz+ constant region of the lambda chains. In this paper, we report the sequence of the three downstream genes of this cluster and show that two of them (C lambda 4 and C lambda 5) are pseudogenes. However, C lambda 6 encodes a Kern+Oz- chain and corresponds to the fourth isotype described among the lambda proteins sequenced so far. A potentially active J lambda (joining) segment, with the canonical heptamer and nonamer sequences for rearrangement, is located 1.5 kilobases upstream of C lambda 6. The amino acid sequence encoded by the C lambda 6 gene is compared with the constant region sequences of various monoclonal Bence Jones lambda proteins. Allotypic and isotypic differences confirm the polymorphism and complexity of the human C lambda locus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. L., Brown L., McKenzie E., Kellow J. E., Young B. D. Cloning and sequence analysis of an Ig lambda light chain mRNA expressed in the Burkitt's lymphoma cell line EB4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2931–2941. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appella E., Ein D. Two types of lambda polypeptide chains in human immunoglobulins based on an amino acid substitution at position 190. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1449–1454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baczko K., Braun D. G., Hess M., Hilschmann N. Die Primärstruktur einer monoklonalen Immunglobulin L-Kette der Subgruppe IV vom lambda-Typ (Bence-Jones-Protein Bau): Untergruppen innerhalb der Subgruppen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Jun;351(6):763–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H., Dmitrovsky E., Hieter P. A., Mitchell K., Leder P., Turoczi L., Kirsch I. R., Hollis G. F. Identification of three new Ig lambda-like genes in man. J Exp Med. 1986 Feb 1;163(2):425–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B. L., Poljak R. J. Amino acid sequence of the (lambda) light chain of a human myeloma immunoglobulin (IgG New). Biochemistry. 1974 Mar 12;13(6):1295–1302. doi: 10.1021/bi00703a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Huang H., Davis M., Calame K., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene is generated from three segments of DNA: VH, D and JH. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):981–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ein D., Fahey J. L. 2 types of lambda polypeptide chains in human immunoglobulins. Science. 1967 May 19;156(3777):947–948. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3777.947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ein D. Nonallelic behavior of the Oz groups in human lambda immunoglobulin chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):982–985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard M., Hess M., Hilschmann N. Die Primärstruktur einer monoklonalen Immunglobulin-L-Kette der Subgruppe I vom lambda-Typ (Bence-Jones-Protein Vor.) Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Jan;355(1):85–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Martinis J., Croce C. M. Assignment of the genes for human lambda immunoglobulin chains to chromosome 22. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):173–175. doi: 10.1038/294173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eulitz M. A new subgroup of human L-chains of the lambda-type. Primary structure of Bence-Jones protein DEL. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 16;50(1):49–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett F. W., Deutsch H. F. A new lambda-chain gene. Immunochemistry. 1975 Aug;12(8):643–652. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett J. W., Deutsch H. F. Primary structure of the Mcg lambda chain. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 24;13(20):4102–4114. doi: 10.1021/bi00717a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett J. W., Deutsch H. F. The variability of human lambda-chain constant regions and some relationships to V-regions sequences. Immunochemistry. 1976 Feb;13(2):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90283-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Moloshok T., Prelli F., Solomon A. Human lambda light-chain constant region gene CMor lambda: the primary structure of lambda VI Bence Jones protein Mor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3415–3419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Moloshok T., Solomon A. Primary structure of the variable region of a human lambda VI light chain: Bence Jones protein SUT. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2490–2493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garver F. A., Chang L., Mendicino J., Isobe T., Osserman E. F. Primary structure of a deleted human lambda type immunoglobulin light chain containing carbohydrate: protein Sm lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4559–4563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garver F. A., Hilschmann N. The primary structure of a monoclonal human lambda-type immunoglobulin L-chain of subgroup II (Bence-Jones protein NEI). Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 15;26(1):10–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiso J., Solomon A., Frangione B. Association of human lambda light chain V/J/C segments: serologic analysis and primary structure of the lambda VI Bence Jones protein THO. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):716–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. H., Yang R. C., Wu R. An improved strategy for rapid direct sequencing of both strands of long DNA molecules cloned in a plasmid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5521–5540. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess M., Hilschmann N., Rivat L., Rivat C., Ropartz C. Isotypes in human immunoglobulin lambda-chains. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 10;234(45):58–61. doi: 10.1038/newbio234058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Hollis G. F., Korsmeyer S. J., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Clustered arrangement of immunoglobulin lambda constant region genes in man. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):536–540. doi: 10.1038/294536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabusch J. R., Deutsch H. F. Primary structure of a human lambda-chain (Weir) of the Mcg type. Mol Immunol. 1982 Jul;19(7):901–906. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90356-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Matthes H. W., Gait M. J., Brenner S. A new selective phage cloning vector, lambda 2001, with sites for XbaI, BamHI, HindIII, EcoRI, SstI and XhoI. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima M., Odani S., Ikenaka T. Amino acid sequence of the lambda type light chain of a human IgGl myeloma protein (MOT) with unusual antigenicity: a possible new subgroup of lambda chain having a unique N-terminal sequence. Mol Immunol. 1980 Nov;17(11):1407–1414. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer B., Steinmetz-Kayne M., Hilschmann N. Die vollständige Aminosäuresequenz des Bence-Jones-proteins new (lambda-Typ) Subgruppen im variablen Teil bei Immunglobulin-L-Ketten vom lambda-Typ. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 Jul;349(7):945–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir G. M., Preud'homme J. L., Bernheim A., Berger R. Correlation between immunoglobulin light chain expression and variant translocation in Burkitt's lymphoma. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):474–476. doi: 10.1038/298474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieu T. S., Deutsch H. F., Tischendorf F. W. Human lambda-chain sequence variations and serologic associations. Immunochemistry. 1977 Jun;14(6):429–433. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(77)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez de Castro J. A., Chiu Y. Y., Poljak R. J. Amino acid sequence of the variable region of the light (lambda) chain from human myeloma cryoimmunoglobulin IgG Hil. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1718–1723. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P. Sequences of five potential recombination sites encoded close to an immunoglobulin kappa constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Hieter P. A., Hollis G. F., Swan D., Otey M. C., Leder P. Chromosomal location of human kappa and lambda immunoglobulin light chain constant region genes. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1480–1490. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merryman C., Frangione B., Franklin E. C., Benacerraf B. Peptide differences in purified mouse antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1967 Jan;4(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(67)90194-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Clegg J. B., Jarvis J. M. Immunoglobulin lambda-chains. The complete amino acid sequence of a Bence-Jones protein. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):631–652. doi: 10.1042/bj1100631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C. Linked groups of residues in immunoglobulin k chains. Nature. 1967 Oct 28;216(5113):330–332. doi: 10.1038/216330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Nozu Y., Titani K., Watanabe S., Hara H., Kitagawa M. Amino acid sequence of lambda chain of human immunoglobulin A. Immunochemistry. 1972 Feb;9(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponstingl H., Hess M., Hilschmann N. Die vollständige Aminosäure-Sequenz des Bence-Jones-Proteins Kern Eine neue Untergruppe der Immunglobulin-L-Ketten vom lambda-typ. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 Jun;349(6):867–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponstingl H., Hess M., Hilschmann N. Zur Strukturregel der Antikörper. Die Primärstruktur einer monoklonalen Immunglobulin-L-Kette von lambda-Typ, Subgruppe IV (Bence-Jones-Protein Kern). V. Die vollständige Aminosäuresequenz und ihre genetische Interpretation. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Feb;352(2):247–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Forster A., Matthews J. G. The breakpoint of the Philadelphia chromosome 22 in chronic myeloid leukaemia is distal to the immunoglobulin lambda light chain constant region genes. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Jul;1(1):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Hüppi K., Heinrich G., Tonegawa S. Sequences at the somatic recombination sites of immunoglobulin light-chain genes. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):288–294. doi: 10.1038/280288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz R., Hilschmann N. Die Primärstrukur eines monoklonalen IgA-Immunoglobulins (IgA Tro.), I. Die Aminosäuresequenz der L-Kette, lambda-Typ, Subgruppe II. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Aug;356(8):1333–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda T., Titani K., Putnam F. W. Amino acid sequence of human lambda chains. II. Chymotryptic peptides and sequence of protein Ha. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4475–4487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda T., Yoshimura K., Kametani F., Isobe T. A new immunoglobulin marker. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 16;117(2):587–592. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L. H., Croce C. M., Showe L. C. Cloning and sequencing of a rearranged V lambda gene from a Burkitt's lymphoma cell line expressing kappa light chains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4921–4934. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R. A., Hollis G. F., Hieter P. A., Korsmeyer S., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Variable amplification of immunoglobulin lambda light-chain genes in human populations. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):172–174. doi: 10.1038/304172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Wikler M., Shinoda T., Putnam F. W. The amino acid sequence of a lambda type Bence-Jones protein. 3. The complete amino acid sequence and the location of the disulfide bridges. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 25;245(8):2171–2176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udey J. A., Blomberg B. Human lambda light chain locus: organization and DNA sequences of three genomic J regions. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(1):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00768834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikler M., Putnam F. W. Amino acid sequence of human lambda chains. 3. Tryptic peptides, chymotryptic peptides, and sequence of protein Bo. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4488–4507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A., Lenoir G., Boué J., Boué A., Gallano P., Huerre C., Szajnert M. F., Jeanpierre M., Lalouel J. M., Kaplan J. C. Lambda Ig constant region genes are translocated to chromosome 8 in Burkitt's lymphoma with t(8;22). Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):1133–1142. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



