Abstract
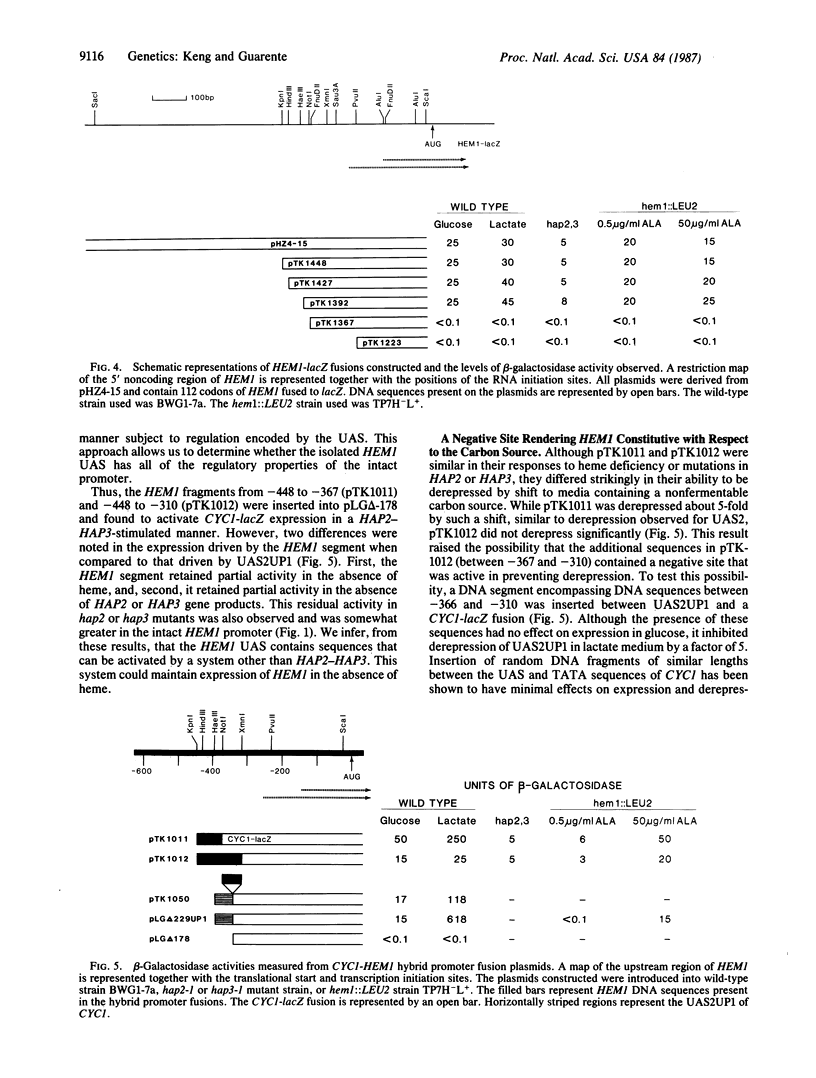
We show that HEM1 (encoding 5-aminolevulinate synthase) expression, while constitutive under all steady-state growth conditions tested, is activated by the HAP2-HAP3 global activation system that controls expression of apocytochromes. This finding creates a paradox because apocytochrome activation by HAP2-HAP3 is highly regulated, subject to induction by heme, and subject to further derepression by a shift from glucose medium to one containing a nonfermentable carbon source. We clarify this issue by showing that HEM1 is subject to two additional layers of control that mask regulatory changes. First is a second activation system acting at a site close to the HAP2-HAP3 target sequence that keeps HEM1 turned on under conditions of heme deficiency. Second is a regulated negative control site downstream of the upstream activation site that counteracts derepression in medium containing a nonfermentable carbon source. Thus, transcription of the constitutive gene is actually a composite of opposing regulatory sites. This complex regulatory arrangement may exist to allow HEM1 to be coordinated transiently with apocytochromes for transition to respiratory growth. Conversely, it may reflect the alteration of HEM1 from a regulated to a constitutive gene over evolution.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bard M., Ingolia T. D. Plasmid-mediated complementation of a delta-aminolevulinic-acid-requiring Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant. Gene. 1984 May;28(2):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90256-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Hoar E. Upstream activation sites of the CYC1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are active when inverted but not when placed downstream of the "TATA box". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7860–7864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lalonde B., Gifford P., Alani E. Distinctly regulated tandem upstream activation sites mediate catabolite repression of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Mason T. Heme regulates transcription of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae via an upstream activation site. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters and lacZ fusions designed to study expression of cloned genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:181–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keng T., Alani E., Guarente L. The nine amino-terminal residues of delta-aminolevulinate synthase direct beta-galactosidase into the mitochondrial matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):355–364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler H. R., Lin C. C. The derepression of delta-aminolevulinate synthetase in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 11;61(3):963–970. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamud D. R., Padrão G. R., Borralho L. M., Arrese M., Panek A. D., Mattoon J. R. Regulation of porphyrin biosynthesis in yeast. Level of delta-aminolevulinic acid in porphyrin mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1983 Oct;16(3):203–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Expression of a beta-galactosidase gene containing the ribosomal protein 51 intron is sensitive to the rna2 mutation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4403–4407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. F., Zitomer R. S. A positive regulatory site and a negative regulatory site control the expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CYC7 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2023–2030. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]