Abstract
Host cell invasion by Toxoplasma gondii is critically dependent upon adhesive proteins secreted from the micronemes. Proteolytic trimming of microneme contents occurs rapidly after their secretion onto the parasite surface and is proposed to regulate adhesive complex activation to enhance binding to host cell receptors. However, the proteases responsible and their exact function are still unknown. In this report, we show that T. gondii tachyzoites lacking the microneme subtilisin protease TgSUB1 have a profound defect in surface processing of secreted microneme proteins. Notably parasites lack protease activity responsible for proteolytic trimming of MIC2, MIC4 and M2AP after release onto the parasite surface. Although complementation with full-length TgSUB1 restores processing, complementation of Δsub1 parasites with TgSUB1 lacking the GPI anchor (Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1) only partially restores microneme protein processing. Loss of TgSUB1 decreases cell attachment and in vitro gliding efficiency leading to lower initial rates of invasion. Δsub1 and Δsub1:: ΔGPISUB1 parasites are also less virulent in mice. Thus TgSUB1 is involved in micronemal protein processing and regulation of adhesive properties of macromolecular adhesive complexes involved in host cell invasion.
Introduction
The apicomplexan phylum of protozoa contains numerous parasites of veterinary (Cryptosporidium, Neospora, Eimeria) and medical (Plasmodium, Cryptosporidium, Toxoplasma) importance. The parasite Toxoplasma gondii causes severe clinical diseases in immunocompromised patients and, when contracted during pregnancy, can lead to birth defects or abnormal development. Apicomplexan parasites share a common substrate dependent locomotion termed gliding motility used for active host cell penetration and tissue migration (Carruthers et al., 1997, Carruthers et al., 1999b, Dubremetz et al., 1998). Secretion of apical organelles called micronemes and rhoptries leads to the formation of an intimate binding interface junction connecting host cell receptors and parasite adhesive proteins. Host cell invasion relies on the translocation of transmembrane adhesive proteins that form a bridge between the host cell and the parasite actomyosin motor which provides motive force for active penetration (Dobrowolski et al., 1996, Meissner et al., 2002b, Keeley et al., 2004, Baum et al., 2006).
Microneme proteins (MIC) contain domains with homology to adhesive motifs from higher eukaryotes that are thought to be involved in the binding to host cell receptors. Several MICs bind carbohydrate receptors on host cells (Fourmaux et al., 1996, Garcia-Réguet et al., 2000, Cerede et al., 2002, Brecht et al., 2001, Harper et al., 2004, Barragan et al., 2005, Saouros et al., 2005, Friedrich et al., 2010). Genetic studies with MIC knock-out mutants have confirmed a significant role for MICs in attachment, invasion and virulence (Huynh et al., 2003, Cerede et al., 2005, Huynh et al., 2006). MIC proteins are assembled into macromolecular adhesive complexes during transit through the secretory pathway (Reiss et al., 2001, Jewett et al., 2004, Meissner et al., 2002a) and are extensively processed during their intracellular trafficking and after release onto the parasite surface (Dowse et al., 2004, Carruthers, 2006). Proteolytic processing of microneme proteins after release onto the parasite surface is essential for successful completion of host cell invasion (Harper et al., 2006, Brossier et al., 2003, Conseil et al., 1999, Teo et al., 2007). Three protease activities have been described on the parasite surface, termed Microneme Protein Protease 1–3 (MPP1, MPP2, MPP3) (Zhou et al., 2004). MPP1 is responsible for intramembranous cleavage of MIC proteins within their transmembrane domains, resulting in shedding of adhesive complexes from the cell surface (Brossier et al., 2005, Dowse et al., 2005). MPP2 and MPP3 are involved in the proteolytic trimming of several components of microneme adhesive complexes including MIC2, M2AP and MIC4. MPP2 and MPP3 are distinguished by their differential susceptibility to ALLN and other protease inhibitors, but their molecular nature has not been identified (Carruthers et al., 2000, Zhou et al., 2004, Brecht et al., 2001). It has been speculated that the surface proteolytic trimming activities of MPP2 and MPP3 are involved in the exposure of adhesive domains of MICs required for tight binding to host cell receptors (Carruthers et al., 2005).
Here we elucidate the role of the T. gondii subtilisin-like serine protease TgSUB1 in MIC surface proteolytic trimming and show TgSUB1 is required for MPP2 and MPP3 activity. TgSUB1 is a GPI-anchored micronemal protease that is first released onto the surface of parasites during invasion and then shed into the media with other micronemal proteins (Miller et al., 2001, Binder et al., 2008). Because of its microneme and surface localization, we hypothesized that TgSUB1 mediates MIC protein processing during host cell invasion. We show that TgSUB1 is involved in the surface processing of several MICs including the adhesive complex M2AP-MIC2 and the protein MIC4. Loss of TgSUB1-dependent MIC surface processing affects parasite cell attachment, host cell invasion, as well as in vitro gliding efficiency. Moreover, parasites lacking TgSUB1 have a defect in virulence leading to a delay in time death in the mouse model.
Results
Tachyzoites lacking TgSUB1 have altered microneme protein processing
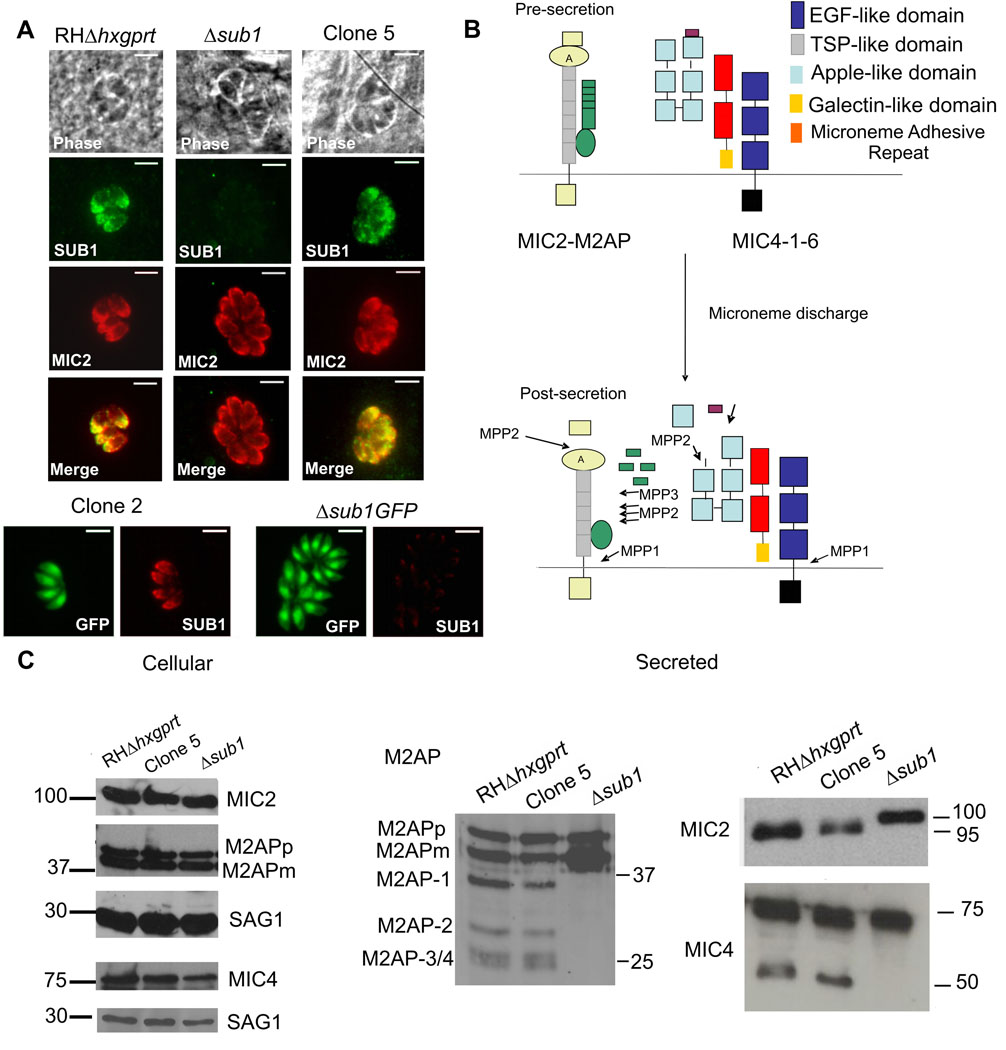
The TgSUB1 gene was disrupted by homologous recombination in two independent cell lines: RH GFP-Δhxgprt and RHΔhxgprt background as described elsewhere (Binder et al., 2008). Loss of TgSUB1 expression was confirmed by Quantitative Real-Time PCR, Western blot and Immunofluorescence analyses (Figure 1A and Supplementary Figure S1). The expression, targeting and intracellular processing of MICs AMA1, MIC2, MIC3, MIC4, MIC5, MIC6 and M2AP were not affected in the Δsub1 strain (Figure 1C, (Binder et al., 2008) and data not shown). To determine if MIC proteolytic processing on the parasite surface was impaired, secretion of microneme proteins MIC2, MIC4 and M2AP, known substrates of MPP2 and MPP3 was analyzed by Western blot. Efficiency of the secretion procedure was confirmed by Western blot analysis to show enhancement of secreted forms and absence of cytosolic proteins (data not shown). M2AP is first cleaved in its C-terminal region by MPP3 generating the fragment M2AP-1 and further cleaved by MPP2 generating 3 additional fragments (M2AP 2–4, Figure 1B) (Zhou et al., 2004). MIC4 (72 kDa) is cleaved within its N-terminus to generate a 70 kDa species and is further processed by MPP2 in its C-terminus to generate 50 and 15 kDa products (Carruthers et al., 2000, Zhou et al., 2004, Brecht et al., 2001). MIC4 50 kDa and M2AP 1–4 secreted products are no longer detected in the Δsub1 strain and this loss of processed forms is associated with accumulation of the M2AP mature form (Figure 1C). Results were similar in both Δsub1 strains (data not shown). In wild-type parasites, MIC2 is cleaved in its N-terminus by MPP2 removing a 5 kDa fragment (Figure 1B) (Carruthers et al., 2000, Zhou et al., 2004), but in the Δsub1 strain, the MIC2 secreted product was of higher molecular weight, indicating that it too was no longer processed (Figure 1C).
Figure 1. TgSUB1 disruption alters MIC proteolytic processing.
(A) Immunofluorescence of Δsub1 strains and sibling clones (Clone 2 for Δsub1 GFP; Clone 5 for Δsub1). Controls include the wild-type RH GFP-Δhxgprt and RHΔhxgprt strains. Siblings correspond to wild-type parasites stably transfected with the selectable marker but without TgSUB1 disruption. TgSUB1 is labeled with the TgSUB1 AE653 rabbit antiserum. MIC2 is labeled with the mouse mAb 6D10 and was used as a marker for microneme localization. Scale bar is 5 µm (B) Schematic representation of the cell surface proteolytic trimming of the micronemal adhesive complexes MIC2-M2AP and MIC1-4–6. “A” denotes the A-domain of MIC2 protein. Microneme Adhesive Repeat refers to the specialized MIC1 domain which discriminates between glycan residues (Blumenschein et al., 2007). Activity of the proteases MPP1-2–3 is represented. Because the first step in M2AP processing is not inhibited by protease inhibitors that inhibit MPP2 (ALLM, ALLN), a second protease activity termed MPP3 was proposed (Zhou et al., 2004). The MPP1 MIC cleavage sites are consistent with MPP1 being a rhomboid serine protease such as the parasite surface rhomboids TgROM 4 or TgROM5 (Brossier et al., 2005, Dowse et al., 2005, Buguliskis et al., 2010). (C) Western Blot analysis of the MIC2-4 and M2AP cellular and secreted products. Blots were probed with appropriate antibodies as described in experimental procedures. Molecular standards are in kDa. The rabbit anti-MIC4 antibody used was raised against the A1 and A2 apple domains, and recognizes the 72 and 70 kDa precursor forms and the 50 kDa secreted product but not the 15 kDa secreted product. M2APp: precursor form; M2APm: mature form.
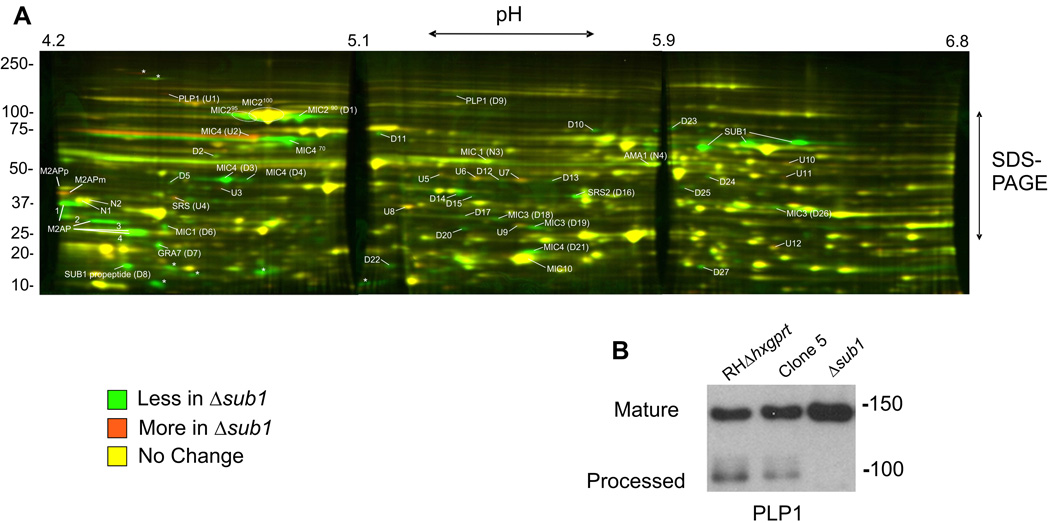
To identify other potential substrates for TgSUB1, we performed a global proteomic analysis of the ESA (excreted-secreted antigen) profile of Δsub1 (GFP background) and its sibling transfectant Clone 2 (which continues to express TgSUB1). ESA preparations were analyzed by two-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis analysis (2D-DIGE analysis; Figure 2A). Proteins that were diminished or absent in the Δsub1 strain are visible as green spots. As expected, TgSUB1 secreted products were not observed in the Δsub1 strain (80 kDa, 70 kDa, 40 kDa products and TgSUB1 prodomain spot D8) (Figure 2A, Supplementary Figure S2 and Table 1). Inhibition of MIC2, MIC4 and M2AP processing was confirmed as depicted by the diminution of the MIC2 95-90 kDa products, M2AP 1–4 products and the MIC4 50 and 15 kDa products (Spots D3-D4-D21, Figure 2A, Supplementary Figure S2 and Table 1). Moreover, 2D-DIGE analysis confirmed the accumulation of the M2AP mature form and revealed the absence of MIC4 70 kDa product and accumulation of the MIC4 72 kDa (spot U2) precursor in the Δsub1 (Figure 2A, Table 1 and Supplementary Figure S2).
Figure 2. 2D-DIGE analysis of microneme secreted products.
(A) Secreted products of the Δsub1GFP and Clone 2 strains were covalently labeled with Cy3 (green) or Cy5 (red) respectively, and separated by a two-dimension gel electrophoresis (pH 4.2–6.8 first dimension and 12.5% SDS-PAGE second dimension). Protein spots that are diminished or absent in the Δsub1 secreted sample compared to the Clone 2 (a sibling transfectant that still expresses TgSUB1), are depicted as green spots while proteins that are increased are depicted as orange spots. Yellow spots depict proteins that do not change significantly in abundance between the two strains. Marked proteins were excised and identified by mass spectrometry analysis. The asterisks indicate spots not sufficiently visible on the Coomassie gel to excise. (B) Western Blot analysis of the PLP1 secreted products. PLP1 was detected with appropriate antibody. Molecular weights are in kDa.
Table 1. Summary of proteins with a signal peptide identified by 2D-DIGE and mass spectrometry.
Spots of interest were excised and proteins were identified by mass spectrometry analysis. Proteins were identified by searching the data against the EPICDB database (http://toro.aecom.yu.edu/biodefense/) using MASCOT and are based on two or more peptide sequences with scores above the 95% confidence threshold. U denotes a protein which abundance is higher (up) in the Δsub1 strain; N a protein which abundance is unchanged (neutral) in the Δsub1 strain and D a protein less abundant (down) in the Δsub1 strain. MW: Molecular Weight; pI: isoelectric point. SRS: SAG related sequence. Ca: calcium. Proteins were identified using ToxoDB.org Release 4 gene predictions. Release 5 gene identification numbers for GT-1, a Type I strain like RH are also shown.
| Spot | Protein | Gene ID Release 4.3 http://www.toxodb.org |
Gene ID Release 5 | MW kDa |
pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | PLP1 | 20.m03849 | TGGT1_016570 | 120 | 4.5 |
| U2 | MIC4 | 25.m00006 | TGGT1_021130 | 63 | 5.1 |
| U4 | SRS | 641.m03153 | TGGT1_121850 | 37 | 4.5 |
| N1 | Ca binding | 44.m00001 | TGGT1_118190 | 35 | 4.3 |
| N2 | Ca binding | 44.m00001 | TGGT1_118190 | 35 | 4.3 |
| N3 | MIC1 | 80.m00012 | TGGT1_031650 | 60 | 5.5 |
| N4 | AMA1 | 55.m00005 | TGGT1_076680 | 60 | 5.9 |
| D1 | MIC2 | 20.m00002 | TGGT1_019450 | 90 | 4.9 |
| D3 | MIC4 | 25.m00006 | TGGT1_021130 | 63 | 5.1 |
| D4 | MIC4 | 25.m00006 | TGGT1_021130 | 63 | 5.1 |
| D6 | MIC1 | 80.m00012 | TGGT1_031650 | 28 | 4.5 |
| D7 | GRA7 | 20.m00005 | TGGT1_017550 | 22 | 4.5 |
| D8 | SUB1 propeptide |
20.m00387 | TGGT1_016650 | 16 | 4.4 |
| D9 | PLP1 | 20.m03849 | TGGT1_016570 | 115 | 5.4 |
| D10 | SUB1 | 20.m00387 | TGGT1_016650 | 82 | 5.1 |
| D16 | SRS2 | 44.m00010 | TGGT1_113990 | 39 | 7 |
| D18 | MIC3 | 641.m00002 | TGGT1_121730 | 35 | 5.5 |
| D19 | MIC3 | 641.m00002 | TGGT1_121730 | 30 | 5.6 |
| D21 | MIC4 | 25.m00006 | TGGT1_021130 | 20 | 5.6 |
| D22 | Hypothetic Protein |
31.m00928 | TGGT1_039470 | 17 | 5.2 |
| D23 | SUB1 | 20.m00387 | TGGT1_016650 | 82 | 5.1 |
| D26 | MIC3 | 641.m00002 | TGGT1_121730 | 38 | 6.1 |
Several additional proteins with differences in abundance were identified by mass spectrometry (Table 1). Among these was perforin like protein 1 (PLP1) which was originally identified in a proteomic screen of secretory products (Zhou et al., 2004). 2D-DIGE analysis revealed accumulation of a precursor form and diminution of a probable processed form (spots U1 and D9; Figure 2A and Table 1). This was confirmed by Western blot analysis, which showed the absence of PLP1 processed product in the Δsub1 strain (Figure 2B).
The abundance of several other proteins in ESA was changed in the Δsub1 strain including the microneme proteins MIC1 and MIC3 (Table 1, Figure 2A). In addition to known micronemal proteins, other secretory proteins with altered abundance including the dense granule protein GRA7 and two SAG related sequence (SRS) proteins (TGGT1_121850 and TGGT_113990; Table 1, Figure 2A, spots D7-D16-U4). Previous studies characterizing ESA components have typically included dense granule proteins and surface antigens (Cesbron-Delauw et al., 1989, Zhou et al., 2004). The differences in ESA profile were reproducible in 3 independent biological replicates analyzed by 2D-DIGE, as well as numerous independent ESA secretion analyses of both Δsub1 strains.
TgSUB1 GPI anchorage is necessary for MPP2 activity
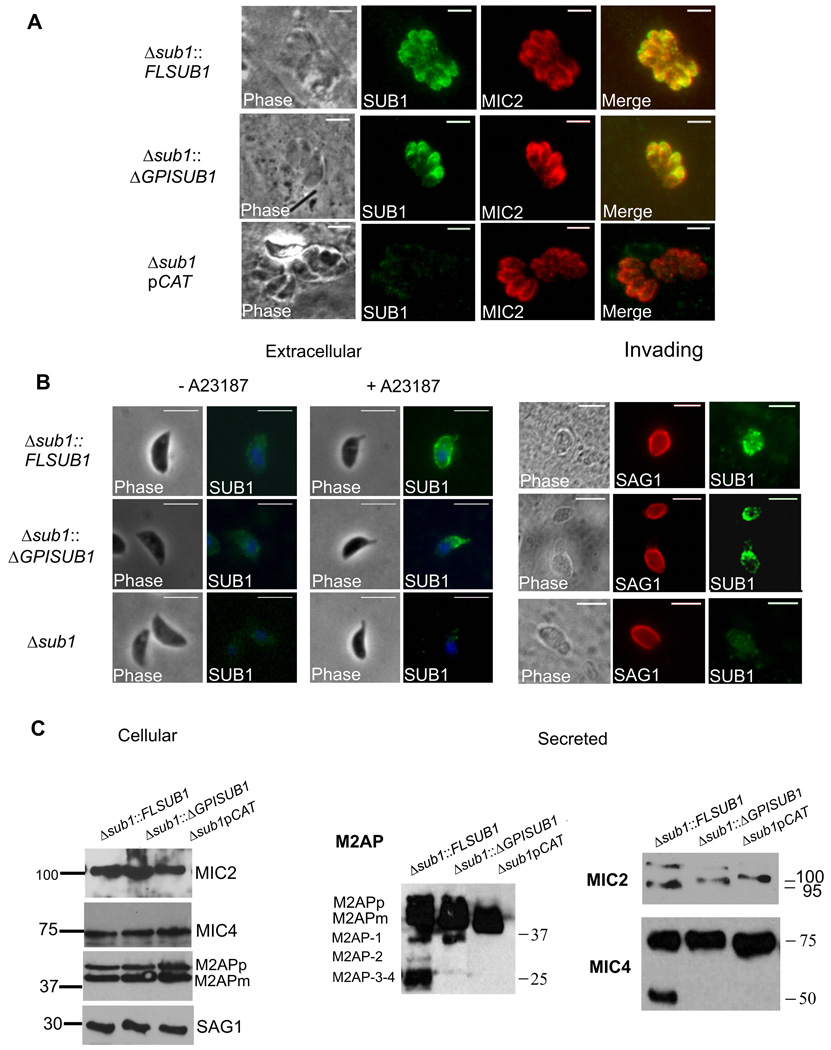
The Δsub1 strain was complemented with full-length TgSUB1 (Δsub1::FLSUB1) or a TgSUB1 lacking the C-terminal GPI signal sequence (Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1). A clone where only the CAT cassette has been integrated was also selected as a control (Δsub1pCAT). TgSUB1 complementation and CAT cassette integration were confirmed by Southern blot (Supplementary Figure S1B). TgSUB1 expression was restored to wild-type levels as shown by quantitative Real-Time PCR and Western blot analyses (Supplementary Figure S1C–D). Both FLSUB1 and ΔGPISUB1 proteins were correctly targeted to the micronemes consistent with prior results showing the GPI anchor is not involved in TgSUB1 microneme targeting (Figure 3A, (Binder et al., 2008)). Upon microneme discharge, TgSUB1 was secreted and correctly processed (Supplementary Figure S1E).
Figure 3. Complementation of the MIC surface processing by TgSUB1 complemented Δsub1 strains.
(A) Immunofluorescence of TgSUB1 complemented Δsub1 strains. All strains were simultaneously labeled with TgSUB1 antiserum AE653 and MIC2 monoclonal antibody 6D10, a marker for micronemes. Scale bar is 5 µm (B) Surface detection of TgSUB1 in the 3 representative strains: Δsub1::FLSUB1, Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 and Δsub1. Extracellular parasites were treated with the ionophore A23187 to induce microneme discharge. Tachyzoite nuclei were stained with DAPI and TgSUB1 was immunolabeled with the TgSUB1-specific antibody AE653 without cellular permeabilization. Freshly egressed parasites were inoculated onto HFF monolayers and invading tachyzoites were immunolabeled with TgSUB1 AE653 antiserum and the mouse anti-SAG1 DG52 monoclonal antibody without permeabilization. Scale bar is 5 µm (C) Western Blot analysis of the MIC2, MIC4 and M2AP cellular and secreted products collected from the Δsub1::FLSUB1, Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 and Δsub1pCAT strains. For MIC2 some cellular MIC2 is evident in addition to secreted MIC2 in the ESA from the 2 complemented lines (migrating just above 100 kDa). Blots were probed with appropriate antibodies as described in Experimental Procedures. Molecular weights are in kDa. M2APp: precursor form; M2APm: mature form.
We performed IFA on extracellular parasites stimulated for microneme secretion and on invading parasites to test if TgSUB1 protein deposition upon the parasite surface after microneme secretion is dependent on the GPI anchor. In both the ΔGPISUB1- and FLSUB1-complemented strains, TgSUB1 was detected on the parasite surface, as observed for many MIC proteins lacking membrane association such as MIC5 (Brydges et al., 2006) and M2AP (Huynh et al., 2003, Rabenau et al., 2001). The expression, targeting and intracellular processing of the rhoptry and microneme proteins MIC2, MIC3, MIC4, MIC5, MIC6, M2AP and ROP 2,3,4 were not affected in the Δsub1 complemented strains (Figure 3C, Supplementary Figure S1F and data not shown).
Complementation of the MIC protein surface processing was investigated by Western Blot analysis of ESA from the complemented strains. Processing of MIC2, M2AP and MIC4 was restored in Δsub1::FLSUB1 consistent with TgSUB1 being required for the proteolytic activity responsible for cell surface trimming of these proteins (Figure 3C). Unexpectedly, only the first processing step of M2AP, which is ascribed to MPP3, was restored in the Δsub1:: ΔGPISUB1 strain suggesting that SUB1 GPI surface anchorage is necessary for restoration of full proteolytic activity, including cleavage of substrates cleaved by MPP2.
Loss of TgSUB1 impairs tachyzoite attachment and invasion efficiency
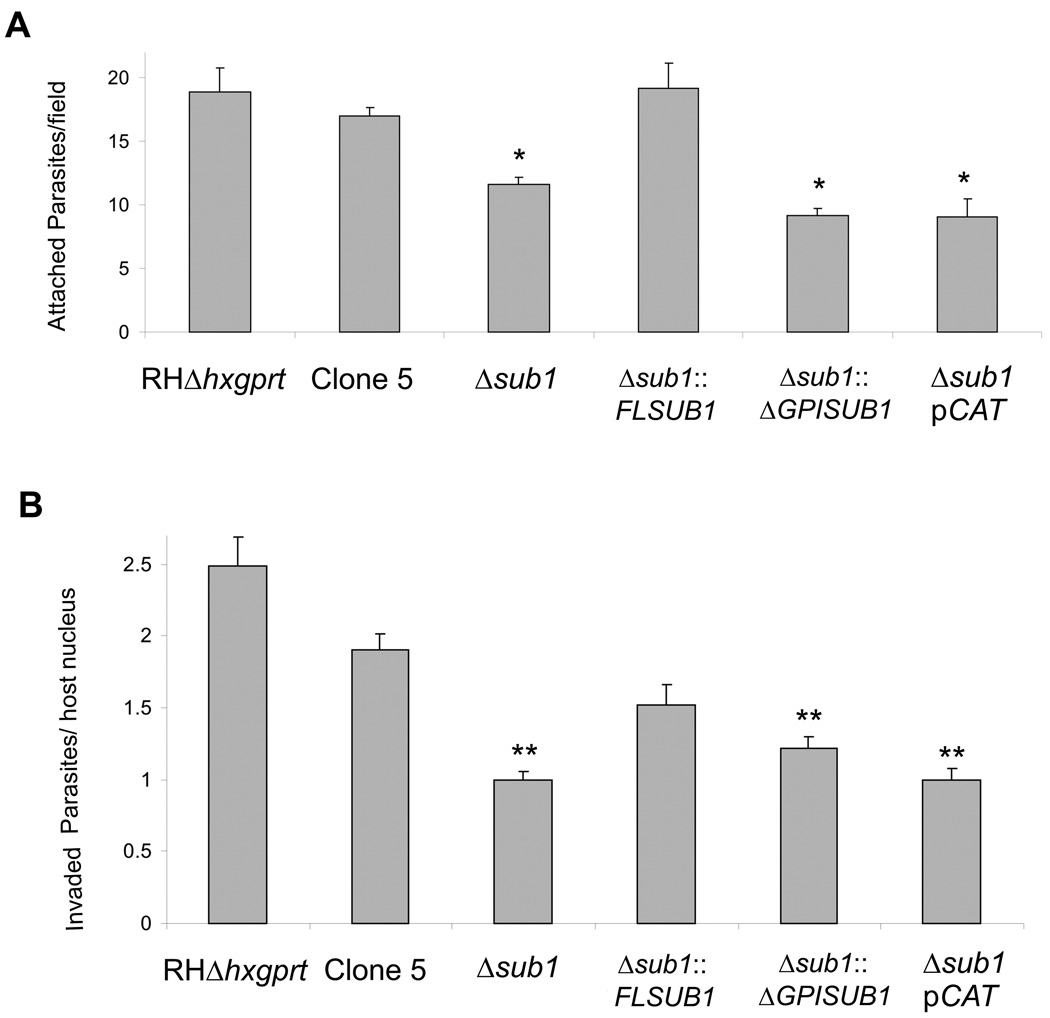
Since surface proteolytic trimming is proposed to be involved in the activation of MICs for host cell interaction, we tested the ability of the different Δsub1 strains to attach to fixed host cells. A significant decrease in attachment (30–40%) was observed for Δsub1, Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 and Δsub1pCAT strains (Figure 4A). The ability of the different strains to invade human foreskin fibroblasts was assessed by a Red/Green invasion assay, which discriminates between parasites that can attach versus those that have successfully invaded a host cell (Huynh et al., 2003). After a 15 minute incubation, invasion of Δsub1, Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 and Δsub1pCAT strains was decreased by 45–60% compared to RHΔhxgprt and Clone 5 (Figure 4B).
Figure 4. Attachment and invasion phenotypes of strains lacking TgSUB1-dependent MIC cell surface processing.
(A) Quantification of attachment to glutaraldehyde-fixed HFF cells expressed as the number of attached parasites counted per field. An asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference compared with RHΔhxgprt, Clone 5 and Δsub1::FLSUB1 (P<0.05, two tailed Student’s t test) (B) Quantification of 15 minute invasion assays expressed in number of invaded parasites per host cell counted. A double asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference compared with RHΔhxgprt and Clone 5 (P<0.05, two tailed Student’s t test). Data are mean values ± SEM.
Complementation with the full-length TgSUB1 gene increased invasion (Δsub1::FLSUB1), but did not completely restore entry to parental levels, a finding that has been seen in several previous studies (Huynh et al., 2003, Cerede et al., 2005). When Δsub1 parasites were allowed to invade for 1 hour, they showed comparable invasion to control parasites (data not shown). This suggests that Δsub1 parasites have a delay in invasion, a phenomenon previously seen for M2AP-deficient parasites (Huynh et al., 2003).
Strains lacking TgSUB1 have a defect in gliding motility
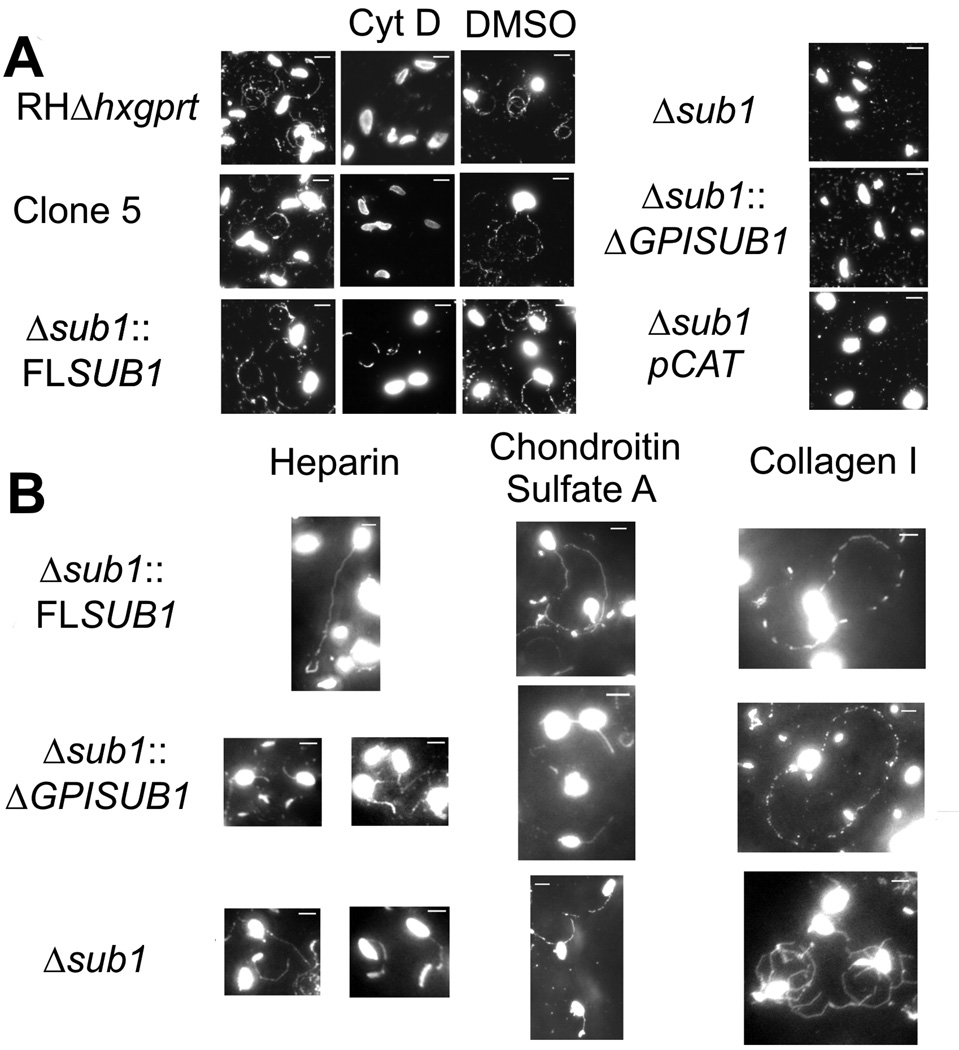
To determine if loss of TgSUB1-dependent MIC surface processing affects other parasite processes, we analyzed parasite gliding motility using a commonly used in vitro assay that assesses trail formation and gliding motility on FBS-coated coverslips. Toxoplasma motility is characterized by three forms: helical, circular and twirling. Helical motility deposits wide-arcing or straight, long trails (non circular) in contrast to circular motility (Hakansson et al., 1999). No trails were detected for Δsub1 and Δsub1pCAT whereas trails were seen for Δsub1::FLSUB1, Clone 5 and RH Δhxgprt, strains that have intact TgSUB1-dependent MIC surface processing (Figure 5A). Very short preliminary trails were detected Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 suggestive of transient gliding movements. Similar results were obtained using long incubation times (data not shown). Parasite gliding was also examined by live video microscopy. Quantification of the different forms of gliding revealed that a greater proportion of the Δsub1 parasites were inactive compared to the Δsub1::FLSUB1 with significantly less helical movement (Table 2), which could account for the lack of trail deposition.
Figure 5. Motility of strains lacking TgSUB1 assessed by trail deposition.
All strains were allowed to glide on glass coverslips coated with FBS (A) or Heparin, Chondroitin sulfate A and Collagen I (B). Trails deposited by gliding parasites were revealed with the mouse anti-SAG1 monoclonal antibody DG52 and visualized by immunofluorescence microscopy. Parasites were also pretreated with the gliding inhibitor cytochalasin D (cytD) as negative control or with DMSO (solvent control). Scale bar is 5 µm.
Table 2. Quantification of movement type of live gliding parasites on FBS or Collagen I.
Live parasites of the indicated strain were allowed to glide on substrate coated dishes and gliding modalities were enumerated by observing individual parasites as described in Experimental procedures. The different forms of motility of the Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 strain could not be reliably assessed on FBS since, rather than actively gliding on the substrate, the parasites frequently moved in the direction of the media flow of the heating element used during the video capture. Parasites that are actively gliding can go against the direction of this flow, and thus Δsub1::FLSUB1 on FBS and collagen, and the Δsub1 and Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 on collagen (and even the Δsub1 on FBS, those few that did glide) could be scored. The Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 on FBS moved mostly in one direction, although they were able to glide circularly against the flow. The weak adhesion of the Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 parasites may make them more susceptible to transient attachment and displacement in media compared to Δsub1 parasites, complicating enumeration of the different gliding modes. ND-not determined.
| Parasite Strain (on FBS) (on Collagen) |
Helical % FBS % Collagen |
Twirling % FBS % Collagen |
Circular % FBS % Collagen |
Inactive % FBS % Collagen |
Non-Productive % FBS % Collagen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δsub1:: FLSUB1 | |||||
| (211 parasites) | 33.2% | 17.1% | 14.7% | 20.0% | 15.2% |
| (128 parasites) | 38.2% | 21.9% | 3.1% | 23.4% | 13.3% |
| Δsub1 | |||||
| (190 parasites) | 4.7% | 15.3% | 8.9% | 54.0% | 17.4% |
| (181 parasites) | 23.2% | 19.3% | 1.1% | 40.8% | 15.5% |
| Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 | |||||
| (205 parasites) | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| (180 parasites) | 42.7% | 9.4% | 1.7% | 32.2% | 13.9% |
Since the defect in gliding on FBS-coated slides was more pronounced than the defect observed in invasion, we analyzed trail formation on other biologically relevant substrates including heparin, chondroitin sulfate A and collagen I with the three representative strains: Δsub1::FLSUB1, Δsub1:: ΔGPISUB1 and Δsub1. Although trails could be detected in all strains with all substrates, fewer and shorter trails were detected for the Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 and Δsub1 strains when gliding on heparin and chondroitin sulfate A (Figure 5B). To further analyze the gliding behavior, the proportion of long trails was determined and trail length was measured (Table 3). Long trails were more frequent for the Δsub1::FLSUB1 strain when gliding on heparin or chondroitin sulfate A compared to the Δsub1::GPISUB1 and the Δsub1 strains. Moreover, there was a significant quantitative difference in gliding distance between the Δsub1::FLSUB1 versus the Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 and Δsub1 strains on heparin and chondroitin sulfate A. Long trail percent and gliding distance were slightly reduced on collagen I for the Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 and Δsub1 strains compared to the Δsub1::FLSUB1, however, the differences were not statistically significant.
Table 3. Gliding behavior of Δsub1 strains varies with the biological substrate.
Gliding behavior of Δsub1::FLSUB1, Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 and Δsub1 strains was determined using a static gliding assay on substrate coated glass slides. Mean distances are expressed in number of parasite body length (Barragan et al., 2002) We denoted a trail as long (LT) when the distance is more than 5 times the parasite body length. Statistically significant differences in long trail proportion and trail distance on Heparin and Chondroitin Sulfate A were observed between the Δsub1::FLSUB1 compared to Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 and Δsub1 strains (P<0.05, two tailed Student’s t test). Data represent 3 independent experiments.
| Δsub1:: FLSUB1 | Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 | Δsub1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % LT | Mean Distance |
% LT | Mean Distance |
% LT | Mean Distance |
|
| Heparin | 26.4±3.4 | 4.3±0.4 | 11.2±2.0 | 2.7±0.4 | 11.2±3.8 | 2.9 ±0.2 |
| Chondroitin Sulfate A | 29.8±6.5 | 4.4±0.5 | 5.2±1.0 | 2.2±0.2 | 12.3±5.0 | 2.9±0.4 |
| Collagen I | 27.0±4.2 | 4.0±0.3 | 22.9±5.9 | 3.2±0.2 | 19.9±5.7 | 3.4±0.6 |
Live video microscopy of parasites gliding on collagen I was used to quantify the different forms of gliding (Table 2). Δsub1 parasites showed greater activity on collagen I than on FBS, with a statistically significant increase in helical motility, explaining the recovery of trails. The videos revealed that slightly more Δsub1::FLSUB1 parasites were active on collagen I compared to Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 parasites but the percent of helical movement were similar, correlating with static gliding data. As gliding motility is also important for calcium-dependent induced egress (Meissner et al., 2002b), we next determined the proportion of lysed vacuoles after inducing egress with calcium ionophore. No significant differences were observed in the proportion of lysed vacuoles between the strains (data not shown).
TgSUB1 expression is required for maximal virulence in the mouse model
We tested the virulence of the different strains in vivo in the mouse model. We first tested the intraperitoneal route of infection, which is the most common method used to study in vivo virulence of Type I non cyst-forming strains. There was no significant difference in the time of death between the strains using a range of inocula (10 to 1000 parasites, data not shown).
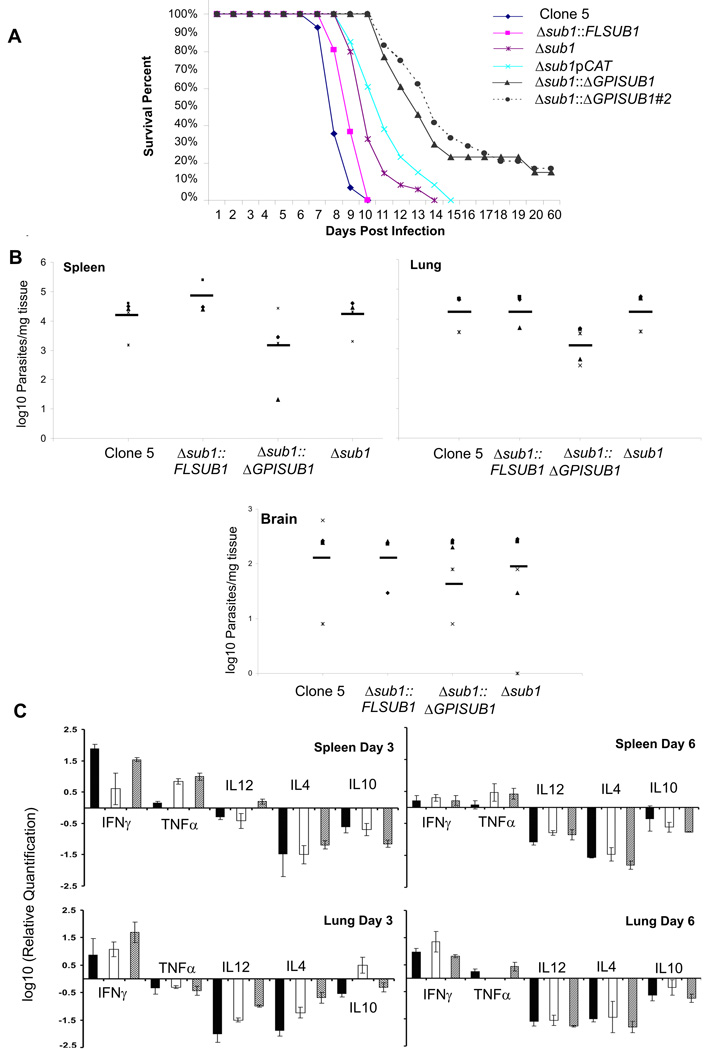
Because dissemination through the vasculature is important during natural T. gondii infection, we next infected the mice intravenously (i.v). Mice infected with 250 Clone 5 or Δsub1::FLSUB1 parasites died within 10 days. Mice infected with the Δsub1 and Δsub1pCAT strains died within 14 and 15 days. Unexpectedly, the Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 strain was more attenuated in i.v infection with 15% of the mice surviving infection (Figure 6A). Similar results were obtained with the second Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 clone (17% survival with 250 parasite inoculum, Figure 6A). Infected mice exhibited clinical evidence of cerebral infection (palsy, atrophy, agitation), and all mice that survived infection were seropositive.
Figure 6. Strains lacking TgSUB1 have decreased virulence in the mouse model.
250 tachyzoites were injected intravenously into groups of 5 female CD-1 mice. (A) Mouse survival was monitored daily over a period of 8 weeks. The Δsub1 and the Δsub1pCAT strains are less virulent than the Clone 5 and the Δsub1::FLSUB1 strains (P <0.05). The Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 was significantly less virulent than the Δsub1::FLSUB1 and Δsub1 strains (P<0.001). Similar results were obtained with a second independent Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 clone (Δsub1:: ΔGPISUB #2). Data are pooled from 3 independent experiments (at least 15 mice total). (B) Parasite tissue burden after 6 days of infection with the Clone 5, Δsub1, Δsub1::FLSUB1 and Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 strains. Spleen and lung parasite burdens were lower for Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 compared to Clone 5, Δsub1, and Δsub1::FLSUB1 strains, but data were statistically significant for the lung only (two-tailed Student’s t-test, P< 0.05). No significant differences were observed in the brain where fewer parasites were detected for all strains. Data are pooled from 2 independent experiments and show burdens for each mouse tested with average value represented by the dark line (C) Mice cytokine tissue levels after 3 and 6 days of infection with Clone 5 (black bars), Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 (white bars) and Δsub1 (gray bars) strains. Significant differences in the cytokine levels were observed at day 3: Spleen: for TNFα between the clone 5 strain compared to the Δsub1 and Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 strains. Lung: for IL12 and IL4 cytokines between the three strains and for IL10 between the Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 strain compared to the clone 5 and Δsub1 strains. At day 6, no significant differences in the cytokine levels were observed except for TNFα between the Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 strain compared to the Δsub1 and clone 5 strains (two-tailed Student’s t-test, P< 0.05).
Inappropriate release of the active TgSUB1 into the blood and host tissues could activate the endothelium and induce a more potent inflammatory response compared to the Δsub1 strain. We therefore quantified parasite burden and host cytokine profiles after intravenous infection with Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1, Δsub1, and Clone 5. Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 parasite burden was diminished in all organs although this difference was statistically significant in the lungs only (Figure 6B). Cytokine profiles elicited by the three strains differed somewhat, but were not suggestive of a more robust inflammatory response to Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 parasites (Figure 6C). These studies are consistent with a defect in either in vivo replication or dissemination for strains lacking full TgSUB1 activity, but more detailed characterization of parasite in vivo viability and host response are required.
Discussion
Cell-cell attachment is a key factor regulating diverse biological processes from immune cell migration, tumor cell spread to pathogen cell invasion. Attachment involves complex molecular interactions controlled by the coordinated expression and multimerization of various adhesive receptors. Frequently the maturation and inactivation of adhesive complexes is controlled by regulated proteolysis. Migratory cells use both adhesion receptors and proteolytic enzymes to regulate their interaction with and response to extracellular matrices (Stefanidakis et al., 2006).
Attachment is a prerequisite for host cell invasion by T. gondii. Coordinated regulated processing of micronemal surface adhesive complexes is likely to play an important role in the host cell invasion process (Carruthers et al., 2005, Carruthers, 2006, Dowse et al., 2004). Microneme proteins (MIC) first undergo a surface proteolytic trimming that has been proposed to activate adhesive domains and promote interaction with host cell receptors. Although study of these processing events has been an area of extensive investigation, the precise role of MIC surface processing was previously unknown and the responsible proteases not identified.
TgSUB1 is found in the micronemes and is exposed on the parasite surface upon microneme secretion (Binder et al., 2008). Δsub1 parasites have a global perturbation of microneme protein processing on the parasite surface with loss of the M2AP, MIC2 and MIC4 processed fragments ascribed to MPP2 activity. Western blot and 2D-DIGE analyses revealed that the M2AP-1, the product generated by the MPP3 protease (Zhou et al., 2004), is absent in Δsub1 parasites. These data indicate that TgSUB1 is required for both MPP2 and MPP3 activity.
Surprisingly, only the M2AP-1 fragment is restored in the Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 but processing of M2AP ascribed to MPP2 was not restored. MPP2 and MPP3 have been distinguished by their differential susceptibility to protease inhibitor ALLN, which blocks MPP2 activity but not MPP3 activity (Zhou et al., 2004). This differential inhibitor susceptibility was the basis for proposing two independent proteases termed MPP2 and MPP3.
We propose an alternative mechanism that reconciles these seemingly conflicting observations to explain how TgSUB1 could be both MPP2 and MPP3. TgSUB1 surface anchorage by GPI is unlikely to affect substrate specificity, but would influence the duration of TgSUB1 association with the cell surface and any microneme protein complexes associated with the cell surface. Microneme protein complexes and TgSUB1 are cleaved upon release onto the cell surface by MPP2 as part of adhesin inactivation and shedding. This proteolysis is enhanced by cytochalasin D treatment (see Supplementary Figure S2), which prevents redistribution of the microneme protein complexes toward the posterior end of the parasite, trapping MPP2 and its substrates together (Zhou et al., 2004). In contrast, lack of the GPI in Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 would decrease the duration of interaction of TgSUB1 and its substrates at the cell surface, potentially decreasing the efficiency of proteolytic cleavage. However, the autocatalytic processing of TgSUB1 is similar whether or not the complemented allele contains a GPI (Supplementary Figure S1E).
We have previously shown that maturation and activation of TgSUB1 (Miller et al., 2001) is not blocked by protease inhibitors. In typical subtilases, this resistance to protease inhibitors is due to inability of the inhibitor to access the active site to prevent proteolytic cleavage.
Similarly, the first steps of microneme complex cleavage by TgSUB1 may not be completely inhibited by ALLN, even if TgSUB1 activity is ALLN sensitive. Prior to activation of microneme secretion, the activity of TgSUB1 will be inhibited by bound prodomain and inaccessible to protease inhibitors such as ALLN. Once microneme secretion is activated by calcium and the TgSUB1 prodomain is released, substrates and ALLN will compete to occupy the TgSUB1 active site. Since TgSUB1 will be rapidly activated after release of the prodomain, some cleavage of substrates by TgSUB1 will take place before ALLN can fully inhibit activity, Thus the first cleavage steps mediated by TgSUB1, if they occur rapidly after activation, might appear to be ALLN-resistant and appear to be mediated MPP3 rather than MPP2.
Although our data suggest that TgSUB1 is responsible for both MPP2 and MPP3 activity, we cannot formally rule out that TgSUB1 is involved in the activation of another processing protease responsible for MIC processing. The sites of self-cleavage of TgSUB1 are similar to mapped sites of cleavage by MPP2 and MPP3 (Supplementary Figure S3). However, our attempts to test the protease activity of TgSUB1 using immunoprecipitated TgSUB1 and M2AP recombinant protein were inconclusive as TgSUB1 degrades rapidly via autoproteolysis, and we have not been able to generate active recombinant TgSUB1.
MIC2, MIC4 and M2AP are shed from the parasite cell surface normally indicating that protease activity responsible for the intramembranous cleavage is not affected in the Δsub1 strain. These are also consistent with MPP1 being a rhomboid serine protease activity (Brossier et al., 2005, Dowse et al., 2005), and genetic studies are consistent with TgROM4 acting as MPP1 (Buguliskis et al., 2010).
Beyond the known substrates of MPP2 and MPP3, TgSUB1 candidate substrates include PLP1, a perforin like protein that induces membrane disruption during parasite egress from host cells (Kafsack et al., 2009). We did not found any defect in egress suggesting that PLP1 processing by TgSUB1 is not required for PLP1 function during egress. The 2D-DIGE analyzed also revealed several proteins that are not predicted to have signal peptides (Supplementary Table S1). This may be an artefact of the greater cell lysis seen with the serum-free conditions used for large-scale ESA preparations needed for proteomic analysis (Zhou et al., 2004), and many of these proteins may not be secreted.
Gliding motility requires formation of successive tight interactions between surface adhesive complexes and the substratum followed by disengagement. Our data suggest that lack of MIC surface processing affects tight interaction with the substratum, impairing helical motility and leading to impaired or delayed motility depending on the substrate. Nascent trails could be detected in static assays for Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 when gliding on FBS, heparin and chondroitin sulfate A. Video gliding on FBS showed that Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 parasites do not move well on the substratum. We hypothesize that partial processing of MICs in the Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 leads to weak parasite-substratum interactions that initiate gliding, leading to the short trails observed in the static assay, but that the interaction is not sufficiently strong to complete a helical glide.
Despite the profound alteration of proteolytic processing associated with loss of TgSUB1, Δsub1 parasites have a surprisingly modest phenotype in vitro and in vivo. Previous studies have shown that T. gondii invasion involves redundant adhesive domains with synergistic roles in parasite virulence (Cerede et al., 2005). T. gondii encodes 12 subtilase genes, so there may be functional redundancy in both microneme adhesins as well as the proteases involved in regulation of adhesin activity. Although loss of TgSUB1-dependent MIC surface processing affects parasite attachment, helical motility and invasion of the host cell, parasites without MPP2 activity are able to compensate. It appears that the resulting defect in adhesion affects efficiency of motility and initiation of parasite-host cell invasion, but does not result in a sustained defect in invasion or parasite replication ((Binder et al., 2008) and Supplementary Figure S1G).
The gliding phenotype of Δsub1 and Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 strains was rescued on collagen I. It has been shown that MIC2 binds to heparin but not collagen I (Harper et al., 2004) suggesting that other MIC complexes may participate in gliding on collagen I. A mutant strain that expresses only 2% of MIC2 protein has a severe defect in gliding motility on FBS with fewer trails that are shorter and mainly circular (Huynh et al., 2006). The phenotype of these parasites is not rescued when gliding on collagen I, indicating that MIC2 is required for gliding on collagen I, but that proteolytic trimming of the MIC2-M2AP complex is not required (Supplementary Figure S4). Previous studies showed that full-length cellular form of MIC2 binds the host cell (Carruthers et al., 1999b). Moreover, the MIC2-I domain binds to heparin whether the 5 kDa N-terminal fragment is present or not (Harper et al., 2004). Collectively, the data suggest that initial MIC2 processing is not crucial for adhesion. We can hypothesize that sequential processing could modulate effective engagement with different host cell ligands. Thus, parasites could compensate the loss of TgSUB1 dependent MICs processing either through binding with other MICs or through differential binding to ligands according to the degree of MICs processing. Unfortunately attempts to test this hypothesis were thwarted by uniformly low cellular binding of recombinant protein reagents tested. It is also possible that TgSUB1 dependent processing is more important for other molecular interactions that have not been examined in our study.
TgSUB1 contributes to maximal virulence in the mouse model. Here too, TgSUB1 may have a more critical function in a biological context that we did not examine. By analogy, the importance of knobs for P. falciparum adherence was only seen under flow conditions that mimic the blood stream (Crabb et al., 1997). MIC2 N-terminal trimming is reported to be necessary for ICAM-1 interaction and is correlated with trans-epithelial migration (Barragan et al., 2005). It is possible that TgSUB1 activity is more critical when parasites cross biological barriers such as the gut epithelium after ingestion of sporozoites or bradyzoites. Unfortunately, efforts to test transmigration ability did not yield consistent results, and the RH background stage does not make bradyzoites, a stage with numerous micronemes whose contents may be required for efficient invasion of gut epithelia.
Finally, recent analyses have revealed that the clone of RH strain parasites used in this study (RH-ERP), has acquired enhanced ability to invade, glide and replicate that is not representative of other virulent Type I strains (Khan et al., 2009). Thus it is possible that the true biological importance of TgSUB1 has been masked by the unusually efficient invasive abilities of our RH background strain. If so, deletion of TgSUB1 may have a greater phenotypic effect upon strains that have been more recently isolated from animal hosts.
Experimental procedures
Parasite maintenance
T. gondii RH strain Δhxgprt parasites (Donald et al., 1998) -and mutants derived from this strain (all originally RH-ERP), were maintained by continual passage in human foreskin fibroblast (HFF). Cells were grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM; Gibco) containing 10% Fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% Penicillin/Streptomycin and 1% Glutamine. Parasites and cells were cultured in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37 °C.
Generation of TgSUB1KO and TgSUB1KO complemented strains
The TgSUB1 gene was disrupted by homologous recombination with a construct containing the HXGPRT minigene flanked by three kilobases of the 5’and 3’ sequence flanking the TgSUB1 coding region. Two strains with TgSUB1 disruption were generated (RH gra1-GFP5S65T-tubcat Δhxgprt and RHΔhxgprt background) (Binder et al., 2008). In each case, a clone that had integrated the TgSUB1 disruption cassette but continued to express TgSUB1 was chosen for parallel phenotypic analysis (Clone 2 for GFP strain and Clone 5 for non GFP strain). Complementation with TgSUB1 was performed in the RH Δsub1Δhxgprt background. Either the full-length TgSUB1 gene or the TgSUB1 gene lacking the sequence encoding for the 26 last amino acids containing the signal for GPI anchorage were amplified from cDNA. The PCR products were cloned into a plasmid containing three kilobases of 5’ and 3’ TgSUB1 flanking sequence by standard cloning procedures. The TgSUB1-complemented strains were generated by co-transfecting the Δsub1 strain with 100 µg Not I-linerarized TgSUB1 complementation construct and 10 µg Not I-linearized plasmid containing a tub-cat selection cassette. Stable lines were obtained by selection with mycophenolic acid/xanthine and chloramphenicol and cloned by limiting dilution. For each complementation, two different clones from independent transformations were isolated and tested.
Indirect immunofluorescence microscopy
For labeling of intracellular tachyzoites: HFF monolayers were grown on glass coverslips in 24 well plates until confluent. Freshly egressed tachyzoites were allowed to infect confluent cells for 20–24 hours. Cells were fixed for 20 minutes in 3% paraformaldehyde and permeabilized for 10 minutes in 0.2% Triton X-100 in PBS1X and blocked (PBS1X, BSA 3%). Antibody dilutions used were: rabbit anti-TgSUB1 AE653 (1:500;(Binder et al., 2008)) and mouse anti-MIC2 mAb 6D10 (1:500, gift of David Sibley, Washington University School of Medicine, USA). Alexa Fluor conjugated secondary antibodies (Molecular Probes) were used at 1:2,000 dilution. Coverslips were mounted on slides with the Vectashield mounting medium (Vector Labs) and viewed with an Olympus Digital Microscope (Albert Einstein College of Medicine Analytical Imaging Facility).
For labeling of extracellular tachyzoites: freshly lysed parasites were resuspended in Hank’s balanced salt solution, with or without 2 µM A23187, and incubated at 37 °C for 5 minutes to induce microneme secretion. The parasites were then added to glass coverslips before being fixed (3% paraformaldehyde) and blocked (PBS, BSA 3%). Parasites were then labeled with a rabbit anti-TgSUB1 AE653 (1:500, PBS, BSA 3%) followed by a conjugated anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Molecular probes, 1:2,000). Alternatively, freshly egressed parasites were resuspended in DMEM media and allowed to infect HFF cells for 5 minutes at 37° C. Invading parasites were immunolabelled with the mouse anti-SAG1 DG52 monoclonal antibody (1:500; gift from John Boothroyd, Stanford University School of Medicine) and the anti-SUB1 rabbit antiserum AE653.
Secretion assay
Freshly lysed tachyzoites (2–3×107 parasites) were filtered, centrifuged and resuspended in DMEM 1% FBS, 20 mM HEPES. Parasites were pre-incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature with 1 µM cytochalasin D. Microneme secretion was induced by adding 1% ethanol and warming parasites to 37 °C for 10 minutes as previously described (Carruthers et al., 1999a). Cells were removed by centrifugation at 1000g 10 minutes 4°C. The supernatant containing the microneme secreted products was used for Western blot analysis. Large-scale secretion preparations for two-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis (2DE DIGE) were generated as described previously (Zhou et al., 2004).
Two-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis
Microneme secreted contents from 1×109 parasites were analyzed by two-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis as previously described (Zhou et al., 2004). Proteins were labeled using amine reactive cyanine dyes (minimal Cy dyes, GE Healthcare) according to the manufacturer recommendations. The microneme secreted supernatant from Clone 2 (GFP-positive) and Δsub1GFP parasites were labeled with two different fluorochrome dyes (Cy5 or Cy3). An equal amount of the two different microneme secreted supernatants were mixed and labeled with a third fluorochrome dye (Cy2) as an internal standard control. An equal amount of the three labeled samples were mixed together and then separated by a 2 dimension gel (pH=4.2–6.8 first dimension and 12.5% SDS-PAGE second dimension). Spots were visualized using a Typhoon™ 9400 imager (GE Healthcare) and analyzed using DeCyder-2D (v.5.0, GE Healthcare). The software analyzes the overlaid signals and detects differentially expressed proteins. Proteins on the two dimensional gel were transferred to Immobilon membrane and stained with Coomassie blue G250 and spots of interest were excised from the gel and digested with sequencing grade modified procine trypsin (Promega, www.promega.com). Tryptic peptides were fractionated by reverse-phase HPLC. Eluted peptides were sequenced by tandem mass spectrometry analysis. Proteins were identified by searching the data against the EPICDB Toxoplasma proteomic database (http://toro.aecom.yu.edu/biodefense; (Madrid-Aliste et al., 2009)) using MASCOT and are based on two or more peptide sequences with scores above the 95% confidence threshold.
Western blotting
Protein lysates were loaded on an 8% SDS gel and then transferred to nitrocellulose membrane. Membranes were probed with rabbit antisera recognizing TgSUB1 (1:10,000 PfSUB1, gift from Michael Blackman, National Institute for Medical Research, United Kingdom), SAG1-p30 (1:10,000, gift from Lloyd Kasper, Dartmouth Medical School) and MIC5 (1:10,000) followed by anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase (HRP; 1:15,000) antibody. Secreted microneme proteins (ESA or excreted secreted antigens) were loaded on SDS gels of different resolution according to the protein probed (from 6% to 10 % acrylamide). Membranes were probed with the following antibodies: mouse anti-MIC2 6D10 1:2,000 (gift of David Sibley, Washington University School of Medicine, USA); rabbit anti-M2AP 1:10,000; rabbit anti-PfSUB1 1:2,500) and rabbit anti-MIC4 1:10,000 (gift from Dominique Soldati-Favre, University of Geneva, Switzerland). The membranes were then probed with a secondary anti-rabbit or anti-mouse antibody (1:5,000–10,000) conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (HRP). Parasite lysis was evaluated by probing the membrane with an antibody directed against cytosolic proteins (mouse anti-actin or tubulin 1:2,000). Signals were revealed with a peroxidase Western blot detection reagent (SuperSignal Pierce). All gels were run under reducing conditions.
Quantitative real-time PCR
RNA from freshly egressed parasites was purified using Trizol followed by chloroform extraction. Then 3.5 µgrams of total RNA were retrotranscribed using the SuperScript kit (Invitrogen). Quantitative Real-time PCR was performed on the 7300 ABI apparatus using the Power SYBR Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR Primers were designed with the Primer Express software (Applied Biosystems) to amplify a 100 bp target gene fragment. PCR was performed in a 10 µl volume containing 7 ng of cDNA and 0.3 µM of each primer. cDNA levels were normalized to cDNA α-tubulin levels. Experiments were performed 3 times with 2 different RNA preparations.
Invasion and attachment assays
Red/green invasion assays were performed as previously described (Huynh et al., 2003). HFF monolayer coverslips were infected with freshly egressed filtered tachyzoites (7.5×106/chamber) for 15 minutes, 37°C. The coverslips were then fixed (paraformaldehyde 3%,), and blocked (PBS1X, BSA 3%). External attached parasites were labeled with a mouse anti-SAG1 DG52 antibody (1:500; gift from John Boothroyd, Stanford University School of Medicine) followed by a conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibody. Samples were then methanol permeabilized, blocked, and all parasites were labeled with a rabbit anti-Toxoplasma antiserum (Y321 1:1,500; gift from Louis Weiss, Albert Einstein College of Medicine) followed by a conjugated anti-rabbit secondary antibody. Data were compiled from 4 independent experiments counting 10 fields/clone/coverslip at 60X magnification. The number of invaded parasites is the difference between the total number of parasites (green) and the number of attached parasites (red).
For attachment assays, 1×107 parasites were loaded with 1 µM calcein-AM, 30 minutes at RT (Invitrogen) and then allowed to attach for 15 min at 37°C on fixed HFF cells (2% glutaraldehyde 5 minutes 4°C , blocking with 0.16 M ethanolamine). Data were compiled from 4 independent experiments counting 20 fields/clone/coverslip at 40X magnification.
Replication/growth rate assay
Freshly lysed filtered parasites (5×104) were allowed to invade and replicate in HFF coverslip monolayers for 24 or 38 hours. Cells were fixed, permeabilized and immunolabelled with the rabbit anti-Toxoplasma antiserum Y321 (1:1,500) followed by a conjugated anti-rabbit secondary antibody. The number of parasites per vacuole was enumerated on duplicate coverslips counting approximately 100 vacuoles per time point. Growth rate was determined in 3 independent experiments.
Induced egress assay
Egress was induced with the ionophore A23187 as previously described (Black et al., 2000). Briefly, HFF 24-well coverslip monolayers were inoculated with 105 parasites and allowed to grow for 38 h. Host cells were incubated for 3 minutes at 37°C with modified Hank’s balanced salt solution (HBSS, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM CaCl2, 10 mM NaHCO3, 20 mM HEPES) containing 2 µM A23187 or DMSO (control). Cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde and vacuoles were labeled by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy.
Static gliding assay
Glass coverslips were coated overnight at 4°C with 50% FBS/50% PBS1X or 50 µg/ml of Heparin, Chondroitin sulfate A or Collagen I (solubilized in acetic acid). Freshly lysed filtered tachyzoites were resuspended in HHE (Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution, 10 mM HEPES, 1 mM EGTA) and 250 µl was inoculated on the coated slides for 30 min at 37°C. Slides were then fixed with 3% paraformaldehyde. Trails left by gliding parasites were visualized at 40X by staining with the mouse anti-SAG1 DG52 antibody followed by a conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibody. Between 40 and 200 trails were enumerated per strain/treatment. Only trails associated with a parasite were counted. A trail was considered as circular if the diameter was approximately the length of a tachyzoite; trails larger in diameter or straight were considered as non-circular. Trail lengths were measured in parasite body length.
Live gliding microscopy
One T25 flask of parasites was filter-purified, pelleted, and resuspended in 10 ml of HHE (Hanks Balanced Salt Solution, 10 mM HEPES, 1 mM EGTA). 2 ml of parasites was placed in a 35 mm glass bottom Petri dish and allowed to settle at RT for 10 minutes, before placing on a 37°C heating block for 5 minutes to activate parasites. The dish was transferred to a heated ring placed on the stage of a Zeiss Axio inverted microscope. Videos were captured at 1 frame/second for 1 minute, using the Axio time-lapse software. The type of gliding movement was enumerated by observing individual parasites for each strain on each substrate. Maximum projection images showing the motility patterns over the 1 minute period were generated by exporting the individual frame and reimporting them as Z-stacks. The time-lapse movies were generated by exporting the frames from the 1 minute period, increasing the speed to 5X, and converted the image series to an avi file.
In vivo virulence assay
Groups of 4 to 5 female CD-1 mice between 7 and 9 old weeks of age were infected intraperitoneally or intravenously with different parasite inocula. The survival of mice after infection was monitored daily over a period of 8 weeks. Plaque assays were performed with the different inocula to ensure equal amounts of viable injected parasites. The seroconversion of all surviving mice was assayed 4 weeks post infection by Western blot analysis by probing mouse serum against RH tachyzoite lysate. Results represent 3 independent experiments. Care and handling of animals was done in accordance with AAALAC guidelines after approval of protocols by the Albert Einstein College of Medicine Animal Use Committee.
Parasite tissue burden and cytokine tissue level quantification
Groups of two or three female CD-1 mice between 7 and 9 old weeks of age were infected intravenously with 250 parasites of the Clone 5, Δsub1, Δsub1::FLSUB1 and Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 strains. Six days after injection; spleen, lung and brain were collected and DNA was purified using TRIzol. Parasite genomic DNA load was determined by quantitative Real-time PCR using parasite specific primers (Tox 9–11; (Reischl et al., 2003)). Number of parasites per mg was calculated using a standard curve generated with genomic DNA from RHΔhxgprt tachyzoites. Groups of 3 mice were infected intravenously with 250 parasites of the Clone 5, Δsub1::ΔGPISUB1 and Δsub1 strains. At days 3 and 6 after injection; RNA was purified using TRIzol. 5 µg of total RNA were retrotranscribed using the SuperScript kit (Invitrogen) and 1 µl of cDNA was used in 10 µl of SYBR green quantitative Real-Time PCR reaction. Cytokine levels are shown as the relative proportion of cDNA compared with uninfected tissue and normalized to GAPDH cDNA levels.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using the Prism Graph pad software. Two-tailed Student’s t-test was used for analysis of invasion, attachment, replication, egress and gliding assays. The level of significance for mouse virulence assays was determined with the Kaplan-Meier estimator. Differences were considered significant if p-value was <0.05.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Funding:
This work was supported by NIH-NIAID R01 AI46985 (to KK) and RO1 AI046675 (VBC). EMB and PKH were supported by NIH NIAID training grant 5T32-A107506, awarded to the Albert Einstein College of Medicine. Some of the data in this manuscript were published as part of a thesis submitted by E.M.B in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Sue Golding Graduate Division of Medical Sciences, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Yeshiva University.
Literature Cited
- Barragan A, Brossier F, Sibley DL. Transepithelial migration of toxoplasma gondii involves an interaction of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) with the parasite adhesin MIC2. Cell. Microbiol. 2005;7:561–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barragan A, Sibley DL. Transepithelial migration of toxoplasma gondii is linked to parasite motility and virulence. J. Exp. Med. 2002;195:1625–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum J, Papenfuss A, Baum B, Speed T, Cowman A. Regulation of apicomplexan actin-based motility. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006;4:621–628. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder EM, Lagal V, Kim K. The prodomain of Toxoplasma gondii GPI-anchored subtilase TgSUB1 mediates its targeting to micronemes. Traffic. 2008;9:1485–1496. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00774.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M, Arrizabalaga G, Boothroyd J. Ionophore-resistant mutants of Toxoplasma gondii reveal host cell permeabilization as an early event in egress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000;20:9399–9408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.24.9399-9408.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenschein TM, Friedrich N, Childs RA, Saouros S, Carpenter EP, Campanero-Rhodes MA, et al. Atomic resolution insight into host cell recognition by Toxoplasma gondii. Embo J. 2007;26:2808–2820. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecht S, Carruthers VB, Ferguson PJD, Giddings OK, Wang G, Jakle U, et al. The toxoplasma micronemal protein MIC4 is an adhesive composed of six conserved apple domains. J. Biol.Chem. 2001;276:4119–4127. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008294200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brossier F, Jewett TJ, Lovett JL, Sibley DL. C-terminal processing of the toxoplasma protein MIC2 is essential for invasion into host cells. J. Biol.Chem. 2003;278:6229–6234. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209837200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brossier F, Jewett TJ, Sibley DL, Urban S. A spatially localized rhomboid protease cleaves cell surface adhesins essential for invasion by Toxoplasma. PNAS. 2005;102:4146–4151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407918102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brydges SD, Zhou XW, Huynh MH, Harper JM, Mital J, Adjogble KD, et al. Targeted deletion of MIC5 enhances trimming proteolysis of Toxoplasma invasion proteins. Eukaryot Cell. 2006;5:2174–2183. doi: 10.1128/EC.00163-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buguliskis JS, Brossier F, Shuman J, Sibley LD. Rhomboid 4 (ROM4) affects the processing of surface adhesins and facilitates host cell invasion by Toxoplasma gondii. Plos Pathog. 2010;6:e1000858. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers V, Blackman M. A new release on life: emerging concepts in proteolysis and parasite invasion. Mol. Microbiol. 2005;55:1617–1630. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers V, Moreno S, Sibley L. Ethanol and acetaldehyde elevate intracellular [Ca2+] and stimulate microneme discharge in Toxoplasma gondii. Biochem. J. 1999a;342:379–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers V, Sibley L. Sequential protein secretion from three distinct organelles of Toxoplasma gondii accompanies invasion of human fibroblasts. Eur. J. Cell. Biol. 1997;73:114–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers VB. Proteolysis and Toxoplasma invasion. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006;36:595–600. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers VB, Giddings OK, Sibley DL. Secretion of micronemal proteins is associated with toxoplasma invasion of host cells. Cell. Microbiol. 1999b;1:225–235. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.1999.00023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers VB, Sherman GB, Sibley DL. The toxoplasma adhesive protein MIC2 is proteolytically processed at multiple sites by two parasite-derived proteases. J. Biol.Chem. 2000;275:14346–14353. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.19.14346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerede O, Dubremetz J, Bout D, Lebrun M. The toxoplasma gondii protein MIC3 requires pro-peptide cleavage and dimerization to function as adhesin. EMBO. 2002;21:2526–2536. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.11.2526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerede O, Dubremetz J, Soete M, Deslee D, Vial H, Bout D, Lebrun M. Synergistic role of micronemal proteins in Toxoplasma gondii virulence. J. Exp. Med. 2005;201:453–463. doi: 10.1084/jem.20041672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesbron-Delauw MF, Guy B, Torpier G, Pierce RJ, Lenzen G, Cesbron JY, et al. Molecular characterization of a 23-kilodalton major antigen secreted by Toxoplasma gondii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86:7537–7541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conseil V, Soete M, Dubremetz J. Serine protease inhibitors block invasion of host cells by Toxoplasma gondii. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 1999;43:1358–1361. doi: 10.1128/aac.43.6.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb B, Cooke B, Reeder J, Waller R, Caruana S, Davern K, et al. Targeted gene disruption shows that knobs enable malaria-infected red cells to cytoadhere under physiological shear stress. Cell. 1997;89:287–296. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80207-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrowolski J, Sibley L. Toxoplasma invasion of mammalian cells is powered by the actin cytoskeleton of the parasite. Cell. 1996;84:933–939. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald RGK, Roos DS. Gene knock-outs and allelic replacements in Toxoplasma gondii: HXGPRT as a selectable marker for hit and run mutagenesis. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1998;91:295–305. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(97)00210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowse TJ, Pascall JC, Brown KD, Soldati D. Apicomplexa rhomboids have a potential role in microneme protein cleavage during host cell invasion. Internat. J. Parasitol. 2005;35:747–756. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2005.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowse TJ, Soldati D. Host cell invasion by the apicomplexans: the significance of microneme protein proteolysis. Current Opinion Microbiol. 2004;7:388–396. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2004.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubremetz J, Garcia-Réguet N, Conseil V, Fourmaux M. Apical organelles and host-cell invasion by Apicomplexa. Int J Parasitol. 1998;28:1007–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(98)00076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourmaux M, Achbarou A, Mercereau-Puijalon O, Biderre C, Briche I, Loyens A, et al. The MIC1 microneme protein of Toxoplasma gondii contains a duplicated receptor-like domain and binds to host cell surface. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1996;83:201–210. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(96)02773-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich N, Santos JM, Liu Y, Palma AS, Leon E, Saouros S, et al. Members of a novel protein family containing microneme adhesive repeat domains act as sialic acid-binding lectins during host cell invasion by apicomplexan parasites. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:2064–2076. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.060988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Réguet N, Lebrun M, Fourmaux M, Mercereau-Puijalon O, Mann T, Beckers C, et al. The microneme protein MIC3 of Toxoplasma gondii is a secretory adhesion that binds to both the surface of the host cells and the surface of the parasite. Cell. Microbiol. 2000;2:353–364. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2000.00064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakansson S, Morisaki H, Heuser J, Sibley LD. Time-lapse video microscopy of gliding motility in Toxoplasma gondii reveals a novel, biphasic mechanism of cell locomotion. Mol Biol Cell. 1999;10:3539–3547. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.11.3539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J, Hoff E, Carruthers V. Multimerization of the Toxoplasma gondii MIC2 integrin-like A-domain is required for binding to heparin and human cells. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2004;134:201–212. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2003.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J, Huynh M, Coppens I, Parussini F, Moreno S, VB C. A Cleavable Propeptide Influences Toxoplasma Infection by Facilitating the Trafficking and Secretion of the TgMIC2-M2AP Invasion Complex. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2006;17:4551–4563. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E06-01-0064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh M, Carruthers V. Toxoplasma MIC2 Is a Major Determinant of Invasion and Virulence. Plos Pathog. 2006;2 doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh M, Rabenau K, Harper J, Beatty W, Sibley L, Carruthers V. Rapid invasion of host cells by Toxoplasma requires secretion of the MIC2-M2AP adhesive protein complex. EMBO Journal. 2003;22:2082–2090. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewett TJ, Sibley LD. The toxoplasma proteins MIC2 and M2AP form a hexameric complex necessary for intracellular survival. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:9362–9369. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M312590200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafsack BF, Pena JD, Coppens I, Ravindran S, Boothroyd JC, Carruthers VB. Rapid membrane disruption by a perforin-like protein facilitates parasite exit from host cells. Science. 2009;323:530–533. doi: 10.1126/science.1165740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeley A, Soldati D. The glideosome: a molecular machine powering motility and host-cell invasion by Apicomplexa. Trends Cell. biol. 2004;14:528–532. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A, Behnke MS, Dunay IR, White MW, Sibley LD. Phenotypic and gene expression changes among clonal type I strains of Toxoplasma gondii. Eukaryot Cell. 2009;8:1828–1836. doi: 10.1128/EC.00150-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrid-Aliste CJ, Dybas JM, Angeletti RH, Weiss LM, Kim K, Simon I, Fiser A. EPIC-DB: a proteomics database for studying Apicomplexan organisms. BMC Genomics. 2009;10:38. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner M, Reiss M, Viebig N, Carruthers VB, Toursel C, Tomavo S, et al. A family of transmembrane microneme proteins of Toxoplasma gondii contain EGF-like domains and function as escorters. J Cell Sci. 2002a;115:563–574. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner M, Schluter D, Soldati D. Role of Toxoplasma gondii myosin A in powering parasite gliding and host cell invasion. Science. 2002b;298:837–840. doi: 10.1126/science.1074553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller SA, Binder EM, Blackman MJ, Carruthers VB, Kim K. A conserved subtilisin-like protein TgSUB1 in microneme organelles of toxoplasma gondii. J. Biol.Chem. 2001;276:45341–45348. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106665200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabenau KE, Sohrabi A, Tripathy A, Reitter C, Ajioka JW, Tomley FM, Carruthers VB. TgM2AP participates in Toxoplasma gondii invasion of host cells and is tightly associated with the adhesive protein TgMIC2. Mol Microbiol. 2001;41:537–547. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reischl U, Bretagne S, Kruger D, Ernault P, Costa JM. Comparison of two DNA targets for the diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis by real-time PCR using fluorescence resonance energy transfer hybridization probes. BMC Infect Dis. 2003;3:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-3-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss M, Viebig N, Brecht S, Fourmaux M, Soete M, Di Cristina M, et al. Identification and characterization of an escorter for two secretory adhesins in Toxoplasma gondii. J. Cell. Biol. 2001;152:563–578. doi: 10.1083/jcb.152.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saouros S, Edwards-Jones B, Reiss M, Sawmynaden K, Cota E, Simpson P, et al. A novel galectin-like domain from Toxoplasma gondii micronemal protein 1 assists the folding, assembly, and transport of a cell adhesion complex. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:38583–38591. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C500365200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanidakis M, Koivunen E. Cell-surface association between matrix metalloproteinases and integrins: role of the complexes in leukocyte migration and cancer progression. Blood. 2006;108:1441–1450. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-005363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo C, Zhou X, Bogyo M, Carruthers V. Cysteine protease inhibitors block Toxoplasma gondii microneme secretion and cell invasion. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2007;51:679–688. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01059-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou XW, Blackman MJ, Howell SA, Carruthers VB. Proteomic analysis of cleavage events reveals a dynamic two-step mechanism for proteolysis of a key parasite adhesive complex. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2004;3:565–576. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M300123-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.