Abstract
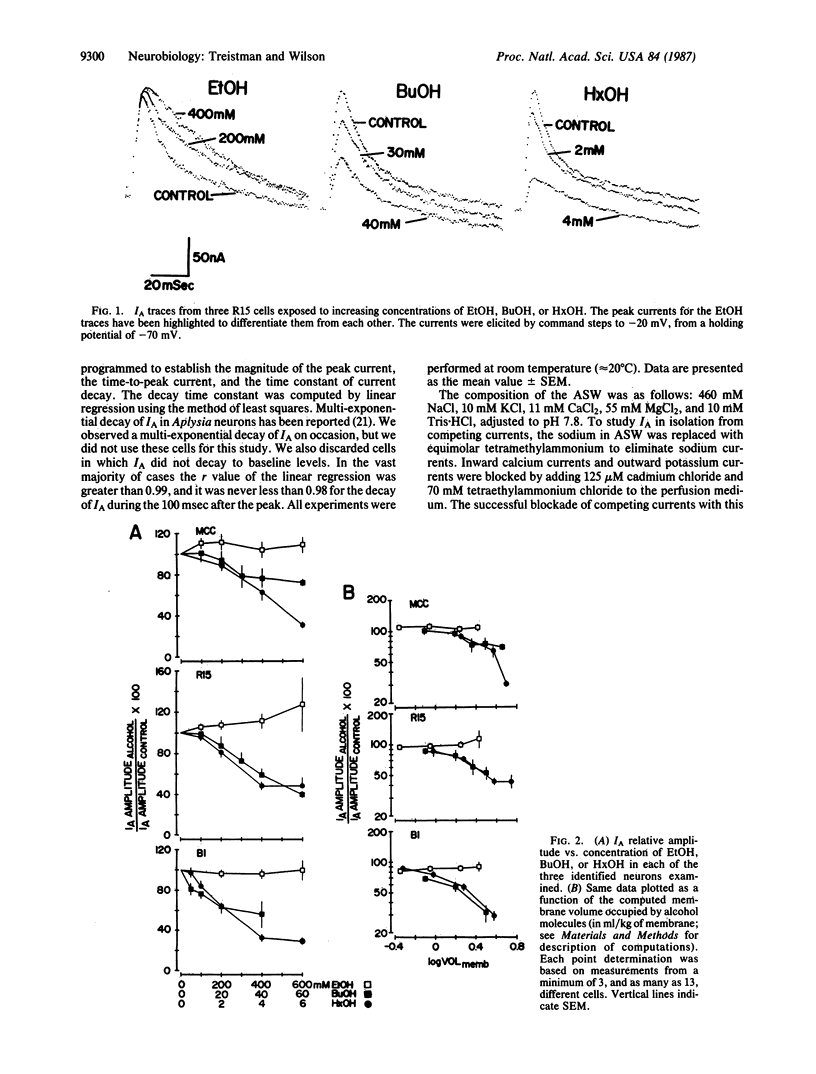
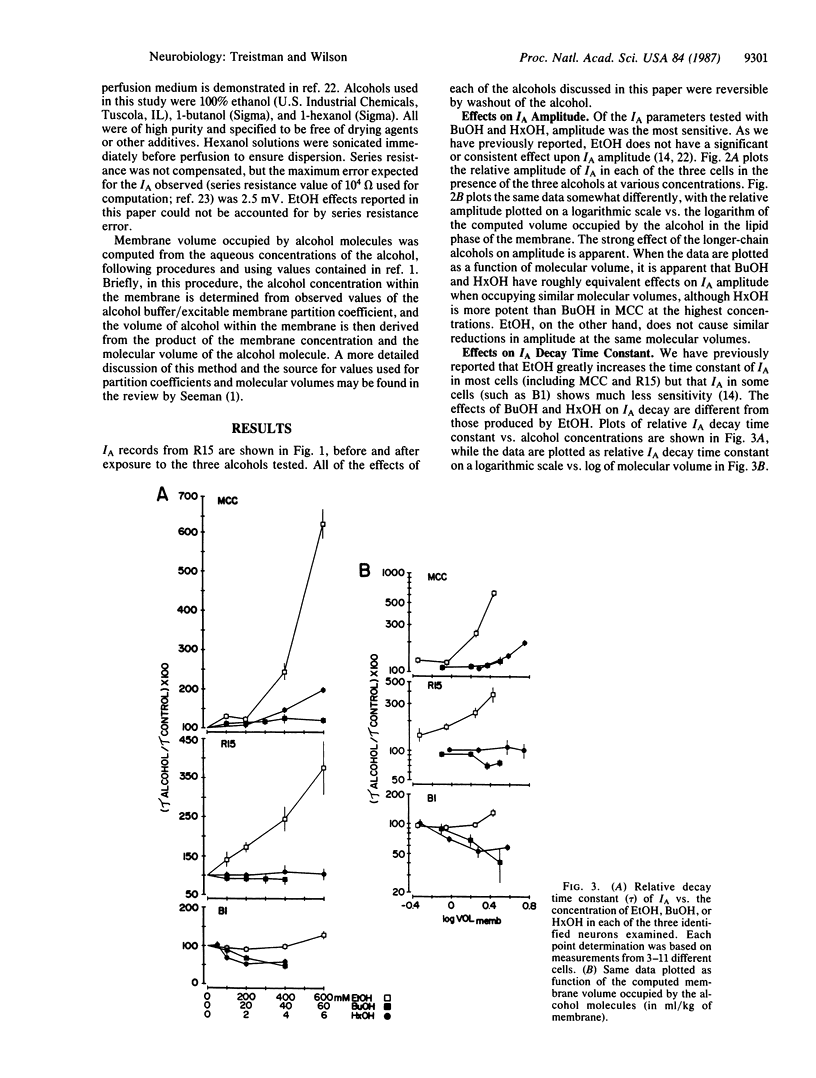
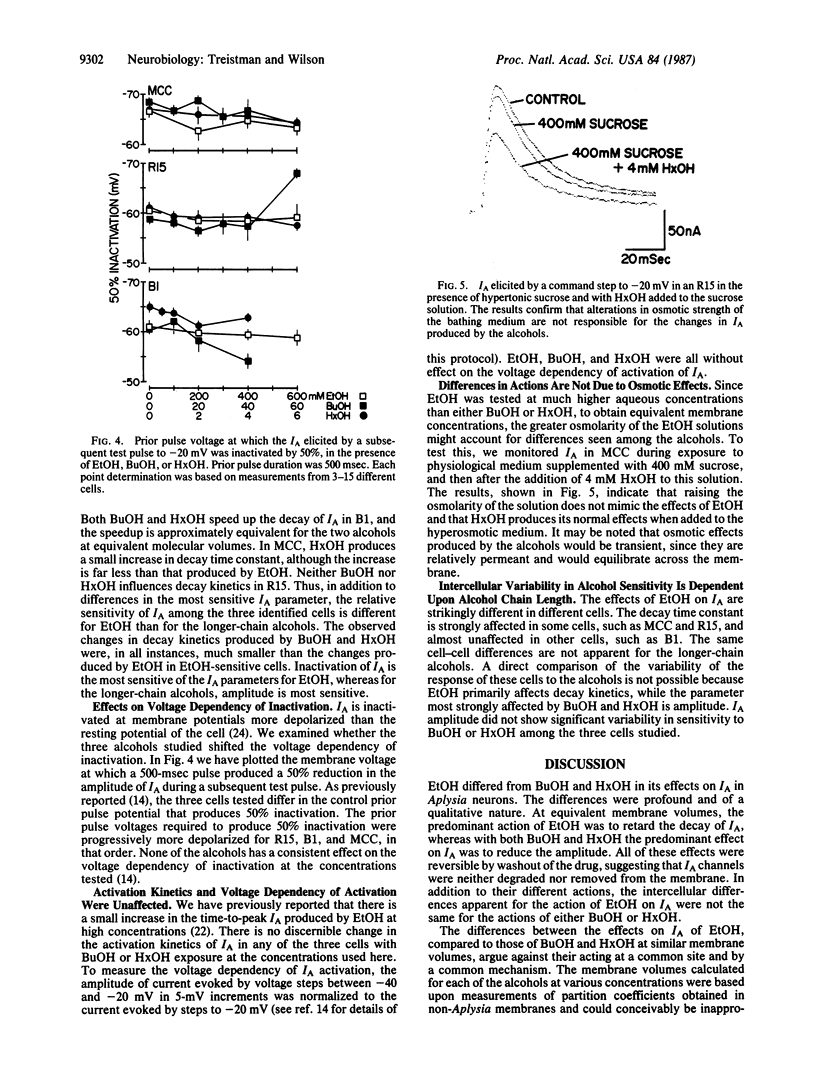
The relationship between alkanol chain length and effects on the transient potassium current, IA, were examined in three identified Aplysia californica neurons with ethanol (EtOH), butanol (BuOH), and hexanol (HxOH). Qualitative differences were found when the actions of EtOH were compared with those of the longer-chain-length alcohols. Whereas EtOH primarily affected the decay time constant of IA, having minimal effects on amplitude, BuOH and HxOH exerted their major effect on the amplitude of IA, reducing it, while their effects on decay kinetics were much less pronounced. The effects of EtOH on IA decay are cell specific among identified neurons of the Aplysia nervous system. The actions of BuOH and HxOH did not mimic these interneuronal differences. These data, coupled with data previously reported by us and others, make it unlikely that EtOH exerts its actions on IA via perturbation of a bulk lipid phase within the membrane.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG C. M., BINSTOCK L. THE EFFECTS OF SEVERAL ALCOHOLS ON THE PROPERTIES OF THE SQUID GIANT AXON. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Nov;48:265–277. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W. Ionic currents in response to membrane depolarization in an Aplysia neurone. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:115–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelain P., Robberecht P., Waelbroeck M., Camus J. C., Christophe J. Modulation by n-alkanols of rat cardiac adenylate cyclase activity. J Membr Biol. 1986;93(1):23–32. doi: 10.1007/BF01871015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Mapping of general anaesthetic target sites provides a molecular basis for cutoff effects. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):349–351. doi: 10.1038/316349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N., Schneider G. T. Effects of some aliphatic alcohols on the conductance change caused by a quantum of acetylcholine at the toad end-plate. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):409–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. Bilateral symmetry and interneuronal organization in the buccal ganglia of Aplysia. Science. 1971 Aug 6;173(3996):550–553. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3996.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Urban B. W. The action of alcohols and other non-ionic surface active substances on the sodium current of the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:411–427. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamaya H., Ma S. M., Lin S. H. Dose-dependent nonlinear response of the main phase-transition temperature of phospholipid membranes to alcohols. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(2):157–161. doi: 10.1007/BF01869933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G. Interactions between anesthetics and lipid mixtures. Normal alcohols. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2448–2454. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyama Y., Akaike N., Nishi K. Effects of n-alkanols on the calcium current of intracellularly perfused neurons of Helix aspersa. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 25;376(2):280–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge L. D., Connor J. A. A mechanism for minimizing temperature effects on repetitive firing frequency. Am J Physiol. 1978 May;234(5):C155–C161. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1978.234.5.C155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle M. J., Brown K. B., Miller K. W. Can the lipid theories of anesthesia account for the cutoff in anesthetic potency in homologous series of alcohols? Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Jan;19(1):49–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. The membrane actions of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Dec;24(4):583–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. G., Jr, Barker J. L., Smith B. M., Colburn T. R. Voltage clamping with microelectrodes. J Neurosci Methods. 1980 Dec;3(2):105–128. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(80)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solc C. K., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Single-channel and genetic analyses reveal two distinct A-type potassium channels in Drosophila. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1094–1098. doi: 10.1126/science.2437657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong J. A. Modulation of potassium current kinetics in bag cell neurons of Aplysia by an activator of adenylate cyclase. J Neurosci. 1984 Nov;4(11):2772–2783. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-11-02772.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suezaki Y., Kamaya H., Ueda I. Molecular origin of biphasic response of main phase-transition temperature of phospholipid membranes to long-chain alcohols. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 8;818(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treistman S. N. Axonal site for impulse initiation and rhythmogenesis in Aplysia pacemaker neurons. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 7;187(1):201–205. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90505-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treistman S. N., Moynihan M. M., Wolf D. E. Influence of alcohols, temperature, and region on the mobility of lipids in neuronal membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 9;898(2):109–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treistman S. N., Wilson A. Effects of ethanol on early potassium currents in Aplysia: cell specificity and influence of channel state. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3207–3214. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03207.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss K. R., Cohen J. L., Kupfermann I. Modulatory control of buccal musculature by a serotonergic neuron (metacerebral cell) in Aplysia. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Jan;41(1):181–203. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



