Abstract
Background
Similar to lipid emulsion propofol, microemulsion propofol also causes a high incidence of pain during intravenous injection. Various methods have been used to minimize the incidence and severity of pain on injection of lipid emulsion propofol. In this study, we investigated the effect of a lidocaine mixture on pain induced by microemulsion propofol injection, and sought to determine the optimal dose of lidocaine that could reduce pain on injecting a propofol-lidocaine mixture.
Methods
One hundred sixty (n = 160) patients of American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status class I or II were randomly allocated to four groups: Group A, control; Group B, 20 mg lidocaine; Group C, 30 mg lidocaine; Group D, 40 mg lidocaine. In each patient, pain on microemulsion propofol solution injection was graded as none, mild, moderate, or severe.
Results
The incidence of pain in groups A, B, C, and D was 97.5%, 80%, 65%, and 50%, respectively. Increasing the lidocaine dose significantly reduced pain (P < 0.05). One patient in Group D (2.5%) had moderate to severe pain, which was significantly lower than groups B (42.5%) and C (32.5%) (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
The lidocaine and propofol mixture is effective in alleviating pain associated with microemulsion propofol injection. Within this dose range and in this patients population, increasing lidocaine dosage significantly reduced pain during injection of microemulsion propofol.
Keywords: Injection pain, Lidocaine, Microemulsion propofol
Introduction
Lipid emulsion propofol (2,6-diisopropylphenol), an intravenous (IV) anesthetic, is commonly used for general anesthesia because of its rapid onset, short duration, and the excellent quality of recovery it provides. Nevertheless, lipid emulsion propofol has been associated with several drawbacks [1-3], and the incidence of pain secondary to lipid emulsion propofol injection varies from 59.1% to 100%, when injection is made into a vein on the dorsum of the hand [4,5].
Lipid-free microemulsion propofol (Aquafol™, Daewon Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea) was newly developed to reduce the risk of lipid solvent-related adverse drug reactions. However, pain on the injection of microemulsion propofol is still an unresolved problem [6], which not only causes distresses in patients, but also present challenges to the anesthesiologists.
The mechanism of pain on propofol injection remains unclear and requires further investigations. Although various methods have been attempted to attenuate this injection pain [4,7-17], adding lidocaine to propofol is the most popular method.
In the present study, we sought to evaluate the efficacy of lidocaine in minimizing microemulsion propofol injection pain, and to determine the optimal dose of lidocaine to be added to microemulsion propofol.
Materials and Methods
The Institutional Review Board of our institution approved the study protocol, and written consent was obtained from all patients prior to study enrollment. One hundred sixty (n = 160) American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I and II patients, aged 16-65 years, and scheduled for elective surgery, were selected. Patients with allergies to any drugs or renal, hepatic, or cardiac problems, neurologic deficits or psychiatric disorders were excluded. None of the patients was premedicated before entering the operation room, and all had a 20-gauge cannula placed into a vein on the dorsum of the nondominant hand. Standard monitoring, including electrocardiography, noninvasive arterial pressure, pulse oximetry, capnography, and body temperature, was performed throughout the procedure.
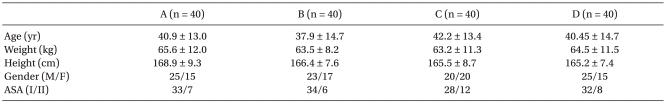
Patients were randomly allocated into one of four groups. Patients in Group A were injected intravenously with 12 ml of microemulsion propofol plus 3 ml of saline. Patients in Group B were injected intravenously with 12 ml of microemulsion propofol, 2 ml of saline, and 1 ml of 2% lidocaine (20 mg). Patients in Group C were injected intravenously with 12 ml of microemulsion propofol, 1.5 ml of saline, and 1.5 ml of 2% lidocaine (30 mg). Patients in Group D were injected intravenously with 12 ml of microemulsion propofol, 1 ml of saline, and 2 ml of 2% lidocaine (40 mg). No significant difference was observed in patient characteristics (Table 1).
Table 1.
Demographic Data
Values are presented as means ± SD. Group A receive 12 ml of microemulsion propofol plus 3 ml of saline, Group B receive 12 ml of microemulsion propofol, 2 ml of saline, and 1 ml of 2% lidocaine (20 mg), Group C receive 12 ml of microemulsion propofol, and 1.5 ml of saline, and 1.5 ml of 2% lidocaine (30 mg), Group D receive 12 ml of microemulsion propofol, 1 ml of saline, and 2 ml of 2% lidocaine (40 mg). There is no significant difference between the groups. ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status.
Propofol was drawn up into a polyethylene syringe by an assistant and made up to a total volume of 15 ml using saline, as necessary. All drugs were kept at room temperature and administered within 20 minutes of preparation. In a double-blind manner, propofol solution was manually injected by an anesthesiologist at a rate of 3 ml every 5 seconds until the patient lost consciousness. All patients were questioned every 5 seconds during the injection regarding pain or discomfort in the arm. The scale of pain was then recorded. The pain scale was defined as follows: no pain; mild pain (tolerable soreness or slight pain); moderate pain (subjective complaint between mild and severe pain); severe pain (pain causing the patient to flex his/her arm to deny injection). If the patient lost consciousness before injecting 15 ml of the solution, the remaining portion would not be administered. We also recorded the time losing consciousness. After recovering from anesthesia, patients were asked if they had any recollection of discomfort or pain during the induction period.
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS (version 17.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The differences in mean pain-intensity scores among the groups were analyzed with the chi-square test for trends. The time of unconsciousness among the groups did not follow a normal distribution, and were analyzed with one-way ANOVA using log-transformed data, followed by Scheffe post hoc test. P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
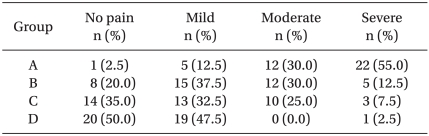
The number of patients in each group who experienced pain or discomfort is shown in Table 2. The incidence of pain in groups A (control), B, C, and D was 97.5%, 80%, 65%, and 50%, respectively. Increasing the lidocaine dosage significantly reduced pain (P < 0.05). The incidence of moderate to severe pain was 85% in the control group and that in the other groups was 42.5% (Group B), 32.5% (Group C), and 2.5% (Group D) (P < 0.05).
Table 2.
Incidence of Pain Reported at the Time of Anesthesia Induction
Group Areceive 12 ml of microemulsion propofol plus 3 ml of saline, Group B receive 12 ml of microemulsion propofol, 2 ml of saline, and 1 ml of 2% lidocaine (20 mg), Group C receive 12ml of microemulsion propofol, and 1.5 ml of saline, and 1.5 ml of 2% lidocaine (30 mg), Group D receive 12 ml of microemulsion propofol, 1 ml of saline, and 2 ml of 2% lidocaine (40 mg).
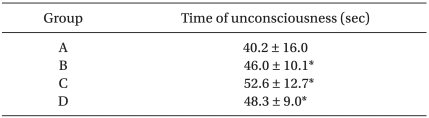
Loss of consciousness was more rapid in Group A than in all other groups (P < 0.05, Table 3). In the recovery room, only one patient who reported pain was unable to recall pain scale and, all patients except one reported the same pain scale at the time of anesthesia induction.
Table 3.
The Time of Unconsciousness
Values are presented as mean ± SD. Group Areceive 12 ml of microemulsion propofol plus 3 ml of saline, Group B receive 12 ml of microemulsion propofol, 2 ml of saline, and 1 ml of 2% lidocaine (20 mg), Group C receive 12 ml of microemulsion propofol, and 1.5 ml of saline, and 1.5 ml of 2% lidocaine (30 mg), Group D receive 12 ml of microemulsion propofol, 1 ml of saline, and 2 ml of 2% lidocaine (40 mg). *P < 0.05 compared with Group A.
Discussion
Microemulsion propofol, consists of 1% propofol, 8% polyethylene glycol 660 hydroxystearate (Solutol HS 15, BASF Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea), and 5% tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol polyethylene glycol ether (Glycofurol, Roche, Basle, Switzerland), is thermodynamically stable, because it does not contain a long chain triglyceride emulsion, unlike the original lipid emulsion propofol. This formulation avoids the risk of lipid solvent-related adverse drug reactions, such as fat embolism, postoperative infection, hypertriglyceridemia and pancreatitis [1-3]. However, similar to other existing propofol formulations, newly developed microemulsion propofol still causes pain on injection. In addition, microemulsion propofol produces more frequent (69.7-89%) and severe pain (51%) upon injection than long-chain triglyceride propofol [6,18]. In our study the overall incidence of pain was 97.5%, and 55% of patient experienced severe pain.
The concentration of free propofol in the aqueous phase and activation of the enzymatic cascade of the plasma kallikreinkinin system are associated with the intensity of pain upon injection [19,20]. Higher aqueous free propofol concentrations of microemulsion propofol produce more frequent and severe pain [6]. However, the mechanism of pain upon injection of propofol is still unclear and requires further investigation. Various methods have been attempted to attenuate this injection pain. They include prior administration of opioid [7], lidocaine [7], prilocaine [8], thiopental [9], metocloproamide [10], ondansetron [11], ephedrine [12], the addition of 10-40 mg lidocaine to the propofol emulsion [4,13,14], cooling the propofol to 4℃ before injection [15], and making use of the antecubital fossa vein for injection [16]. These methods do not eradicate pain completely, but do decrease the incidence or severity of injection pain. To date, adding lidocaine to propofol is the most popular method to reduce injection pain of lipid emulsion propofol. Indeed, 30 mg of lidocaine is the optimal dose typically used to reduce pain on injection [17]. Lidocaine mixed with lipid emulsion propofol reduces its pH, lowers propofol concentration in the aqueous phase, and results in reduced pain [21]. Lidocaine mixed with propofol is more effective than pretreatment with lidocaine for decreasing propofol injection pain [16]. The pH of microemulsion propofol (7.51 ± 0.01) is similar to that of the lipid emulsion, and aqueous free propofol concentration is seven times higher than that of lipid emulsion [6].
It is well accepted that injecting through a large vein, such as the antecubital fossa vein, is an effective way to reduce pain on propofol injection. This is presumably because the drug contacts the mid-stream in the venous lumen and due to reduced contact with the sensitive vein wall. The drug may also be buffered effectively by the blood, with which it can mix freely [16]. Nonetheless, a cannula is usually placed into a vein on the dorsum of the nondominant hand, because many anesthesiologists prefer ease of access, ease of detecting extravasation, and there is a low incidence of neural or arterial damage. Premedications, such as benzodiazepine, analgesic opioid, and anticholinergics appears to have little effect on the incidence of pain during propofol injection [22-24], but other premedications, such as hydroxyzine may reduce pain severity [25], so we did not premedicate.
Lidocaine may induce cardiovascular, neurotoxic and other complications. However, less than 1 mg/kg can be used safely [26]. Thus, our study applied 20-40 mg of lidocaine. The results of this study show the effect of adding lidocaine to microemulsion propofol in reducing pain during injection.
More study is needed, as the loss of consciousness was more rapid in Group A than in all other groups. Similar to our findings, two other studies suggested decreased anesthetic potency of propofol when administered as lidocaine mixed with propofol in rats [27] and women [10]. In contrast to our finding, two studies showed clinically insignificant effects in the study ranged from 200 : 10 to 200 : 50 propofol/lidocaine mg ratio [28] and 10 : 1 propofol 1%/lodocaine1% volume ratio [29].
In conclusion, a lidocaine and propofol mixture is effective in alleviating pain associated with microemulsion propofol injection. Within this dose range and in this patients population, increasing lidocaine dosage significantly reduced pain during injection of microemulsion propofol.
Footnotes
This work was supported by Grant from Inje University, 2009.
References
- 1.Bennett SN, McNeil MM, Bland LA, Arduino MJ, Villarino ME, Perrotta DM, et al. Postoperative infections traced to contamination of an intravenous anesthetic, propofol. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:147–154. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199507203330303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Devlin JW, Lau AK, Tanios MA. Propofol-associated hypertriglyceridemia and pancreatitis in the intensive care unit: an analysis of frequency and risk factors. Pharmacotherapy. 2005;25:1348–1352. doi: 10.1592/phco.2005.25.10.1348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kim KM, Choi BM, Park SW, Lee SH, Christensen LV, Zhou J, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of propofol microemulsion and lipid emulsion after an intravenous bolus and variable rate infusion. Anesthesiology. 2007;106:924–934. doi: 10.1097/01.anes.0000265151.78943.af. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Johnson RA, Harper NJ, Chadwick S, Vohra A. Pain on injection of propofol: methods of alleviation. Anaesthesia. 1990;45:439–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1990.tb14328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hynynen M, Korttila K, Tammisto T. Pain on i.v. injection of propofol (ICI 35 868) in emulsion formulation. Short communication. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1985;29:651–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1985.tb02274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sim JY, Lee SH, Park DY, Jung JA, Ki KH, Lee DH, et al. Pain on injection with microemulsion propofol. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009;67:316–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03358.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kobayashi Y, Naganuma R, Seki S, Aketa K, Ichimiya T, Namiki A. Reduction of pain on injection of propofol: a comparison of fentanyl with lidocaine. Masui. 1998;47:963–967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Eriksson M. Prilocaine reduces injection pain caused by propofol. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1995;39:210–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1995.tb04045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Agarwal A, Ansari MF, Gupta D, Pandey R, Raza M, Singh PK, et al. Pretreatment with thiopental for prevention of pain associated with propofol injection. Anesth Analg. 2004;98:683–686. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000103266.73568.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fujii Y, Uemura A. Effect of metoclopramide on pain on injection of propofol. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2004;32:653–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ambesh SP, Dubey PK, Sinha PK. Ondansetron pretreatment to alleviate pain on propofol injection: a randomized, controlled, double-blinded study. Anesth Analg. 1999;89:197–199. doi: 10.1097/00000539-199907000-00035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cheong MA, Kim KS, Choi WJ. Ephedrine reduces the pain from propofol injection. Anesth Analg. 2002;95:1293–1296. doi: 10.1097/00000539-200211000-00035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gehan G, Karoubi P, Quinet F, Leroy A, Rathat C, Pourriat JL. Optimal dose of lignocaine for preventing pain on injection of propofol. Br J Anaesth. 1991;66:324–326. doi: 10.1093/bja/66.3.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Helbo-Hansen S, Westergaard V, Krogh BL, Svendsen HP. The reduction of pain on injection of propofol: the effect of addition of lignocaine. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1988;32:502–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1988.tb02774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.McCrirrick A, Hunter S. Pain on injection of propofol: the effect of injectate temperature. Anaesthesia. 1990;45:443–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1990.tb14329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Scott RP, Saunders DA, Norman J. Propofol: clinical strategies for preventing the pain of injection. Anaesthesia. 1988;43:492–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1988.tb06641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gajraj NM, Nathanson MH. Preventing pain during injection of propofol: the optimal dose of lidocaine. J Clin Anesth. 1996;8:575–577. doi: 10.1016/s0952-8180(96)00133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dubey PK, Kumar A. Pain on injection of lipid-free propofol and propofol emulsion containing medium-chain triglyceride: a comparative study. Anesth Analg. 2005;101:1060–1062. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000166951.72702.05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Klement W, Arndt JO. Pain on injection of propofol: effects of concentration and diluent. Br J Anaesth. 1991;67:281–284. doi: 10.1093/bja/67.3.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Doenicke AW, Roizen MF, Rau J, Kellermann W, Babl J. Reducing pain during propofol injection: the role of the solvent. Anesth Analg. 1996;82:472–474. doi: 10.1097/00000539-199603000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Eriksson M, Englesson S, Niklasson F, Hartvig P. Effect of lignocaine and pH on propofol-induced pain. Br J Anaesth. 1997;78:502–506. doi: 10.1093/bja/78.5.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Fragen RJ, de Grood PM, Robertson EN, Booij LH, Crul JF. Effects of premedication on diprivan induction. Br J Anaesth. 1982;54:913–916. doi: 10.1093/bja/54.9.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Briggs LP, Bahar M, Beers HT, Clarke RS, Dundee JW, Wright PJ, et al. Effect of preanaesthetic medication on anaesthesia with ICI 35, 868. Br J Anaesth. 1982;54:303–306. doi: 10.1093/bja/54.3.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Briggs LP, White M. The effects of premedication on anaesthesia with propofol ('Diprivan') Postgrad Med J. 1985;61(Suppl 3):35–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bilaine J, Desmonts JM. Effect of premedication with atropine or hydroxyzine on induction and maintenance of anaesthesia with propofol ('Diprivan') Postgrad Med J. 1985;61(Suppl 3):38–39. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nightingale P, Healy TE, Hargreaves J, McGuinness K, Kay B. Propofol in emulsion form: induction characteristics and venous sequelae. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1985;2:361–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Eriksson M, Englesson S, Hörte I, Hartvig P. The anaesthetic potency of propofol in the rat is reduced by simultaneous intravenous administration of lignocaine. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1999;16:315–319. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2346.1999.00489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lilley EM, Isert PR, Carasso ML, Kennedy RA. The effect of the addition of lignocaine on propofol emulsion stability. Anaesthesia. 1996;51:815–818. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1996.tb12607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tan LH, Hwang NC. The effect of mixing lidocaine with propofol on the dose of propofol required for induction of anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2003;97:461–464. doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000066357.63011.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]