Abstract
Both early teen marriage and dropping out of high school have historically been associated with a variety of negative outcomes, including higher poverty rates throughout life. Are these negative outcomes due to preexisting differences, or do they represent the causal effect of marriage and schooling choices? To better understand the true personal and societal consequences, in this article, I use an instrumental variables (IV) approach that takes advantage of variation in state laws regulating the age at which individuals are allowed to marry, drop out of school, and begin work. The baseline IV estimate indicates that a woman who marries young is 31 percentage points more likely to live in poverty when she is older. Similarly, a woman who drops out of school is 11 percentage points more likely to be poor. The results are robust to a variety of alternative specifications and estimation methods, including limited information maximum likelihood (LIML) estimation and a control function approach. While grouped ordinary least squares (OLS) estimates for the early teen marriage variable are also large, OLS estimates based on individual-level data are small, consistent with a large amount of measurement error.
Historically, individuals were allowed to enter into a marriage contract at a very young age. In Ancient Rome, the appropriate minimum age was regarded as 14 for males and 12 for females. When Rome became Christianized, these age minimums were adopted into the ecclesiastical law of the Catholic Church. This canon law governed most marriages in Western Europe until the Reformation. When England broke away from the Catholic Church, the Anglican Church carried with it the same minimum age requirements for the prospective bride and groom. The minimum age requirements of 12 and 14 were eventually written into English civil law. By default, these provisions became the minimum marriage ages in colonial America. These common laws inherited from the British remained in force in America unless a specific state law was enacted to replace them (see “Marriage Law,” Encyclopædia Britannica 2005; http://www.britannica.com).
While Roman, Catholic, English, and early American law may have allowed marriage at 12 for girls and 14 for boys, many questioned the advisability of such early unions. Researchers and policymakers around the turn of the twentieth century recognized that teens may be especially ill-prepared to assume the familial responsibilities and financial pressures associated with marriage.1 As a result of the changing economic and social landscape of the United States, in the latter part of the nineteenth century and throughout the twentieth century, individual states began to slowly raise the minimum legal age at which individuals were allowed to marry. In the United States, as in most developed countries, age restrictions have been revised upward so that they are now between 15 and 21 years of age.
During this same time period, dramatic changes were also occurring in the educational system of the United States (see Goldin 1998, 1999; Goldin and Katz 1997, 2003; Lleras-Muney 2002). Free public schooling at the elementary level spread across the United States in the middle of the nineteenth century, and free secondary schooling proliferated in the early part of the twentieth century. As secondary schooling became more commonplace, states began to pass compulsory schooling laws. States often also passed child labor laws that stipulated minimum age or schooling requirements before a work permit would be granted. These state-specific compulsory schooling and child labor laws are correlated with the legal restrictions on marriage age, indicating that it might be important to consider the impact of all the laws simultaneously.
There are at least two rationales often given for the use of state laws as policy instruments to limit teenagers’ choices. The first argument is that teens do not accurately compare short-run benefits versus long-run costs. If teens are making myopic decisions, restrictive state laws could prevent decisions they will later regret. It is also argued that the adverse effects associated with teenagers’ choices impose external costs on the rest of society. If these effects can be prevented, external costs (such as higher welfare expenditures) would also argue for restrictive state laws. Both teenage marriage and dropping out of high school are closely associated with a variety of negative outcomes, including poverty later in life. To assess the relevance of either argument, however, it is important to know whether the observed effects are causal.
Any observed negative effects may be due to preexisting differences rather than a causal relationship between teen marriage (or schooling choices) and adverse adult outcomes. Women who marry as teens or drop out of school may come from more disadvantaged backgrounds or possess other unobserved characteristics that would naturally lead to worse outcomes. For example, teens choosing to marry young might have lower unobserved earnings ability, making it hard to draw conclusions about the causal relationship between teenage marriage and poverty.
To identify the effect of a teenager’s marriage and schooling choices on future poverty, I use state-specific marriage, schooling, and child labor laws as instruments. Variation in these laws across states and over time can be used to identify the causal impact that teen marriage and high school completion have on future economic well-being. Although compulsory schooling laws have been used as instruments in a variety of settings, this appears to be the first time marriage laws have been used as instruments. The idea of the marriage law instrument is that states with restrictive marriage laws will prevent some teenagers from marrying who would have married young had they lived in a state with more permissive laws.
Using the marriage, schooling, and labor laws affecting teens as instruments for early marriage and high school completion, I find strong negative effects for both variables on future poverty status. The baseline instrumental variables (IV) estimates imply that a woman who marries young is 31 percentage points more likely to live in poverty when she is older. Similarly, a woman who drops out of school is 11 percentage points more likely to be living in a family whose income is below the poverty line. The IV results are robust to a variety of alternative specifications and estimation methods, including limited information maximum likelihood (LIML) estimation and a control function approach. In comparison, the ordinary least squares (OLS) estimates are very sensitive to how the data is aggregated, particularly for the early marriage variable. OLS estimates using grouped data are also large, while OLS estimates using individual-level data indicate a small effect for early teen marriage. Auxiliary data indicate a large amount of measurement error in the early marriage variable, suggesting the presence of attenuation bias in the individual-level OLS estimates.
The remainder of the article proceeds as follows. I first briefly review the negative outcomes associated with teenage marriage and dropping out of school and discuss alternative perspectives on why teens might make these decisions. The following section describes the data and presents OLS estimates. The next section discusses the early marriage, compulsory schooling, and child labor laws that will be used as instruments. I then present the instrumental variable estimates and conduct several specification and robustness checks, including a discussion of measurement error issues and a reconciliation with the literature on teenage childbearing.
EARLY MARRIAGE AND DROPOUT DECISIONS
Previous research points to a variety of social, family, health, and financial outcomes that are strongly correlated with early teen marriage and low education. Women who marry while in their teens are two-thirds more likely to divorce within 15 years of their wedding compared with women who postpone marriage. In addition, women who marry in their teens tend to have more children and to have those children earlier.2 Teenage marriage is also associated with much lower education levels; women who marry before the age of 19 are 50% more likely to drop out of high school and four times less likely to graduate from college (U.S. census data tabulations; Klepinger, Lundberg, and Plotnick 1999; Ribar 1994). There is an even larger literature documenting the negative outcomes associated with low education, including lower wages and higher unemployment rates (Katz and Autor 1999), worse health (Berger and Leigh 1989; Lleras-Muney 2005), and higher crime rates (Lochner and Moretti 2004).
The negative outcomes associated with early marriage and dropping out of high school have the potential to affect not only the individual making the decision but also her children and the rest of society. For example, a high divorce rate combined with low wages and a larger family size increases the number of children living in poverty and receiving state assistance (Bane 1986; Moffit 1992). Children of teenage mothers also have lower birth weights, have a higher rate of infant homicide, are often the victims of child abuse and neglect, have academic and behavioral problems in school, and are more likely to engage in crime (Goerge and Lee 1997; Overpeck et al. 1998; Hotz, McElroy, and Sanders 1997; Hunt 2003).
Given these negative outcomes, why would an individual choose to marry young or drop out of high school? Traditional economic analysis focuses on rational and forward-looking individuals (Becker 1974; Becker, Landes, and Michael 1977). A woman chooses whether to accept a teen marriage offer (or drop out of school) based on the relative attractiveness of her alternatives. In this paradigm, a young woman fully anticipates the future consequences of her decisions, subject to some uncertainty about how things will actually turn out. Women who marry early can have a high likelihood of ending up poor later in life, yet can still be optimizing. However, even if the individual is optimizing, society might still be concerned about the effects of poverty on her children and the costs associated with transfer programs.
An alternative perspective for why teens marry young is based on psychological and behavioral economic models. In a discussion of risky behavior among youth, O’Donoghue and Rabin (2001) explored extensions to the traditional approach that can help in modeling the decisions of adolescents. They argued that teens may not accurately compare short-run benefits versus long-run costs because teens discount the future too heavily. Two closely related explanations are that teens have time-inconsistent preferences or projection bias. These models provide an explanation for why teenagers engage in risky behavior, such as drinking, smoking, drug use, unprotected sex, and criminal activity, even though these behaviors can have substantial negative consequences in the long run (Gruber 2001). Looking at schooling decisions, Oreopoulos (2007) argued that myopia helps explain why some teens drop out of school early. The various psychological explanations for poor decision-making by youth generally share the feature that teens make choices they will later regret.
Although teen marriage and low education are associated with a variety of below-average outcomes, it is not necessarily true that these choices caused the bad outcomes. For example, differences may be due to preexisting characteristics of women who marry young versus later, rather than any causal relationship between teen marriage and negative adult outcomes. To my knowledge, no previous research has studied the causal effect of early marriage. Yet, understanding the causal effect of teens’ choices is key for understanding whether they are making choices they will later regret or which impose costs on their children and society. If teenage marriage and dropping out of high school are largely driven by unobserved personal characteristics that are the primary cause of negative outcomes, legal interventions to prevent these choices may make little difference. However, if strong causal effects exist, then state laws restricting teenagers’ choices have the potential to greatly lessen the chances of future poverty.
While issues of causality have received little attention in the context of teenage marriage, a related line of research has attempted to disentangle the effects of teenage child-bearing on education and wages from preexisting differences between those who parent early and those who delay childbearing. Early research using OLS revealed large and significant consequences associated with teenage childbearing (Moore and Waite 1977). Subsequent approaches attempting to deal with selection bias have reached disparate conclusions. For example, studies by Angrist and Evans (1996), Grogger and Bronars (1993), and Klepinger, Lundberg, and Plotnick (1999) that used a variety of instrumental variables concluded that teenage childbearing has negative consequences. However, Geronimus and Korenman (1992), using sister fixed effects, and Hotz, McElroy, and Sanders (1997 and Hotz, McElroy, and Sanders (2005) and Hotz, Mullin, and Sanders (1997), using random miscarriages as an instrument, found little evidence of a negative effect. The debate is ongoing, with recent work by Ashcraft and Lang (2006) and Fletcher and Wolfe (2008) using variations on the miscarriage instrument and finding negative effects.
DATA AND OLS ESTIMATES
Data
The data for this article combine information on state-specific marriage, schooling, and labor laws with data from the 1960, 1970, and 1980 decennial censuses (Ruggles et al. 2004). Supplementary data is obtained from Vital Statistics marriage certificate data and the National Fertility Surveys. The U.S. census data are ideal for obtaining precise information about teenage marriage at the state level because of the large number of individuals in the survey. For 7% of the entire U.S. population in 1980 (state, metro, and urban/rural samples), 3% in 1970 (Form 1 state, neighborhood, and metro samples), and 1% in 1960 (general sample), the census has information regarding age at first marriage, along with limited demographic, educational attainment, and economic variables.
Even though the census data sets are cross-sectional surveys conducted every 10 years, they contain information about women from a variety of cohorts. Because the surveys ask retrospective questions about age at first marriage and women are different ages when the survey is administered, a large data set with time-varying information can be created from the cross sections. All three census years are combined to create a data set for women born between 1920 and 1954. These women were age 15 during the period 1935 to 1969, which corresponds to the approximate age they were at risk for becoming early teen brides. The sample is further restricted to U.S.-born women who were between the ages of 20 and 60 when the census was taken. Data are also restricted to the 41 states with available data on marriage laws, compulsory schooling laws, and child labor laws.
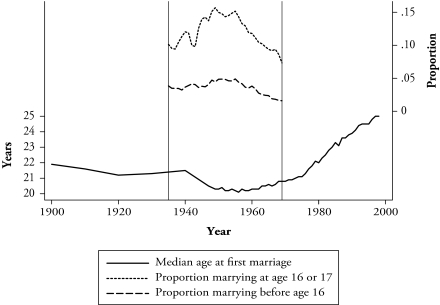
The census data reveal that early teen marriage, which I define as marrying before the age of 16, has historically accounted for a nontrivial fraction of all marriages in the United States. In the sample used in this article, 3.5% of women reported first marrying under the age of 16,3 compared with 11.9% of women first marrying at ages 16 or 17 (4.5% at age 16 and 7.4% at age 17). The top two series in Figure 1 graph the fraction of women marrying at these ages over time. The percentage of early teen marriages starts out at 3.8% for the 1935 cohort, reaches a peak of 4.9% in the early 1950s, and then declines to 1.6% by the end of the sample. This pattern is mirrored for the fraction of women marrying at age 16 or 17.
Figure 1.
Proportion of Women Marrying Young and Women’s Median Age at First Marriage
Notes: Data on the fraction of teenage marriages are from the author’s tabulations of U.S. census data. All other data series are from various tables in Carter et al. (2006). Vertical lines denote the time period analyzed in this article (1935–1969).
To put these patterns into perspective, the bottom series in Figure 1 graphs the median age at first marriage for a long time horizon. The plot reveals that the time period of interest in this article (1935–1969) corresponds to a period in history when marriage ages were remarkably low by historical standards. The median age at marriage for women fell almost two years from the start of the century to reach a low of 20.1 in 1956. Since the 1970s, the median age has risen dramatically, so that by the end of the 1990s, the median age was 25.
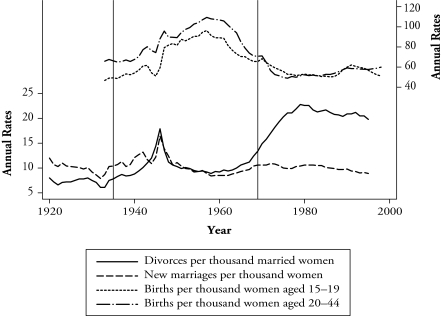
Figure 2 plots other well-known secular trends that were also occurring in the middle of the 1900s. There was a sharp decline in overall fertility during World War II, followed by a dramatic increase in the postwar period. Fertility started to decline by the end of the 1950s, reaching a low in the late 1970s, during which the rate was half that of the peak. The trends in the top half of Figure 2—couples starting their marriages and bearing children sooner in the postwar period—are recognized as being largely responsible for the baby boom between 1946 and 1964. Similarly, the baby bust resulted from delayed marriage and fertility. The same fertility pattern holds for teenage childbearing as well. At the peak in 1957, there were 96 births per 1,000 15- to 19-year-old women in the United States.4 A comparison of Figures 1 and 2 makes apparent that the trends in early teen marriage coincide with those for teen childbearing.
Figure 2.
Marriage, Divorce, and Fertility Rates Over Time
Notes: Data are from various tables in Carter et al. (2006). Vertical lines denote the time period analyzed in this article (1935–1969).
To add further perspective, the bottom half of Figure 2 plots marriage and divorce rates over time. Marriage and divorce rates fell during the Great Depression and spiked following World War II. Divorce rates also rose sharply starting in the late 1960s before reaching a plateau in the 1980s. Further insights into the changes in and possible causes of these dramatic shifts in marriage and divorce can be found in Stevenson and Wolfers (2007).
These secular trends have several implications for the current study. First, it will be important to allow for different effects by time period. In the regression analyses that follow, separate dummy variables will be included for year of birth, current age (in year intervals), and census year. Second, the findings should be interpreted in the appropriate historical context because the cultural, legal, and economic environment is very different today.
In addition to early marriage, another key variable for the analysis is the high school dropout rate. Carter et al. (2006) documented that dropout rates have fallen over time. Of the women born between 1921 and 1930, 52.3% had not finished high school by age 19. This percentage falls monotonically over time, so that for women born between 1971 and 1980, only 15.1% of 19-year-olds had not finished high school.5 Completion rates rise as women age and have the opportunity to go back to school; for example, women in their 30s who were born between 1921 and 1930 have a dropout rate of 42.9%.
As a summary measure of well-being, I use a variable that indicates whether the woman lives in a poor family according to the government definition of poverty. Whether a woman lives in poverty depends on family income, family size (including the number of children in the family), and whether the householder is over age 65. Approximately 10% of all women in my sample are classified as poor, with this rate more than doubling for those who marry before the age of 16.
This poverty variable captures the cumulative impact of a variety of past decisions by a woman. As such, it is a useful summary measure of the consequences of early marriage and dropping out of high school. For example, a woman who marries young may have additional children, gain less work experience, and divorce sooner, all of which likely increase the chances of future poverty. Although individuals can enter and exit poverty throughout the life cycle, Bane and Ellwood (1986) found that “the majority of poor persons at any time are in the midst of a rather long spell of poverty.” In addition, Rank and Hirschl (2001) found that once poverty occurs, it is likely to occur again.
The large fraction of early teen marriages for the women in the sample is ideal for this article. There are over 140,000 of these early teen marriages in the combined census sample. The large number of high school dropouts and the dramatic decrease over time, which does not parallel the pattern in early marriage rates, make the data well-suited to separate the two effects. Perhaps the biggest advantage of the data, however, is that this era of high teen marriage rates and declining dropout rates coincides with a time period when many states were revising their early marriage, compulsory schooling, and child labor laws. These laws are discussed in the next section, after the OLS estimates are presented.
OLS Estimates
How are poverty, early teen marriage, and dropping out of high school related? I begin by presenting OLS estimates of the effect of early teen marriage and dropout status on poverty. The top panel of Table 1 displays results for individual-level data, which include more than 3 million observations. The estimates in column 1 do not include any controls and indicate that early marriage and dropping out of high school increase the chance of poverty by around 4% and 13%, respectively. Including additional control variables in columns 2–4 decreases the estimates slightly, to around 3% and 12%, respectively. These estimates suggest that dropping out of high school has a sizable impact on future poverty, but that teen marriage has relatively small effect.
Table 1.
OLS Estimates of the Effect of Early Teen Marriage and Dropping Out of High School on Poverty, Using Individual and Grouped Data (dependent variable = poor)
| OLS Estimates |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
| Early Teen Marriage | 0.043* (0.005) | 0.037* (0.003) | 0.033* (0.002) | 0.032* (0.002) | 0.029* (0.002) |
| High School Dropout | 0.134* (0.010) | 0.125* (0.007) | 0.122* (0.007) | 0.121* (0.007) | 0.123* (0.007) |
| Control Variables | |||||
| Census year, race, and age dummy variables | X | X | X | X | |
| State of birth and birth cohort dummy variables | X | X | X | ||
| Region of birth trends | X | X | |||
| Allocated Observations Included | X | ||||
| R2 | .041 | .079 | .082 | .082 | .084 |
| Number of observations | 3,256,434 | 3,256,434 | 3,256,434 | 3,256,434 | 3,489,385 |
| Grouped OLS Estimates |
|||||
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
| Early Teen Marriage | 1.065* (0.135) | 0.453* (0.090) | 0.329* (0.063) | 0.264* (0.054) | 0.071† (0.041) |
| High School Dropout | 0.026 (0.022) | 0.119* (0.029) | 0.166* (0.024) | 0.129* (0.035) | 0.136* (0.033) |
| Control Variables | |||||
| Census year, race, and age dummy variables | X | X | X | X | |
| State of birth and birth cohort dummy variables | X | X | X | ||
| Region of birth trends | X | X | |||
| Allocated Observations Included | X | ||||
| R2 | .421 | .815 | .871 | .874 | .884 |
| Observations (number of cells) | 3,567 | 3,567 | 3,567 | 3,567 | 3,567 |
Notes: Standard errors, adjusted for clustering by state of birth to account for arbitrary autocorrelation over time, are shown in parentheses. Data are from the 1960, 1970, and 1980 U.S. censuses. The sample is restricted to women between the ages of 20 and 60 who were born in one of the 41 states with valid marriage, compulsory schooling, and child labor laws. The dependent variable, poor, is a dummy variable equal to 1 if the woman currently lives in a family that is at or below the poverty line. Early teen marriage is defined as marrying between the ages of 12 and 15 (14 or 15 in the 1970 and 1980 censuses), and high school dropout is defined as fewer than 12 years of completed schooling. Year dummy variables are indicators for each of the three census years, race is a dummy variable for whether the respondent is white, and current age dummy variables are single-year indicators for a woman’s current age. Dummy variables for state of birth are indicators for each of the 41 states, and dummy variables for cohort of birth are single-year indicators for each birth cohort. Region of birth trends are separate linear cohort year trends for each of the four birth regions. In the second panel, the data are aggregated to state of birth × year of birth × census year cell means. Allocated observations refer to observations whose value for the variable age at first marriage has been logically edited or hot decked by the Census Bureau.
p < .10;
p < .05
In contrast to the individual-level estimates, the grouped data results in the bottom panel of Table 1 present a very different picture. In the bottom panel, the data is aggregated to state of birth × year of birth × census year cell means. In contrast to OLS, the estimates in columns 1–4 are much larger, and the inclusion of controls affects both the dropout and teenage marriage coefficients. After including controls for (1) census year, race, and current age dummy variables, (2) state of birth and birth cohort dummy variables, and (3) region of birth trends, the coefficients on early teen marriage and dropout are 26.4 and 12.9, respectively. These coefficients are large; they imply a 26% increase in future poverty for early teen brides and a 13% increase for those who do not finish high school. A key question is whether there are additional omitted variables that would drive either of these coefficients closer to zero.
Column 5 expands the sample to include allocated observations. The Census Bureau allocates values for age at first marriage when data are missing or inconsistent. First, a logical edit is performed if possible, using information from other variables and other household members. When this is not possible, the census uses a hot-deck allocation method to assign a value from an individual with similar characteristics.6 Allocation rates are much higher for early teen marriages compared with the rest of the sample, especially in 1980. Additionally, the hot-deck procedure used in 1980 (and to a lesser extent in 1960 and 1970) suffers from bracketing issues for early teen marriages, with sharp spikes in marriage rates occurring for women whose current age is a multiple of five. When these allocated marriages are included in column 5, the coefficient on early teen marriages drops, particularly in the grouped OLS panel. As I show later, these allocated marriages do not have much of an impact on the IV estimates, suggesting that these allocated marriages are largely noise. Therefore, unless otherwise noted, all allocated marriages are dropped from the data.
What explains the different estimates for early teen marriage when comparing the individual versus grouped data in Table 1? An analysis of auxiliary data later in the article indicates a large amount of measurement error in the early marriage variable. This suggests the presence of attenuation bias in the individual-level OLS estimates, whereas aggregation should minimize this type of bias. Of course, if appropriate instruments can be found, misspecification due to omitted variables or measurement error can be eliminated at both the individual and aggregate level. As I show later, the individual-level IV and aggregate IV estimates are both large and remarkably similar.
STATE LAWS AND THEIR EFFECT ON EARLY MARRIAGE AND SCHOOLING
State Marriage, Schooling, and Labor Laws
The OLS estimates presented in the previous section potentially suffer from both omitted variable bias and measurement error. One solution to these problems is to use an instrumental variables approach. Ideally, instruments would induce exogenous variation in early teen marriage but would be uncorrelated with unobserved characteristics that affect both poverty and the decision to marry young. Similarly, the instruments would induce exogenous variation in high school graduation but be orthogonal to the error term in the poverty equation. I use changes in state marriage, schooling, and labor laws over time as instruments for early marriage and dropping out of high school. By preventing some teens who would like to marry or drop out of high school from doing so, these legal restrictions can help identify the causal effects on poverty free of selection bias.
In the United States, wide variation has historically existed regarding the minimum age individuals are legally allowed to marry. The laws that regulate teenage marriage have appeared in the World Almanac and Book of Facts starting in the late 1800s. Since 1935, information has consistently been reported on the minimum marriage age with parental (or court) consent, separately for males and females. I collected this information annually for the years 1935 to 1969 for the 41 states with reliable information on marriage laws during this time period.7
There are two sets of laws specifying minimum age requirements for marriage. The first is the minimum age with parental (or court) consent, while the other is the minimum age without parental consent. In this article, I focus on the marriage age laws with parental consent, partly because there is little variation over time or across states in the laws without parental consent during the period of my data. Prior to 1971, approximately 80% of states specified an age of 18 for marriage without parental consent for women, and approximately 85% specified an age of 21 for men. In 1971, men and women were granted the right to vote at age 18, which seems to have spurred most states to change their statutes for the legal age of marriage without parental consent for both men and women to age 18. (For a discussion and an interesting analysis of these laws, see Blank, Charles, and Sallee 2008.)
Laws with parental consent do not eliminate all early teenage marriages. Some teens may find ways to lie about their age or may travel to states with lower age requirements to get married. In addition, in most states, the marriage law specifies that the courts have the right to grant exceptions to women based on “moral” and “welfare” arguments (as explained in the footnotes to tables in the World Almanac and Book of Facts, various years). These statutes imply that a judge could grant permission for an early teenage marriage if the teenage woman was pregnant. How often judges actually granted exceptions is hard to know ex post facto, but given the relatively low rate of illegitimate births and abortions during much of this period, exceptions for pregnancy were probably common.
The fact that restrictive laws do not prevent 100% of early teenage marriages does not make them invalid instruments. Rather, the strength of the instrument set is that restrictive state laws make it harder to marry young, thereby preventing some fraction of teen marriages that otherwise would have occurred.
I also use the compulsory schooling and labor laws originally collected by Acemoglu and Angrist (2001) and subsequently modified by Goldin and Katz (2003). These laws typically specify a minimum age or amount of schooling before a youth can drop out of school or obtain a work permit. Using Goldin and Katz’s approach, compulsory school attendance is defined as the minimum of (1) the required years of schooling before dropping out and (2) the difference between the minimum dropout age and the maximum enrollment age (lagged 8 years). Child labor is defined as the maximum of (1) the required years of schooling before receiving a work permit and (2) the difference between the minimum work age and the maximum enrollment age (lagged 8 years). The value of the marriage, schooling, and labor laws assigned to a woman are based on the set of laws for her birth state that are in force when she would have been age 15.
Table 2 summarizes the changes in these laws across five-year time periods (in the regression analysis, year-by-year values are used). A more detailed listing by state and year for the early marriage laws can be found in Dahl (2005), and for the compulsory schooling and child labor laws in Acemoglu and Angrist (2001) and Goldin and Katz (2003). For the period 1935–1939, 41% of states specified that a woman had to be 16 or older before marrying. Over time, several states raised their age requirements, so that by 1965–1969, 70% of states required a woman to be at least 16 before marrying. Summarizing the law changes another way, the average minimum marriage age across states was 14.6 years at the beginning of the sample period, but rose by approximately one year to 15.7 years by the end of the sample. There have also been similar increases in the requirements governing school attendance and child labor. In 1935–1939, 24% of states required at least nine years of compulsory schooling; by 1965–1969, this rose to 63% of states. Similarly, in 1935–1939, only 2% of states had a child labor requirement of nine years or more; by 1965–1969, 38% of states had such a requirement. Later in the article, I will also investigate the impact of divorce and use unilateral divorce laws as instruments, although the table reveals that few states enacted unilateral divorce laws prior to 1970.
Table 2.
Summary of State Laws by Time Period, With Tests for Independence of the Laws
| Time Period |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State Laws | All Years (1) | 1935–1939 (2) | 1940–1944 (3) | 1945–1949 (4) | 1950–1954 (5) | 1955–1959 (6) | 1960–1964 (7) | 1965–1969 (8) |
| Marriage Laws (%) | ||||||||
| Legal restriction | ||||||||
| Common law | 4.4 | 14.6 | 8.8 | 5.9 | 1.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Minimum marriage age ≤ 13 | 3.1 | 3.4 | 3.4 | 2.4 | 3.4 | 4.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| Minimum marriage age = 14 | 16.7 | 21.5 | 18.1 | 17.1 | 17.1 | 17.1 | 14.2 | 11.7 |
| Minimum marriage age = 15 | 18.6 | 19.5 | 18.5 | 18.1 | 19.5 | 20.0 | 19.0 | 15.6 |
| Minimum marriage age ≥ 16 | 57.2 | 41.0 | 51.2 | 56.6 | 58.5 | 58.5 | 64.4 | 70.2 |
| χ2 test of independence with: | ||||||||
| Compulsory schooling laws | 324.3*** | |||||||
| Child labor laws | 266.6*** | |||||||
| Divorce laws | 20.3*** | |||||||
| Compulsory Schooling Laws (%) | ||||||||
| Compulsory attendance = 7 | 10.0 | 17.6 | 18.5 | 9.3 | 6.8 | 5.4 | 7.3 | 4.9 |
| Compulsory attendance = 8 | 47.3 | 58.0 | 57.1 | 57.6 | 47.8 | 42.4 | 36.6 | 31.7 |
| Compulsory attendance = 9 | 30.1 | 12.7 | 14.6 | 23.4 | 34.1 | 35.6 | 41.5 | 48.8 |
| Compulsory attendance ≥ 10 | 12.6 | 11.7 | 9.8 | 9.8 | 11.2 | 16.6 | 14.6 | 14.6 |
| χ2 test of independence with: | ||||||||
| Child labor laws | 290.1*** | |||||||
| Divorce laws | 217.9*** | |||||||
| Child Labor Laws (%) | ||||||||
| Child labor = 6 | 13.5 | 19.5 | 19.5 | 17.6 | 16.1 | 11.2 | 6.8 | 3.9 |
| Child labor = 7 | 21.5 | 22.0 | 22.0 | 22.4 | 21.0 | 25.9 | 19.5 | 18.0 |
| Child labor = 8 | 44.7 | 56.1 | 56.1 | 48.8 | 38.0 | 34.6 | 39.5 | 40.0 |
| Child labor ≥ 9 | 20.2 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 11.2 | 25.9 | 28.3 | 34.1 | 38.0 |
| χ2 test of independence with: | ||||||||
| Divorce laws | 31.0*** | |||||||
| Divorce Laws (%) | ||||||||
| Unilateral divorce | 4.0 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 3.4 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 7.8 |
| Sample Size | 1,435 | 205 | 205 | 205 | 205 | 205 | 205 | 205 |
Notes: Entries are the fraction of states with a specified law averaged over the five-year time interval. Sample size is the number of state-years; there are 41 states with laws available and 35 years, for a total of 1,435 observations. χ2 test of independence is a test for the independence of the rows and the columns in a cross tabulation of the two sets of laws over all state-years.
p < .001
Table 2 also reports the results of chi-square tests for the pairwise independence of the marriage, schooling, labor, and divorce laws. These tests all strongly reject the null hypothesis that the various state laws are independent. Although not shown, the interrelated nature of the marriage and schooling/labor laws cannot be attributed solely to trends over time. After time trends in the laws are regressed out, the state laws are still highly related.
Since the marriage, schooling, and labor laws affecting youth are so highly correlated, it could be important to account for all three simultaneously when estimating instrumental variable regression models. Past research has used the compulsory schooling and child labor laws as instruments for education in models describing human capital externalities (Acemoglu and Angrist 2001), crime (Lochner and Moretti 2004), mortality (Lleras-Muney 2005), intergenerational transmission of human capital (Oreopoulos, Page, and Stevens 2006), and fertility (Black, Devereux, and Salvanes 2004; Leon 2004). In many of these applications, there may not be a need to instrument for early teen marriage. However, for some outcomes, part of the observed effects might be due to changes in marriage laws (and early marriage rates) but mistakenly attributed to changes in compulsory schooling laws (and education levels) instead. In the IV regressions that follow, I use all three sets of laws in poverty regressions that instrument for early marriage and high school completion.
The Impact of State Laws on Early Teen Marriage
How effective are state-specific marriage laws at restricting the age individuals marry? Other work has examined the effectiveness of compulsory schooling and child labor laws on high school graduation and is not repeated here (see Acemoglu and Angrist 2001; Goldin and Katz 2003; Lleras-Muney 2002; Lochner and Moretti 2004; Margo and Finegan 1996). The combined census samples reveal that restrictive laws are associated with a smaller number of early teen marriages (i.e., marriages occurring before age 16). In states with legal minima of 12–13, 14, 15, and 16+, the percentage of women who are early teen brides is, respectively, 6.5%, 4.3%, 3.5%, and 2.9%.8 Of course, these differences could partly be due to time trends or variation across states with differing laws. In the IV regressions appearing in the next section, these factors will be accounted for.
Are the laws actually reducing the number of teen marriages, or would states with restrictive laws naturally have lower teen marriage rates anyway? If states’ laws actually prevent early teen marriages, one would expect to see a jump in the number of marriages occurring immediately after the specified minimum age. I use the 1968 and 1969 Vital Statistics Marriage Detail files, which collect data from marriage certificates, to examine the timing of teen marriages.9 For women who married between the ages of 14 and 16 in 1968 or 1969, Figure 3 plots the fraction of women marrying at different ages (measured in two-month intervals) who are residents of states with different legal age minima.
Figure 3.
The Timing of Marriages for Women by Type of State Marriage Law, 1968 and 1969 Vital Statistics Marriage Certificate Data
Notes: Data were collected from marriage certificates by the National Center for Health Statistics. Marriage rates are grouped in two-month intervals. The sample is restricted to women who married for the first time, who married between the ages of 14 and 16, and who were residents of and got married in a state that is in a marriage-reporting area (MRA) and has information on marriage laws. The marriage certificate data include all records for small states and a random sample for larger states; the probabilities in the figure are weighted (unweighted probabilites are very similar). The 27 states included in this figure have the following minimum marriage age with parental consent in 1968 and 1969 for women: 13 years in New Hampshire (included with the 14-year age minimum states in the first graph); 14 years in Alabama, New York, Utah; 15 years in Mississippi, Missouri, Oregon; and 16 years in California, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Montana, Nebraska, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Dakota, Tennessee, Vermont, Virginia, Wisconsin, Wyoming.
Sharp increases in the fraction marrying occur where expected, assuming the laws are enforced. For example, in states where the legal minimum is 14 years, a fair number of women actually marry at this young age. Moreover, there is not much of a jump in marriages once women turn age 15. In contrast, in states where the legal minimum is 15 years, there is a sudden rise in the number of marriages immediately after women reach the minimum age of 15. For another example, consider women marrying at age 16. In the third graph, where the legal minimum age is 16, there is a sharp and large increase in the number of marriages occurring immediately after women turn 16. In comparison, the rise surrounding age 16 is much less pronounced in states with minimum ages of 14 or especially 15.10 The graphs suggest that restrictive state laws effectively delay or prevent at least some early teen marriages.
Another way to test whether state laws impact the probability of marrying young is to see whether teens travel to a state with a lower age requirement to get married. If so, this is an indication that restrictive laws impose costs on those wishing to marry before the law in their state of residence allows. Some young teens will cross state lines, while others will be deterred by these costs. The extent to which teens cross state lines to marry in states with more permissive laws can be examined using the residence state and marriage state information in the Vital Statistics data sets.
Before looking at the entire United States, first consider the case for women residing in Tennessee. Tennessee is a long, narrow state, with population centers scattered throughout the state. Tennessee had an age requirement of 16 years for women to marry in 1968 and 1969, the period for which Vital Statistics data are available. Tennessee is bordered by eight states with varying age minima. Six of these states have valid marriage certificate and marriage law information.11 If the marriage age law at that time was binding in Tennessee, we might expect to see that those who wanted to marry earlier than the law allowed in Tennessee to travel to Alabama, Mississippi, or Missouri, where the age minimum was lower. However, we should not see as many prospective teen brides traveling to Georgia, Kentucky, or Virginia, where the age requirement of 16 was the same as in Tennessee.
The pattern of out-of-state marriages strongly supports the idea that Tennessee teens traveled to bordering states with more permissive laws in order to marry young (data not shown). Twenty-two percent of women from Tennessee who married before the age of 16 traveled to Alabama, Mississippi, or Missouri to marry, compared with only 4% who traveled to Georgia, Kentucky, or Virginia. This is not because Alabama, Mississippi, and Missouri are more convenient or attractive places to get married in general, however. For Tennessee brides who married at age 16, 4% traveled to Alabama, Mississippi, or Missouri; this compares with 18% who traveled to Georgia, Kentucky, or Virginia. It appears that the set of neighboring states with an age requirement identical to Tennessee’s are the preferred marriage destinations, but that brides wishing to marry below the age of 16 go out of their way to marry in a state with a lower age requirement.12
Table 3 extends the Tennessee analysis of out-of-state marriages to all of the states in the sample. I categorize women based on the earliest age they can marry in their state of residence with their parents’ consent. I then tabulate the percentage of women who marry (1) in their state of residence, (2) in a state with a lower minimum age than their residence state, and (3) in a state with an equal or higher minimum age than their residence state. For women who married between the ages of 12 and 15, 15.3% of those living in states with a legal minimum age of 16 went to states with lower age limits to marry. In contrast, individuals living in states with legal minima of 13, 14, or 15 years were much more likely to remain in their residence state to marry (only 5% traveled outside their residence state to marry).
Table 3.
Pattern of Out-of-State Marriages by Restrictiveness of State Laws, 1968 and 1969 Vital Statistics Marriage Certificate Data
| Married Outside State of Residence (%) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earliest Age a Woman Can Marry With Parental Consent in Residence State | Married in State of Residence (1) | State With Lower Minimum Age (2) | State With Equal or Higher Minimum Age (3) | Difference Column (2) – (3) | Number of Observationsa |
| Age at First Marriage = 12–15 | |||||
| Earliest age = 13 or 14 | 94.6 (1.2) | 0 | 5.4 (1.2) | −5.4 (1.2) | 482 [3,889] |
| Earliest age = 15 | 94.7 (1.0) | 3.9 (0.9) | 1.4 (0.5) | 2.5 (1.0) | 581 [3,842] |
| Earliest age = 16 | 77.8 (1.0) | 15.3 (0.9) | 6.9 (0.7) | 8.4 (1.0) | 1,919 [16,654] |
| Age at First Marriage = 16 | |||||
| Earliest age = 13 or 14 | 94.1 (0.9) | 0 | 5.9 (0.9) | −5.9 (0.9) | 1,160 [9,935] |
| Earliest age = 15 | 93.7 (1.0) | 2.1 (0.5) | 4.2 (0.9) | −2.1 (1.0) | 1,133 [7,701] |
| Earliest age = 16 | 88.0 (0.4) | 3.2 (0.2) | 8.8 (0.4) | −5.6 (0.5) | 7,128 [69,042] |
| Difference in Difference | |||||
| Earliest age = 13 or 14 | 0.5 (1.5) | ||||
| Earliest age = 15 | 4.6 (1.4) | ||||
| Earliest age = 16 | 14.0 (1.2) | ||||
Notes: Standard errors are shown in parentheses. Data were collected from marriage certificates by the National Center for Health Statistics. The sample is restricted to first marriages of women who are residents of and get married in 1 of the 32 states that are in a marriage-reporting area (MRA) and have information on marriage laws. See footnote 9 in the text for a list of available MRA states. The marriage certificate data include all records for small states and a random sample for larger states; the probabilities in the table are weighted (unweighted probabilities are very similar).
Weighted observations are shown in brackets.
Of course, the patterns observed in the top panel of Table 3 could be the result of the location of states with various laws or the general attractiveness of marrying in different states. To control for this possibility, in the middle panel of Table 3, I tabulate marriage patterns for women who married at age 16. For these women, the marriage laws should not be binding. Indeed, fewer of the women facing an age minimum of 16 left their residence states to marry. In contrast to the top panel, women in states with laws specifying a legal minimum of 16 who chose to marry outside their states of residence were much more likely to marry in states with an equal or higher minimum age law.
A simple difference-in-differences estimate makes clear that women crossed state lines to marry young. To construct the estimate, I first compare the fraction of women who married in a state with a lower minimum versus a higher minimum. Subtracting this difference for women who married between ages 12 and 15 from the difference for women who married at age 16 yields the estimate. For states with a marriage age requirement of 13 or 14, the difference in difference is close to 0 and not significant, as expected. For states with an age minimum of 15, the estimated difference in difference is 4.6% and is significantly different from 0. An even greater contrast shows up for the states specifying a minimum age of 16, with a large and significant estimate of 14.0%. These results imply that restrictive marriage laws increase the costs to potential teen brides and likely prevent some desired early teen marriages.
As a final check on the validity of the laws as instruments, I explore the timing of law changes. One potential concern is that states that pass more restrictive laws would have experienced larger reductions in early teen marriage rates even in the absence of a law change. However, if law changes are exogenous, then future values of the laws should not affect current early marriage rates conditional on current laws.13 To check this, I add the state laws in place 10 years in the future into a regression describing early teen marriage rates, where the regression also includes the current set of laws (and the full set of controls appearing in the baseline IV specification in Table 4). The results from this exercise indicate that future laws do not significantly determine current early marriage rates, while current laws do. The F statistic for the effect of future laws is 0.92 (p value = .44), while the F statistic for the effect of current laws is 14.6 (p value = .01).
Table 4.
Baseline Instrumental Variables Estimates of the Effects of Early Teen Marriage and Dropping Out of High School on Poverty
| Variable | Second Stage: Dependent Variable = Poor | First Stage |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable = Early Teen Marriage | Dependent Variable = Dropout | ||
| Early Teen Marriage | 0.306* (0.096) | ||
| Dropout | 0.112* (0.035) | ||
| Marriage Laws (≤13 excluded) | |||
| Common law | 0.001 (0.003) | 0.010 (0.011) | |
| Minimum marriage age = 14 | −0.08† (0.004) | −0.004 (0.018) | |
| Minimum marriage age = 15 | −0.011* (0.003) | −0.014 (0.015) | |
| Minimum marriage age ≥ 16 | −0.005 (0.004) | −0.007 (0.017) | |
| Compulsory Attendance Laws (7 excluded) | |||
| Compulsory attendance = 8 | 0.000 (0.001) | −0.008 (0.006) | |
| Compulsory attendance = 9 | −0.005* (0.003) | −0.028* (0.006) | |
| Compulsory attendance ≥ 10 | 0.003 (0.002) | −0.012 (0.009) | |
| Child Labor Laws (6 excluded) | |||
| Child labor = 7 | 0.005* (0.002) | −0.002 (0.008) | |
| Child labor = 8 | 0.007* (0.002) | −0.005 (0.006) | |
| Child labor ≥ 9 | 0.010* (0.003) | −0.014 (0.009) | |
| F statistic (state of birth clustering) | 15.68 | 5.44 | |
| p value | .0001 | .0001 | |
| R2 | .019 | .102 | |
| Number of Observations | 3,256,434 | ||
Notes: Standard errors, adjusted for clustering by state of birth, are shown in parentheses. All regressions include dummy variables for census year, race, age, state of birth, and cohort of birth, and region of birth trends. See the notes to Table 1.
p < .10;
p < .05
INSTRUMENTAL VARIABLE ESTIMATES
First Stage
To investigate the effects of teenage marriage and high school completion on subsequent poverty, I use state marriage, schooling, and labor laws as instrumental variables. The bottom panel in Table 4 presents the first-stage estimates. Since I am instrumenting for both early marriage and dropout status, there are two sets of regression estimates. Column 2 regresses a dummy variable for early teen marriage on the set of marriage, schooling, and labor laws. Additional controls mirror those used in column 4 of Table 1.
The marriage laws significantly reduce the number of teens who marry before the age of 16; ceteris paribus, states with a legislated minimum of 13 or less are between 0.5 and 1.1 percentage points more likely to have early marriages than states with more restrictive marriage laws. In states without a legislated minimum, common law (which specifies a minimum of 12 years) prevails; the estimated effect of a common law is similar to a legislated minimum of 13 or less.
Interestingly, the child labor laws seem to work in the opposite direction—more restrictive child labor laws actually increase the probability of an early marriage. A woman born in a state with a child labor law age restriction of 9 or greater has a 1 percentage point higher probability of marriage at an early age. One possible explanation is that early marriage becomes more attractive to a young woman if her other options, such as working, are more limited. The third set of laws that deal with compulsory schooling is smaller and less significant.
Column 3 of Table 4 presents the same set of coefficient estimates for the first-stage dropout regressions. As expected, the compulsory schooling laws have a relatively large and jointly significant effect on whether a young woman finishes high school. The marriage laws have nontrivial coefficient estimates but are imprecisely estimated and therefore not significant. One reason why dropout status might project onto the marriage laws is that the marriage laws are highly correlated with the compulsory schooling laws. The marriage laws are measured every year, but the schooling laws are only measured intermittently.14 In the years for which schooling laws are interpolated noisily, effects may load onto the marriage laws instead. More restrictive child labor laws seem to discourage some women from dropping out of school, but the estimates are not statistically significant.
For all of the estimates, F statistics are reported for the joint significance of the instruments. The F statistic is 15.68 for the early teen marriage equation and 5.44 for the dropout equation. All of the standard errors reported in Table 4 (and throughout the article) are adjusted for clustering by state of birth to account for arbitrary correlation over time. Bertrand, Duflo, and Mullainathan (2004) have shown that failure to account for such correlation can lead to severely biased confidence intervals for the estimated coefficients. This is particularly likely to be important in IV analyses, which use laws over time as instruments, because there is typically a long time component and plausible serial correlation.15
Estimates
The top panel of Table 4 presents the baseline results for the instrumented poverty regression. Early teen marriage and dropping out of high school both have sizable effects on the probability a woman will end up in poverty. The estimates imply that marrying young is associated with a 30.6 percentage point increase in the probability of living in poverty. Dropping out of high school is associated with an 11.2 percentage point increase in poverty.
I now present a series of alternative estimation approaches to assess the robustness of the baseline result. Table 1 revealed that aggregation made a large difference for OLS estimates: the individual-level results suggested a small impact of early teen marriage on poverty, while the group-level OLS estimates suggested a large effect. The first column in Table 5 repeats the baseline IV analysis, but this time with grouped data. The data are aggregated at the state of birth × year of birth × census year level. The grouped-data IV estimates are remarkably similar to the individual-level IV estimates (0.314 versus 0.306 for early teen marriage and 0.112 versus 0.112 for dropout). The similarity of the coefficient estimates is not surprising since the instruments are constant for all individuals in a state-cohort group, effectively aggregating both the individual-level and group-level estimates. The standard errors also change very little when using the grouped data, increasing by about 10% for early teen marriage and not at all for dropout. Because the aggregated data produces very similar point estimates and slightly more conservative standard errors, in what follows, I present results for aggregated data unless otherwise noted.16
Table 5.
Alternative Estimators for the Baseline Model (dependent variable = poor)
| Variable | Grouped IV | Grouped LIML | Migration Adjusted | Control Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early Teen Marriage | 0.314* (0.107) | 0.315* (0.109) | 0.318* (0.111) | 0.281* (0.108) |
| Dropout | 0.112* (0.034) | 0.112* (0.035) | 0.112* (0.033) | 0.123* (0.036) |
| û (estimated Early Teen Marriage residual) | −0.015 (0.165) | |||
| û × Early Teen Marriage | 3.648† (2.045) | |||
| û × Dropout | −0.375 (0.527) | |||
| v̂ (estimated Dropout residual) | 0.015 (0.106) | |||
| v̂ × Early Teen Marriage | 3.405* (1.510) | |||
| v̂ × Dropout | −0.440† (0.267) | |||
| F Statistic for Control Function | 3.58 | |||
| p value | .0062 | |||
| F Statistic for Early Marriage, First Stage | 14.52 | 14.52 | 13.09 | |
| p value | .0001 | .0001 | .0001 | |
| F Statistic for Dropout, First Stage | 5.15 | 5.15 | 5.81 | |
| p value | .0001 | .0001 | .0001 | |
| Number of Observations | 3,567 | 3,567 | 3,567 | 3,567 |
Notes: Standard errors, adjusted for clustering by state of birth, are shown in parentheses. All regressions include dummy variables for census year, race, age, state of birth, and cohort of birth, and region of birth trends. Data are aggregated to state of birth × year of birth × census year cell means. See the notes to Table 1. The migration-adjusted approach is described in the text and the control function approach is described in the text and the appendix.
p < .10;
p < .05
As is well known, weak instruments can lead to biased IV estimates; under general conditions and finite samples, weak instruments bias the estimates in the same direction as OLS estimates (see Bound, Jaeger, and Baker 1995; Staiger and Stock 1997). The first-stage F statistics appearing in Table 4 are significant but of moderate size. To help assess whether weak instruments might be biasing the results, the second column in Table 5 reports LIML estimates for the baseline model. The consensus in the literature is that when there are many instruments or weak instruments, LIML tends to exhibit less bias compared to least squares IV, and LIML confidence intervals typically also have better coverage rates (Stock 2002).17 The LIML results are virtually identical to the grouped IV estimates. This suggests that weak instruments are not a major issue for estimation.
The next task is to assess the impact migration has on the assignment of state laws for marriage, schooling, and work and the subsequent IV estimates. As a reminder, laws are assigned based on a woman’s state of birth, although ideally we would like to use the state a woman lived in at age 15. Because some women have migrated out of their birth state and into a state with a different set of laws by age 15, the instruments are measured with error. I assess how this affects the IV estimates in column 3 of Table 5.
To see how I examine the issue, notice that the expected value of the ideal (but unobserved) state laws can be calculated if migration probabilities are known. Let zij* be a dummy variable indicating the state law woman i faces at age 15, given she was born in state j. The asterisk indicates that this variable is not observed, given that she may have moved from her birth state by age 15. However, if migration probabilities are known, the expected value of this variable can be calculated as
where pjk represents the probability that a woman will live in state k at age 15 given that she was born in state j, and wk is the law in force in state k for the relevant year. The same logic applies when there are several variables for the state laws.
It is straightforward to show that substituting in E[zij*] for zij* yields consistent estimates in an IV framework. The remaining issue is how to consistently estimate the conditional migration probabilities, pjk. Although this information is not available for all women, the migration patterns for women who were age 15 at the time of the census enumeration can be estimated because the census records both state of birth and state of current residence. I use 15-year-old women in the 1960 census to estimate these migration probabilities. I then calculate the expected value of the laws based on the state a woman lived in at age 15 as outlined above and use these expected laws as instruments.18 The migration-adjusted estimates in column 3 of Table 5 are very similar to the baseline estimates, indicating that the assignment of state marriage laws based on state of birth is a reasonable approach.
If there is heterogeneity in an individual’s “return” to marrying young or dropping out of school, the assumptions needed for IV to consistently estimate an average treatment effect are stronger (Björklund and Moffit 1987; Card 1999, 2001; Heckman and Vytlacil 1998; Willis and Rosen 1979; Wooldridge 1997). In the current context, a sufficient set of conditions is that the instruments are independent of (1) the individual returns to marrying young and dropping out of high school, (2) any individual-specific intercept term in the outcome equation, and (3) the reduced-form residuals in the first-stage early marriage and dropout equations (see Heckman and Vytlacil 1998).
To assess the impact of heterogeneous returns, I pursue a control function approach similar to the one proposed by Garen (1984) and discussed by Card (2001). The basic idea of a control function approach is to make some assumptions about the relationship between the observed variables (controls and instruments) and the individual-specific returns and individual-specific intercept term. One then includes additional terms in the outcome regression to control for these relationships. (The appendix details the assumptions and estimating equation.) The resulting control function estimates appear in column 4 of Table 5. Compared with the baseline IV estimates, the early marriage estimate is approximately 10% smaller and the dropout estimate is approximately 10% larger. These results suggest that heterogeneity across individuals plays a minor role in estimation of the average treatment effect.
Additional Estimates
To further investigate heterogeneity in the returns to marrying young and dropping out of school, the first two panels in Table 6 present additional IV estimates by race and region of country. The IV estimate of the early teen marriage effect for the black sample is 0.46, which is much larger than the baseline estimate or the estimate for the white sample (although the estimate for whites is imprecisely estimated and not significant). The marriage instruments also have more power for the black sample than the white sample. The dropout coefficients are similar for whites and blacks, but statistically insignificant for blacks. When looking at estimates by region of the country, it becomes clear that most of the identification is coming from southern states, which is not surprising given that much of the variation in laws occurs in this region of the country. Interestingly, the dropout coefficients fall for both the black and white samples in panel B. (OLS estimates for these and other groupings can be found in Dahl 2005.)
Table 6.
Additional Grouped IV Estimates (dependent variable = poor)
| Specification | Black | White | South | Non-South | Entire Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. By Race | |||||
| Early teen marriage | 0.464* (0.205) | 0.227 (0.332) | |||
| Dropout | 0.085 (0.114) | 0.109* (0.057) | |||
| F statistic for early marriage equation | 52.54 | 5.92 | |||
| F statistic for dropout equation | 5.53 | 4.84 | |||
| Number of observations | 3,304 | 3,567 | |||
| B. By Region of Country | |||||
| Early teen marriage | 0.384* (0.112) | 0.377 (0.440) | |||
| Dropout | 0.061† (0.032) | 0.063 (0.060) | |||
| F statistic for early marriage equation | 178.44 | 2.40 | |||
| F statistic for dropout equation | 27.45 | 39.19 | |||
| Number of observations | 1,218 | 2,349 | |||
| C. Adding Marriage Laws for Women Without Consent and for Men With and Without Consent as Instruments | |||||
| Early teen marriage | 0.368* (0.113) | ||||
| Dropout | 0.157* (0.022) | ||||
| F statistic for early marriage equation | 47.98 | ||||
| F statistic for dropout equation | 35.34 | ||||
| Number of observations | 3,567 | ||||
| D. Using Total Family Income as the Dependent Variable | |||||
| Early teen marriage | −25.596* (10.380) | ||||
| Dropout | −5.470 (4.495) | ||||
| F statistic for early marriage equation | 14.52 | ||||
| F statistic for dropout equation | 5.15 | ||||
| Number of observations | 3,567 | ||||
| E. Including Allocated Observations | |||||
| Early teen marriage | 0.334* (0.103) | ||||
| Dropout | 0.110* (0.042) | ||||
| F statistic for early marriage equation | 15.96 | ||||
| F statistic for dropout equation | 5.27 | ||||
| Number of observations | 3,567 | ||||
Notes: Standard errors, adjusted for clustering by state of birth, are shown in parentheses. All regressions include dummy variables for census year, race, age, state of birth, and cohort of birth, and region of birth trends. Data are aggregated to state of birth × year of birth × census year cell means. Family income is measured in thousands of dollars. See the notes to Table 1.
p < .10;
p < .05
The last three panels in Table 6 present additional robustness checks for the IV estimates. This article has focused on the laws governing marriage with parental consent for women. There are also laws specifying the minimum marriage age without parental consent for women and laws for men. As discussed earlier, there is little variation in the laws without consent for either women or men before 1970, so I cannot effectively use these to instrument for marriages at later ages. The laws for men with parental consent are highly correlated with the laws for women with parental consent, and are usually two years higher. Panel C uses all of the marriage laws, for men and women, with and without consent, as instruments. These additional instruments result in modest increases in the IV estimates for both the early marriage and dropout variables.
In the results presented so far, the dependent variable has been poverty, a binary outcome. I now explore the effect of early marriage and dropping out of high school on family income, a continuous outcome. While this variable arguably does not capture a family’s financial well-being as accurately (since it does not account for family size or the number of children), it provides a useful robustness check. The effects of early marriage and dropout status on family income are large, presenting a picture similar to the poverty regressions. An additional robustness exercise includes observations in which the age at first marriage variable was allocated by the Census Bureau. Including these observations has a large impact on the OLS estimates appearing in the bottom panel of Table 1. In contrast, the IV estimates are robust to the inclusion or exclusion of these allocated observations.
As a final exercise, Table 7 investigates the effect of divorce on poverty. I begin by presenting estimates similar to those in column 4 of Table 1, but with an additional variable for whether a woman is currently divorced. The estimated effect is substantial. Currently divorced is associated with a 21.5% increase in the probability of poverty, an effect similar in magnitude to the estimated effect of an early teen marriage. In this regression, the early teen marriage coefficient falls slightly compared with Table 1, from 26.4% to 23.5%. The IV estimate in column 2 instruments for early teen marriage and dropout status using the same specification as Table 4 but also adds in the currently divorced variable as an additional control. The resulting IV estimate for early teen marriage falls to 26.4% (compared with 30.6% in Table 4).
Table 7.
OLS and IV Estimates of the Effect of Divorce on Poverty (dependent variable = poor)
| Variable | Grouped OLS | IV | IV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early Teen Marriage | 0.235* (0.059) | 0.264* (0.133) | 0.380* (0.129) |
| Dropout | 0.128* (0.035) | 0.112* (0.033) | 0.125* (0.043) |
| Currently Divorced | 0.215* (0.037) | 0.159* (0.003) | −0.114 (0.117) |
| Instrumenting for Early Marriage and Dropout? | X | X | |
| Instrumenting for Divorce? | X | ||
| F Statistic for Early Marriage, First Stage | 13.67 | 14.83 | |
| p value | .0001 | .0001 | |
| F Statistic for Dropout, First Stage | 5.32 | 6.61 | |
| p value | .0001 | .0001 | |
| F Statistic for Divorce, First Stage | 14.68 | ||
| p value | .0001 | ||
| R2 | .877 | ||
| Number of Observations | 3,567 | 2,870,390 | 2,870,390 |
Notes: Standard errors, adjusted for clustering by state of birth, are shown in parentheses. All regressions include dummy variables for census year, race, age, state of birth, and cohort of birth, and region of birth trends. Data are aggregated to state of birth × year of birth × census year cell means in the first column, but at the individual level for the IV regressions. See the notes to Table 1.
p < .05
Since divorce might not be exogenous, it would be useful to instrument for this variable. Previous research has analyzed the effect of changes in divorce laws on divorce rates and stocks (Friedberg 1998; Parkman 1992; Peters 1986; Wolfers 2006). Research in this area has looked at the impact of divorce laws on outcomes such as labor supply, suicide, investment in marriage-specific capital, children’s well-being, and family distress (Gray 1998; Gruber 2004; Stevenson 2007; Stevenson and Wolfers 2006). Thus, one possibility is to use these divorce laws as instruments.
I follow the approach taken by Wolfers (2006) and Gruber (2004) and use unilateral divorce laws as an instrument for the stock of divorces. I assign divorce laws based on current state of residence (using Gruber’s coding), which necessitates the use of individual-level data. The divorce coefficient appearing in column 3 of Table 7 is negative but not statistically significant. The early marriage coefficient rises to 38%, while the dropout coefficient does not change much compared with the baseline estimate. While the results of this exercise are interesting, they should be interpreted with caution because most of the changes in divorce laws, as well as most of the rise in divorce rates, occur after my sample period (see Table 2).
Discussion
The IV estimates indicate that the causal effects of early teen marriage and dropout status on future poverty are substantial. The baseline estimates imply that marrying young increases the chances a young bride will end up in poverty later in life by around 31 percentage points. Dropping out of high school has a somewhat smaller, but still substantial, 11 percentage point effect on future poverty. These results are robust to the level of aggregation, LIML estimation, corrections for migration, and a control function approach. The individual-level OLS estimates for early teen marriage are small, while aggregated OLS estimates yield an estimate that is of the same magnitude as the IV estimates.
To better understand why the IV and aggregated OLS estimates differ so much from the individual-level OLS estimates, I now explore the role of measurement error. In census data, age at first marriage is calculated from the reported date of first marriage and date of birth (month and year). Usually only one person fills in the census form for the entire household. This is likely to exacerbate measurement error because the person completing the census may not have accurate information about other household members’ dates of birth and first marriage. In 1970 and 1980, the census form instructs individuals to “give your best estimate” when either of these dates is “not known.”19
Since the fraction of early teen marriages is so small, any mismeasurement of date of birth or date of marriage—the two variables used to construct age at first marriage—is likely to lead to a very large downward bias in the OLS estimate of the early teen marriage coefficient. With just a small amount of measurement error, the incorrectly classified teen brides can outnumber the true teen brides, resulting in substantial attenuation bias.
To better understand the prevalence of measurement error in reported dates, consider the 1975 National Fertility Survey (NFS). This was the fifth in a series of surveys conducted every five years to examine marital fertility and family planning. The interesting feature of the survey in 1975 is that the researchers chose to reinterview a selected sample of women from the 1970 survey. The reinterview sample includes 2,355 white women in their first marriages who were continuously married, whose age at marriage was less than 25 years, and whose husbands had also been married only once. Both the 1975 and 1970 surveys ask date of birth and date of first marriage, with both sets of answers being recorded in the 1975 sample. So for this subset of women, I can calculate a lower bound on misreports by comparing the same woman’s answers over a five-year time horizon.
Table 8 tabulates how often the responses from the 1975 survey do not match the responses from the 1970 survey. For the entire sample, dates of birth do not concur 4% of the time, and dates of marriage do not concur 12% of the time. The result is that a woman’s age at marriage measured in years will not line up for 11% of the observations in the sample. Mismatch rates are also reported in Table 8 for groupings based on a woman’s reported marriage age in the 1970 survey. For those marrying at or below the age of 15 in the 1970 survey, 8% of birth dates and 35% of marriage dates do not align across survey years. For this group, 39% of the implied marriage ages differ across the surveys. Misreporting generally declines as a woman’s reported marriage age rises, and the amount of error in these other groups is modest in comparison. The amount of measurement error in the census is likely to be even larger because the 1975 NFS sampled only women who had never divorced and had women answer questions about themselves.
Table 8.
Marriage Age Misreports in the 1975 and 1970 National Fertility Surveys
| Reported Age of Marriage in 1970 Survey | Percentage of 1975 Responses Not Matching With 1970 Responses |
Number of Observations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date of Birth | Date of Marriage | Marriage Age (in Years) | ||
| ≤ 15 | 7.7† | 34.6* | 38.5* | 52 |
| 16 | 3.5 | 15.9† | 12.4 | 113 |
| 17 | 5.7* | 16.1* | 17.1* | 211 |
| 18 | 3.5 | 14.0* | 11.5 | 400 |
| 19–24 | 3.0 | 10.2 | 9.1 | 1,579 |
| Any Age | 3.5 | 12.2 | 11.0 | 2,355 |
Notes: Standard errors are shown in parentheses. Data come from the subsample of women from the 1970 National Fertility Survey who were reinterviewed in the 1975 National Fertility Survey. Marriage age is calculated from date of marriage and date of birth.
Significantly different from the 19–24 entry at the 10% level.
Significantly different from the 19–24 entry at the 5% level.
Measurement error can plausibly explain the difference between the individual OLS estimates and the grouped OLS or IV estimates. One remaining question is why the grouped OLS and IV estimates are so large. The results in Table 7 put some perspective on the size of the effect: early teen marriage results in an increase in poverty that is on par with the effect of divorce (when treated exogenously) or almost three times the effect of dropping out of school. These effects are larger than those found in much of the literature for teenage childbearing discussed earlier. How can the current results be reconciled with that literature?
There are at least two reasons why the estimated effect of early teenage marriage might not be comparable to the effects estimated for teenage childbearing in the literature. First, the sample periods differ greatly. Most of the research on teenage childbearing focuses on births occurring in the 1970s or later because many of these studies have used data from the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth or the Panel Study of Income Dynamics. In contrast, I focus here on women who were 15 years old between 1935 and 1969. Comparing the two time periods, there are large differences in access to birth control and abortion, social norms, and labor market opportunities for married women and women with children. Birth control became widely available to young, single women starting in the late 1960s and had large effects on women’s career and marriage decisions (Goldin and Katz 2002). Abortion also became legalized in the early 1970s, first in select states and then nationwide with Roe v. Wade in 1973. To highlight one change in what was socially acceptable over time, consider illegitimacy rates, which rose from 3.9% in 1950, to 10.7% in 1970, to 28.0% in 1990 (Ventura and Bachrach 2000). Female labor force participation rates for married women also increased dramatically over this time period, steadily increasing from 15% in 1940 to over 50% by 1980 and almost 75% by 1990 (Goldin 2006). In sum, there were many changes starting in the 1970s that could make teenage motherhood after that period not comparable to my sample of early teen brides earlier in the century.
The second reason for why the estimated effect of early teen marriage is so large compared with the estimates for teen childbearing is that this article looks at a sample of particularly young teenagers—those marrying at or before age 15—while the teen child-bearing literature typically examines the effect of births to teenagers less than or equal to age 19. There may be a large difference between marrying (or having a child) at or before the age of 15 versus between the ages of 16 and 19.
Some of these differences can be highlighted using the 1965 and 1970 National Fertility Surveys.20 Women who married at age 15 or younger divorced within five years of marriage 18% of the time, compared with 12% for women who married at age 16 or 17 and 7% for women who married at age 18 or 19. Eighty-seven percent of early teen brides had not finished high school, compared with 66% and 29% of brides who married at ages 16–17 and 18–19, respectively.21 These early teen brides had children early, with 63% having one child by the age of 16 and 25% having two children by the age of 18. This compares with rates of 10% and 8% for those marrying between 16 and 17, and 1% and 0.5% for those marrying between 18 and 19.
Moreover, early teen brides married men who were also relatively young and less educated. Twenty percent of women marrying at age 15 or younger married a man who was 17 or younger. In contrast, only 10% of women marrying between 16 and 17 and 3% of women marrying between 18 and 19 did so. The dropout rate of early teen brides’ husbands is 65%, compared with 53% for women marrying between 16 and 17 and 36% marrying between 18 and 19. These tabulations from the NFS show that those who marry very young have substantially different divorce rates, fertility rates, schooling completion, and husbands, even in comparison with women who marry just a few years later.
One other interesting comparison can be drawn from the NFS data. In 1965, the survey asked respondents if they would encourage a daughter to marry at a younger age, the same age, or an older age as they did. Ninety-one percent of early teen brides answered “older,” compared with 48% for the rest of the sample. This provides some indication that early teen brides would not necessarily make the same decision to marry so young if they had it to do over again.
CONCLUSION
Do the negative effects associated with early teen marriage and dropping out of school reflect unmeasured characteristics or the true consequences of a teen’s choices? To better understand the effect of women’s early decisions on future life outcomes, this article examines variation over time and across states in the laws that regulate early marriage, school attendance, and child labor. Based on using these laws as instruments for early marriage and high school completion, the results indicate strong negative effects on poverty status that are not due to self selection. The baseline IV estimates imply that women who marry young are 31 percentage points more likely to live in poverty when they are older. Similarly, women who drop out of school are 11 percentage points more likely to be in families below the poverty line. The IV results are robust to a variety of alternative specifications and estimation methods, including LIML estimation and a control function approach. In comparison, OLS estimates are sensitive to how the data are aggregated; regressions on individual-level data estimate small effects for early teen marriage, while aggregated data estimate large effects. I argue that the difference is due to a large amount of measurement error in the early marriage variable, resulting in substantial attenuation bias in the individual-level OLS regressions but not the aggregated OLS or IV regressions.
The results imply that the decisions women make early in life can have long-lasting consequences. The IV estimates suggest that legal restrictions that prevent early marriage and mandate high school completion have the potential to greatly reduce the chances of future poverty for a woman and her family. The implication is that legal restrictions on teenagers’ choices can reduce external costs imposed on society, and it is possible they also prevent some teens from making decisions they will later regret.
Acknowledgments
I thank Eli Berman, Mark Bils, David Card, Julie Cullen, David Dahl, David Lee, Lance Lochner, Enrico Moretti, Uta Schoenberg, and seminar participants at several universities for valuable comments and suggestions.
APPENDIX
This appendix describes the control function approach taken for estimates appearing in Table 5. Consider the following outcome equation, which allows for individual-specific coefficients and an individual-specific intercept term:
| (A1) |
where yi is a dummy variable for poverty, mi is early teen marriage, and di is divorce. For ease of exposition, other control variables are excluded and coefficients have been written as deviations from their averages.
The equations for early teen marriage and divorce are
| (A2) |
| (A3) |
where zi is the vector of marriage, schooling, and work laws for individual i’s state.
Begin by assuming that E(ei | mi,di,zi) = 0, E(ui | zi) = 0, and E(vi | zi) = 0 and that the three individual-specific terms αi, γi, and δi are mean independent of zi. Following Garen (1984) and Card (2001), further assume that
Under these linearity assumptions, it follows that
This equation can be consistently estimated using the estimated residuals ûi and v̂i from Eqs. (A2) and (A3) in place of ui and vi.
Footnotes
The Russell Sage Foundation commissioned an early study to raise awareness about “child” marriages and document state-specific minimum-age laws (May 1929). Concurrently, Richmond and Hall (1929) harshly criticized early teen marriage as a result of their investigation of 240 women who married before the age of 16. They concluded that “the effects of child marriage do not cease with childhood. Both physically and socially the marriage relation can be permanently influenced by immature mating” (p. 124).
Married teen mothers are 40% more likely to have a second birth within 24 months of their first birth compared with unmarried teenage mothers (Kalmuss and Namerow 1994). For the sample period used in this article, 23% of women who married in their teens gave birth to five or more children, versus 8% for those who married later in life (U.S. census tabulations). See also Kiernan (1986).
Age at first marriage is calculated from each woman’s date of first marriage and date of birth. In 1980, valid responses included ages as low as 12; in 1960 and 1970, the lowest valid response was age 14.
The fertility rate for 15- to 17-year-old women is available starting in 1960. From 1960 to 1998, the 15- to 17-year-old rate is 59% of the 15- to 19-year-old rate, on average, and the two series roughly have the same time pattern.
The dropout rate at age 19 for women is 52.3% for the 1921–1930 birth cohort, 43.1% for 1931–1940, 36.7% for 1941–1950, 25.9% for 1951–1960, 20.7% for 1961–1970, and 15.1% for 1971–1980 (Carter et al. 2006).
For example, in the 1980 census, entries for the age at first marriage variable “were allocated from one of seven matrices in which reported marital history responses were stored. The matrices contained data on various combinations of characteristics, such as age, marital status, sex, the presence or absence of a spouse, the presence of the person’s own children in the household, and the number of times the husband or wife had been married” (U.S. Census Bureau 1986: chap. 12, p. 19).
Information was collected from each year’s World Almanac. If a state’s law was missing or changed for one (or at most two) years and then returned to its previous value, that year’s law was replaced with the value from the surrounding years. This procedure resulted in 12 changes out of a total of 1,435 state-year laws. If these 12 changes are not made, the results that follow are virtually identical. Alaska and Hawaii are excluded since their compulsory schooling and child labor laws are not available. Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, New Jersey, North Carolina, South Carolina, and West Virginia are excluded since the World Almanac reports unstable, noisy data on their state laws (i.e., multiple up and down changes spanning several years in the marriage laws). If these eight states are included in the analysis, the estimates are less precisely estimated, but the general conclusions hold.
Although not shown, there is a persistent difference in early teen marriage rates over time. The trends across states with restrictive or permissive laws both follow the same general pattern shown in Figure 1.
Data from 1968 and 1969 are used because data from earlier years are not readily available. Data are collected for the 42 registered marriage-reporting areas (MRAs). Marriage certificate data are not reported in 1968 and 1969 for the non-MRA states of Arizona, Arkansas, Nevada, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Texas, and Washington. In addition, six MRA states collect marriage age data in years but do not record age in months (District of Columbia, Idaho, Indiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, and Ohio) and hence are excluded from the analysis in Figure 3. MRA states for which marriage law information is unavailable are also excluded from Table 3.
There are also noticeable rises surrounding the time a young woman has a birthday regardless of the legal restriction. For example, there are moderate jumps at age 16 even in states where the legal minimum is 14 or 15 years old. Two possible explanations are that parents or the courts may not give their consent to let young women marry until they reach their 16th birthday or that young women themselves do not wish to marry until they turn 16.
Arkansas is not in an MRA, so no marriage certificate data are available; North Carolina does not have information available on marriage laws.
Jerry Lee Lewis, the rock singer, and Myra Gale Brown are perhaps the most famous example of a Tennessee couple traveling across state lines to marry. In 1957, Lewis took his 13-year-old second cousin to Hernando, Mississippi, where they were married. At the time, the minimum marriage age was only 12 in Mississippi, while it was 16 in Tennessee.
Black, Devereux, and Salvanes (2004) and Lochner and Moretti (2004) performed similar analyses for compulsory schooling laws and found that future laws do not affect current dropout rates in a state.
The compulsory school and child labor laws were collected approximately every five years. I adopt the approach of Acemoglu and Angrist (2001) and interpolate by extending older data.
Failure to adjust the standard errors in the first stage and the corresponding F statistics makes a large difference in the current analysis. Without clustering, the F statistics to rise to 29.22 for the dropout equation and to 22.35 for the marriage equation. Clustering at the state of birth × year of birth level, the F statistic is 12.96 for the dropout equation and 15.48 for the marriage equation.
Bertrand, Duflo, and Mullainathan (2004) showed that clustering does not always do a good job of correcting the standard errors if the within-group sample is large. Aggregating the data should produce more conservative standard errors in such situations.
Of course, if the instruments are weak enough, both the least squares IV and the LIML confidence intervals can have the wrong coverage rates. With a single endogenous variable, solutions include inverting the Anderson-Rubin test statistic or implementing the conditional likelihood ratio test of Moreira (2003). These approaches do not readily extend to the case in which there are two or more endogenous variables, which is the situation in this article.
This implicitly assumes that migration patterns have not changed over time. As a check on this assumption, I alternatively used 15-year-olds from the 1970 census, and the IV estimates were very similar (.317 for early teen marriage and .111 for dropout). Expanding the age window to 14- to 16-year-olds also yielded similar estimates.
Research has found several sources for misreporting of date of birth, including ignorance, miscommunication, distortion to meet preconceived social norms, and errors in processing (Mason and Cope 1987). These same measurement error issues are likely compounded for reports of date of first marriage.
In the combined 1965 and 1970 NFS sample, there are 654 marriages before age 16; 2,080 marriages at ages 16–17; and 3,458 at ages 18–19.
For tabulations of dropout status, I include only women (or men, when considering husband’s education) currently over the age of 25 so as to focus on individuals who are more likely to have completed their education.
REFERENCES
- Acemoglu D, Angrist J. How Large Are Human-Capital Externalities? Evidence From Compulsory Schooling Laws. In: Bernanke BS, Rogoff K, editors. NBER Macro Annual 2000. Vol. 15. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2001. pp. 9–74. [Google Scholar]
- Angrist J, Evans W. NBER Working Paper No. 5406. National Bureau of Economic Research; Cambridge, MA: 1996. Schooling and Labor Market Consequences of the 1970 State Abortion Reforms. [Google Scholar]
- Ashcraft A, Lang K. NBER Working Paper No. 12485. National Bureau of Economic Research; Cambridge, MA: 2006. The Consequences of Teenage Childbearing. [Google Scholar]
- Bane MJ. Household Composition and Poverty. In: Danziger S, Weinberg D, editors. Fighting Poverty: What Works and What Doesn’t. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1986. pp. 209–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bane MJ, Ellwood DT. Slipping Into and Out of Poverty: The Dynamics of Spells. Journal of Human Resources. 1986;21:1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Becker GS. A Theory of Marriage. In: Schultz T, editor. Economics of the Family. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1974. pp. 299–344. [Google Scholar]
- Becker GS, Landes EM, Michael RT. An Economic Analysis of Marital Instability. Journal of Political Economy. 1977;85:1141–88. [Google Scholar]
- Berger M, Leigh JP. Schooling, Self-Selection, and Health. Journal of Human Resources. 1989;24:433–55. [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand M, Duflo E, Mullainathan S. How Much Should We Trust Differences-in-Differences Estimates? Quarterly Journal of Economics. 2004;119:249–75. [Google Scholar]
- Björklund A, Moffit R. The Estimation of Wage Gains and Welfare Gains in Self-selection. Review of Economics and Statistics. 1987;69:42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Black S, Devereux P, Salvanes K. NBER Working Paper No. 10911. National Bureau of Economic Research; Cambridge, MA: 2004. Fast Times at Ridgemont High? The Effect of Compulsory Schooling Laws on Teenage Births. [Google Scholar]
- Blank R, Charles K, Sallee J. NBER Working Paper No. 13667. National Bureau of Economic Research; Cambridge, MA: 2008. Do State Laws Affect the Age at Marriage? A Cautionary Tale About Avoidance Behavior. [Google Scholar]
- Bound J, Jaeger D, Baker R. Problems with Instrumental Variables Estimation When the Correlation Between the Instruments and the Endogenous Explanatory Variables Is Weak. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 1995;90:443–50. [Google Scholar]
- Card D. The Causal Effect of Education on Earnings. In: Ashenfelter O, Card D, editors. Handbook of Labor Economics. 3A. Amsterdam and New York: North Holland; 1999. pp. 1801–63. [Google Scholar]
- Card D. Estimating the Return to Schooling: Progress on Some Persistent Econometric Problems. Econometrica. 2001;64:1127–60. [Google Scholar]
- Carter SB, Gartner SS, Haines MR, Olmstead AL, Sutch R, Wright G, editors. Historical Statistics of the United States: Millennial Edition. New York: Cambridge University Press; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dahl G. NBER Working Paper No. 11328. National Bureau of Economic Research; Cambridge, MA: 2005. Early Teen Marriage and Future Poverty. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J, Wolfe B. NBER Working Paper No. 13847. National Bureau of Economic Research; Cambridge, MA: 2008. Education and Labor Market Consequences of Teenage Child-bearing: Evidence Using the Timing of Pregnancy Outcomes and Community Fixed Effects. [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg L. Did Unilateral Divorce Raise Divorce Rates? Evidence From Panel Data. American Economic Review. 1998;88:608–27. [Google Scholar]
- Garen J. The Returns to Schooling: A Selectivity Bias Approach With a Continuous Choice Variable. Econometrica. 1984;52:1199–218. [Google Scholar]
- Geronimus A, Korenman S. The Socioeconomic Consequences of Teen Childbearing Reconsidered. Quarterly Journal of Economics. 1992;107:1187–214. [Google Scholar]
- Goerge R, Lee BJ. Abuse and Neglect of the Children. In: Maynard R, editor. Kids Having Kids. Washington, DC: Urban Institute Press; 1997. pp. 205–30. [Google Scholar]
- Goldin C. America’s Graduation from High School: The Evolution and Spread of Secondary Schooling in the Twentieth Century. Journal of Economic History. 1998;58:345–74. [Google Scholar]
- Goldin C. NBER Historical Working Paper No. 119. National Bureau of Economic Research; Cambridge, MA: 1999. A Brief History of Education in the United States. [Google Scholar]
- Goldin C. The Quiet Revolution That Transformed Women’s Employment, Education, and Family. 2006 Ely Lecture, American Economic Association Meetings; Boston MA. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Goldin C, Katz L. NBER Working Paper No. 6144. National Bureau of Economic Research; Cambridge, MA: 1997. Why the United States Led in Education: Lessons From Secondary School Expansion, 1910 to 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Goldin C, Katz L. The Power of the Pill: Oral Contraceptives and Women’s Career and Marriage Decisions. Journal of Political Economy. 2002;110:730–70. [Google Scholar]
- Goldin C, Katz L. NBER Working Paper No. 10075. National Bureau of Economic Research; Cambridge, MA: 2003. Mass Secondary Schooling and the State: The Role of State Compulsion in the High School Movement. [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. Divorce Law Changes, Household Bargaining, and Married Women’s Labor Supply. American Economic Review. 1998;88:628–42. [Google Scholar]
- Grogger J, Bronars S. The Socioeconomic Consequences of Teenage Childbearing: Findings From a Natural Experiment. Family Planning Perspectives. 1993;25:156–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber J. Risky Behavior Among Youths: An Economic Analysis, Introduction. In: Gruber J, editor. Risky Behavior Among Youths: An Economic Analysis. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 2001. pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber J. Is Making Divorce Easier Bad for Children? The Long-Run Implications of Unilateral Divorce. Journal of Labor Economics. 2004;22:799–833. [Google Scholar]
- Heckman J, Vytlacil E. Instrumental Variables Methods for the Correlated Random Coefficient Model: Estimating the Rate of Return to Schooling When the Return is Correlated With Schooling. Journal of Human Resources. 1998;23:974–87. [Google Scholar]
- Hotz VJ, McElroy SW, Sanders SG. Impacts of Teenage Childbearing on Mothers and the Consequences of Those Impacts for Government. In: Maynard R, editor. Kids Having Kids. Washington, DC: Urban Institute Press; 1997. pp. 55–94. [Google Scholar]
- Hotz VJ, McElroy SW, Sanders SG. Teenage Childbearing and Its Life Cycle Consequences: Exploiting a Very Natural Experiment. Journal of Human Resources. 2005;40:683–715. [Google Scholar]
- Hotz VJ, Mullin CH, Sanders SG. Bounding Causal Effects Using Data From a Contaminated Natural Experiment: Analyzing the Effects of Teenage Childbearing. Review of Economic Studies. 1997;64:575–603. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. NBER Working Paper No. 9632. National Bureau of Economic Research; Cambridge, MA: 2003. Teen Births Keep American Crime High. [Google Scholar]
- Kalmuss D, Namerow P. Subsequent Childbearing Among Teenage Mothers: The Determinants of a Closely Spaced Second Birth. Family Planning Perspectives. 1994;26:149–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L, Autor D. Changes in the Wage Structure and Earnings Inequality. In: Ashenfelter O, Card D, editors. Handbook of Labor Economics. Vol. 3. Amsterdam: North-Holland; 1999. pp. 1463–555. [Google Scholar]
- Kiernan K. Teenage Marriage and Marital Breakdown: A Longitudinal Study. Population Studies. 1986;40:35–54. [Google Scholar]
- Klepinger D, Lundberg S, Plotnick R. How Does Adolescent Fertility Affect the Human Capital and Wages of Young Women? Journal of Human Resources. 1999;34:421–48. [Google Scholar]
- Leon A. Working paper. Economics Department, University of Pittsburgh; 2004. The Effect of Education on Fertility: Evidence From Compulsory Schooling Laws. [Google Scholar]
- Lleras-Muney A. Were Compulsory Attendance and Child Labor Laws Effective: An Analysis From 1915 to 1939. Journal of Law and Economics. 2002;45:401–35. [Google Scholar]
- Lleras-Muney A. The Relationship Between Education and Adult Mortality in the United States. Review of Economic Studies. 2005;72:189–221. [Google Scholar]
- Lochner L, Moretti E. The Effect of Education on Crime: Evidence from Prison Inmates, Arrests, and Self-Reports. American Economic Review. 2004;94:155–89. [Google Scholar]
- Margo R, Finegan TA. Compulsory Schooling Legislation and School Attendance in Turn-of-the-Century America: A ‘Natural Experiment’ Approach. Economics Letters. 1996;53:103–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mason K, Cope L. Sources of Age and Date-of-Birth Misreporting in the 1900 U.S. Census. Demography. 1987;24:563–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G. Marriage Laws and Decisions in the United States. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 1929. [Google Scholar]
- Moffit R. Incentive Effects of the U.S. Welfare System: A Review. Journal of Economic Literature. 1992;30:1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Moore KA, Waite LJ. Early Childbearing and Educational Attainment. Family Planning Perspectives. 1977;9:220–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreira M. A Conditional Likelihood Ratio Test for Structural Models. Econometrica. 2003;71:1027–48. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donoghue T, Rabin M. Risky Behavior Among Youths: Some Issues From Behavioral Economics. In: Gruber J, editor. Risky Behavior Among Youths: An Economic Analysis. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 2001. pp. 29–68. [Google Scholar]
- Oreopoulos P. Do Dropouts Drop Out Too Soon? Wealth, Health, and Happiness From Compulsory Schooling. Journal of Public Economics. 2007;91:2213–29. [Google Scholar]
- Oreopoulos P, Page M, Stevens A. The Intergenerational Effects of Compulsory Schooling. Journal of Labor Economics. 2006;24:729–60. [Google Scholar]
- Overpeck MD, Brenner RA, Trumble AC, Trifiletti LB, Berendes HW. Risk Factors for Infant Homicide in the United States. New England Journal of Medicine. 1998;339:1211–16. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199810223391706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkman A. Unilateral Divorce and the Labor Force Participation Rate of Married Women, Revisited. American Economic Review. 1992;82:671–78. [Google Scholar]
- Peters HE. Marriage and Divorce: Informational Constraints and Private Contracting. American Economic Review. 1986;76:437–54. [Google Scholar]
- Rank MR, Hirschl TA. The Occurrence of Poverty Across the Life Cycle: Evidence From the PSID. Journal of Policy Analysis and Management. 2001;20:737–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ribar D. Teenage Fertility and High School Completion. Review of Economics and Statistics. 1994;76:413–24. [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M, Hall J. Marriage and the State. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 1929. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggles S, Sobek M, Alexander T, Fitch CA, Goeken R, Hall PK, King M, Ronnander C. Integrated Public Use Microdata Series: Version 3.0 [Machine-readable database] Minneapolis, MN: Minnesota Population Center; 2004. [producer and distributor]. Available online at http://www.ipums.org. [Google Scholar]
- Staiger D, Stock JH. Instrumental Variables Regression With Weak Instruments. Econometrica. 1997;65:557–86. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. The Impact of Divorce Laws on Investment in Marriage-Specific Capital. Journal of Labor Economics. 2007;25:75–94. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B, Wolfers J. Bargaining in the Shadow of the Law: Divorce Laws and Family Distress. Quarterly Journal of Economics. 2006;121:267–88. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B, Wolfers J. Marriage and Divorce: Changes and Their Driving Forces. Journal of Economic Perspectives. 2007;21:27–52. [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. International Encyclopedia for the Social and Behavioral Sciences. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2002. Instrumental Variables in Economics and Statistics; pp. 15721–24. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Census Bureau. 1980 Census of Population and Housing: History. U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of the Census; Washington, DC: 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura SJ, Bachrach CA. National Vital Statistics Reports. 16. Vol. 48. National Center for Health Statistics; Hyattsville, MD: 2000. Nonmarital Childbearing in the United States, 1940–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis R, Rosen S. Education and Self-Selection. Journal of Political Economy. 1979;87:S7–S36. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfers J. Did Unilateral Divorce Raise Divorce Rates? A Reconciliation and New Results. American Economic Review. 2006;96:1802–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wooldridge J. On Two-Stage Least Squares Estimation of the Average Treatment Effect in a Random Coefficient Model. Economics Letters. 1997;56:129–33. [Google Scholar]
- Various years (1935–1969) New York: Press Publication Company; The World Almanac and Book of Facts. [Google Scholar]