Full text
PDF


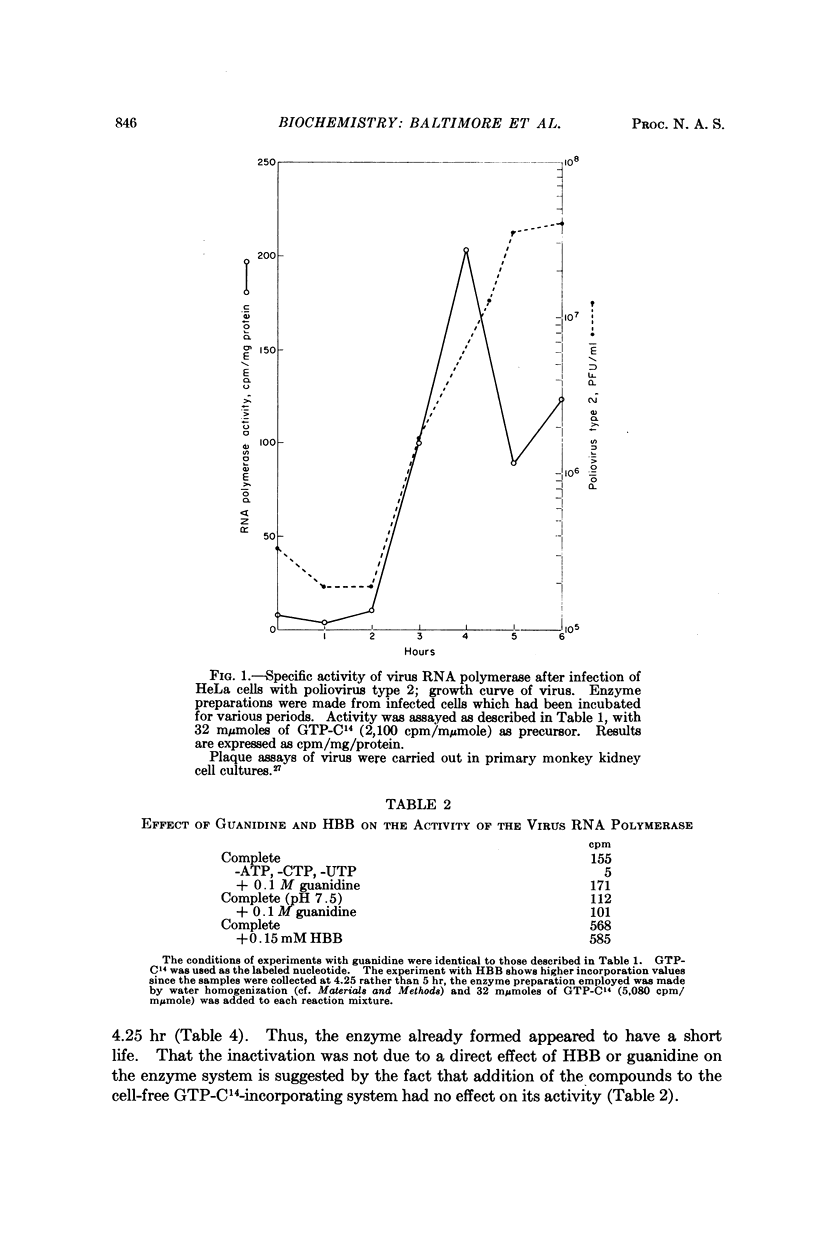



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALTIMORE D., FRANKLIN R. M. Preliminary data on a virus-specific enzyme system responsible for the synthesis of viral RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Nov 27;9:388–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTIMORE D., FRANKLIN R. M. The effect of Mengovirus infection on the activity of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of L-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1383–1390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHOPPIN P. W., EGGERS H. J. Heterogeneity of Coxsackie B4 virus: two kinds of particles which differ in antibody sensitivity, growth rate, and plaque size. Virology. 1962 Nov;18:470–476. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWTHER D., MELNICK J. L. Studies of the inhibitory action of guanidine on poliovirus multiplication in cell cultures. Virology. 1961 Sep;15:65–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARNELL J. E., Jr, LEVINTOW L., THOREN M. M., HOOPER J. L. The time course of synthesis of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1961 Mar;13:271–279. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGGERS H. J., TAMM I. 2,(alpha-hydroxybenzyl)-benzimidazole (HBB) as an aid in virus classification. Virology. 1961 Apr;13:545–546. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGGERS H. J., TAMM I. Spectrum and characteristics of the virus inhibitory action of 2-(alpha-hydroxybenzyl)-benzimidazole. J Exp Med. 1961 Apr 1;113:657–682. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN R. M., BALTIMORE D. Patterns of macromolecular synthesis in normal and virus-infected mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:175–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. Depression of host-controlled RNA synthesis in human cells during poliovirus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan 15;49:23–28. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMMEN H. O., KLEMPERER H. G., CANELLAKIS E. S. The binding of nucleoside di- and triphosphates by a rat-liver component. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jul 22;51:175–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)91032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LODDO B., FERRARI W., BROTZU G., SPANEDDA A. In vitro inhibition of infectivity of polio viruses by guanidine. Nature. 1962 Jan 6;193:97–98. doi: 10.1038/193097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LODDO B., FERRARI W., SPANEDDA A., BROTZU G. In vitro guanidino-resistance and guanidino-dependence of poliovirus. Experientia. 1962 Nov 15;18:518–519. doi: 10.1007/BF02151608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LODDO B., MUNTONI S., SPANEDDA A., BROTZU G., FERRARI W. Guanidine conditioned infectivity of ribonucleic acid extracted from a strain of guanidine-dependent polio-1-virus. Nature. 1963 Jan 19;197:315–315. doi: 10.1038/197315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELNICK J. L., CROWTHER D., BARRERA-ORO J. Rapid development of drug-resistant mutants of poliovirus. Science. 1961 Aug 25;134(3478):557–557. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3478.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHANS D., NOTANI G., SCHWARTZ J. H., ZINDER N. D. Biosynthesis of the coat protein of coliphage f2 by E. coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1424–1431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGHTSEL W. A., DICE J. R., McALPINE R. J., TIMM E. A., McLEAN I. W., Jr, DIXON G. J., SCHABEL F. M., Jr Antiviral effect of guanidine. Science. 1961 Aug 25;134(3478):558–559. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3478.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM I., BABLANIAN R. On the role of ribonucleic acid in animal virus synthesis. II. Studies with ribonuclease. J Exp Med. 1960 Mar 1;111:351–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM I., EGGERS H. J. Differences in the selective virus inhibitory action of 2-(alpha-hydroxybenzyl)-benzimidazole and guanidine HCl. Virology. 1962 Nov;18:439–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM I., NEMES M. M., OSTERHOUT S. On the role of ribonucleic acid in animal virus synthesis. I. Studies with 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole. J Exp Med. 1960 Mar 1;111:339–349. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.3.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER J., MADDEN M. J., DARNELL J. E. The interaction of poliovirus RNA with Escherichia coli ribosomes. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:393–399. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN E. F., HEETER M., DARNELL J. E. RNA synthesis in poliovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:400–408. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




