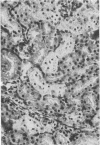
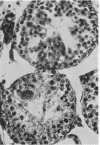
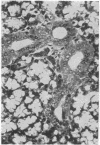
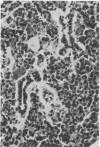
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMAROSE A. P., CZAJKA D. M. Cytopathic effects of deuterium oxide on the male gonads of the mouse and dog. Exp Cell Res. 1962 Feb;26:43–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borek E., Rittenberg D. ANOMALOUS GROWTH OF MICROORGANISMS PRODUCED BY CHANGES IN ISOTOPES IN THEIR ENVIRONMENT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Jun;46(6):777–782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.6.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS P. R., HARDING C. V. Blockade of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis by deuterium oxide. Science. 1961 Apr 14;133(3459):1131–1133. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3459.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS P. R., SPINDEL W. Heavy water inhibition of cell division: an approach to mechanism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Oct 7;90:500–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb23267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES A. M., CALVIN M. Production of sterility in mice by deuterium oxide. Science. 1958 Jun 20;127(3312):1445–1446. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3312.1445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ J. J., CRESPI H. L., CZAJKA D. M., FINKEL A. J. Course of deuteriation and some physiological effects of deuterium in mice. Am J Physiol. 1962 Nov;203:907–913. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.5.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ J. J., CRESPI H. L., HASTERLIK R. J., THOMSON J. F., FINKEL A. J. Some observations on biological effects of deuterium, with special reference to effects on neoplastic processes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1957 May;18(5):641–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSES V., HOLM-HANSEN O., CALVIN M. Response of Chlorella to a deuterium environment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Apr;28(1):62–70. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90428-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAGGART N., HYTTEN F. E. Saliva-serum ratios of deuterium oxide after administration of heavy water. Nature. 1959 Aug 8;184(Suppl 7):457–458. doi: 10.1038/184457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON J. F., KLIPFEL F. J. Changes in renal function in rats drinking heavy water. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Apr;97(4):758–759. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON J. F. Physiological effects of D20 in mammals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 25;84:736–744. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb39105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urey H. C. THE SEPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE ISOTOPES OF HYDROGEN. Science. 1933 Dec 22;78(2034):566–571. doi: 10.1126/science.78.2034.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]