Abstract
Objective To investigate whether sleep deprived people are perceived as less healthy, less attractive, and more tired than after a normal night’s sleep.
Design Experimental study.
Setting Sleep laboratory in Stockholm, Sweden.
Participants 23 healthy, sleep deprived adults (age 18-31) who were photographed and 65 untrained observers (age 18-61) who rated the photographs.
Intervention Participants were photographed after a normal night’s sleep (eight hours) and after sleep deprivation (31 hours of wakefulness after a night of reduced sleep). The photographs were presented in a randomised order and rated by untrained observers.
Main outcome measure Difference in observer ratings of perceived health, attractiveness, and tiredness between sleep deprived and well rested participants using a visual analogue scale (100 mm).
Results Sleep deprived people were rated as less healthy (visual analogue scale scores, mean 63 (SE 2) v 68 (SE 2), P<0.001), more tired (53 (SE 3) v 44 (SE 3), P<0.001), and less attractive (38 (SE 2) v 40 (SE 2), P<0.001) than after a normal night’s sleep. The decrease in rated health was associated with ratings of increased tiredness and decreased attractiveness.
Conclusion Our findings show that sleep deprived people appear less healthy, less attractive, and more tired compared with when they are well rested. This suggests that humans are sensitive to sleep related facial cues, with potential implications for social and clinical judgments and behaviour. Studies are warranted for understanding how these effects may affect clinical decision making and can add knowledge with direct implications in a medical context.
Introduction
The recognition [of the case] depends in great measure on the accurate and rapid appreciation of small points in which the diseased differs from the healthy state
Joseph Bell (1837-1911)
Good clinical judgment is an important skill in medical practice. This is well illustrated in the quote by Joseph Bell,1 who demonstrated impressive observational and deductive skills. Bell was one of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s teachers and served as a model for the fictitious detective Sherlock Holmes.2 Generally, human judgment involves complex processes, whereby ingrained, often less consciously deliberated responses from perceptual cues are mixed with semantic calculations to affect decision making.3 Thus all social interactions, including diagnosis in clinical practice, are influenced by reflexive as well as reflective processes in human cognition and communication.
Sleep is an essential homeostatic process with well established effects on an individual’s physiological, cognitive, and behavioural functionality4 5 6 7 and long term health,8 but with only anecdotal support of a role in social perception, such as that underlying judgments of attractiveness and health. As illustrated by the common expression “beauty sleep,” an individual’s sleep history may play an integral part in the perception and judgments of his or her attractiveness and health. To date, the concept of beauty sleep has lacked scientific support, but the biological importance of sleep may have favoured a sensitivity to perceive sleep related cues in others. It seems warranted to explore such sensitivity, as sleep disorders and disturbed sleep are increasingly common in today’s 24 hour society and often coexist with some of the most common health problems, such as hypertension9 10 and inflammatory conditions.11
To describe the relation between sleep deprivation and perceived health and attractiveness we asked untrained observers to rate the faces of people who had been photographed after a normal night’s sleep and after a night of sleep deprivation. We chose facial photographs as the human face is the primary source of information in social communication.12 A perceiver’s response to facial cues, signalling the bearer’s emotional state, intentions, and potential mate value, serves to guide actions in social contexts and may ultimately promote survival.13 14 15 We hypothesised that untrained observers would perceive sleep deprived people as more tired, less healthy, and less attractive compared with after a normal night’s sleep.
Methods
Using an experimental design we photographed the faces of 23 adults (mean age 23, range 18-31 years, 11 women) between 14.00 and 15.00 under two conditions in a balanced design: after a normal night’s sleep (at least eight hours of sleep between 23.00-07.00 and seven hours of wakefulness) and after sleep deprivation (sleep 02.00-07.00 and 31 hours of wakefulness). We advertised for participants at four universities in the Stockholm area. Twenty of 44 potentially eligible people were excluded. Reasons for exclusion were reported sleep disturbances, abnormal sleep requirements (for example, sleep need out of the 7-9 hour range), health problems, or availability on study days (the main reason). We also excluded smokers and those who had consumed alcohol within two days of the protocol. One woman failed to participate in both conditions. Overall, we enrolled 12 women and 12 men.
The participants slept in their own homes. Sleep times were confirmed with sleep diaries and text messages. The sleep diaries (Karolinska sleep diary) included information on sleep latency, quality, duration, and sleepiness. Participants sent a text message to the research assistant by mobile phone (SMS) at bedtime and when they got up on the night before sleep deprivation. They had been instructed not to nap. During the normal sleep condition the participants’ mean duration of sleep, estimated from sleep diaries, was 8.45 (SE 0.20) hours. The sleep deprivation condition started with a restriction of sleep to five hours in bed; the participants sent text messages (SMS) when they went to sleep and when they woke up. The mean duration of sleep during this night, estimated from sleep diaries and text messages, was 5.06 (SE 0.04) hours. For the following night of total sleep deprivation, the participants were monitored in the sleep laboratory at all times. Thus, for the sleep deprivation condition, participants came to the laboratory at 22.00 (after 15 hours of wakefulness) to be monitored, and stayed awake for a further 16 hours. We therefore did not observe the participants during the first 15 hours of wakefulness, when they had had a slightly restricted sleep, but had good control over the last 16 hours of wakefulness when sleepiness increased in magnitude. For the sleep condition, participants came to the laboratory at 12.00 (after five hours of wakefulness). They were kept indoors two hours before being photographed to avoid the effects of exposure to sunlight and the weather. We had a series of five or six photographs (resolution 3872×2592 pixels) taken in a well lit room, with a constant white balance (×900l; colour temperature 4200 K, Nikon D80; Nikon, Tokyo). The white balance was differently set during the two days of the study and affected seven photographs (four taken during sleep deprivation and three during a normal night’s sleep). Removing these participants from the analyses did not affect the results. The distance from camera to head was fixed, as was the focal length, within 14 mm (between 44 and 58 mm). To ensure a fixed surface area of each face on the photograph, the focal length was adapted to the head size of each participant.
For the photo shoot, participants wore no makeup, had their hair loose (combed backwards if long), underwent similar cleaning or shaving procedures for both conditions, and were instructed to “sit with a straight back and look straight into the camera with a neutral, relaxed facial expression.” Although the photographer was not blinded to the sleep conditions, she followed a highly standardised procedure during each photo shoot, including minimal interaction with the participants. A blinded rater chose the most typical photograph from each series of photographs. This process resulted in 46 photographs; two (one from each sleep condition) of each of the 23 participants. This part of the study took place between June and September 2007.
In October 2007 the photographs were presented at a fixed interval of six seconds in a randomised order to 65 observers (mainly students at the Karolinska Institute, mean age 30 (range 18-61) years, 40 women), who were unaware of the conditions of the study. They rated the faces for attractiveness (very unattractive to very attractive), health (very sick to very healthy), and tiredness (not at all tired to very tired) on a 100 mm visual analogue scale. After every 23 photographs a brief intermission was allowed, including a working memory task lasting 23 seconds to prevent the faces being memorised. To ensure that the observers were not primed to tiredness when rating health and attractiveness they rated the photographs for attractiveness and health in the first two sessions and tiredness in the last. To avoid the influence of possible order effects we presented the photographs in a balanced order between conditions for each session.
Statistical analyses
Data were analysed using multilevel mixed effects linear regression, with two crossed independent random effects accounting for random variation between observers and participants using the xtmixed procedure in Stata 9.2. We present the effect of condition as a percentage of change from the baseline condition as the reference using the absolute value in millimetres (rated on the visual analogue scale). No data were missing in the analyses.
Results
Sixty five observers rated each of the 46 photographs for attractiveness, health, and tiredness: 138 ratings by each observer and 2990 ratings for each of the three factors rated. When sleep deprived, people were rated as less healthy (visual analogue scale scores, mean 63 (SE 2) v 68 (SE 2)), more tired (53 (SE 3) v 44 (SE 3)), and less attractive (38 (SE 2) v 40 (SE 2); P<0.001 for all) than after a normal night’s sleep (table 1). Compared with the normal sleep condition, perceptions of health and attractiveness in the sleep deprived condition decreased on average by 6% and 4% and tiredness increased by 19%.
Table 1.
Multilevel mixed effects regression on effect of how sleep deprived people are perceived with respect to attractiveness, health, and tiredness
| Factors observed | Mean (SE) | Fixed effects* | SD (SE) random effects† | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal sleep | Sleep deprivation | z score | P value | Observer | Face | Residual | |||
| Health | 68 (2) | 63 (2) | −8.4 | 0.001 | 13 (1) | 7 (1) | 13 (0) | ||
| Attractiveness | 40 (2) | 38 (2) | −3.8 | 0.001 | 11 (1) | 6 (1) | 11 (0) | ||
| Tiredness | 44 (3) | 53 (3) | 12.4 | 0.001 | 10 (1) | 11 (2) | 18 (2) | ||
*Wald test.
†Evaluated using likelihood ratio test. Observers’ perceptions were rated using visual analogue scales of 100 mm, with 100 as the highest score. P=0.001 for all random effects.
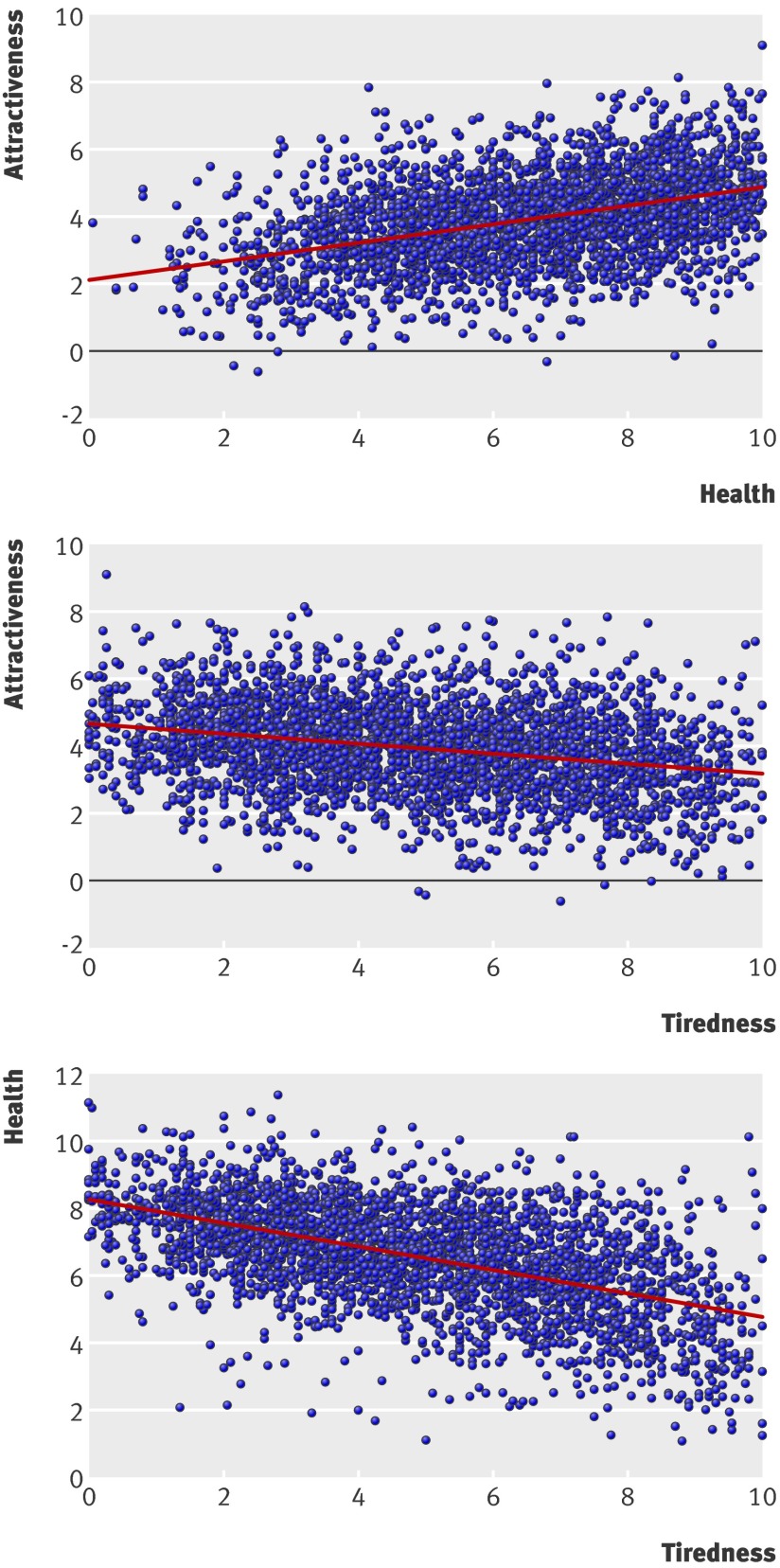
A 10 mm increase in tiredness was associated with a −3.0 mm change in health, a 10 mm increase in health increased attractiveness by 2.4 mm, and a 10 mm increase in tiredness reduced attractiveness by 1.2 mm (table 2). These findings were also presented as correlation, suggesting that faces with perceived attractiveness are positively associated with perceived health (r=0.42, fig 1) and negatively with perceived tiredness (r=−0.28, fig 1). In addition, the average decrease (for each face) in attractiveness as a result of deprived sleep was associated with changes in tiredness (−0.53, n=23, P=0.03) and in health (0.50, n=23, P=0.01). Moreover, a strong negative association was found between the respective perceptions of tiredness and health (r=−0.54, fig 1). Figure 2 shows an example of observer rated faces.
Table 2.
Associations between health, tiredness, and attractiveness
| Dependent variable | Predictor | Fixed effects* | SD (SE) random effects† | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient‡ | z score | P value | Observer | Face | Residual | ||||
| Health | Tiredness | −3.0 (0.1) | −24 | 0.001 | 12 (1) | 4 (1) | 13 (0) | ||
| Attractiveness | Health | 2.4 (0.1) | 17 | 0.001 | 11 (1) | 5 (1) | 11 (0) | ||
| Attractiveness | Tiredness | −1.2 (0.1) | −11 | 0.001 | 11 (1) | 5 (1) | 11 (0) | ||
Mixed effects regression models used crossed random intercepts for both observers (those rating photographs) and faces (photographed participants).
*Estimated coefficient of predictor on dependent variable and result from Wald test of statistical significance.
†Likelihood ratio test was used to test significance of random effects. P<0.001 for all random effects.
‡Change (mm) in dependent variable when predictor variable changes 10 mm.
Fig 1 Relations between health, tiredness, and attractiveness of 46 photographs (two each of 23 participants) rated by 65 observers on 100 mm visual analogue scales, with variation between observers removed using empirical Bayes’ estimates
Fig 2 Participant after a normal night’s sleep (left) and after sleep deprivation (right). Faces were presented in a counterbalanced order
To evaluate the mediation effects of sleep loss on attractiveness and health, tiredness was added to the models presented in table 1 following recommendations.16 The effect of sleep loss was significantly mediated by tiredness on both health (P<0.001) and attractiveness (P<0.001). When tiredness was added to the model (table 1) with an estimated coefficient of −2.9 (SE 0.1; P<0.001) the independent effect of sleep loss on health decreased from −4.2 to −1.8 (SE 0.5; P<0.001). The effect of sleep loss on attractiveness decreased from −1.6 (table 1) to −0.62 (SE 0.4; P=0.133), with tiredness estimated at −1.1 (SE 0.1; P<0.001). The same approach applied to the model of attractiveness and health (table 2), with a decrease in the association from 2.4 to 2.1 (SE 0.1; P<0.001) with tiredness estimated at −0.56 (SE 0.1; P<0.001).
Discussion
Sleep deprived people are perceived as less attractive, less healthy, and more tired compared with when they are well rested. Apparent tiredness was strongly related to looking less healthy and less attractive, which was also supported by the mediating analyses, indicating that a large part of the found effects and relations on appearing healthy and attractive were mediated by looking tired. The fact that untrained observers detected the effects of sleep loss in others not only provides evidence for a perceptual ability not previously subjected to experimental control, but also supports the notion that sleep history gives rise to socially relevant signals that provide information about the bearer. The adaptiveness of an ability to detect sleep related facial cues resonates well with other research, showing that small deviations from the average sleep duration in the long term are associated with an increased risk of health problems and with a decreased longevity.8 17 Indeed, even a few hours of sleep deprivation inflict an array of physiological changes, including neural, endocrinological, immunological, and cellular functioning, that if sustained are relevant for long term health.7 18 19 20 Here, we show that such physiological changes are paralleled by detectable facial changes.
These results are related to photographs taken in an artificial setting and presented to the observers for only six seconds. It is likely that the effects reported here would be larger in real life person to person situations, when overt behaviour and interactions add further information. Blink interval and blink duration are known to be indicators of sleepiness,21 and trained observers are able to evaluate reliably the drowsiness of drivers by watching their videotaped faces.22 In addition, a few of the people were perceived as healthier, less tired, and more attractive during the sleep deprived condition. It remains to be evaluated in follow-up research whether this is due to random error noise in judgments, or associated with specific characteristics of observers or the sleep deprived people they judge. Nevertheless, we believe that the present findings can be generalised to a wide variety of settings, but further studies will have to investigate the impact on clinical studies and other social situations.
Importantly, our findings suggest a prominent role of sleep history in several domains of interpersonal perception and judgment, in which sleep history has previously not been considered of importance, such as in clinical judgment. In addition, because attractiveness motivates sexual behaviour, collaboration, and superior treatment,13 sleep loss may have consequences in other social contexts. For example, it has been proposed that facial cues perceived as attractive are signals of good health and that this recognition has been selected evolutionarily to guide choice of mate and successful transmission of genes.13 The fact that good sleep supports a healthy look and poor sleep the reverse may be of particular relevance in the medical setting, where health estimates are an essential part. It is possible that people with sleep disturbances, clinical or otherwise, would be judged as more unhealthy, whereas those who have had an unusually good night’s sleep may be perceived as rather healthy. Compared with the sleep deprivation used in the present investigation, further studies are needed to investigate the effects of less drastic acute reductions of sleep as well as long term clinical effects.
Conclusions
People are capable of detecting sleep loss related facial cues, and these cues modify judgments of another’s health and attractiveness. These conclusions agree well with existing models describing a link between sleep and good health,18 23 as well as a link between attractiveness and health.13 Future studies should focus on the relevance of these facial cues in clinical settings. These could investigate whether clinicians are better than the average population at detecting sleep or health related facial cues, and whether patients with a clinical diagnosis exhibit more tiredness and are less healthy looking than healthy people. Perhaps the more successful doctors are those who pick up on these details and act accordingly.
Taken together, our results provide important insights into judgments about health and attractiveness that are reminiscent of the anecdotal wisdom harboured in Bell’s words, and in the colloquial notion of “beauty sleep.”
What is already known on this topic
Short or disturbed sleep and fatigue constitute major risk factors for health and safety
Complaints of short or disturbed sleep are common among patients seeking healthcare
The human face is the main source of information for social signalling
What this study adds
The facial cues of sleep deprived people are sufficient for others to judge them as more tired, less healthy, and less attractive, lending the first scientific support to the concept of “beauty sleep”
By affecting doctors’ general perception of health, the sleep history of a patient may affect clinical decisions and diagnostic precision
We thank B Karshikoff for support with data acquisition and M Ingvar for comments on an earlier draft of the manuscript, both without compensation and working at the Department for Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Sweden.
Contributors: JA designed the data collection, supervised and monitored data collection, wrote the statistical analysis plan, carried out the statistical analyses, obtained funding, drafted and revised the manuscript, and is guarantor. TS designed and carried out the data collection, cleaned the data, drafted, revised the manuscript, and had final approval of the manuscript. JA and TS contributed equally to the work. MI wrote the statistical analysis plan, carried out the statistical analyses, drafted the manuscript, and critically revised the manuscript. EJWVS provided statistical advice, advised on data handling, and critically revised the manuscript. AO provided advice on the methods and critically revised the manuscript. ML provided administrative support, drafted the manuscript, and critically revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding: This study was funded by the Swedish Society for Medical Research, Rut and Arvid Wolff’s Memory Fund, and the Osher Center for Integrative Medicine.
Competing interests: All authors have completed the Unified Competing Interest form at www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf (available on request from the corresponding author) and declare: no support from any company for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any companies that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Ethical approval: This study was approved by the Karolinska Institutet’s ethical committee. Participants were compensated for their participation.
Participant consent: Participant’s consent obtained.
Data sharing: Statistical code and dataset of ratings are available from the corresponding author at john.axelsson@ki.se.
Cite this as: BMJ 2010;341:c6614
References
- 1.Deten A, Volz HC, Clamors S, Leiblein S, Briest W, Marx G, et al. Hematopoietic stem cells do not repair the infarcted mouse heart. Cardiovasc Res 2005;65:52-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Doyle AC. The case-book of Sherlock Holmes: selected stories. Wordsworth, 1993.
- 3.Lieberman MD, Gaunt R, Gilbert DT, Trope Y. Reflection and reflexion: a social cognitive neuroscience approach to attributional inference. Adv Exp Soc Psychol 2002;34:199-249. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Drummond SPA, Brown GG, Gillin JC, Stricker JL, Wong EC, Buxton RB. Altered brain response to verbal learning following sleep deprivation. Nature 2000;403:655-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Harrison Y, Horne JA. The impact of sleep deprivation on decision making: a review. J Exp Psychol Appl 2000;6:236-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Huber R, Ghilardi MF, Massimini M, Tononi G. Local sleep and learning. Nature 2004;430:78-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Spiegel K, Leproult R, Van Cauter E. Impact of sleep debt on metabolic and endocrine function. Lancet 1999;354:1435-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kripke DF, Garfinkel L, Wingard DL, Klauber MR, Marler MR. Mortality associated with sleep duration and insomnia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2002;59:131-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Olson LG, Ambrogetti A. Waking up to sleep disorders. Br J Hosp Med (Lond) 2006;67:118, 20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rajaratnam SM, Arendt J. Health in a 24-h society. Lancet 2001;358:999-1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ranjbaran Z, Keefer L, Stepanski E, Farhadi A, Keshavarzian A. The relevance of sleep abnormalities to chronic inflammatory conditions. Inflamm Res 2007;56:51-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Haxby JV, Hoffman EA, Gobbini MI. The distributed human neural system for face perception. Trends Cogn Sci 2000;4:223-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rhodes G. The evolutionary psychology of facial beauty. Annu Rev Psychol 2006;57:199-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Todorov A, Mandisodza AN, Goren A, Hall CC. Inferences of competence from faces predict election outcomes. Science 2005;308:1623-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Willis J, Todorov A. First impressions: making up your mind after a 100-ms exposure to a face. Psychol Sci 2006;17:592-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Krull JL, MacKinnon DP. Multilevel modeling of individual and group level mediated effects. Multivariate Behav Res 2001;36:249-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ayas NT, White DP, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Speizer FE, Malhotra A, et al. A prospective study of sleep duration and coronary heart disease in women. Arch Intern Med 2003;163:205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bryant PA, Trinder J, Curtis N. Sick and tired: does sleep have a vital role in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2004;4:457-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cirelli C. Cellular consequences of sleep deprivation in the brain. Sleep Med Rev 2006;10:307-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Irwin MR, Wang M, Campomayor CO, Collado-Hidalgo A, Cole S. Sleep deprivation and activation of morning levels of cellular and genomic markers of inflammation. Arch Intern Med 2006;166:1756-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schleicher R, Galley N, Briest S, Galley L. Blinks and saccades as indicators of fatigue in sleepiness warnings: looking tired? Ergonomics 2008;51:982-1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wierwille WW, Ellsworth LA. Evaluation of driver drowsiness by trained raters. Accid Anal Prev 1994;26:571-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Horne J. Why we sleep—the functions of sleep in humans and other mammals. Oxford University Press, 1988.