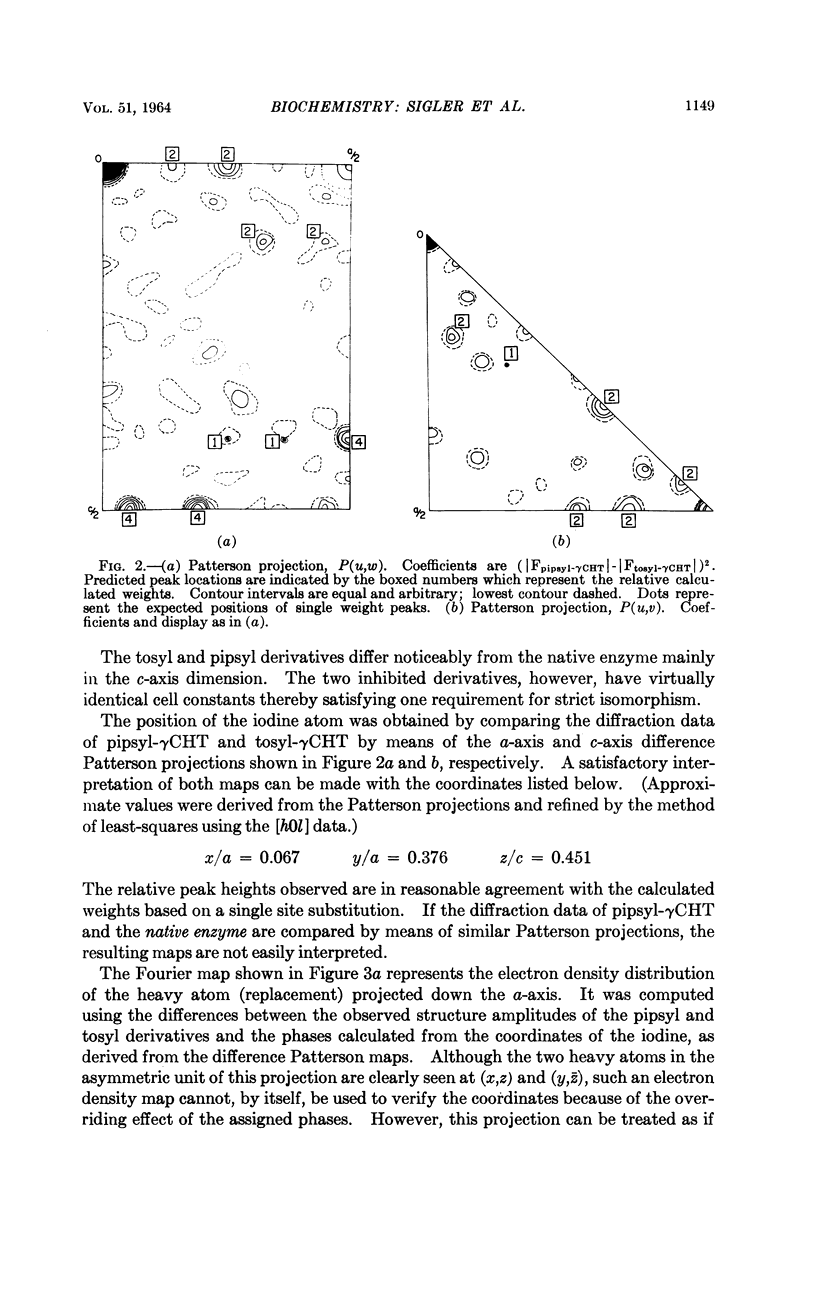
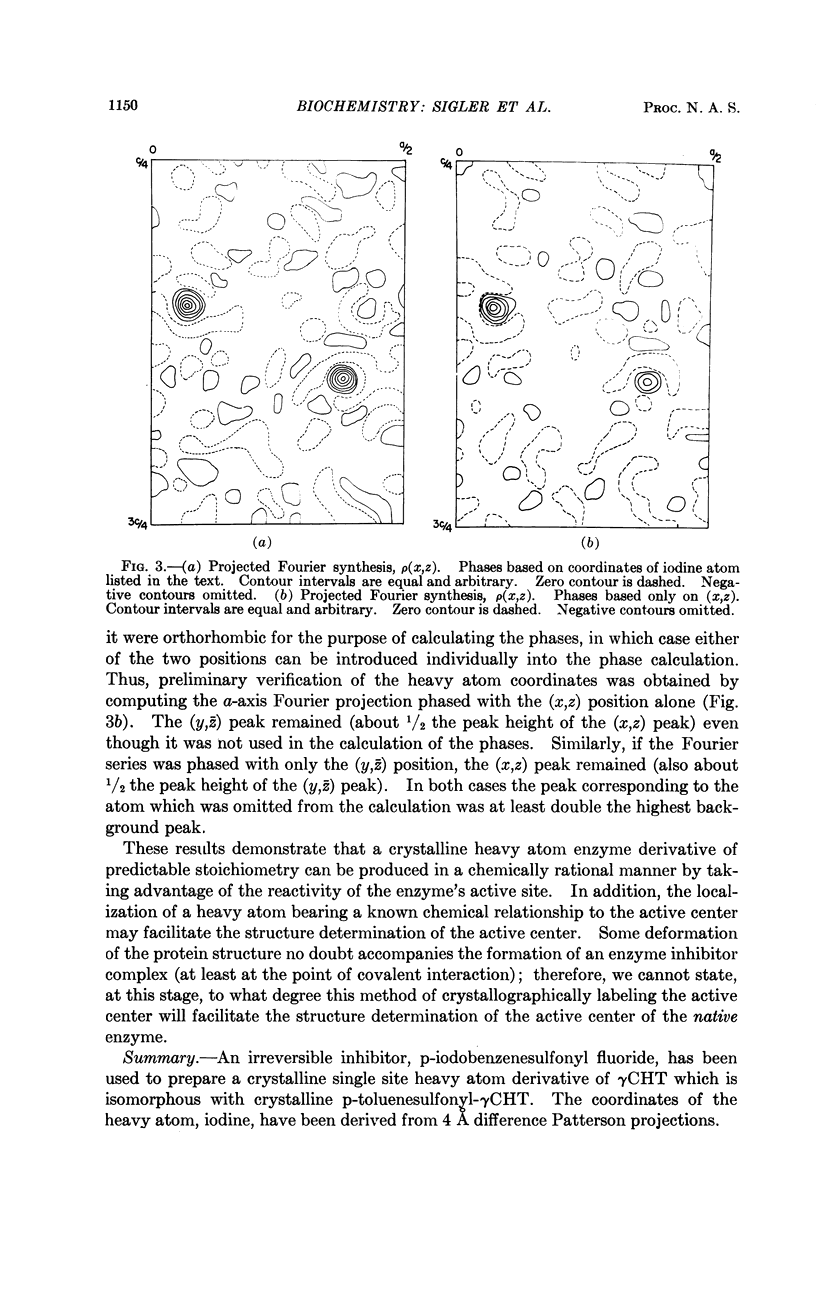
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GOLD A. M., FAHRNEY D. E. The mechanism of reactivation of phenylmethanesulfonyl alpha-chymotrypsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jan 18;10:55–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL B. C. A modified spectrophotometric determination of chymotrypsin, trypsin, and thrombin. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Dec;37:1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALLOS J., RIZOK D. THE STUDY OF THE ACTIVE CENTER OF CHYMOTRYPSIN. II. P-TOLUENESULFONYLCHYMOTRYPSIN. J Mol Biol. 1963 Nov;7:599–601. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OOSTERBAAN R. A., VAN ADRICHEM M. E. Isolation of acetyl peptides from acetylchymotrypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Feb;27(2):423–425. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFER N. K., MAY S. C., Jr, SUMMERSON W. H. Serine phosphoric acid from diisopropylphosphoryl chymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1953 May;202(1):67–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRUMEYER D. H., WHITE W. N., KOSHLAND D. E., Jr ROLE OF SERINE IN CHYMOTRYPSIN ACTION. CONVERSION OF THE ACTIVE SERINE TO DEHYDROALANINE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Nov;50:931–935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


