Abstract
Objectives
Active telephone recruitment (‘cold calling’) can enrol almost 45 times more smokers to cessation services than media. However, the effectiveness of proactive telephone counselling with cold-called smokers from the broader community is unknown. This study examined whether proactive telephone counselling improved abstinence, quit attempts and reduced cigarette consumption among cold-called smokers.
Methods
From 48 014 randomly selected electronic telephone directory numbers, 3008 eligible smokers were identified and 1562 (51.9%) smokers recruited into the randomised controlled trial. Of these, 769 smokers were randomly allocated to proactive telephone counselling and 793 to the control (ie, mailed self-help) conditions. Six counselling calls were offered to intervention smokers willing to quit within a month and four to those not ready to quit. The 4-month, 7-month and 13-month follow-up interviews were completed by 1369 (87.6%), 1278 (81.8%) and 1245 (79.9%) participants, respectively.
Results
Proactive telephone counselling participants were significantly more likely than controls to achieve 7-day point prevalence abstinence at 4 months (13.8% vs 9.6%, p=0.005) and 7 months (14.3% vs 11.0%, p=0.02) but not at 13 months. There was a significant impact of telephone counselling on prolonged abstinence at 4 months (3.4% vs 1.8%, p=0.02) and at 7 months (2.2% vs 0.9%, p=0.02). At 4 months post recruitment, telephone counselling participants were significantly more likely than controls to have made a quit attempt (48.6% vs 42.9%, p=0.01) and reduced cigarette consumption (16.9% vs 9.0%, p=0.0002).
Conclusions
Proactive telephone counselling initially increased abstinence and quitting behaviours among cold-called smokers. Given its superior reach, quitlines should consider active telephone recruitment, provided relapse can be reduced.
Trial registration
Australian New Zealand Clinical Trial Registry; ACTRN012606000221550.
Keywords: Telephone counselling, quitline, smoking cessation, randomised controlled trial, addiction, cessation
Introduction
Proactive telephone counselling involves counsellor-initiated counselling calls and may be offered to treatment seekers after their initial contact or to smokers referred to the quitline.1 Yet only 1% to 7% of adult smokers use quitlines annually2–4 despite about 40% of smokers making a quit attempt each year.5 Active recruitment strategies that involve recruiter-initiated contact with smokers, such as active telephone recruitment or ‘cold calling’, may increase quitline use given it is acceptable to smokers6 and can recruit almost 45 times more smokers to cessation interventions than media.7
Most randomised controlled trials (RCTs) examining proactive telephone counselling recruited smokers seeking treatment.8–23 Of those that measured 7-day point prevalence abstinence the majority found a significant effect of proactive telephone counselling at 3 months,15 18 22 but not at 6 months15 17 20 or 12 months17 18. In relation to prolonged abstinence a significant treatment effect was mainly reported.8–15 Two trials revealed that proactive telephone counselling significantly increased quit attempts during the first 3 months.12 13 However, others reported no short-term or long-term impact.8 9 16 In regards to reduction in daily cigarette consumption, proactive telephone counselling had a partial19 or no10 18 impact.
Smokers who seek cessation interventions are not representative of the smoking population. For instance, quitline callers are more likely to be women, younger, higher educated, more addicted,24 25 have previously quit24 and be ready to quit within 30 days25 than smokers in the general population. Proactive telephone counselling trials with treatment seekers have limited generalisability to all smokers, especially since many included only smokers ready to quit within 30 days.11–13 16 17 However, it is uncertain whether proactive telephone counselling would be as effective with actively recruited smokers as for treatment seekers. The cost of extending the reach of quitlines can only be justified if proactive telephone counselling of actively recruited smokers is effective and achieves acceptable cessation rates.
A limited number of RCTs have evaluated the effectiveness of proactive telephone counselling among actively recruited smokers.26–33 One of two trials that measured 7-day point prevalence abstinence found a significant effect of proactive telephone counselling at 3 months,27 but most reported no impact at 6 months28 33 and at 12 months.27 32 None of these studies reported a significant impact of proactive telephone counselling on prolonged abstinence within 12 months 26 27 30 33 or quit attempts.26–28 Proactive telephone counselling was found to reduce cigarette consumption at 3 months,31 6 months26 and 12 months.31
Of the proactive telephone counselling trials with actively recruited smokers, three recruited participants via mail,30–32 one used mail supplemented by telephone33 and four used active telephone recruitment.26–29 The trials that used active telephone recruitment targeted a particular segment of the smoking population: women having cervical cancer screening,28 clients from a health maintenance organisation,27 parents with young children26 and general community smokers interested in quitting.29 Given active telephone recruitment could increase the proportion of smokers using quitlines7 34 it is important to examine the efficacy of proactive telephone counselling among cold-called smokers from the broader general population.
This study recruited adult daily smokers by telephone from the broader general population and assessed the short-term and long-term effectiveness of proactive telephone counselling on (i) 7-day point prevalence abstinence and prolonged abstinence, (ii) making a quit attempt and (iii) reducing cigarette consumption by at least 50%.
Methods
Participants
Recruitment occurred between September 2005 and April 2007. Eligibility requirements were: daily tobacco use; aged 18 years or older; New South Wales (NSW) resident, Australia; and English speaking. Smokers were eligible regardless of their quitting intention.
Recruitment and evaluation
Overall, 48 014 telephone numbers were randomly selected from the NSW Electronic White Pages telephone directory. Households were mailed an information letter and a trained interviewer telephoned within 2 weeks. Of 43 710 households reached, 3008 contained at least 1 eligible smoker. If two or more eligible smokers were residents, a computerised age grid randomly selected one smoker. This smoker was invited to join the RCT and if he/she gave verbal consent completed a baseline computer-assisted telephone interview (CATI; n=1562). Subsequently, the CATI used a random number generator created by an independent programmer to allocate the smoker to proactive telephone counselling (n=769) or self-help materials (control: n=793). Assessors were blind to participant condition during the baseline interview.
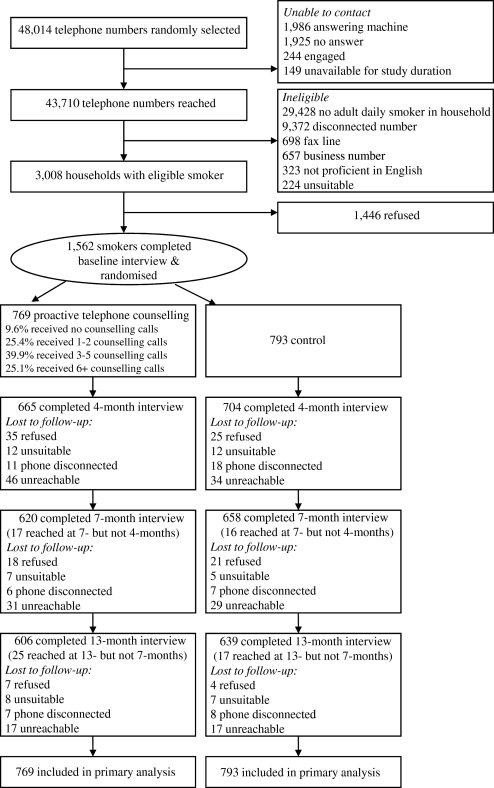
Between January 2006 and June 2008, CATIs were conducted at 4 months, 7 months and 13 months post recruitment to assess smoking cessation. Given follow-up interviews included condition-specific items assessors were not blind to participant condition. However, assessors were independent of the researchers and NSW Quitline. Figure 1 outlines participant recruitment and assessment.
Figure 1.
Recruitment and progress through the trial.
The University of Newcastle Human Research Ethics Committee and the Hunter New England Human Research Ethics Committee granted ethics approval.
Conditions
Proactive telephone counselling
The contact details of each intervention participant, preferred days and times to call, and responses to selected baseline interview items were included in a referral form and securely emailed to the NSW Quitline the next working day.
The NSW Quitline called all intervention participants regardless of their quitting intention. The initial proactive counselling call typically occurred within 1 week of referral and aimed to provide smokers with motivation to set a quit date or move closer to quitting. At the end of the initial counselling call, participants were asked if they were willing to quit within a month and counselling calls offered according to their quitting intention. Six attempts were made over a week to reach the participant for each counselling session. At the end of each counselling call the next session was scheduled (if accepted). Although calls were offered as per the schedule, each call was booked according to participant preference.
‘Ready to quit’ callback schedule
Participants ready to quit within a month were offered an additional five proactive telephone counselling calls: on the quit date, and at 3, 7, 14 and 30 days after the quit date. This evidence-based call schedule accounts for the greatest probability of relapse, involves calls being scheduled close to the critical first 2 weeks following a quit attempt12 and mimics the standard call schedule offered by NSW Quitline.
The content of the ‘ready to quit’ calls included: assessing smoking status (eg, stopped, cut down, relapsed, smoking the same), identifying and coping with triggers (eg, alcohol, stress, tea/coffee, meals), information on effective quitting aids (eg, nicotine replacement therapy (NRT), bupropion), setting tasks to assist with quitting (eg, listing goals, listing triggers and strategies to deal with triggers) and relapse prevention strategies and promotion of self-efficacy.
Those who relapsed and set a new quit date within a month restarted the ‘ready to quit’ schedule, whereas those who did not were offered a call in 1 month's time.
‘Not ready to quit’ callback schedule
Participants not ready to quit within a month were offered an additional three proactive telephone counselling calls at 1 month, 3 months and 5 months after the initial counselling call. The ‘not ready to quit’ calls involved motivational interviewing (MI) that focused on encouraging participants to move towards setting a quit date. These calls included assessing smoking status, setting tasks to encourage quitting, talking about available quitting strategies and promotion of self-efficacy.
If those in the ‘not ready to quit’ schedule indicated during counselling that they were now willing to quit within a month, they began the ‘ready to quit’ callback schedule on their nominated quit date.
Maximum number of counselling calls
To allow for changes in readiness to quit a maximum of 12 proactive counselling calls were offered regardless of quitting intention.
Advisor training
NSW Quitline training
NSW Quitline advisors receive comprehensive theoretical and practical training, including supervision with an experienced mentor before undertaking telephone counselling. A refresher course on cognitive–behavioural therapy and MI is also provided. Most (70%) advisors who delivered the intervention attended booster MI training sessions to assist with supporting smokers who were not ready to quit.
Study protocols training
Advisors contacted participants only after attending a 2 h training session where researchers outlined the study protocols. The researchers provided feedback to advisors on intervention delivery bimonthly.
Controls
Control participants were mailed a non-tailored quit kit the next working day after their baseline interview. These materials were identical to those the NSW Quitline offers to their callers.
The quit kit contained the following: a letter outlining the contents and the quitline phone number, Quit Because You Can booklet (a guide to quitting), Products to Help You Quit Smoking brochure that described effective pharmacotherapy and behavioural quitting strategies, You Can Quit pocket guide that included suggestions on how to remain smoke free, a Quitline brochure, explaining the telephone counselling services offered and a ‘no smoking’ sticker.
These self-help materials outlined the risks of smoking, triggers associated with smoking, effective quitting aids such as pharmacotherapies, withdrawal symptoms and cravings and coping with setbacks. These topics are similar to those that were discussed with intervention participants.
Measures
Baseline interview
Baseline interview question topics included sociodemographics (eg, education), smoking-related issues (eg, cigarettes smoked per day) and other behaviour (eg, alcohol consumption) (see table 1).
Table 1.
Participant characteristics at baseline
| Characteristic | Proactive telephone counselling (n=769)† | Controls (n=793)‡ | p Value§ |
| Gender, % | |||
| Male | 50.2 | 48.5 | 0.5 |
| Female | 49.8 | 51.5 | |
| Age, years | |||
| Mean (SD) | 45.4 (12.7) | 44.4 (13.8) | 0.2 |
| Median | 45 | 44 | |
| Country of birth, % | |||
| Australia | 81.8 | 79.9 | 0.4 |
| Other | 18.2 | 20.1 | |
| Education, % | |||
| Primary only | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| Year 7–10 | 32.9 | 31.3 | |
| HSC or TAFE | 46.7 | 46.2 | |
| University or tertiary | 18.2 | 19.2 | |
| Other | 1.3 | 2.4 | |
| Marital status, % | |||
| Married/de facto | 52.6 | 57.4 | 0.01* |
| Divorced/separated | 23.4 | 16.8 | |
| Widowed | 3.9 | 4.7 | |
| Never married | 20.1 | 21.1 | |
| Employment status, % | |||
| Employed full time | 45.1 | 44.6 | 0.4 |
| Employed part time/casual | 20.8 | 18.5 | |
| Unemployed | 6.1 | 6.9 | |
| Student | 2.0 | 2.6 | |
| Retired | 9.6 | 11.5 | |
| Permanently unable to work | 6.0 | 4.7 | |
| Home duties | 7.5 | 9.2 | |
| Other | 2.9 | 1.9 | |
| Area of residence, % | |||
| Metropolitan | 43.4 | 42.0 | 0.6 |
| Non-metropolitan | 56.6 | 58.0 | |
| Age began regular smoking | |||
| Mean (SD) | 17.3 (4.4) | 17.6 (4.7) | 0.2 |
| Median | 17 | 17 | |
| Time to first cigarette, min | |||
| Mean (SD) | 47.1 (84.4) | 55.4 (114.4) | 0.1 |
| Median | 20 | 20 | |
| Cigarettes per day | |||
| Mean (SD) | 19.9 (9.6) | 18.9 (9.9) | 0.03* |
| Median | 20 | 20 | |
| Ever quit for ≥24 h, % | |||
| Yes | 89.1 | 89.7 | 0.7 |
| No/don't know | 10.9 | 10.3 | |
| Quit attempt in past 12 months, % | |||
| Yes | 47.6 | 47.3 | 0.9 |
| No | 52.4 | 52.7 | |
| Quitting intentions, % | |||
| Will quit in next 30 days | 29.0 | 26.9 | 0.3 |
| Will quit in next 6 months | 40.8 | 38.7 | |
| Will not quit in next 6 months | 25.7 | 29.9 | |
| Don't know | 4.4 | 4.5 | |
| Other household smokers, % | |||
| Yes | 24.1 | 25.0 | 0.7 |
| No | 75.9 | 75.0 | |
| Alcohol consumption | |||
| Daily | 18.9 | 15.7 | 0.4 |
| Weekly | 42.1 | 43.8 | |
| Less than weekly | 21.9 | 23.8 | |
| Don't drink alcohol | 17.1 | 16.7 | |
*p<0.05.
Missing data range 0–7.
Missing data range 0–7.
Categorical outcomes were analysed with a χ2 test and continuous outcomes with a t test.
HSC, Higher School Certificate (Year 12); TAFE, Technical and Further Education.
Process measures
The number and duration of counselling calls received by proactive telephone counselling participants (to assess intervention integrity) and by control participants who called the quitline themselves (to assess potential contamination) was extracted from the NSW Quitline database. Additionally, during each follow-up interview control participants were asked whether they called the quitline.
Use of other quitting aids
During the 13-month assessment respondents indicated if they had used other quitting aids (ie, NRT, bupropion, group counselling, general practitioner advice) since baseline.
Outcome measures
The primary outcomes as recommended by an expert workgroup35 were self-reported 7-day point prevalence abstinence (ie, abstinence for at least 7-days immediately preceding follow-up) and prolonged abstinence (ie, sustained abstinence after an initial period in which smoking is not counted as a failure) assessed at 4 months, 7 months and 13 months post recruitment.
To achieve 7-day point prevalence abstinence, participants had to answer ‘no’ to ‘Have you smoked at least part of a cigarette in the last 7 days?’ and ‘Have you used any of those other forms of tobacco, for example pipes or cigars, in the last 7 days?’. Prolonged abstinence was measured from a 1-month post-recruitment grace period (to give smokers an opportunity to quit) to each follow-up and between interviews,35 resulting in prolonged abstinence of 3 months, 6 months, 9 months and 12 months. To achieve prolonged abstinence participants had to answer ‘no’ to ‘Since [date] did you smoke at all, even part of a cigarette?’ and ‘Since [date] have you used any other forms of tobacco, for example, pipes or cigars?’. The [date] related to the end of the 1-month post-recruitment grace period during the 4-month interview and the preceding follow-up at the 7-month and 13-month assessments.
Secondary outcomes related to the proportion of smokers making a quit attempt and reducing their cigarette consumption by at least 50%. During the 4-month interview, all participants (given all smoked at baseline) were asked whether they had quit for 1 day or longer since baseline. At the 7-month and 13-month assessments the proportion that made a quit attempt was based on those who had smoked at some time since the previous interview. The proportion that reduced their cigarette consumption by at least 50% was calculated among respondents who smoked daily at the follow-up interviews.
Sample size
A total of 770 participants were needed per group at 13 months post recruitment to detect a difference of 5% for 7-day point prevalence (ie, 15% vs 10%) and 3% for prolonged abstinence (ie, 6% vs 3%) based on a significance level of 5% and 80% power.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was completed using SAS software V. 9.1 (SAS, Cary, North Carolina, USA). χ2 tests and t tests were used to examine whether participants' baseline characteristics differed by condition.
To compare 7-day point prevalence abstinence, prolonged abstinence, quit attempts or at least 50% cigarette reduction by condition, logistic regression analysis was used to adjust for between-group differences at baseline (ie, marital status and cigarette consumption). Analysis was on intention to treat and for 7-day point prevalence and prolonged abstinence those who refused or could not be reached for follow-up were presumed to be smokers. For the quit attempt and cigarette reduction analyses, only those providing follow-up data were included. Tests of significance were performed at α=0.05.
Results
Baseline characteristics and attrition
Of 3008 eligible smokers, 1562 (51.9%) were recruited. Table 1 describes participants' baseline characteristics by condition. Apart from relatively small divergences in marital status and cigarettes smoked per day, there were no other significant between-group differences at baseline.
The 4-month, 7-month and 13-month interviews were completed by 1369 (87.6%), 1278 (81.8%) and 1245 (79.9%) participants, respectively. Attrition rates did not differ significantly by condition for any assessment.
Process measures
Among proactive telephone counselling participants (n=769), 90% accepted at least one and 65% three or more counselling calls. Of those who received any counselling calls (n=695), the mean was 4.4 calls (SD 2.9; median=4). The mean duration of each consecutive counselling call was: 12.4 min (SD 10.0; median=10); 7.7 min (SD 7.8; median=5); 7.9 min (SD 7.6; median=5); 7.6 min (SD 7.6; median=5); 7.0 min (SD 6.2; median=5); and 7.6 min (SD 8.2; median=5).
According to self-report, 7.8% of control participants called the quitline themselves for telephone support (ie, contamination rate). The corresponding proportion from the quitline database check was 2.5% but as quitline callers can remain anonymous this figure was expected to be an underestimate of quitline use.
Use of other quitting aids
During the 13-month assessment respondents were asked about any use of quitting aids since baseline. Overall, 40.6% (41.9% intervention, 39.3% control) used NRT, 21.1% (23.3% intervention, 19.1% control) general practitioner advice, 7.2% (8.3% intervention, 6.3% control) bupropion and 1.4% (1.2% intervention; 1.6% control) group counselling. When asked about other strategies used, 0.1% (0.2% intervention; 0% control) reported using web-assisted interventions. There were no significant differences in the use of any quitting strategies (other than telephone counselling) by condition.
Smoking cessation rates
Table 2 reports the 7-day point prevalence and prolonged abstinence rates at each assessment. Those offered proactive telephone counselling were significantly more likely than control participants to achieve 7-day point prevalence abstinence at 4 months (13.8% vs 9.6%, p=0.005) and 7 months post recruitment (14.3% vs 11.0%, p=0.02). At the 13-month interview there was no significant difference by condition (15.2% vs 14.4%, p=0.4).
Table 2.
Point prevalence and prolonged abstinence at 4 months, 7 months and 13 months post recruitment†
| Smoking cessation measure and follow-up time point | Proactive telephone counselling (n=769) | Controls (n=793) | Adjusted p Value‡ | ||
| n | % | n | % | ||
| 7-day point prevalence abstinence at: | |||||
| 4 months post recruitment | 106 | 13.8 | 76 | 9.6 | 0.005* |
| 7 months post recruitment | 110 | 14.3 | 87 | 11.0 | 0.02* |
| 13 months post recruitment | 117 | 15.2 | 114 | 14.4 | 0.4 |
| 3-month prolonged abstinence at: | |||||
| 4 months post recruitment | 26 | 3.4 | 14 | 1.8 | 0.02* |
| 7 months post recruitment | 46 | 6.0 | 36 | 4.5 | 0.1 |
| 6-month prolonged abstinence at: | |||||
| 7 months post recruitment | 17 | 2.2 | 7 | 0.9 | 0.02* |
| 13 months post recruitment | 44 | 5.7 | 44 | 5.5 | 0.7 |
| 9-month prolonged abstinence at: | |||||
| 13 months post recruitment | 25 | 3.3 | 27 | 3.4 | 0.9 |
| 12-month prolonged abstinence at: | |||||
| 13 months post recruitment | 11 | 1.4 | 6 | 0.8 | 0.1 |
*p<0.05.
Missing data counted as smokers.
Adjusted for baseline marital status and cigarettes smoked per day.
Proactive telephone counselling participants were significantly more likely than controls to achieve 3-month prolonged abstinence at 4 months post recruitment (3.4% vs 1.8%, p=0.02) and 6-month prolonged abstinence during the 7-month interview (2.2% vs 0.9%, p=0.02). The 3-month prolonged abstinence measure failed to reach significance at 7-month follow-up. No measure of prolonged abstinence differed significantly by condition at 13 months post recruitment.
Quit attempts
As shown in table 3, during the 4-month interview the proactive telephone counselling group (48.6%) was significantly more likely than the control (42.9%) to have made a quit attempt since baseline (p=0.01). Between the 4–7 month, 7–13 month and baseline to 13-month periods, there was no significant difference in quit attempts by condition.
Table 3.
Proportion making a quit attempt between the follow-up periods
| Quit attempt | Proactive telephone counselling | Controls | Adjusted p Value† | ||||
| N | n | % | N | n | % | ||
| Baseline to 4 months | 664 | 323 | 48.6 | 704 | 302 | 42.9 | 0.01* |
| 4–7 months | 574 | 213 | 37.1 | 622 | 216 | 34.7 | 0.3 |
| 7–13 months | 562 | 232 | 41.3 | 595 | 223 | 37.5 | 0.1 |
| Baseline to 13 months‡ | 566 | 384 | 67.8 | 610 | 390 | 63.9 | 0.09 |
*p<0.05.
Adjusted for baseline marital status and cigarettes smoked per day.
Includes those who completed all assessments (ie, baseline, 4-month, 7-month and 13-month interviews).
Cigarette reduction among daily smokers
Table 4 illustrates that proactive telephone counselling participants who smoked daily at 4 months were significantly more likely than their control group counterparts to have reduced their cigarette consumption by at least 50% since baseline (16.9% vs 9.0%, p=0.0002). However, a treatment effect was not found between 4–7 months, 7–13 months or baseline to 13 months.
Table 4.
At least 50% reduction in cigarette consumption among daily smokers
| 50% reduction in cigarette consumption: | Proactive telephone counselling | Controls | Adjusted p Value† | ||||
| N | n | % | N | n | % | ||
| Baseline to 4 months | 504 | 85 | 16.9 | 589 | 53 | 9.0 | 0.0002* |
| 4–7 months | 411 | 18 | 4.4 | 480 | 23 | 4.8 | 0.8 |
| 7–13 months | 378 | 18 | 4.8 | 430 | 24 | 5.6 | 0.4 |
| Baseline to 13 months | 449 | 64 | 14.3 | 484 | 52 | 10.7 | 0.3 |
*p<0.05.
Adjusted for baseline marital status and cigarettes smoked per day.
Discussion
This is the first trial to assess the efficacy of using active telephone recruitment exclusively (‘cold calling’) followed by proactive telephone counselling among daily smokers from the broader general population. At 4 and 7 months post recruitment proactive telephone counselling significantly increased 7-day point prevalence abstinence. However, this was not sustained longer term. The North American Quitline Consortium recently recommended assessing quit rates at 7 months36 however many previous trials have done so at 6 months. If we assume that our 4-month, 7-month and 13-month assessments are similar to the 3-month, 6-month and 12-month assessments in other trials, respectively, comparisons can be made. The 7-day point prevalence abstinence findings were consistent with trials of treatment seekers that reported a significant proactive telephone counselling effect at 3 months,15 18 22 and 6 months18 but not at 12 months.17 18 Apart from two trials that reported much higher proportions,15 18 our 7-day point prevalence abstinence rates for proactive telephone counselling participants at 4 months (13.8%), 7 months (14.3%) and 13 months (15.2%) were similar to those of treatment seekers: 10% to 15% at 3 months,17 20 22 15% to 20% at 6 months17 20 and 14% to 17% at 12 months.17 22 Our results were also consistent with most trials of actively recruited smokers that reported no impact of proactive telephone counselling on 7-day point prevalence abstinence at 12 months.27 32
Proactive telephone counselling significantly increased 3-month prolonged abstinence at 4 months and 6-month prolonged abstinence at 7 months but not for any measure at 13 months post recruitment. Given most trials with treatment seekers reported that proactive telephone counselling significantly increased prolonged abstinence8–15 the present findings are only partially consistent. The proportion of proactive telephone counselling participants who achieved prolonged abstinence appears lower than corresponding rates with treatment seekers,8 9 12 13 15 16 particularly the 12-month prolonged abstinence rate (1.4%). This may reflect that giving smokers who had not volunteered for treatment a month in order to make a quit attempt and achieve abstinence is not a long enough grace period to facilitate measurement of prolonged abstinence. Research suggests that 3% to 5% of self-quitters achieve prolonged abstinence at 6 months.37 The intervention group's 3-month prolonged abstinence at 7 months (6.0%) and 6-month prolonged abstinence at 13 months (5.7%) were higher. Past trials with actively recruited smokers reported proactive telephone counselling had no impact on prolonged abstinence within 12 months,26 27 30 33 therefore this is the first time that significant prolonged abstinence findings with actively recruited smokers have been found at 4-month and 7-month follow-ups.
Making a quit attempt was significantly more likely for proactive telephone counselling participants than controls at 4 months post recruitment. However, this was not maintained longer term. Similarly, proactive telephone counselling increased treatment seekers' quit attempts in the first 3 months,12 13 but not at 6 or 12 months post recruitment.8 16 Unlike previous trials with actively recruited smokers,26–28 this trial demonstrated that proactive telephone counselling can facilitate quit attempts in the short term among actively recruited smokers. The finding that proactive telephone counselling produced a significant reduction in daily smokers' cigarette consumption at 4 months but not longer term was partly consistent with previous results with treatment seekers19 or actively recruited smokers26 31 that reported short-term and longer-term treatment effects.
The RE-AIM (‘Reach, Efficacy, Adoption, Implementation, and Maintenance’) framework proposes that the combined effects of the intervention's reach, efficacy, adoption, implementation and maintenance determines the public health impact of the intervention.38 Given 52% of eligible smokers were recruited,34 compared to the 1% to 7% of adult smokers calling quitlines annually2–4 this trial dramatically increased the reach of proactive telephone counselling. Efficacy was also found up to 7 months post recruitment. However, there was no difference between the intervention and control groups in long-term maintenance of smoking cessation. This raises the question of whether the mailing of self-help materials to cold-called smokers is a more cost-efficient option.
The results consistently show short-term but not longer-term effects of proactive telephone counselling with actively recruited smokers. While intervention participants were receiving proactive telephone counselling their cessation outcomes were superior to the control group. More booster telephone sessions23 over a longer period or re-enrolling participants back into quitline treatment39 may have helped maintain the initial proactive telephone counselling benefit. Further research is needed to determine if such strategies would increase the efficacy of proactive telephone counselling with cold-called smokers longer term.
Limitations included the following. First, that the reach of active telephone recruitment was restricted because the telephone directory did not contain unlisted or mobile phone numbers. Random digit dialling may have increased the reach of recruitment. Second, participants were not asked about their mental health or use of illicit drugs at baseline. Therefore, the potential influence of such factors on the proportion of smokers achieving abstinence is unknown. Third, no biochemical validation of self-reported cessation was conducted. An expert workgroup recommended that it is unnecessary for large-scale population-based trials without face-to-face contact to conduct biochemical validation.40 Given evidence that disconfirmation rates are low and do not differ significantly between conditions41 the lack of biochemical validation is unlikely to have influenced the outcomes. Fourth, an untreated control group was not included because it was not appropriate to withhold treatment having actively recruited smokers. Fifth, the impact on participant abstinence of other household smokers using the self-help materials mailed to the control group or phoning the quitline to receive similar support to their intervention group housemates is unknown. Finally, tobacco control activities in NSW during the trial such as media campaigns, new graphic warnings on cigarette packets and increased smoking restrictions inside licensed premises may have improved outcomes but are likely to have impacted both conditions equally.
Proactive telephone counselling initially increased abstinence, quit attempts and cigarette reduction among smokers actively recruited by telephone. Given 52% of eligible smokers were recruited,34 compared to the 1% to 7% of adult smokers calling quitlines annually,2–4 active telephone recruitment has considerable potential for facilitating more successful quit attempts provided longer-term efficacy and cessation rates broadly similar to smokers seeking treatment can be achieved. Quitlines should consider intervening with smokers actively recruited by telephone, provided effective means of reducing relapse can be incorporated.
What this paper adds.
Active telephone recruitment, or ‘cold calling’ is acceptable and can enrol almost 45 times more smokers to cessation services than media.
The limited number of previous trials that used active telephone recruitment targeted a particular segment of the smoking population, thus the effectiveness of proactive telephone counselling with cold-called smokers from the broader community is unknown.
This study assessed the effectiveness of proactive telephone counselling among cold-called smokers from the broader general population and found that proactive telephone counselling significantly increased abstinence up to 7 months post recruitment and quit attempts or cigarette reduction up to 4 months post recruitment. These treatment effects however were not sustained longer term.
Acknowledgments
This project was undertaken by the Centre for Health Research & Psycho-oncology (CHeRP) and Hunter New England Population Health (HNEPH). CHeRP is funded by the Cancer Council NSW, the University of Newcastle and receives infrastructure support from the Hunter Medical Research Institute and the University of Newcastle Priority Research Centre for Health Behaviour. HNEPH is a unit of Hunter New England Health and receives infrastructure support from the Hunter Medical Research Institute and the University of Newcastle Priority Research Centre for Health Behaviour. The authors would like to sincerely thank the staff at the NSW Quitline and the Cancer Institute NSW for providing the proactive telephone counselling. We are very grateful to Professor Ron Borland for his helpful and generous advice and to Vibeke Hansen and Amy Waller for their help with data collection. The views expressed are not necessarily those of the Cancer Council NSW and Hunter New England Health.
Footnotes
Funding: Funding was received from the Australian Research Council, National Heart Foundation, Hunter New England Population Health and the Cancer Council NSW.
Competing interests: None.
Ethics approval: This study was conducted with the approval of the University of Newcastle Human Research Ethics Committee and the Hunter New England Human Research Ethics Committee.
Contributors: Study concept: JW, CLP, RAW, JK, JD; study design: CLP, JW, FT, RAW, JK, SLD, CL, JD, AG; acquisition of data: FT, CLP, SLD; statistical analysis: FT, CL; draft of manuscript: FT; comments on manuscript: CLP, JW, RAW, JK, SLD, CL, AG, JD; obtained funding: JW, CLP, JK, RAW, JD, AG.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Telephone quitlines: a resource for development, implementation, and evaluation. Final edn Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health, 2004 [Google Scholar]
- 2.Swartz Woods S, Haskins AE. Increasing reach of quitline services in a US state with comprehensive tobacco treatment. Tob Control 2007;16(Suppl 1):i33–6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Miller CL, Wakefield M, Roberts L. Uptake and effectiveness of the Australian telephone Quitline service in the context of a mass media campaign. Tob Control 2003;12:ii53– 8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cummins SE, Bailey L, Campbell S, et al. Tobacco cessation quitlines in North America: a descriptive study. Tob Control 2007;16(Suppl 1):i9–15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Cigarette smoking among adults–United States, 2007. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2008;57:1221–6 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tzelepis F, Paul CL, Walsh RA, et al. Active telephone recruitment to quitline services: are non-volunteer smokers receptive to cessation support? Nicotine Tob Res 2009;11:1205–15 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.McDonald PW. Population-based recruitment for quit-smoking programs: an analytic review of communication variables. Prev Med 1999;28:545–57 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Borland R, Segan CJ, Livingston PM, et al. The effectiveness of callback counselling for smoking cessation: a randomized trial. Addiction 2001;96:881–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Borland R, Balmford J, Segan C, et al. The effectiveness of personalized smoking cessation strategies for callers to a Quitline service. Addiction 2003;98:837–46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Orleans CT, Schoenbach VJ, Wagner EH, et al. Self-help quit smoking interventions: effects of self-help materials, social support instructions, and telephone counseling. J Consult Clin Psychol 1991;59:439–48 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rabius V, McAlister AL, Geiger A, et al. Telephone counseling increases cessation rates among young adult smokers. Health Psychol 2004;23:539–41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhu S-H, Stretch V, Balabanis M, et al. Telephone counseling for smoking cessation: effects of single-session and multiple-session interventions. J Consult Clin Psychol 1996;64:202–11 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhu S-H, Anderson CM, Tedeschi GJ, et al. Evidence of real-world effectiveness of a telephone quitline for smokers. N Engl J Med 2002;347:1087–93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.McAlister AL, Rabius V, Geiger A, et al. Telephone assistance for smoking cessation: one year cost effectiveness estimations. Tob Control 2004;13:85–6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Miguez MC, Becona E. Evaluating the effectiveness of a single telephone contact as an adjunct to a self-help intervention for smoking cessation in a randomized controlled trial. Nicotine Tob Res 2008;10:129–35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gilbert H, Sutton S. Evaluating the effectiveness of proactive telephone counselling for smoking cessation in a randomized controlled trial. Addiction 2006;101:590–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Smith PM, Cameron R, McDonald PW, et al. Telephone counseling for population-based smoking cessation. Am J Health Behav 2004;28:231–41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brown SL, Hunt G, Owen N. The effect of adding telephone contact to self-instructional smoking-cessation materials. Behav Change 1992;9:216–22 [Google Scholar]
- 19.Miguez MC, Vazquez FL, Becona E. Effectiveness of telephone contact as an adjunct to a self-help program for smoking cessation: a randomized controlled trial in Spanish smokers. Addict Behav 2002;27:139–44 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ossip-Klein DJ, Carosella AM, Krusch DA. Self-help interventions for older smokers. Tob Control 1997;6:188–93 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Prochaska JO, DiClemente CC, Velicer WF, et al. Standardized, individualized, interactive, and personalized self-help programs for smoking cessation. Health Psychol 1993;12:399–405 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rimer BK, Orleans CT, Fleisher L, et al. Does tailoring matter? The impact of a tailored guide on ratings and short-term smoking-related outcomes for older smokers. Health Educ Res 1994;9:69–84 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rabius V, Pike KJ, Hunter J, et al. Effects of frequency and duration in telephone counselling for smoking cessation. Tob Control 2007;16(Suppl 1):i71–4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Abdullah ASM, Lam TH, Chan SSC, et al. Which smokers use the smoking cessation Quitline in Hong Kong, and how effective is the Quitline? Tob Control 2004;13:415–21 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Prout MN, Martinez O, Ballas J, et al. Who uses the Smoker's Quitline in Massachusetts? Tob Control 2002;11(Suppl 2):ii74–5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Abdullah ASM, Mak YW, Loke AY, et al. Smoking cessation intervention in parents of young children: a randomised controlled trial. Addiction 2005;100:1731–40 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Curry SJ, McBride C, Grothaus LC, et al. A randomized trial of self-help materials, personalized feedback, and telephone counseling with nonvolunteer smokers. J Consult Clin Psychol 1995;63:1005–14 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.McBride CM, Scholes D, Grothaus LC, et al. Evaluation of a minimal self-help smoking cessation intervention following cervical cancer screening. Prev Med 1999;29:133–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lando HA, Hellerstedt WL, Pirie PL, et al. Brief supportive telephone outreach as a recruitment and intervention strategy for smoking cessation. Am J Public Health 1992;82:41–6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Aveyard P, Griffin C, Lawrence T, et al. A controlled trial of an expert system and self-help manual intervention based on the stages of change versus standard self-help materials in smoking cessation. Addiction 2003;98:345–54 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lichtenstein E, Andrews JA, Lee ME, et al. Using radon risk to motivate smoking reduction: evaluation of written materials and brief telephone counselling. Tob Control 2000;9:320–6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lichtenstein E, Boles SM, Lee ME, et al. Using radon risk to motivate smoking reduction II: randomized evaluation of brief telephone counseling and a targeted video. Health Educ Res 2008;23:191–201 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Prochaska JO, Velicer WF, Fava JL, et al. Counselor and stimulus control enhancements of a stage-matched expert system intervention for smokers in a managed care setting. Prev Med 2001;32:23–32 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tzelepis F, Paul CL, Walsh RA, et al. Telephone recruitment into a randomized controlled trial of quitline support. Am J Prev Med 2009;37:324–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hughes J, Keely J, Niaura R, et al. Measures of abstinence in clinical trials: issues and recommendations. Nicotine Tob Res 2003;5:13–26 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Campbell HS, Ossip-Klein D, Bailey L, et al. Minimal dataset for quitlines: a best practice. Tob Control 2007;16(Suppl 1):i16–20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hughes JR, Keely J, Naud S. Shape of the relapse curve and long-term abstinence among untreated smokers. Addiction 2004;99:29–38 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Glasgow RE, Vogt TM, Boles SM. Evaluating the public health impact of health promotion interventions: the RE-AIM framework. Am J Pub Health 1999;89:1322–7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Carlini BH, Zbikowski SM, Javitz HS, et al. Telephone-based tobacco-cessation treatment: re-enrollment among diverse groups. Am J Prev Med 2008;35:73–6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.SRNT Subcommittee on Biochemical Verification Biochemical verification of tobacco use and cessation. Nicotine Tob Res 2002;4:149–59 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Glasgow RE, Mullooly JP, Vogt TM, et al. Biochemical validation of smoking status: pros, cons, and data from four low-intensity intervention trials. Addict Behav 1993;18:511–27 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]