Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To assess the utility of a point-of-care (POC) capillary blood glucose measurement as compared with routine clinical parameters in predicting undiagnosed diabetes in a low-resource rural India setting.
RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS
Nine hundred and ninety-four participants aged >30 years and stratified by age and sex were randomly selected from 20 villages in India. A clinical questionnaire, sampling for laboratory venous fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and POC capillary blood glucose assay were performed simultaneously. Diabetes diagnosis was based on the World Health Organization (WHO) definition using FPG. The capacity of the POC glucose to predict the presence of diabetes was assessed and compared with the questionnaire using area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUCs).
RESULTS
The AUC for POC glucose alone in predicting diabetes was 0.869 (95% CI 0.810–0.929). This was significantly better (P < 0.001 for AUC comparison) than the models based upon clinical variables alone (AUC for the best clinical model including age, BMI, hypertension, waist circumference: 0.694 [95% CI 0.621–0.766]). POC glucose appropriately reclassified the risk of up to one-third of participants ranked according to the clinical models. Adding the clinical variables to the POC glucose assay did not significantly improve the discriminatory capability beyond that achieved with the POC glucose measurement alone (all P > 0.37).
CONCLUSIONS
POC glucose testing appears to be a simple and reliable tool for identifying undiagnosed diabetes in a high-risk, resource-poor rural population. However, studies evaluating the cost effectiveness of introducing POC glucose testing are needed prior to widespread implementation.
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is rapidly increasing around the world (1). Developing countries are facing the largest increases both in absolute and relative terms (1). It is predicted that this will have devastating consequences on the economies and health systems of these countries. Successful prevention and early management of diabetes is therefore a major health priority (1,2).
In many regions, up to 50% of people with diabetes remain undiagnosed (1,3,4). Failure to improve these levels of detection will mean that the opportunity to improve health outcomes with early intervention will be lost. Early treatment with successful glucose control significantly reduces the morbidity and mortality associated with diabetes (5,6). Earlier detection of diabetes also allows for the implementation of other treatments that reduce the vascular complications of diabetes (5,6).
Universal screening for diabetes is not currently recommended due to a lack of good evidence for an accurate test. However, targeted screening is advocated in certain ethnic groups deemed at increased risk of diabetes (2). For some ethnic groups, implementation of targeted screening may require the entire population to be screened. This applies for instance to Asian Indian populations, which are at greater risk of developing diabetes (7) and have a high prevalence of diabetes both in urban (4) and rural settings (3). However to successfully apply screening to such populations requires accurate, safe, and low-cost diagnostic strategies that are easy to implement (8).
In resource-poor settings, clinical variables–based risk assessment questionnaires or point-of-care (POC) glucose analysis may be reasonable screening tools (9). Both require little expertise and allow an individual's risk of having undiagnosed diabetes to be immediately determined so that only those at high risk require a confirmatory diagnostic test. However, the value of risk assessment questionnaires (9–13) and POC glucose analysis (14–16) in resource-poor settings remains unclear. Additionally the performance of these different screening methods has not been compared in rural Asian Indian populations.
The aim of this study was to quantify and compare the accuracy of strategies based on POC glucose, clinical variables, and the combination of both in predicting undiagnosed diabetes in an asymptomatic, resource-poor rural Asian Indian population.
RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS
This study was conducted as part of the Andhra Pradesh Rural Health Initiative (APRHI) (17). In brief, 20 villages (total population 75,089) were selected from the East and West Godavari regions that were broadly representative of these two districts on the basis of their population size and distance from the nearest large town. The Byrraju Foundation (a local nongovernment organization committed to improving rural health) had recently conducted a population census in these 20 villages with data collection on individuals' age, sex, and contact details. This enabled a random selection of a representative sample of 1,085 participants (aged >30 years) for this study based on age and sex stratification. The study was approved by the ethics committees of the CARE Hospital, Hyderabad in India, and the University of Sydney in Australia.
Baseline assessment
The survey was conducted in 2005. Trained staff administered a structured questionnaire, performed a brief physical examination, and laboratory tests. The questionnaire included questions relating to demographic and socioeconomic characteristics, personal and family histories, and lifestyle. Physical examination included measurements of blood pressure and anthropometric variables. Known cardiovascular disease was based on self-reported history of heart attack, angina, or stroke. Diagnosis of hypertension was based on self-reported history of hypertension, use of blood pressure-lowering medications, or an average of two blood pressure recordings ≥140 mmHg (systolic) and/or ≥90 mmHg (diastolic).
The laboratory assessments included a fasting (≥8 h) capillary POC finger-prick glucose analysis and fasting venous blood glucose and lipid measurements. Fasting capillary plasma glucose was measured using B. Braun USV meters (Melsungen, Germany). Venous blood samples collected in the villages were immediately refrigerated and transferred on ice to the field laboratory within 4 h of collection for separation, glucose analysis, and freezing at −20°C. Venous plasma glucose assessment used the glucose oxidase peroxidase method. Frozen samples were transferred to a central internationally accredited laboratory in the CARE Hospital, Hyderabad, where cholesterol and subfractions were analyzed.
Participants with a history of diabetes (self-reported history of doctor-diagnosed diabetes or self-reported current pharmacological diabetes control treatments) were excluded from the analysis. Newly diagnosed diabetes was defined according to the 1999 World Health Organization (WHO) criteria and was based on the fasting venous glucose sample being ≥7 mmol/l (18).
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed with SAS/STAT version 9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). Results were reported as percentages and mean (SD or median [interquartile range]). The concordance between venous plasma and POC glucose measurements was assessed with the Pearson correlation coefficient. Systematic bias in the two measurements at any given level of blood glucose was examined using Bland and Altman plots (19). Logistic regressions were used to assess the association between POC capillary glucose, clinical prediction models (using two diabetes risk scores developed in urban India [9,13]), and the presence of new diabetes. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) then assessed and compared the ability of the POC glucose, clinical prediction models, and the combination of both to predict the presence of diabetes (20). This was complemented with the calculation of the integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) statistic (21). The performance of POC glucose and the two Indian diabetes scores was further assessed at different thresholds for defining the high risk of undiagnosed diabetes (i.e., POC glucose [mmol/l] <5 vs. ≥5; <5.6 vs. ≥5.6; <6.1 vs. ≥6.1; <7 vs. ≥7) and the recommended thresholds for the Indian risk scores (i.e., Mohan's score <60 vs. ≥60; Ramachandran's score ≤21 vs. >21) (9,13). The net reclassification improvement (21) was then used to evaluate risk reclassification with the use of POC glucose in participants with and without diabetes within Indian risk score categories.
RESULTS
Baseline profile of participants with and without diabetes
Of the 1,085 participants initially studied, 91 participants were excluded: 90 with previously diagnosed diabetes and 1 with missing data for BMI and waist circumference leaving a total of 994 participants (51% women). Of the 994 participants, 45 (4.5%) had undiagnosed diabetes based on elevated fasting venous plasma glucose. Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of participants according to whether they did or did not have diabetes.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the study participants (n = 994)
| Variables | Newly diagnosed diabetes based on fasting venous glucose |
P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | ||
| n | 45 | 949 | |
| Age (years) | 53 (13) | 48 (14) | 0.03 |
| Men (%) | 20 (44.4) | 464 (48.9) | 0.67 |
| Family history of diabetes* (n [%]) | 6 (13.3) | 91 (9.6) | 0.41 |
| Hypertension† (n [%]) | 13 (29.5) | 163 (17.2) | 0.04 |
| History of cardiovascular disease‡ (n [%]) | 2 (4.5%) | 63 (6.6%) | 0.99 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.5 (5) | 21.8 (4.2) | 0.01 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 84 (11) | 78 (11) | 0.001 |
| Waist-to-hip ratio | 0.90 (0.06) | 0.87 (0.07) | 0.02 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 130 (23) | 123 (20) | 0.02 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 81 (12) | 76 (11) | 0.01 |
| Fasting venous blood glucose (mmol/l) | 9.2 (3.5) | 5.2 (0.7) | <0.001 |
| Fasting POC blood glucose (mmol/l) | 8.8 (4.3) | 5.5 (0.9) | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/l) | 5.0 (1.1) | 4.7 (1.2) | 0.04 |
| LDL cholesterol (mmol/l) | 3.1 (1) | 2.9 (0.9) | 0.13 |
| HDL cholesterol (mmol/l) | 1.2 (0.2) | 1.2 (0.3) | 0.93 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/l) | 1.12 (0.8–1.6) | 1.11 (0.81–1.6) | 0.21 |
| Use of lipid-lowering therapy* | 0 | 6 (0.6%) | 1.0 |
| Use of aspirin* | 0 | 21 (2.2%) | 0.63 |
Data are reported as mean (SD), number (%), or median (interquartile range).
*Self-reported.
†Hypertension diagnosis if self-reported prior diagnosis of hypertension from their doctor, self-reported use of prescription medications for hypertension, if they had a systolic blood pressure (based on 2 visits) ≥140 mmHg, or if they had a diastolic blood pressure (based on 2 visits) ≥90 mmHg.
‡Cardiac disease if self-reported prior diagnosis of heart attack, angina, or stroke from their doctor.
Agreement between POC capillary and venous plasma glucose analysis
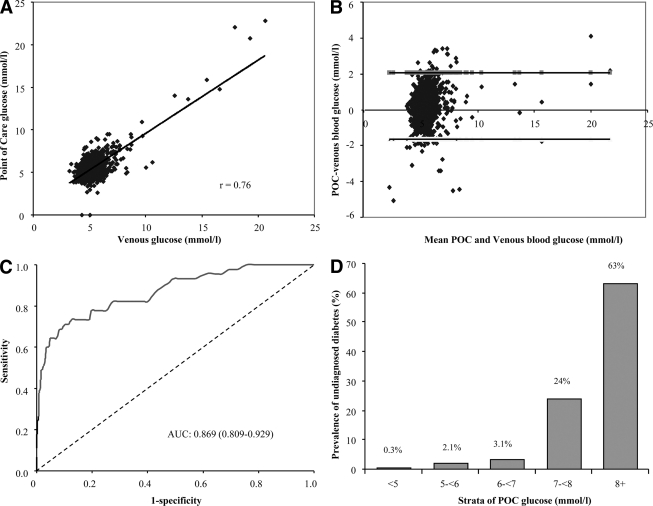
There was a high positive correlation between POC capillary and venous plasma glucose values (r = 0.76, P < 0.001) (Fig. 1A). On Bland and Altman plots, there was no evidence of systematic bias in the two measurements at any given blood glucose level (Fig. 1B). The prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes increased from 0.3% in the lower stratum of POC capillary glucose (POC glucose <5 mmol/l) to 63% in the upper stratum (POC glucose ≥ 8 mmol/l) (Fig. 1D). Of all those with undiagnosed diabetes, 20% had a POC capillary glucose value of <6 mmol/l.
Figure 1.
Concordance between laboratory venous blood glucose analysis and POC glucose analysis. A: Pearson correlation and scatter plot (n = 994). B: Differences vs. means plot (Bland and Altman plot) of fasting capillary blood glucose measured by POC glucose testing (B. Braun) glucose meter and the venous laboratory glucose measurement. The horizontal top and bottom line represent ± 2 SD. C: Discriminatory power of POC glucose in predicting undiagnosed diabetes (participants were categorized as diabetics and nondiabetics based on fasting venous blood glucose measurement). D: Prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes (based on laboratory venous glucose analysis) in strata defined by POC capillary blood glucose level.
Clinical predictors of diabetes versus POC capillary glucose
Unadjusted estimates of the association between clinical variables, POC capillary glucose, and the presence of undiagnosed diabetes are shown in supplementary Table 1, available in an online appendix at http://care.diabetesjournals.org/cgi/content/full/dc10-1270/DC1. Age, hypertension, blood pressure variables, BMI, waist circumference, hip circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, and POC capillary glucose were all significantly associated with undiagnosed diabetes. Sex, family history of diabetes, and physical activity were not significantly associated with undiagnosed diabetes.
The discriminatory power of POC capillary glucose for predicting the presence of diabetes was very good with an AUC of 0.869 (95% CI 0.810–0.929) overall (Fig. 1C), 0.884 (0.795–0.975) in men, 0.861 (0.780–0.942) in women, and 0.796 (0.571–1.000), 0.996 (0.913–0.999), 0.822 (0.661–0.984), and 0.839 (0.732–0.945) in the age-groups 30–39, 40–49, 50–59, and ≥60 years, respectively. When the POC capillary glucose was compared with each of the significant individual clinical variables, its discriminatory power for predicting undiagnosed diabetes was always better (supplementary Table 1). Among those without diabetes (based on venous glucose; 949 participants), the discriminatory power of POC glucose for predicting impaired fasting glycemia (venous plasma glucose: ≥6.1 to <7.0 mmol/l) was 0.716 (0.656–0.773). The AUC for the prediction of both diabetes and impaired fasting glucose was 0.768 (0.722–0.815) overall, 0.736 (0.665–0.806) in men, and 0.801 (0.742–0.860) in women.
The performance of the prediction models is shown in Table 2. The AUC (95% CI) for the Indian risk scores were 0.662 (0.581–0.743) and 0.678 (0.597–0.759), respectively. These were significantly lower than that for POC glucose alone (all P < 0.0001). Similarly, other clinical models developed from these data never performed as well as POC glucose alone. The basic clinical model (model 1) included age, BMI, and hypertension. Alternative models also included one of following: waist circumference, hip circumference, or waist-to-hip ratio. For these new clinical models, the highest discriminatory power was achieved with the combination of model 1 and waist circumference (AUC 0.694 [CI 95% 0.621–0.766]). When POC capillary glucose was added to this model, the AUC significantly increased to 0.867 (0.803–0.932) (P < 0.0001 for the difference in AUC). However when the performance of this model was compared with that of POC capillary glucose alone, there was no significant difference between the two in predicting diabetes (P = 0.89). Similarly, adding POC glucose to any of our new clinical models did not increase the AUC beyond that of the POC glucose alone (Table 2). Based on the IDI statistics (Table 2), adding POC glucose to either of the Indian diabetes scores did not improve models beyond POC glucose alone. However a significant increase in the IDI from 1.63 to 1.74 (all P ≤ 0.04) was observed when POC glucose was added to the newly developed clinical models. This indicates a marginal enhancement in the discriminatory capabilities of the models using POC and clinical variables instead of POC alone.
Table 2.
Multivariable association between clinical variables, POC capillary glucose, and presence of diabetes
| AUC | P* | Calibration χ2 (P)† | IDI (P)‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical variables alone | ||||
| Model 1 = age + BMI + hypertension | 0.670 (0.585–0.755) | <0.0001 | 5.67 (0.13) | N/A |
| Model 1 + waist | 0.694 (0.621–0.766) | <0.0001 | 5.73 (0.13) | N/A |
| Model 1 + hip | 0.681 (0.601–0.760) | <0.0001 | 0.79 (0.85) | N/A |
| Model 1 + WHR | 0.680 (0.600–0.760) | <0.0001 | 1.69 (0.64) | N/A |
| Mohan's diabetes risk score | 0.662 (0.581–0.743) | <0.0001 | 7.43 (0.06) | N/A |
| Ramachandran's diabetes risk score | 0.678 (0.597–0.759) | <0.0001 | 0.75 (0.86) | N/A |
| POC glucose alone | 0.869 (0.809–0.929) | N/A | 3.87 (0.28) | N/A |
| Clinical variables + POC glucose§ | ||||
| Model 2 = Model 1 + POC glucose | 0.867 (0.803–0.932) | 0.72 | 2.11 (0.55) | 1.64 (0.04) |
| Model 2 + waist | 0.868 (0.804–0.932) | 0.89 | 2.14 (0.54) | 1.74 (0.02) |
| Model 2 + hip | 0.875 (0.813–0.937) | 0.37 | 1.32 (0.72) | 1.72 (0.04) |
| Model 2 + WHR | 0.868 (0.803–0.932) | 0.74 | 2.12 (0.55) | 1.63 (0.04) |
| Mohan's diabetes risk score + POC glucose | 0.879 (0.819–0.938) | 0.24 | 1.77 (0.63) | 0.36 (0.54) |
| Ramachandran's diabetes risk score + POC glucose | 0.874 (0.812–0.935) | 0.44 | 1.83 (0.61) | 0.21 (0.62) |
WHR, waist-to-hip ratio.
*Compared to AUC of POC glucose alone.
†Hosmer and Lemeshow calibration χ2 test and the accompanying P value, based on 5 subgroups of participants and 3 df.
‡IDI and P value comparing POC glucose alone and POC glucose + clinical variables.
§All P values <0.0001 for AUC comparison between models with clinical variables alone and the equivalents with POC glucose.
The performance of the clinical scores and POC glucose at prespecified thresholds is shown in supplementary Table 2. As expected, the sensitivity and negative predictive value of POC capillary glucose for diagnosing diabetes diminished at higher glucose level cutoffs, while the specificity and positive predictive value increased. Performance measures were always better for POC glucose than for clinical scores. At each of the thresholds studied (5.6, 6.1, and 7 mmol/l), POC glucose appropriately reclassified the risk of between 13 and 30% of participants, ranked according to clinical scores (supplementary Table 3).
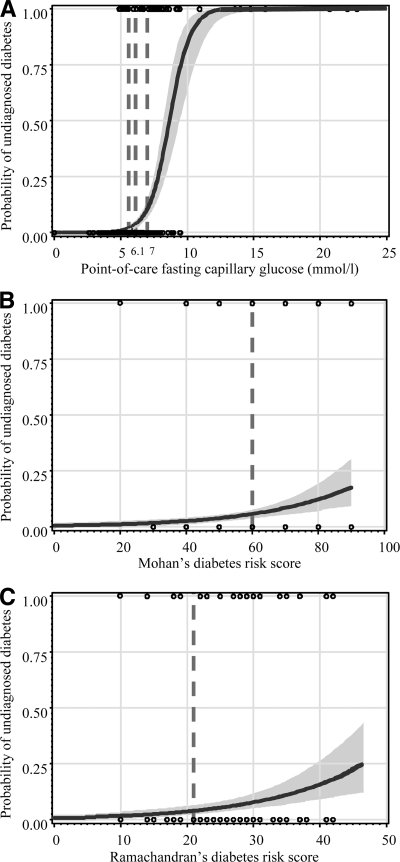
There was no evidence of a threshold clinical score above which undiagnosed diabetes was predicted with certainty, while such a threshold was apparent for POC glucose (Fig. 2). Similarly, there was no threshold to rule out undiagnosed diabetes based on the clinical scores, while a POC glucose threshold of 5 mmol/l would identify the 70.6% participants in whom all those with diabetes (100%) were found (Fig. 2 and supplementary Table 3).
Figure 2.
Logistic curves showing the predicted and observed probability of undiagnosed diabetes at different levels of POC capillary glucose (A), Mohan's diabetes risk score (B), and Ramachandran's diabetes risk score (C). For each figure panel, the curve is for the predicted probability and the shaded area is for the 95% CI. The black circles are for the observed probability (1.00 for those with undiagnosed diabetes and 0.00 for those without diabetes). Solid horizontal and vertical lines are added at regular intervals to assist interpretation. Vertical broken lines are also displayed at the cutoff points of capillary glucose and risk (5.6, 6.1, and 7 mmol/l), Mohan's score (60), and Ramachandran's score (21) used to define high risk of undiagnosed diabetes.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study of the utility of POC capillary glucose and routine clinical variables in predicting undiagnosed diabetes in a resource-poor rural setting has four main findings. First, as anticipated there was a strong positive correlation between venous plasma glucose levels and POC capillary glucose levels. Second, POC capillary glucose provided a very good discriminatory capacity for identifying those with undiagnosed diabetes. Third, POC capillary glucose assays performed significantly better than a range of models based on clinical variables and appropriately reclassified the risk of a significant proportion of participants ranked according to clinical risk models. And finally, adding clinical variables to the POC capillary glucose did not improve its discriminatory capacity for identifying undiagnosed diabetes.
WHO currently recommends that diabetes be diagnosed by measuring venous fasting blood glucose. In those individuals strongly suspected of having diabetes but with a normal fasting glucose or impaired fasting glycemia, a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is advocated (22). These tests are rather complex, require skilled health care workers and laboratory facilities for the analysis of samples, and are often not available in low-resource settings. The POC capillary glucose test is a more attractive, alternative diagnostic test and is increasingly being used for this purpose in remote or resource-poor areas (22) because it is relatively inexpensive (<$2 dollars per test) and provides immediate test results. Our data would support the use of a single POC glucose test for identifying those individuals with diabetes, however the discriminatory capacity would likely be improved by a second confirmatory blood glucose assay (14). While measures of the performance of POC glucose such as positive and negative predictive value will vary according to the prevalence of diabetes in different populations, the sensitivity, specificity, and AUC would be expected to remain similar.
Several prior studies have analyzed the utility of POC capillary glucose as a diagnostic test with varied results (14–16). Two of these studies specifically examined the utility of POC testing among high-risk populations (15,16). One study in the Australian indigenous population (15) found that POC glucose had good discriminatory capacity for predicting undiagnosed diabetes (using fasting venous glucose as the standard), and the other study in Maori (16) found that POC glucose had acceptable discriminatory capacity (using OGTT as the gold standard). The differing levels of discrimination achieved may reflect diabetes presenting as fasting hyperglycemia compared with diabetes presenting as postprandial hyperglycemia. In the early stages of diabetes, glucometabolic derangements primarily affect postprandial glucose levels. Therefore, fasting POC glucose assays will miss some cases of diabetes that would be identified on the basis of a 2-h glucose assay after an OGTT.
Our data suggest that performing a POC capillary glucose assay and using a threshold level of 7.0 mmol/l would result in the identification of 65% of those with undiagnosed diabetes. If the threshold was decreased to 6.1 mmol/l, ∼80% would be identified. Reducing the threshold further would detect few additional cases as the prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes within the lower strata is very low (<3%).
There has been a lot of recent interest in the use of clinical risk assessment questionnaires or derived risk scores for detecting undiagnosed diabetes (9–13). Our study compared the utility of risk assessment based on clinical variables with POC glucose testing. We found that the POC glucose test was always better at predicting undiagnosed diabetes, and the combination of a POC glucose test and clinical risk assessment variables was no better than POC glucose alone. The performance of the risk assessment questionnaire was likely adversely impacted by poor knowledge of the participants' medical and family histories and limited access to diagnostic facilities. This was especially evident when considering the small proportion (13%) of individuals with new diabetes who had previously reported a family history of diabetes. Based on the epidemiological data from urban areas in India, the actual prevalence would be expected to be closer to 40% (23). The performance of the Indian risk scores, which were evaluated against 2-h postprandial glucose criteria, also could have been underestimated by the lack of an OGTT in our sample.
Performance measures for the two Indian risk scores in our rural sample were similar to those reported in the original urban populations (9,13). Indeed these tools appear equally useful in rural settings where they would help to direct the need for definitive diagnostic tests toward the half of the population where three-quarters of undiagnosed diabetes occurs.
With three-quarters of Indians living outside cities and increasing rates of diabetes in nonurban populations, the rural nature of this study is a key strength. Likewise our extensive analysis that assesses the predictive accuracy of POC glucose across the whole range of the measurements in the sample adds substantively to the evidence provided by prior reports that have assessed diagnostic accuracy only on the basis of prespecified cutoffs of POC capillary glucose levels (24). The main limitation of this study is that the diagnosis of diabetes was based on a single fasting venous glucose measurement. While this may be valid for epidemiological purposes, it is at variance with routine clinical practice where diabetes is diagnosed on the basis of two consecutive samples.
In conclusion, Asian Indians are reporting an increasing prevalence of diabetes, but a large proportion of cases remain undiagnosed. WHO has recommended targeted screening, and our results support the use of the POC capillary glucose test for identifying new cases of diabetes in low-resource rural settings on the Indian subcontinent. Studies evaluating the cost-effectiveness of introducing POC glucose testing are needed prior to widespread implementation.
Acknowledgments
Andhra Pradesh Rural Health Initiative (APRHI) has been developed as a collaboration between four partners: Byrraju Foundation in Hyderabad, India; Centre for Chronic Disease Control (CCDC) in Delhi, India; Care Foundation in Hyderabad, India; and The George Institute for Global Health in Sydney, Australia.
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
G.E.R., A.P.K., and S.Z. analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. R.J., C.C., B.N., and A.P. researched the data. All coauthors contributed to discussion and reviewed/edited the manuscript.
Footnotes
The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
See accompanying editorial, p. 244.
References
- 1.International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. 4th ed Brussels: International Diabetes Federation, 2009 [Google Scholar]
- 2.World Health Organization Screening for Type 2 Diabetes: Report of a World Health Organisation and International Diabetes Federation Meeting [Internet], 2003. Available from www.who.int/diabetes/publications/en/screening_mnc03.pdf Accessed 15 April 2010
- 3.Chow CK, Raju PK, Raju R, Reddy KS, Cardona M, Celermajer DS, Neal BC: The prevalence and management of diabetes in rural India. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1717–1718 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Kapur A, Vijay V, Mohan V, Das AK, Rao PV, Yajnik CS, Prasanna Kumar KM, Nair JDDiabetes Epidemiology Study Group in India (DESI) High prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in India: National Urban Diabetes Survey. Diabetologia 2001;44:1094–1101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gaede P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH, Pedersen O: Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;358:580–591 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Control Group, Turnbull FM, Abraira C, Anderson RJ, Byington RP, Chalmers JP, Duckworth WC, Evans GW, Gerstein HC, Holman RR, Moritz TE, Neal BC, Ninomiya T, Patel AA, Paul SK, Travert F, Woodward M: Intensive glucose control and macrovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2009;52:2288–2298 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zimmet PZ: Diabetes epidemiology as a tool to trigger diabetes research and care. Diabetologia 1999;42:499–518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Engelgau MM, Narayan KM, Herman WH: Screening for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000;23:1563–1580 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mohan V, Deepa R, Deepa M, Somannavar S, Datta M: A simplified Indian Diabetes Risk Score for screening for undiagnosed diabetic subjects. J Assoc Physicians India 2005;53:759–763 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bang H, Edwards AM, Bomback AS, Ballantyne CM, Brillon D, Callahan MA, Teutsch SM, Mushlin AI, Kern LM: Development and validation of a patient self-assessment score for diabetes risk. Ann Intern Med 2009;151:775–783 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lindström J, Tuomilehto J: The diabetes risk score: a practical tool to predict type 2 diabetes risk. Diabetes Care 2003;26:725–731 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.He G, Sentell T, Schillinger D: A new public health tool for risk assessment of abnormal glucose levels. Prev Chronic Dis 2010;7:A34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Vijay V, Wareham NJ, Colagiuri S: Derivation and validation of diabetes risk score for urban Asian Indians. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2005;70:63–70 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kruijshoop M, Feskens EJ, Blaak EE, de Bruin TW: Validation of capillary glucose measurements to detect glucose intolerance or type 2 diabetes mellitus in the general population. Clin Chim Acta 2004;341:33–40 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Marley JV, Davis S, Coleman K, Hayhow BD, Brennan G, Mein JK, Nelson C, Atkinson D, Maguire GP: Point-of-care testing of capillary glucose in the exclusion and diagnosis of diabetes in remote Australia. Med J Aust 2007;186:500–503 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rush E, Crook N, Simmons D: Point-of-care testing as a tool for screening for diabetes and pre-diabetes. Diabet Med 2008;25:1070–1075 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chow CK, Naidu S, Raju K, Raju R, Joshi R, Sullivan D, Celermajer DS, Neal BC: Significant lipid, adiposity and metabolic abnormalities amongst 4535 Indians from a developing region of rural Andhra Pradesh. Atherosclerosis 2008;196:943–952 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.World Health Organization Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications: Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1999 [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bland JM, Altman DG: Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986;1:307–310 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL: Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988;44:837–845 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pencina MJ, D'Agostino RB, Sr, D'Agostino RB, Jr, Vasan RS: Evaluating the added predictive ability of a new marker: from area under the ROC curve to reclassification and beyond. Stat Med 2008;27:157–172 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.World Health Organization, International Diabetes Federation Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia: report of a WHO/IDF Consultation. Geneva; World Health Organization, 2006 [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kumar S, Mukherjee S, Mukhopadhyay P, Pandit K, Raychaudhuri M, Sengupta N, Ghosh S, Sarkar S, Mukherjee S, Chowdhury S: Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in a selected population with special reference to influence of family history and anthropometric measurements: the Kolkata policeman study. J Assoc Physicians India 2008;56:841–844 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Glümer C, Carstensen B, Sandbaek A, Lauritzen T, Jørgensen T, Borch-Johnsen KInter99 study A Danish diabetes risk score for targeted screening: the Inter99 study. Diabetes Care 2004;27:727–733 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]