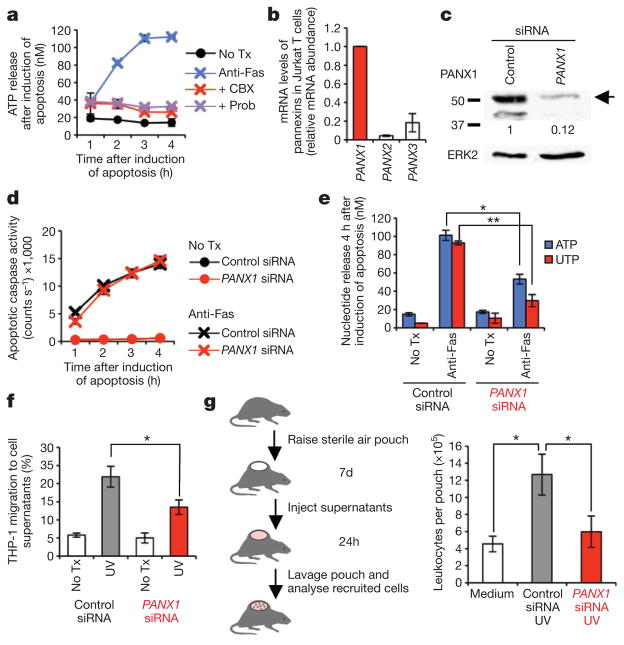
Figure 1. Release of find-me signals by apoptotic cells is pannexin-1-dependent.
a, Time course of ATP release from apoptotic Jurkat cells in the presence of 500 μM carbenoxolone (CBX) or 2 mM probenecid (Prob). n = 3. No Tx, no treatment. b, mRNA levels for PANX1, PANX2 and PANX3 in Jurkat cells determined by qPCR, normalized to PANX1. n = 2. c, PANX1 protein expression in Jurkat cells transfected with control or PANX1 siRNA. Glycosylated PANX1 (upper band; arrow) was quantified. d, e, PANX1 knockdown does not affect the progression of apoptosis (assessed by apoptotic caspase activity) (d, n = 3), but decreases ATP (e, n = 10) and UTP (e, n = 3) release 4 h after apoptosis induction. *, P < 10−5; **, P < 0.01. f, Transwell migration of THP-1 monocytes towards apoptotic cell supernatants from PANX1-siRNA-treated cells (4 h after ultraviolet (UV) treatment). *, P < 0.05. Representative of four independent experiments. g, Left, Schematic of mouse air pouch model for monitoring chemotactic activity of apoptotic cell supernatants in vivo. Right, CD45+ leukocytes migrating into the pouch were determined after injecting apoptotic cell supernatants from siRNA-transfected cells. n = 9–10 mice per group. *, P < 0.05, by ANOVA with Bonferroni post-analysis. Error bars, s.e.m., except in b, f, where they represent s.d.