Abstract
In the title compound, C15H13ClN2OS, the dihedral angles between the sulfourea group and the benzene ring and the chlorobenzene ring are 35.8 (6) and 81.6 (6)° respectively. An intramolecular N—H⋯O interaction occurs. In the crystal, a combination of intermolecular π–π stacking interactions [centroid–centroid distance = 4.0616 (16) Å] and N—H⋯S hydrogen bonds stabilizes the structure.
Related literature
For general background to the chemistry and biological activity of thiourea derivatives and their use, see: Jain & Rao (2003 ▶); Zeng et al. (2003 ▶); Xu et al. (2004 ▶); Zheng et al. (2004 ▶); D’hooghe et al. (2005 ▶); Saeed et al. (2008 ▶, 2009 ▶, 2010 ▶).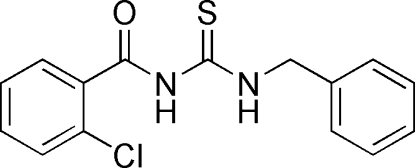
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H13ClN2OS
M r = 304.78
Triclinic,
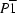
a = 7.347 (2) Å
b = 9.658 (3) Å
c = 11.003 (3) Å
α = 110.150 (5)°
β = 90.767 (3)°
γ = 104.058 (3)°
V = 707.0 (4) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.41 mm−1
T = 153 K
0.40 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Rigaku AFC10/Saturn724+ diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Higashi, 1995 ▶) T min = 0.852, T max = 0.886
5691 measured reflections
2481 independent reflections
2194 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.017
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.029
wR(F 2) = 0.073
S = 1.01
2481 reflections
189 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEPIII (Burnett & Johnson, 1996 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810023822/pk2248sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810023822/pk2248Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1N⋯S1i | 0.86 (2) | 2.53 (2) | 3.3698 (18) | 166.2 (18) |
| N2—H2N⋯O1 | 0.82 (2) | 2.01 (2) | 2.669 (2) | 137 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i) 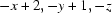 .
.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Analytical and Testing Center of Sichuan University for the X-ray measurements.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
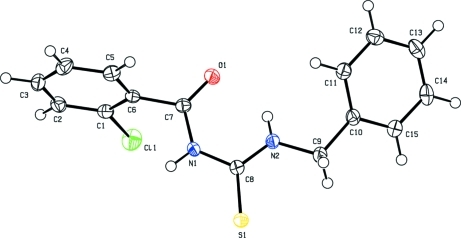
N-(benzylcarbamothioyl)-2-chlorobenzamide derivatives are of great importance owing to their wide-ranging biological properties (Zeng et al. (2003)). The title compound is one of the key intermediates in our synthetic investigations of antiviral drugs. We report here its crystal structure. As shown in Fig. 1, the dihedral angle of 35.8 (6)° and 81.6 (6)° between the connecting sulfourea unit and the benzene ring, and between the 2-chloro-benzene ring and the connecting sulfourea group, respectively. A combination of intermolecular π-π packing interaction, N—H···O and N—H···S hydrogen bonds help stabilize the structure. In addition, weak C—H···π interactions are also present.
Experimental
A solution of 0.23 g (3 mmol) of ammonium thiocyanate in 7 ml of acetonitrile was added to a solution of 0.52 g (3 mmol) of 2-chlorobenzoyl chloride in 2.5 ml of toluene. The mixture was heated for 5 min at 40°C and filtered from ammonium chloride, the filtrate was added to a solution of 0.32 g (3 mmol) of phenylmethanamine in 5 ml of acetonitrile, the mixture was stirred for 3 h at room temperature and evaporated, and the residue was washed with ethanol and recrystallized from ethanol. Yield 0.77 g (85%). Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation from a solution of dichloromethane.
Refinement
Amine hydrogens were located in a difference map and refined freely. The reminaing H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å) and refined using a riding model, with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level.
Crystal data
| C15H13ClN2OS | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 304.78 | F(000) = 316 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.432 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.347 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 2259 reflections |
| b = 9.658 (3) Å | θ = 3.2–27.5° |
| c = 11.003 (3) Å | µ = 0.41 mm−1 |
| α = 110.150 (5)° | T = 153 K |
| β = 90.767 (3)° | Block, colorless |
| γ = 104.058 (3)° | 0.40 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm |
| V = 707.0 (4) Å3 |
Data collection
| Rigaku AFC10/Saturn724+ diffractometer | 2481 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Rotating Anode | 2194 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.017 |
| Detector resolution: 28.6 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.3°, θmin = 3.2° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −8→8 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Higashi, 1995) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.852, Tmax = 0.886 | l = −13→13 |
| 5691 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.029 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.073 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.01 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0368P)2 + 0.265P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2481 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 189 parameters | Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.69955 (6) | 0.10088 (5) | 0.08296 (4) | 0.03365 (14) | |
| S1 | 0.81096 (6) | 0.64421 (5) | 0.00524 (4) | 0.02590 (13) | |
| O1 | 0.71779 (16) | 0.46704 (14) | 0.34073 (11) | 0.0283 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.84005 (19) | 0.48399 (15) | 0.15434 (13) | 0.0203 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.62797 (19) | 0.63073 (16) | 0.20842 (13) | 0.0219 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.9133 (2) | 0.18430 (18) | 0.18156 (14) | 0.0202 (3) | |
| C2 | 1.0373 (2) | 0.09656 (19) | 0.18009 (15) | 0.0243 (4) | |
| H2 | 1.0062 | −0.0087 | 0.1267 | 0.029* | |
| C3 | 1.2074 (2) | 0.1651 (2) | 0.25780 (16) | 0.0264 (4) | |
| H3 | 1.2953 | 0.1069 | 0.2562 | 0.032* | |
| C4 | 1.2512 (2) | 0.3177 (2) | 0.33806 (16) | 0.0261 (4) | |
| H4 | 1.3678 | 0.3632 | 0.3919 | 0.031* | |
| C5 | 1.1247 (2) | 0.40367 (18) | 0.33975 (15) | 0.0226 (3) | |
| H5 | 1.1539 | 0.5079 | 0.3956 | 0.027* | |
| C6 | 0.9550 (2) | 0.33762 (17) | 0.25978 (14) | 0.0181 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.8239 (2) | 0.43410 (17) | 0.25728 (15) | 0.0192 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.7526 (2) | 0.58559 (17) | 0.12955 (14) | 0.0193 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.5298 (2) | 0.74124 (19) | 0.19805 (16) | 0.0254 (4) | |
| H9A | 0.4528 | 0.6995 | 0.1126 | 0.030* | |
| H9B | 0.6234 | 0.8366 | 0.2031 | 0.030* | |
| C10 | 0.4041 (2) | 0.77650 (17) | 0.30540 (15) | 0.0201 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.4601 (2) | 0.79494 (18) | 0.43245 (15) | 0.0227 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.5805 | 0.7838 | 0.4530 | 0.027* | |
| C12 | 0.3419 (2) | 0.82945 (18) | 0.52955 (16) | 0.0253 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.3805 | 0.8400 | 0.6158 | 0.030* | |
| C13 | 0.1679 (2) | 0.84838 (18) | 0.50053 (17) | 0.0279 (4) | |
| H13 | 0.0868 | 0.8722 | 0.5668 | 0.033* | |
| C14 | 0.1120 (2) | 0.83262 (19) | 0.37480 (17) | 0.0285 (4) | |
| H14 | −0.0065 | 0.8474 | 0.3552 | 0.034* | |
| C15 | 0.2287 (2) | 0.79521 (19) | 0.27727 (16) | 0.0248 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.1884 | 0.7823 | 0.1907 | 0.030* | |
| H1N | 0.924 (3) | 0.459 (2) | 0.1044 (18) | 0.030 (5)* | |
| H2N | 0.605 (3) | 0.593 (2) | 0.2644 (19) | 0.032 (5)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0275 (2) | 0.0300 (2) | 0.0343 (3) | 0.00316 (18) | −0.00924 (18) | 0.00382 (19) |
| S1 | 0.0321 (2) | 0.0347 (3) | 0.0234 (2) | 0.01932 (19) | 0.01270 (17) | 0.01826 (19) |
| O1 | 0.0315 (7) | 0.0388 (7) | 0.0274 (6) | 0.0197 (6) | 0.0153 (5) | 0.0201 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0235 (7) | 0.0238 (7) | 0.0197 (7) | 0.0131 (6) | 0.0087 (6) | 0.0103 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0253 (7) | 0.0261 (7) | 0.0240 (7) | 0.0137 (6) | 0.0106 (6) | 0.0158 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0195 (8) | 0.0234 (8) | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0018 (6) | 0.0077 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0319 (9) | 0.0219 (8) | 0.0223 (8) | 0.0115 (7) | 0.0074 (7) | 0.0086 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0250 (9) | 0.0334 (9) | 0.0304 (9) | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0087 (7) | 0.0176 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0183 (8) | 0.0344 (9) | 0.0298 (9) | 0.0058 (7) | 0.0004 (7) | 0.0175 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0233 (8) | 0.0213 (8) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0030 (7) | 0.0018 (6) | 0.0095 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0194 (8) | 0.0211 (8) | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0062 (6) | 0.0062 (6) | 0.0103 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0193 (8) | 0.0198 (8) | 0.0187 (8) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0027 (6) | 0.0080 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0200 (8) | 0.0195 (8) | 0.0189 (8) | 0.0065 (6) | 0.0025 (6) | 0.0066 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0302 (9) | 0.0292 (9) | 0.0269 (9) | 0.0174 (7) | 0.0105 (7) | 0.0157 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0223 (8) | 0.0159 (7) | 0.0248 (8) | 0.0066 (6) | 0.0066 (6) | 0.0095 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0216 (8) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0262 (9) | 0.0071 (7) | 0.0036 (6) | 0.0108 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0308 (9) | 0.0222 (8) | 0.0226 (8) | 0.0061 (7) | 0.0059 (7) | 0.0082 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0293 (9) | 0.0228 (9) | 0.0325 (10) | 0.0089 (7) | 0.0150 (7) | 0.0094 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0207 (9) | 0.0278 (9) | 0.0393 (10) | 0.0115 (7) | 0.0066 (7) | 0.0114 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0259 (9) | 0.0256 (8) | 0.0259 (9) | 0.0109 (7) | 0.0029 (7) | 0.0101 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C1 | 1.7409 (16) | C5—C6 | 1.390 (2) |
| S1—C8 | 1.6752 (16) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C7 | 1.2207 (19) | C6—C7 | 1.500 (2) |
| N1—C7 | 1.371 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.506 (2) |
| N1—C8 | 1.3913 (19) | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| N1—H1N | 0.85 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| N2—C8 | 1.318 (2) | C10—C15 | 1.389 (2) |
| N2—C9 | 1.459 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.390 (2) |
| N2—H2N | 0.82 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.388 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.383 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.386 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.383 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.382 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C13—C14 | 1.384 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.386 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C14—C15 | 1.387 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.385 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C7—N1—C8 | 127.85 (13) | N2—C8—N1 | 116.48 (14) |
| C7—N1—H1N | 116.5 (13) | N2—C8—S1 | 124.11 (12) |
| C8—N1—H1N | 115.2 (13) | N1—C8—S1 | 119.41 (11) |
| C8—N2—C9 | 122.95 (14) | N2—C9—C10 | 110.88 (13) |
| C8—N2—H2N | 117.3 (13) | N2—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C9—N2—H2N | 119.8 (13) | C10—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.61 (15) | N2—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—Cl1 | 119.44 (13) | C10—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—Cl1 | 118.95 (12) | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.1 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.67 (15) | C15—C10—C11 | 118.98 (14) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.7 | C15—C10—C9 | 118.94 (14) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.7 | C11—C10—C9 | 122.06 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.76 (15) | C12—C11—C10 | 120.64 (15) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C12—C11—H11 | 119.7 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C10—C11—H11 | 119.7 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.94 (15) | C13—C12—C11 | 119.88 (16) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C13—C12—H12 | 120.1 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C11—C12—H12 | 120.1 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.07 (15) | C12—C13—C14 | 119.91 (15) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.0 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.0 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.92 (14) | C13—C14—C15 | 120.18 (15) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 121.51 (14) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.54 (14) | C15—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| O1—C7—N1 | 124.11 (14) | C14—C15—C10 | 120.39 (15) |
| O1—C7—C6 | 122.83 (13) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 113.03 (13) | C10—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.7 (2) | C5—C6—C7—N1 | 98.18 (17) |
| Cl1—C1—C2—C3 | 179.23 (12) | C9—N2—C8—N1 | 177.65 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.6 (2) | C9—N2—C8—S1 | −1.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.8 (2) | C7—N1—C8—N2 | −5.7 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.8 (2) | C7—N1—C8—S1 | 173.68 (13) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.9 (2) | C8—N2—C9—C10 | −177.02 (15) |
| Cl1—C1—C6—C5 | 179.18 (11) | N2—C9—C10—C15 | −141.11 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 177.52 (14) | N2—C9—C10—C11 | 40.6 (2) |
| Cl1—C1—C6—C7 | −2.4 (2) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | 0.9 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.6 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 179.12 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −176.77 (14) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −1.1 (2) |
| C8—N1—C7—O1 | 4.5 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.1 (2) |
| C8—N1—C7—C6 | −173.81 (14) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.1 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—O1 | 101.52 (19) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −1.4 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—O1 | −80.1 (2) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.4 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—N1 | −80.19 (18) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | −177.92 (15) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1N···S1i | 0.86 (2) | 2.53 (2) | 3.3698 (18) | 166.2 (18) |
| N2—H2N···O1 | 0.82 (2) | 2.01 (2) | 2.669 (2) | 137 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: PK2248).
References
- Burnett, M. N. & Johnson, C. K. (1996). ORTEPIII Report ORNL-6895. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee, USA.
- D’hooghe, M., Waterinckx, A. & De Kimpe, N. (2005). J. Org. Chem.70, 227–232. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Higashi, T. (1995). ABSCOR, Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Jain, V. K. & Rao, J. T. (2003). J. Inst. Chem. (India), 75, 24–26.
- Rigaku/MSC (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Saeed, S., Bhatti, M. H., Yunus, U. & Jones, P. G. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Saeed, S., Rashid, N., Jones, P. G., Ali, M. & Hussain, R. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem.45, 1323–1331. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Saeed, S., Rashid, N., Tahir, A. & Jones, P. G. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o1870–o1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y., Hua, W., Liu, X. & Zhu, D. (2004). Chin. J. Org. Chem.24, 1217–1222.
- Zeng, R. S., Zou, J. P., Zhi, S. J., Chen, J. & Shen, Q. (2003). Org. Lett 5, 1657–1659. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W., Yates, S. R., Papiernik, S. K. & Guo, M. (2004). Environ. Sci. Technol.38, 6855–6860. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810023822/pk2248sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810023822/pk2248Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report