Abstract
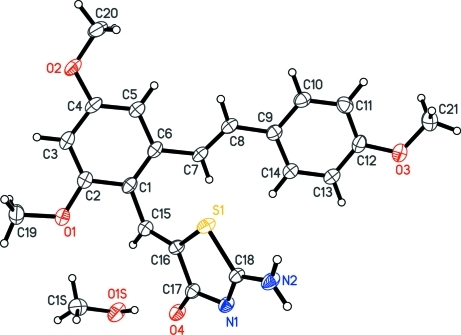
In the crystal structure of the title compound, C21H20N2O4S·CH3OH, molecules are linked into chains by a series of intermolecular N—H⋯O, N—H⋯N and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The molecular structure shows a double bond with Z geometry, connecting the thiazolone and resveratrol units. The dihedral angle between the thiazolone ring and the nearest dimethoxybenzene ring is 53.02 (7)°.
Related literature
For related structure–activitystudies, see; Aggarwal et al. (2004 ▶); Pettit et al. (1995 ▶); Cushman et al. (1991 ▶).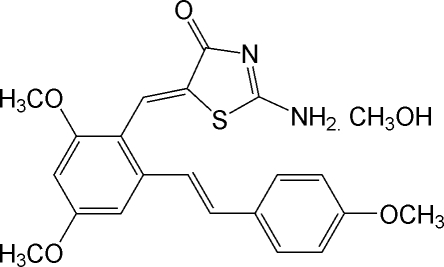
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H20N2O4S·CH4O
M r = 428.49
Monoclinic,
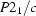
a = 10.6243 (2) Å
b = 22.2530 (5) Å
c = 9.0562 (2) Å
β = 93.028 (1)°
V = 2138.10 (8) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 1.65 mm−1
T = 90 K
0.15 × 0.08 × 0.02 mm
Data collection
Bruker X8 Proteum diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2006 ▶) T min = 0.777, T max = 0.968
31098 measured reflections
3911 independent reflections
3631 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.044
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.043
wR(F 2) = 0.112
S = 1.13
3911 reflections
276 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.51 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2006 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2006 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: XP in SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and local procedures.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810018520/fj2286sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810018520/fj2286Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2A⋯O4i | 0.88 | 2.07 | 2.926 (2) | 163 |
| N2—H2A⋯N1i | 0.88 | 2.64 | 3.175 (2) | 120 |
| N2—H2B⋯O1Sii | 0.88 | 2.05 | 2.872 (2) | 154 |
| O1S—H1S⋯O4 | 0.84 | 1.88 | 2.716 (2) | 172 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 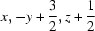 ; (ii)
; (ii) 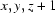 .
.
Acknowledgments
This investigation was supported by NIH/National Cancer Institute grant PO1 CA104457 (PAC) and by NSF MRI grant CHE 0319176 (SP).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Many natural products possessing a trimethoxybenzene ring, e.g., colchicines, and podophyllotoxins, are potent cytotoxic agents and exert their antitumor properties by their antitubulin activity. In view of the activity of such trimethoxybenzenes, similar structurally related stilbene moieties have been studied. The trihydroxy compound, resveratrol, a naturally occurring phytoalexin (trans-3, 4, 5-trihydroxystilbene) present in grapes, berries, peanuts,and red wine [Aggarwal et al.,2004, Pettit et al., 1995) is reported to be a potential cancer chemotherapeutic agent based on its striking inhibitory effects on cellular events associated with cancer initiation, promotion, and progression. (Cushman et al., 1991). These observations encouraged us to design and synthesise a series of novel trimethoxy resveratrol analogs that were expected to function as potent cytotoxic agents against lung and breast cancer cells. The structural characterization of the title compound by x-ray analysis was performed to determine the geometry (E vs Z) of the double bond connecting the thiozolone ring and the resveratrol moiety, which cannot be easily determined by NMR spectroscopic analysis, and to obtain detailed information on the structural conformation of the molecule, that may be useful in structure-activity relationship (SAR) analysis. The title compound was synthesized in two steps. In step one, the formylation of (E)-1, 3-dimethoxy-5- (4-methoxystyryl)benzene with a slight excess of phosphorous oxychloride in dimethylformamide at 0 °C resulted the formation of trans-2-formyl-3, 4', 5-trimethoxystilbene. In step two, the reaction of trans-2-formyl-3, 4', 5-trimethoxystilbene with the active methelene compound, 2-aminothiazol-4(5H)-one in presence of ammonium acetate in acetic acid under microwave irradiation conditions yielded the title compound, (Z)-2-amino-5-[2,4-dimethoxy-6- (4-methoxystyryl)benzylidene]thiazol-4(5H)-one in 90% yield. The x-ray analysis studies revealed that the double bond connecting the thiazolone and resveratrol moieties has the Z geometry. The dihedral angle between the plane of the thiazolone ring and the plane of the nearest phenyl ring is 53.02 (7)°. The crystal packing is stabilized by a series of N—H···O, N—H···N and O—H···O intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
Experimental
A mixture of trans-2-formyl-3,4',5-trimethoxystilbene (50 mg, 1 mmol), 2-aminothiazol-4(5H)-one (20.44 mg, 1.1 mmol), ammonium acetate (13.56 mg, 1.1 mmol) and acetic acid (0.25 ml) was irradiated in a domestic microwave oven for 60 sec with intermittent cooling to room temperature every 20 sec. The reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature, and treated with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution. The precipitate thus obtained was collected by filtration, washed with cold water and dried, to afford the crude product. Crystallization from methanol gave a white crystalline product of (Z)-2-amino-5-[2,4-dimethoxy-6-(4-methoxystyryl) benzylidene]thiazol-4(5H)-one methanolate, which was suitable for x-ray analysis. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 3.77 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 3.82 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 3.86 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 6.54-6.55 (d, J=2 Hz, 1H), 6.90-6.91 (m, 1H), 6.93-6.95 (d, J=2 Hz, 3H), 7.20-7.23 (d, J=16 Hz, 1H), 7.47-7.49 (d, J=9 Hz, 2H), 7.61 (s, 1H), 8.83 (s, 1H), 9.12 (s, 1H) ppm. 13C NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 55.6, 55.9, 56.3, 98.1, 102.8, 114.9, 115.9, 124.2,125.7, 128.6, 130.2, 131.6, 134.6, 138.4, 150.5, 158.9, 159.9, 161.6, 176.6, 180.3, 181.3. M. P: 172-175 °C
Refinement
H atoms were found in difference Fourier maps and subsequently placed in idealized positions with constrained distances of 0.98 Å (RCH3), 0.95 Å (CArH), and with Uiso(H) values set to either 1.2Ueq or 1.5Ueq (RCH3, OH) of the attached atom.
Figures
Fig. 1.
A view of the molecule with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C21H20N2O4S·CH4O | F(000) = 904 |
| Mr = 428.49 | Dx = 1.331 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 9054 reflections |
| a = 10.6243 (2) Å | θ = 4.0–68.4° |
| b = 22.2530 (5) Å | µ = 1.65 mm−1 |
| c = 9.0562 (2) Å | T = 90 K |
| β = 93.028 (1)° | Lath, yellow |
| V = 2138.10 (8) Å3 | 0.15 × 0.08 × 0.02 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker X8 Proteum diffractometer | 3911 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus rotating anode | 3631 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graded multilayer optics | Rint = 0.044 |
| Detector resolution: 5.6 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 68.4°, θmin = 4.0° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −12→12 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2006) | k = −26→26 |
| Tmin = 0.777, Tmax = 0.968 | l = −10→10 |
| 31098 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.112 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.13 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0357P)2 + 2.3067P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3911 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 276 parameters | Δρmax = 0.51 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.73380 (5) | 0.59495 (2) | 0.83763 (5) | 0.02575 (15) | |
| O1 | 0.84106 (14) | 0.45171 (6) | 0.46089 (17) | 0.0294 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.79198 (16) | 0.69625 (7) | 0.70367 (18) | 0.0233 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.67303 (19) | 0.48654 (9) | 0.5941 (2) | 0.0230 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.56944 (16) | 0.31027 (7) | 0.6733 (2) | 0.0401 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.78786 (18) | 0.70133 (8) | 0.95934 (19) | 0.0288 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.8067 | 0.7398 | 0.9591 | 0.035* | |
| H2B | 0.7766 | 0.6828 | 1.0435 | 0.035* | |
| C2 | 0.73882 (19) | 0.43671 (9) | 0.5382 (2) | 0.0247 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.15908 (16) | 0.72923 (7) | 1.04700 (19) | 0.0379 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.7014 (2) | 0.37874 (9) | 0.5646 (2) | 0.0287 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.7459 | 0.3457 | 0.5260 | 0.034* | |
| O4 | 0.79309 (15) | 0.66720 (6) | 0.46217 (15) | 0.0276 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.5968 (2) | 0.36913 (9) | 0.6495 (2) | 0.0285 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.5283 (2) | 0.41643 (9) | 0.7024 (2) | 0.0254 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.4560 | 0.4090 | 0.7571 | 0.031* | |
| C6 | 0.56614 (19) | 0.47574 (9) | 0.6748 (2) | 0.0227 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.49002 (19) | 0.52638 (9) | 0.7237 (2) | 0.0230 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.4958 | 0.5629 | 0.6702 | 0.028* | |
| C8 | 0.41358 (19) | 0.52599 (9) | 0.8360 (2) | 0.0252 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.4032 | 0.4890 | 0.8861 | 0.030* | |
| C9 | 0.34427 (19) | 0.57835 (9) | 0.8881 (2) | 0.0249 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.2585 (2) | 0.57198 (10) | 0.9977 (2) | 0.0280 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.2434 | 0.5330 | 1.0359 | 0.034* | |
| C11 | 0.1938 (2) | 0.62079 (10) | 1.0535 (2) | 0.0296 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.1356 | 0.6150 | 1.1283 | 0.036* | |
| C12 | 0.2153 (2) | 0.67762 (10) | 0.9992 (2) | 0.0296 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.2998 (2) | 0.68532 (10) | 0.8890 (3) | 0.0363 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.3138 | 0.7243 | 0.8502 | 0.044* | |
| C14 | 0.3634 (2) | 0.63662 (10) | 0.8357 (3) | 0.0325 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.4219 | 0.6428 | 0.7614 | 0.039* | |
| C15 | 0.71662 (18) | 0.54678 (9) | 0.5548 (2) | 0.0223 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.7306 | 0.5531 | 0.4533 | 0.027* | |
| C16 | 0.73910 (19) | 0.59395 (9) | 0.6445 (2) | 0.0224 (4) | |
| C17 | 0.77662 (18) | 0.65520 (9) | 0.5932 (2) | 0.0218 (4) | |
| C18 | 0.77655 (19) | 0.67159 (9) | 0.8345 (2) | 0.0227 (4) | |
| C19 | 0.9131 (2) | 0.40406 (10) | 0.4010 (3) | 0.0352 (5) | |
| H19A | 0.9469 | 0.3783 | 0.4815 | 0.053* | |
| H19B | 0.9829 | 0.4211 | 0.3480 | 0.053* | |
| H19C | 0.8590 | 0.3802 | 0.3326 | 0.053* | |
| C20 | 0.4740 (2) | 0.29656 (11) | 0.7742 (3) | 0.0427 (6) | |
| H20A | 0.4925 | 0.3177 | 0.8678 | 0.064* | |
| H20B | 0.4726 | 0.2531 | 0.7921 | 0.064* | |
| H20C | 0.3917 | 0.3095 | 0.7316 | 0.064* | |
| C21 | 0.0789 (2) | 0.72365 (12) | 1.1677 (3) | 0.0387 (6) | |
| H21A | 0.0098 | 0.6959 | 1.1407 | 0.058* | |
| H21B | 0.0443 | 0.7631 | 1.1909 | 0.058* | |
| H21C | 0.1276 | 0.7081 | 1.2543 | 0.058* | |
| O1S | 0.80228 (17) | 0.61397 (7) | 0.19308 (17) | 0.0374 (4) | |
| H1S | 0.7956 | 0.6277 | 0.2787 | 0.056* | |
| C1S | 0.8883 (2) | 0.56477 (11) | 0.1984 (3) | 0.0355 (5) | |
| H1S1 | 0.9573 | 0.5731 | 0.2717 | 0.053* | |
| H1S2 | 0.9226 | 0.5593 | 0.1009 | 0.053* | |
| H1S3 | 0.8442 | 0.5281 | 0.2262 | 0.053* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0407 (3) | 0.0184 (3) | 0.0178 (3) | −0.0068 (2) | −0.0021 (2) | 0.00092 (18) |
| O1 | 0.0325 (8) | 0.0229 (7) | 0.0330 (8) | 0.0030 (6) | 0.0050 (6) | −0.0030 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0327 (9) | 0.0184 (8) | 0.0185 (8) | −0.0006 (7) | −0.0005 (7) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0286 (10) | 0.0183 (10) | 0.0215 (10) | 0.0002 (8) | −0.0055 (8) | −0.0022 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0421 (9) | 0.0152 (7) | 0.0638 (12) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0108 (8) | 0.0004 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0457 (11) | 0.0208 (9) | 0.0196 (9) | −0.0054 (8) | −0.0004 (8) | −0.0007 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0267 (10) | 0.0236 (10) | 0.0232 (10) | 0.0020 (8) | −0.0036 (8) | −0.0015 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0432 (9) | 0.0266 (8) | 0.0448 (10) | 0.0034 (7) | 0.0121 (7) | −0.0054 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0316 (11) | 0.0203 (10) | 0.0337 (12) | 0.0045 (8) | −0.0033 (9) | −0.0026 (9) |
| O4 | 0.0431 (9) | 0.0214 (7) | 0.0185 (7) | −0.0005 (6) | 0.0018 (6) | 0.0010 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0326 (11) | 0.0160 (10) | 0.0363 (12) | −0.0020 (8) | −0.0043 (9) | 0.0008 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0273 (10) | 0.0201 (10) | 0.0284 (11) | −0.0008 (8) | −0.0032 (8) | −0.0001 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0276 (10) | 0.0184 (9) | 0.0211 (10) | 0.0008 (8) | −0.0071 (8) | −0.0023 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0264 (10) | 0.0162 (9) | 0.0256 (11) | −0.0015 (8) | −0.0059 (8) | −0.0007 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0295 (11) | 0.0190 (10) | 0.0263 (11) | −0.0028 (8) | −0.0047 (8) | 0.0000 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0279 (10) | 0.0236 (10) | 0.0227 (10) | −0.0024 (8) | −0.0028 (8) | −0.0019 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0356 (11) | 0.0236 (11) | 0.0244 (11) | −0.0031 (9) | −0.0015 (9) | 0.0018 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0312 (11) | 0.0348 (12) | 0.0230 (11) | −0.0035 (9) | 0.0022 (8) | −0.0023 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0322 (11) | 0.0238 (11) | 0.0325 (12) | 0.0008 (9) | −0.0002 (9) | −0.0076 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0440 (13) | 0.0215 (11) | 0.0446 (14) | −0.0035 (10) | 0.0121 (11) | −0.0015 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0364 (12) | 0.0229 (11) | 0.0390 (13) | −0.0042 (9) | 0.0098 (10) | −0.0040 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0259 (10) | 0.0215 (10) | 0.0192 (10) | 0.0014 (8) | −0.0020 (8) | 0.0012 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0249 (10) | 0.0188 (10) | 0.0232 (10) | −0.0005 (8) | −0.0015 (8) | 0.0023 (8) |
| C17 | 0.0252 (10) | 0.0195 (10) | 0.0206 (10) | 0.0012 (8) | −0.0010 (8) | 0.0011 (8) |
| C18 | 0.0258 (10) | 0.0186 (9) | 0.0234 (10) | −0.0023 (8) | −0.0001 (8) | −0.0017 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0337 (12) | 0.0319 (12) | 0.0401 (13) | 0.0067 (10) | 0.0038 (10) | −0.0053 (10) |
| C20 | 0.0417 (14) | 0.0210 (11) | 0.0662 (18) | −0.0025 (10) | 0.0092 (12) | 0.0090 (11) |
| C21 | 0.0366 (13) | 0.0387 (13) | 0.0413 (14) | 0.0073 (10) | 0.0058 (10) | −0.0064 (11) |
| O1S | 0.0644 (11) | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0199 (8) | 0.0013 (8) | 0.0020 (7) | 0.0003 (6) |
| C1S | 0.0409 (13) | 0.0380 (13) | 0.0275 (12) | −0.0060 (10) | 0.0017 (10) | −0.0014 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—C16 | 1.753 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.390 (3) |
| S1—C18 | 1.765 (2) | C9—C14 | 1.399 (3) |
| O1—C2 | 1.365 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.394 (3) |
| O1—C19 | 1.431 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C18 | 1.324 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.380 (3) |
| N1—C17 | 1.358 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.403 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.388 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.418 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.378 (3) |
| C1—C15 | 1.468 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C4 | 1.362 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C20 | 1.433 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.341 (3) |
| N2—C18 | 1.310 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| N2—H2A | 0.8800 | C16—C17 | 1.501 (3) |
| N2—H2B | 0.8800 | C19—H19A | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.375 (3) | C19—H19B | 0.9800 |
| O3—C12 | 1.375 (3) | C19—H19C | 0.9800 |
| O3—C21 | 1.426 (3) | C20—H20A | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.401 (3) | C20—H20B | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C20—H20C | 0.9800 |
| O4—C17 | 1.237 (2) | C21—H21A | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.380 (3) | C21—H21B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.406 (3) | C21—H21C | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | O1S—C1S | 1.425 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.469 (3) | O1S—H1S | 0.8400 |
| C7—C8 | 1.334 (3) | C1S—H1S1 | 0.9800 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C1S—H1S2 | 0.9800 |
| C8—C9 | 1.470 (3) | C1S—H1S3 | 0.9800 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | ||
| C16—S1—C18 | 88.54 (9) | C14—C13—C12 | 120.2 (2) |
| C2—O1—C19 | 118.01 (17) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| C18—N1—C17 | 111.41 (17) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 118.67 (18) | C13—C14—C9 | 121.8 (2) |
| C6—C1—C15 | 123.84 (18) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.1 |
| C2—C1—C15 | 117.36 (18) | C9—C14—H14 | 119.1 |
| C4—O2—C20 | 118.05 (18) | C16—C15—C1 | 128.05 (19) |
| C18—N2—H2A | 120.0 | C16—C15—H15 | 116.0 |
| C18—N2—H2B | 120.0 | C1—C15—H15 | 116.0 |
| H2A—N2—H2B | 120.0 | C15—C16—C17 | 124.40 (18) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 124.34 (19) | C15—C16—S1 | 126.89 (16) |
| O1—C2—C1 | 114.37 (18) | C17—C16—S1 | 108.69 (14) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.28 (19) | O4—C17—N1 | 122.94 (18) |
| C12—O3—C21 | 117.11 (18) | O4—C17—C16 | 123.11 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.93 (19) | N1—C17—C16 | 113.95 (17) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.5 | N2—C18—N1 | 123.57 (18) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.5 | N2—C18—S1 | 119.09 (15) |
| O2—C4—C5 | 123.9 (2) | N1—C18—S1 | 117.32 (15) |
| O2—C4—C3 | 114.60 (19) | O1—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 121.50 (19) | O1—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.6 (2) | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.2 | O1—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.2 | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 120.01 (18) | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 119.95 (18) | O2—C20—H20A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.97 (19) | O2—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 126.26 (19) | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 116.9 | O2—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 116.9 | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 125.10 (19) | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 117.5 | O3—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 117.5 | O3—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C14 | 116.7 (2) | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 120.47 (19) | O3—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C14—C9—C8 | 122.80 (19) | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 122.3 (2) | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 118.9 | C1S—O1S—H1S | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 118.9 | O1S—C1S—H1S1 | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 119.4 (2) | O1S—C1S—H1S2 | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 120.3 | H1S1—C1S—H1S2 | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 120.3 | O1S—C1S—H1S3 | 109.5 |
| O3—C12—C11 | 124.8 (2) | H1S1—C1S—H1S3 | 109.5 |
| O3—C12—C13 | 115.6 (2) | H1S2—C1S—H1S3 | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.7 (2) | ||
| C19—O1—C2—C3 | 1.1 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.2 (3) |
| C19—O1—C2—C1 | 179.79 (18) | C21—O3—C12—C11 | 4.0 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—O1 | 179.80 (17) | C21—O3—C12—C13 | −175.4 (2) |
| C15—C1—C2—O1 | 3.9 (3) | C10—C11—C12—O3 | −178.8 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.5 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.6 (3) |
| C15—C1—C2—C3 | −177.44 (19) | O3—C12—C13—C14 | 178.5 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | 178.09 (19) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.0 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.5 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | 1.0 (4) |
| C20—O2—C4—C5 | −8.1 (3) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | −0.5 (3) |
| C20—O2—C4—C3 | 172.3 (2) | C8—C9—C14—C13 | −178.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—O2 | −178.10 (19) | C6—C1—C15—C16 | 52.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 2.3 (3) | C2—C1—C15—C16 | −132.2 (2) |
| O2—C4—C5—C6 | 178.4 (2) | C1—C15—C16—C17 | −176.34 (19) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −2.0 (3) | C1—C15—C16—S1 | 5.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.8 (3) | C18—S1—C16—C15 | 179.4 (2) |
| C15—C1—C6—C5 | 177.43 (19) | C18—S1—C16—C17 | 0.77 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −175.00 (18) | C18—N1—C17—O4 | −176.10 (19) |
| C15—C1—C6—C7 | 0.7 (3) | C18—N1—C17—C16 | 3.4 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.1 (3) | C15—C16—C17—O4 | −1.8 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 176.70 (19) | S1—C16—C17—O4 | 176.94 (16) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −157.3 (2) | C15—C16—C17—N1 | 178.79 (19) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 25.9 (3) | S1—C16—C17—N1 | −2.5 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 176.15 (18) | C17—N1—C18—N2 | 179.14 (19) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 174.4 (2) | C17—N1—C18—S1 | −2.8 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—C14 | −8.0 (3) | C16—S1—C18—N2 | 179.25 (18) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | 0.1 (3) | C16—S1—C18—N1 | 1.12 (17) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 177.91 (19) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2A···O4i | 0.88 | 2.07 | 2.926 (2) | 163 |
| N2—H2A···N1i | 0.88 | 2.64 | 3.175 (2) | 120 |
| N2—H2B···O1Sii | 0.88 | 2.05 | 2.872 (2) | 154 |
| O1S—H1S···O4 | 0.84 | 1.88 | 2.716 (2) | 172 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (ii) x, y, z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FJ2286).
References
- Aggarwal, B. B., Bhardwaj, A., Aggarwal, R. S., Seeram, N. P., Shishodia, S. & Takada, Y. (2004). Anticancer Res.24, 2783–2840. [PubMed]
- Bruker (2006). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cushman, M., Nagarathnam, D., Gopal, D., Chakraborti, A. K., Lin, C. M. & Hamel, E. (1991). J. Med. Chem.34, 2579–2588. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Pettit, G. R., Singh, S. B., Boyd, M. R., Hamel, E., Pettit, R. K., Schmidt, J. M. & Hogan, F. (1995). J. Med. Chem.38, 1666–1672. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810018520/fj2286sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810018520/fj2286Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report