Abstract
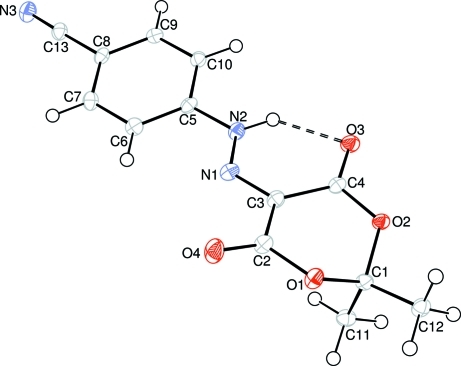
In the title compound, C13H11N3O4, the dioxane ring adopts an envelope conformation with the C atom bonded to the dimethyl group in the flap position [deviation = 0.613 (1) Å]. The nitrile group and the attached benzene ring are roughly coplanar [maximum deviation = 0.087 (1) Å]. An intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond involving the hydrazinyl group generates an S(6) ring. The N—N and C—N bond lengths indicate that the compound may be a mixture of the azo and hydrazone tautomeric forms but the presence of the N-bound H atom supports the hydrazone form. The crystal structure is stabilized by weak intermolecular C—H⋯O, C—H⋯N and C—H⋯π interactions.
Related literature
For the applications of related azo compounds, see: Branger et al. (1997 ▶); Buchel et al. (1995 ▶); Gale et al. (1998 ▶); Ikeda & Tsutsumi (1995 ▶); Kang et al. (2000 ▶); Karcı et al. (2004 ▶); Kim et al. (1995 ▶); Kobrakov et al. (2004 ▶); Natansohn et al. (1992 ▶); Rochon et al. (1995 ▶). For related hydrazone structures, see: Çolak et al. (2010 ▶); Pavlovic et al. (2009 ▶); Seferoğlu et al. (2008 ▶); Seferoğlu et al. (2009 ▶); Wojciechowski & Szymezak (2007 ▶).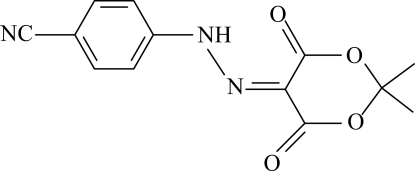
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H11N3O4
M r = 273.25
Monoclinic,
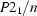
a = 9.7617 (2) Å
b = 11.0023 (2) Å
c = 11.4753 (3) Å
β = 93.796 (1)°
V = 1229.76 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.46 × 0.43 × 0.29 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.950, T max = 0.968
11746 measured reflections
3098 independent reflections
2591 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.029
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.108
S = 1.04
3098 reflections
225 parameters
All H-atom parameters refined
Δρmax = 0.38 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810024025/ci5104sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810024025/ci5104Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C5–C10 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯O3 | 0.92 (2) | 1.958 (16) | 2.6674 (13) | 132 (1) |
| C9—H9⋯N1i | 0.94 (2) | 2.624 (15) | 3.5320 (16) | 164 (1) |
| C10—H10⋯N3ii | 0.99 (2) | 2.485 (15) | 3.3876 (16) | 152 (1) |
| C12—H123⋯O2iii | 0.97 (2) | 2.527 (17) | 3.4454 (15) | 159 (1) |
| C12—H122⋯Cg1iv | 0.98 (2) | 2.491 (15) | 3.4575 (13) | 171 (1) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 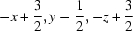 ; (ii)
; (ii) 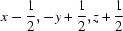 ; (iii)
; (iii) 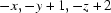 ; (iv)
; (iv) 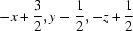 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to Anadolu University and the Medicinal Plants and Medicine Research Centre of Anadolu University, Eskişehir, Turkey, for the use of X-ray diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
It has been known for many years that the azo compounds are widely used class of dyes due to their applications in various fields such as the dyeing of textile fibers, the coloring of different materials, colored plastics and electrochemical sensors (Kobrakov et al., 2004; Karcı et al., 2004; Gale et al., 1998). Azo dyes have been attracting intensive interest for their potential use in optical data storage (Natansohn et al., 1992), optical switching (Ikeda & Tsutsumi, 1995), polarization holography (Kim et al., 1995; Rochon et al., 1995), optical modulation (Buchel et al., 1995), nonlinear optics (Branger et al., 1997) and photolabile surfactants (Kang et al., 2000).
The dyes may exist in two possible tautomeric forms, namely azo form and hydrazone form. The azo-hydrazone tautomerism is quite interesting from a theoretical and practical point of view because the two tautomers have different properties. Azo dyes are known to exist in the azo-hydrazone tautomeric forms (Çolak et al., 2010; Pavlovic et al., 2009; Seferoğlu et al., 2009; Seferoğlu et al., 2008; Wojciechowski & Szymezak, 2007). We herein report the crystal structure of the title compound, (I).
The title compound, (I), contains benzonitrile and 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane -4,6-dione groups connected via a hydrazinyl group (Fig. 1). In (I), N1—N2 [1.3082 (14) Å] bond length is between the N═N double bond [1.20–1.28 Å for a real azo compound] and N—N single bond [longer than 1.4 Å] lengths. The N1—C3 and N2—C5 bond lengths are 1.3116 (14) and 1.4075 (14) Å, respectively. The carbonyl O atoms O3 and O4 slightly deviate from the N1/C2–C4 plane by 0.255 (2) and 0.259 (2) Å, respectively. So, the title compound may exist both in azo and hydrazone tautomeric forms, and is mainly in the hydrazone tautomeric form. The C8—C13 [1.4418 (15) Å] bond length is longer for a C(sp2)—C(sp1) bond, but in agreement with the previously reported value [1.442 (3) Å; Çolak et al., 2010).
An intramolecular N2—H2···O3 hydrogen bond (Table 1) results in the formation of a nearly planar [with a maximum deviation of 0.056 (1) Å for atom C4] six-membered ring C (O3/N1/N2/H2/C3/C4), which is oriented with respect to the benzonitrile ring B (C5–C10) at a dihedral angle of 7.8 (43)°. Atoms N1, N2, N3 and C13 are displaced by -0.162 (2), 0.038 (2), 0.049 (2) and 0.028 (2) Å from the plane of ring B, respectively. The benzonitrile and hydrazinyl groups (4-hydrazinylbenzonitrile) are essentially coplanar [with a maximum deviation of -0.087 (1) Å for atom N1]. The dioxane ring A (O1/O2/C1–C4) is not planar having envelope conformation with atom C1 displaced by 0.613 (1) Å from the plane of the other ring atoms.
In the crystal structure, weak C—H···O and C—H···N hydrogen bonds (Table 1) may be effective in the stabilization of the crystal packing. There also exists a weak C—H···π interaction (Table 1).
Experimental
A hydrochloric acid solution (2.5 ml) of 4-aminobenzonitrile (1.18 g, 10 mmol) and an aqueous solution (10 ml) of sodium nitrite (0.69 g, 10 mmol) were mixed and stirred at 273 K for 1 h. To this solution, an ethanol solution (10 ml) of the coupling component 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4,6-dione (1.44 g, 10 mmol) was added and the stirring was continued at 273 K for 4 h. The resulting product was filtered and washed with water, dried and crystallized from ethanol (yield 1.88 g, 69%; m.p. 440–442 K).
Refinement
H atoms were located in difference Fourier maps and refined isotropically.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. The dashed line indicates a hydrogen bond.
Crystal data
| C13H11N3O4 | F(000) = 568 |
| Mr = 273.25 | Dx = 1.476 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 4103 reflections |
| a = 9.7617 (2) Å | θ = 2.6–28.4° |
| b = 11.0023 (2) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| c = 11.4753 (3) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 93.796 (1)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 1229.76 (5) Å3 | 0.46 × 0.43 × 0.29 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3098 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2591 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.029 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.5°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | h = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.950, Tmax = 0.968 | k = −14→14 |
| 11746 measured reflections | l = −15→8 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.108 | All H-atom parameters refined |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0626P)2 + 0.2729P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3098 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 225 parameters | Δρmax = 0.38 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.16363 (8) | 0.74524 (7) | 0.85585 (7) | 0.0172 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.17892 (8) | 0.56739 (7) | 0.97179 (7) | 0.01470 (19) | |
| O3 | 0.35656 (9) | 0.44276 (8) | 0.96914 (7) | 0.0187 (2) | |
| O4 | 0.32521 (9) | 0.79574 (8) | 0.73794 (8) | 0.0249 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.44403 (10) | 0.56888 (9) | 0.76510 (9) | 0.0165 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.51381 (10) | 0.46953 (9) | 0.78943 (9) | 0.0159 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.4942 (16) | 0.4243 (15) | 0.8538 (15) | 0.028 (4)* | |
| N3 | 1.03756 (11) | 0.29578 (10) | 0.47015 (10) | 0.0232 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.08704 (11) | 0.64589 (10) | 0.90176 (10) | 0.0143 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.27845 (12) | 0.71950 (11) | 0.79881 (10) | 0.0172 (2) | |
| C3 | 0.34022 (12) | 0.59901 (10) | 0.82608 (10) | 0.0155 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.29477 (11) | 0.52812 (10) | 0.92521 (10) | 0.0144 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.62374 (11) | 0.43844 (10) | 0.72180 (10) | 0.0148 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.64458 (13) | 0.49922 (11) | 0.61746 (10) | 0.0173 (2) | |
| H6 | 0.5852 (15) | 0.5636 (14) | 0.5904 (13) | 0.020 (4)* | |
| C7 | 0.75216 (13) | 0.46401 (11) | 0.55177 (10) | 0.0175 (2) | |
| H7 | 0.7668 (15) | 0.5059 (14) | 0.4788 (13) | 0.024 (4)* | |
| C8 | 0.83788 (12) | 0.36875 (11) | 0.59035 (10) | 0.0155 (2) | |
| C9 | 0.81720 (12) | 0.30898 (11) | 0.69557 (10) | 0.0161 (2) | |
| H9 | 0.8752 (14) | 0.2457 (14) | 0.7224 (12) | 0.020 (4)* | |
| C10 | 0.70992 (12) | 0.34407 (11) | 0.76131 (10) | 0.0159 (2) | |
| H10 | 0.6926 (14) | 0.3023 (14) | 0.8350 (13) | 0.021 (4)* | |
| C11 | 0.01442 (13) | 0.57371 (11) | 0.80405 (10) | 0.0178 (2) | |
| H111 | 0.0795 (15) | 0.5338 (14) | 0.7556 (13) | 0.022 (4)* | |
| H112 | −0.0444 (15) | 0.5101 (14) | 0.8393 (13) | 0.023 (4)* | |
| H113 | −0.0456 (15) | 0.6270 (15) | 0.7544 (14) | 0.026 (4)* | |
| C12 | −0.00717 (13) | 0.70098 (11) | 0.98606 (10) | 0.0169 (2) | |
| H121 | 0.0494 (16) | 0.7364 (15) | 1.0534 (13) | 0.026 (4)* | |
| H122 | −0.0616 (15) | 0.7636 (14) | 0.9446 (13) | 0.021 (4)* | |
| H123 | −0.0673 (16) | 0.6388 (16) | 1.0133 (15) | 0.035 (4)* | |
| C13 | 0.94875 (12) | 0.32918 (11) | 0.52248 (10) | 0.0177 (2) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0168 (4) | 0.0111 (4) | 0.0244 (4) | 0.0003 (3) | 0.0057 (3) | 0.0024 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0132 (4) | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0169 (4) | 0.0027 (3) | 0.0012 (3) | 0.0015 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0164 (4) | 0.0178 (4) | 0.0220 (4) | 0.0033 (3) | 0.0011 (3) | 0.0027 (3) |
| O4 | 0.0244 (5) | 0.0191 (5) | 0.0321 (5) | 0.0004 (4) | 0.0096 (4) | 0.0083 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0144 (5) | 0.0146 (5) | 0.0204 (5) | −0.0002 (4) | 0.0009 (4) | −0.0023 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0151 (5) | 0.0149 (5) | 0.0179 (5) | 0.0004 (4) | 0.0031 (4) | −0.0005 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0227 (6) | 0.0233 (6) | 0.0244 (5) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0076 (4) | 0.0001 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0111 (5) | 0.0182 (5) | 0.0005 (4) | 0.0010 (4) | 0.0024 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0152 (6) | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0208 (5) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0025 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0143 (5) | 0.0140 (5) | 0.0184 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | 0.0017 (4) | −0.0006 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0127 (5) | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0170 (5) | −0.0010 (4) | 0.0008 (4) | −0.0027 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0119 (5) | 0.0143 (5) | 0.0182 (5) | −0.0024 (4) | 0.0014 (4) | −0.0037 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0178 (6) | 0.0137 (5) | 0.0205 (5) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0014 (4) | 0.0001 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0196 (6) | 0.0155 (5) | 0.0178 (5) | −0.0026 (4) | 0.0039 (4) | 0.0004 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0134 (5) | 0.0155 (5) | 0.0179 (5) | −0.0031 (4) | 0.0028 (4) | −0.0022 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0137 (5) | 0.0160 (5) | 0.0185 (5) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0001 (4) | −0.0002 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0144 (5) | 0.0177 (5) | 0.0155 (5) | −0.0026 (4) | 0.0010 (4) | −0.0004 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0174 (6) | 0.0170 (6) | 0.0188 (5) | 0.0019 (5) | −0.0009 (4) | −0.0015 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0162 (6) | 0.0141 (5) | 0.0207 (5) | 0.0032 (4) | 0.0037 (4) | 0.0007 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0178 (6) | 0.0167 (6) | 0.0188 (5) | −0.0029 (4) | 0.0024 (4) | 0.0006 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.4435 (13) | C6—C7 | 1.3878 (16) |
| O1—C2 | 1.3645 (13) | C6—H6 | 0.954 (15) |
| O2—C1 | 1.4493 (13) | C7—C8 | 1.3949 (17) |
| O2—C4 | 1.3533 (13) | C7—H7 | 0.974 (15) |
| O3—C4 | 1.2081 (14) | C8—C9 | 1.4012 (16) |
| O4—C2 | 1.2009 (14) | C8—C13 | 1.4418 (15) |
| N1—N2 | 1.3082 (14) | C9—C10 | 1.3854 (15) |
| N1—C3 | 1.3116 (14) | C9—H9 | 0.936 (15) |
| N2—C5 | 1.4075 (14) | C10—H10 | 0.986 (15) |
| N2—H2 | 0.922 (17) | C11—C1 | 1.5117 (16) |
| N3—C13 | 1.1473 (15) | C11—H111 | 0.976 (15) |
| C1—C12 | 1.5055 (15) | C11—H113 | 0.984 (16) |
| C2—C3 | 1.4812 (16) | C11—H112 | 1.007 (16) |
| C3—C4 | 1.4718 (15) | C12—H122 | 0.975 (15) |
| C5—C6 | 1.3981 (16) | C12—H121 | 0.999 (16) |
| C5—C10 | 1.3932 (17) | C12—H123 | 0.967 (17) |
| C2—O1—C1 | 118.66 (9) | C7—C6—H6 | 119.7 (9) |
| C4—O2—C1 | 118.29 (8) | C6—C7—C8 | 119.80 (11) |
| N2—N1—C3 | 120.47 (10) | C6—C7—H7 | 119.6 (9) |
| N1—N2—C5 | 119.38 (10) | C8—C7—H7 | 120.6 (9) |
| N1—N2—H2 | 119.3 (10) | C7—C8—C9 | 120.56 (10) |
| C5—N2—H2 | 121.1 (10) | C7—C8—C13 | 120.76 (10) |
| O1—C1—O2 | 109.71 (9) | C9—C8—C13 | 118.68 (11) |
| O1—C1—C11 | 110.85 (9) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.9 (9) |
| O1—C1—C12 | 106.43 (9) | C10—C9—C8 | 119.72 (11) |
| O2—C1—C11 | 109.92 (9) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.4 (9) |
| O2—C1—C12 | 105.40 (9) | C5—C10—H10 | 119.5 (9) |
| C12—C1—C11 | 114.31 (10) | C9—C10—C5 | 119.50 (10) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 114.85 (10) | C9—C10—H10 | 121.0 (9) |
| O4—C2—O1 | 119.33 (11) | C1—C11—H111 | 111.6 (9) |
| O4—C2—C3 | 125.66 (11) | C1—C11—H113 | 110.4 (9) |
| N1—C3—C2 | 115.57 (10) | C1—C11—H112 | 108.6 (9) |
| N1—C3—C4 | 124.16 (11) | H111—C11—H112 | 109.0 (12) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.88 (10) | H111—C11—H113 | 108.9 (13) |
| O2—C4—C3 | 116.02 (10) | H113—C11—H112 | 108.3 (12) |
| O3—C4—O2 | 119.38 (10) | C1—C12—H121 | 108.9 (9) |
| O3—C4—C3 | 124.52 (10) | C1—C12—H122 | 107.9 (8) |
| C6—C5—N2 | 121.03 (11) | C1—C12—H123 | 109.4 (10) |
| C10—C5—N2 | 117.89 (10) | H121—C12—H123 | 110.0 (13) |
| C10—C5—C6 | 121.08 (10) | H122—C12—H121 | 110.9 (13) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.9 (9) | H122—C12—H123 | 109.6 (13) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.34 (11) | N3—C13—C8 | 178.56 (13) |
| C2—O1—C1—O2 | 51.23 (12) | O4—C2—C3—N1 | −9.81 (19) |
| C2—O1—C1—C11 | −70.35 (13) | O4—C2—C3—C4 | 163.35 (12) |
| C2—O1—C1—C12 | 164.79 (10) | N1—C3—C4—O2 | −174.73 (10) |
| C1—O1—C2—O4 | 163.20 (11) | N1—C3—C4—O3 | 8.59 (19) |
| C1—O1—C2—C3 | −21.07 (14) | C2—C3—C4—O2 | 12.73 (16) |
| C4—O2—C1—O1 | −50.36 (12) | C2—C3—C4—O3 | −163.95 (11) |
| C4—O2—C1—C12 | −164.59 (9) | N2—C5—C6—C7 | −178.47 (10) |
| C4—O2—C1—C11 | 71.77 (12) | C10—C5—C6—C7 | 0.62 (18) |
| C1—O2—C4—O3 | −163.46 (10) | N2—C5—C10—C9 | 178.44 (10) |
| C1—O2—C4—C3 | 19.68 (14) | C6—C5—C10—C9 | −0.67 (18) |
| C3—N1—N2—C5 | 179.24 (10) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.05 (18) |
| N2—N1—C3—C2 | 173.80 (10) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.65 (18) |
| N2—N1—C3—C4 | 0.97 (18) | C6—C7—C8—C13 | 178.87 (11) |
| N1—N2—C5—C6 | −11.37 (17) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.60 (18) |
| N1—N2—C5—C10 | 169.52 (10) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | −178.93 (11) |
| O1—C2—C3—N1 | 174.77 (10) | C8—C9—C10—C5 | 0.06 (17) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −12.07 (16) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg1 is the centroid of the C5–C10 ring. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···O3 | 0.92 (2) | 1.958 (16) | 2.6674 (13) | 132 (1) |
| C9—H9···N1i | 0.94 (2) | 2.624 (15) | 3.5320 (16) | 164 (1) |
| C10—H10···N3ii | 0.99 (2) | 2.485 (15) | 3.3876 (16) | 152 (1) |
| C12—H123···O2iii | 0.97 (2) | 2.527 (17) | 3.4454 (15) | 159 (1) |
| C12—H122···Cg1iv | 0.98 (2) | 2.491 (15) | 3.4575 (13) | 171 (1) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+3/2, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (iii) −x, −y+1, −z+2; (iv) −x+3/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CI5104).
References
- Branger, C., Lequan, M., Lequan, R. M., Large, M. & Kajzar, F. (1997). Chem. Phys. Lett.272, 265–270.
- Bruker (2005). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Buchel, M., Sekkat, Z., Paul, S., Weichart, B., Menzel, H. & Knoll, W. (1995). Langmuir, 11, 4460–4466.
- Çolak, N., Aksakal, D., Andaç, Ö. & Büyükgüngör, O. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1165–o1166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Gale, P. A., Chen, Z., Drew, M. G. B., Heath, J. A. & Beer, P. D. (1998). Polyhedron, 4, 405–412.
- Ikeda, T. & Tsutsumi, O. (1995). Science, 268, 1873–1875. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kang, H. C., Lee, B. M., Yoon, J. & Yoon, M. (2000). J. Colloid Interface Sci.231, 255–264. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Karcı, F., Şener, İ. & Deligöz, H. (2004). Dyes Pigments, 62, 131–140.
- Kim, D. Y., Tripathy, S. K., Li, L. & Kumar, J. (1995). Appl. Phys. Lett.66, 1166–1168.
- Kobrakov, K. I., Glyadyaeva, O. Yu., Stankevich, G. S. & Kovtun, L. G. (2004). Fibre Chem.36, 41–42.
- Natansohn, A., Rochon, P., Gosselin, J. & Xie, S. (1992). Macromolecules, 25, 2268–2273.
- Pavlovic, G., Racane, L., Cicak, H. & Tralic-Kulenovic, V. (2009). Dyes Pigments, 83, 354–362.
- Rochon, P., Battalla, E. & Natansohn, A. (1995). Appl. Phys. Lett.66, 136–138.
- Seferoğlu, Z., Ertan, N., Hökelek, T. & Şahin, E. (2008). Dyes Pigments, 77, 614–625.
- Seferoğlu, Z., Ertan, N., Kickelbick, G. & Hökelek, T. (2009). Dyes Pigments, 82, 20–25.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowski, K. & Szymezak, A. (2007). Dyes Pigments, 75, 45–51.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810024025/ci5104sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810024025/ci5104Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report