Abstract
The title compound, C12H12ClN3S, features a thiazolyl ring having an envelope conformation with the –CH2– group bonded to the S atom forming the flap. The C=N double bond has a Z configuration. The crystal structure shows intermolecular C—H⋯S hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For the biological activity of thiazole componds, see: Hense et al. (2002 ▶). For a related structure, see: Cunico et al. (2007 ▶). For the synthesis, see: Jeschke et al. (2002 ▶).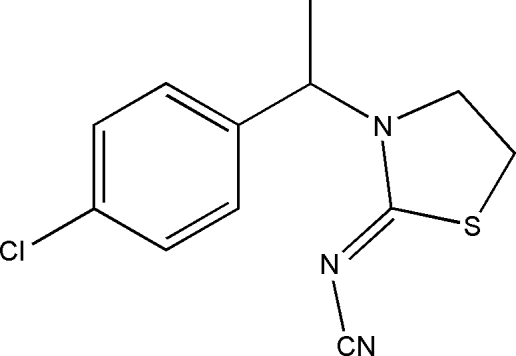
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H12ClN3S
M r = 265.76
Orthorhombic,

a = 5.8850 (12) Å
b = 7.5965 (15) Å
c = 28.273 (6) Å
V = 1264.0 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.45 mm−1
T = 113 K
0.14 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Saturn diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.940, T max = 0.957
9219 measured reflections
3019 independent reflections
2640 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.062
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.046
wR(F 2) = 0.113
S = 1.06
3019 reflections
155 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.38 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.34 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 6200 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: −0.09 (9)
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810029879/ng5002sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810029879/ng5002Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C10—H10A⋯S1i | 0.97 | 2.87 | 3.799 (4) | 160 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Recently, compounds containing the 2-(thiazolidin-2-ylidene)malononitrile group have attracted much interest because its containing a thiazole ring system are well known as efficient insecticide in pesticides, and have good plant-growth regulatory activity for a wide variety of crops e.g. thiacloprid (Hense et al., 2002). A new compound, (I), which containing thiazole ring has higher insecticide activity. We report here the crystal structure and synthesis of (I).
In (I) (Fig. 1), the bond lengths and angles are normal and in a agreement with those common to a previously reported structure (Cunico, et al., 2007). The thiazole ring is in and envelope conformation with the –CH2– group bonded to the S atom forming the flap. The carbon-nitrogen double bond of the molecule is trans. Flack x parameter = -0.0865 (with e.s.d. 0.0872) (Flack, 1983). The crystal structure involves C—H···S intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
Experimental
(Z)-(thiazolidin-2-ylideneamino)formonitrile 1.27 g (10.0 mmol) and potassium carbonate (10.0 mmol) were dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide(DMF) (15 ml) which was stirred 0.5 h at room temperature. Then 1-chloro-4-(1-chloroethyl)benzene 1.75 g (10.0 mmol) was added dropwising within 2 h at 283 K. The mixture was stirred for 8 h at 428 K. Upon cooling at room temperature. Then water (20 ml) was added. The mixture was extracted with CH2Cl2 (15 ml) and the organic layer was washed with water and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The excess CH2Cl2 was removed on a water vacuum pump to obtain the oily product. Crystallized from methanol to afford the title compound 2.0 g (76% yield) (Jeschke, et al., 2002.). Single crystals suitable for X-ray measurement were obtained by recrystallization from the mixture of acetone and methanol at room temperature.
Refinement
All C-bound H atoms were placed in calculated positions, with C—H = 0.93–0.98 Å, and included in the final cycles of refinement using a riding model, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for the aryl and 1.5 Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms. Friedel pairs = 6200.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 40% probability level.
Crystal data
| C12H12ClN3S | F(000) = 552 |
| Mr = 265.76 | Dx = 1.397 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 193 reflections |
| a = 5.8850 (12) Å | θ = 1.4–27.9° |
| b = 7.5965 (15) Å | µ = 0.45 mm−1 |
| c = 28.273 (6) Å | T = 113 K |
| V = 1264.0 (4) Å3 | Block, white |
| Z = 4 | 0.14 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn diffractometer | 3019 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: rotating anode | 2640 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| confocal | Rint = 0.062 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.9°, θmin = 1.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2005) | h = −7→7 |
| Tmin = 0.940, Tmax = 0.957 | k = −9→8 |
| 9219 measured reflections | l = −29→37 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.113 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0534P)2 + 0.0295P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3019 reflections | Δρmax = 0.38 e Å−3 |
| 155 parameters | Δρmin = −0.34 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 6200 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.31420 (16) | −0.62970 (7) | 0.98241 (2) | 0.0438 (2) | |
| S1 | 0.18444 (12) | 0.16944 (8) | 0.77090 (2) | 0.03081 (17) | |
| N2 | 0.2773 (4) | 0.3380 (3) | 0.85392 (7) | 0.0279 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.3024 (4) | 0.1982 (3) | 0.82718 (8) | 0.0238 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.2990 (4) | −0.1331 (3) | 0.93777 (8) | 0.0267 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.2024 | −0.0368 | 0.9407 | 0.032* | |
| N1 | 0.4250 (4) | 0.0594 (2) | 0.84129 (6) | 0.0255 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.4992 (4) | −0.1158 (3) | 0.91192 (8) | 0.0242 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.5466 (4) | 0.0572 (3) | 0.88698 (8) | 0.0257 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.4806 | 0.1507 | 0.9065 | 0.031* | |
| C8 | 0.7950 (5) | 0.1029 (4) | 0.87970 (9) | 0.0369 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.8064 | 0.2125 | 0.8630 | 0.055* | |
| H8B | 0.8672 | 0.0117 | 0.8616 | 0.055* | |
| H8C | 0.8686 | 0.1135 | 0.9099 | 0.055* | |
| C12 | 0.1462 (5) | 0.4672 (3) | 0.83801 (8) | 0.0294 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.2409 (4) | −0.2905 (3) | 0.95914 (8) | 0.0288 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.1055 | −0.3011 | 0.9759 | 0.035* | |
| C4 | 0.5886 (5) | −0.4192 (3) | 0.93042 (9) | 0.0316 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.6860 | −0.5152 | 0.9284 | 0.038* | |
| C3 | 0.3874 (5) | −0.4315 (3) | 0.95515 (8) | 0.0285 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.0347 (5) | 0.5868 (3) | 0.82737 (8) | 0.0414 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.6432 (5) | −0.2610 (3) | 0.90865 (8) | 0.0292 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.7778 | −0.2518 | 0.8916 | 0.035* | |
| C11 | 0.4588 (7) | −0.0759 (4) | 0.80600 (9) | 0.0479 (8) | |
| H11A | 0.6166 | −0.0769 | 0.7961 | 0.058* | |
| H11B | 0.4235 | −0.1901 | 0.8195 | 0.058* | |
| C10 | 0.3144 (8) | −0.0437 (4) | 0.76555 (12) | 0.0648 (12) | |
| H10A | 0.1977 | −0.1336 | 0.7638 | 0.078* | |
| H10B | 0.4039 | −0.0488 | 0.7368 | 0.078* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0702 (5) | 0.0288 (3) | 0.0324 (4) | −0.0048 (3) | 0.0066 (4) | 0.0021 (3) |
| S1 | 0.0384 (4) | 0.0355 (3) | 0.0185 (3) | −0.0011 (3) | −0.0028 (3) | 0.0002 (2) |
| N2 | 0.0319 (11) | 0.0266 (9) | 0.0252 (11) | −0.0013 (9) | −0.0015 (9) | −0.0014 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0227 (11) | 0.0302 (11) | 0.0186 (11) | −0.0047 (10) | 0.0030 (10) | 0.0020 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0253 (12) | 0.0304 (11) | 0.0246 (12) | 0.0062 (11) | 0.0008 (10) | 0.0000 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0305 (11) | 0.0255 (10) | 0.0204 (11) | 0.0005 (9) | −0.0029 (9) | −0.0032 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0232 (11) | 0.0293 (11) | 0.0201 (12) | −0.0007 (9) | −0.0038 (9) | −0.0022 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0267 (12) | 0.0289 (12) | 0.0215 (13) | −0.0010 (10) | −0.0029 (10) | −0.0016 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0319 (14) | 0.0419 (14) | 0.0368 (16) | −0.0080 (13) | −0.0029 (12) | 0.0067 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0371 (15) | 0.0332 (12) | 0.0179 (12) | −0.0011 (11) | 0.0008 (10) | −0.0010 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0284 (13) | 0.0332 (12) | 0.0249 (13) | −0.0021 (10) | 0.0014 (10) | −0.0010 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0376 (14) | 0.0252 (11) | 0.0319 (14) | 0.0079 (11) | −0.0017 (11) | −0.0064 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0386 (14) | 0.0260 (11) | 0.0210 (13) | −0.0031 (11) | −0.0019 (10) | −0.0016 (10) |
| N3 | 0.0575 (17) | 0.0394 (12) | 0.0273 (13) | 0.0087 (12) | −0.0025 (11) | −0.0006 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0296 (14) | 0.0329 (11) | 0.0252 (14) | 0.0034 (11) | 0.0024 (10) | −0.0026 (10) |
| C11 | 0.069 (2) | 0.0489 (16) | 0.0254 (15) | 0.0203 (17) | −0.0048 (14) | −0.0132 (13) |
| C10 | 0.097 (3) | 0.0508 (18) | 0.046 (2) | 0.027 (2) | −0.038 (2) | −0.0243 (14) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C3 | 1.746 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9600 |
| S1—C9 | 1.750 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9600 |
| S1—C10 | 1.797 (3) | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| N2—C9 | 1.311 (3) | C12—N3 | 1.161 (3) |
| N2—C12 | 1.327 (3) | C2—C3 | 1.380 (4) |
| C9—N1 | 1.338 (3) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.383 (3) | C4—C3 | 1.378 (4) |
| C1—C6 | 1.393 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.388 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C11 | 1.446 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.477 (3) | C11—C10 | 1.446 (4) |
| C6—C5 | 1.394 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C6—C7 | 1.517 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C7—C8 | 1.516 (4) | C10—H10A | 0.9700 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9800 | C10—H10B | 0.9700 |
| C9—S1—C10 | 91.16 (13) | N3—C12—N2 | 174.7 (3) |
| C9—N2—C12 | 118.0 (2) | C3—C2—C1 | 118.8 (2) |
| N2—C9—N1 | 121.8 (2) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.6 |
| N2—C9—S1 | 125.49 (18) | C1—C2—H2 | 120.6 |
| N1—C9—S1 | 112.73 (17) | C3—C4—C5 | 118.9 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.3 (2) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.6 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.3 | C5—C4—H4 | 120.6 |
| C6—C1—H1 | 119.3 | C4—C3—C2 | 121.7 (2) |
| C9—N1—C11 | 115.4 (2) | C4—C3—Cl1 | 119.64 (19) |
| C9—N1—C7 | 122.06 (19) | C2—C3—Cl1 | 118.6 (2) |
| C11—N1—C7 | 121.9 (2) | C4—C5—C6 | 121.0 (2) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.3 (2) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 118.8 (2) | C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 122.9 (2) | C10—C11—N1 | 110.1 (2) |
| N1—C7—C8 | 110.2 (2) | C10—C11—H11A | 109.6 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 109.10 (19) | N1—C11—H11A | 109.6 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 116.0 (2) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.6 |
| N1—C7—H7 | 107.0 | N1—C11—H11B | 109.6 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 107.0 | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.1 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 107.0 | C11—C10—S1 | 109.6 (2) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 | C11—C10—H10A | 109.7 |
| C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 | S1—C10—H10A | 109.7 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 | C11—C10—H10B | 109.7 |
| C7—C8—H8C | 109.5 | S1—C10—H10B | 109.7 |
| H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 | H10A—C10—H10B | 108.2 |
| H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 | ||
| C12—N2—C9—N1 | −177.6 (2) | C1—C6—C7—C8 | 152.3 (2) |
| C12—N2—C9—S1 | 2.1 (3) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −30.3 (3) |
| C10—S1—C9—N2 | 179.1 (3) | C9—N2—C12—N3 | 177 (100) |
| C10—S1—C9—N1 | −1.1 (2) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.1 (4) |
| N2—C9—N1—C11 | −173.2 (2) | C5—C4—C3—C2 | −0.6 (4) |
| S1—C9—N1—C11 | 7.0 (3) | C5—C4—C3—Cl1 | 179.5 (2) |
| N2—C9—N1—C7 | −2.4 (4) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (4) |
| S1—C9—N1—C7 | 177.89 (18) | C1—C2—C3—Cl1 | 179.7 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.1 (4) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.6 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 176.5 (2) | C1—C6—C5—C4 | 0.2 (4) |
| C9—N1—C7—C8 | −98.3 (3) | C7—C6—C5—C4 | −177.3 (2) |
| C11—N1—C7—C8 | 72.0 (3) | C9—N1—C11—C10 | −10.7 (4) |
| C9—N1—C7—C6 | 133.2 (2) | C7—N1—C11—C10 | 178.5 (3) |
| C11—N1—C7—C6 | −56.5 (3) | N1—C11—C10—S1 | 9.2 (4) |
| C1—C6—C7—N1 | −82.5 (3) | C9—S1—C10—C11 | −4.8 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—N1 | 94.9 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C10—H10A···S1i | 0.97 | 2.87 | 3.799 (4) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y−1/2, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: NG5002).
References
- Cunico, W., Gomes, C. R. B., Wardell, S. M. S. V., Low, J. N. & Glidewell, C. (2007). Acta Cryst. C63, o411–o414. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Hense, A., Fischer, A. & Gesing, E. R. (2002). WO Patent 2002096872.
- Jeschke, P., Beck, M. E. & Kraemer, W. (2002). German Patent 10119423.
- Rigaku (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810029879/ng5002sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810029879/ng5002Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



