Abstract
In the title compound, C12H11ClN2, the dihedral angle between the benzene and pyridyl rings is 48.03 (8)°. Twists are also evident in the molecule, in particular about the Na–Cb (a = amine and b = benzene) bond [C—N—C—C = −144.79 (18)°]. In the crystal, inversion dimers linked by pairs of N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds result in the formation of eight-membered {⋯NCNH}2 synthons [or R 2 2(8) loops].
Related literature
For background to the fluorescence properties of compounds related to the title compound, see: Kawai et al. (2001 ▶); Abdullah (2005 ▶).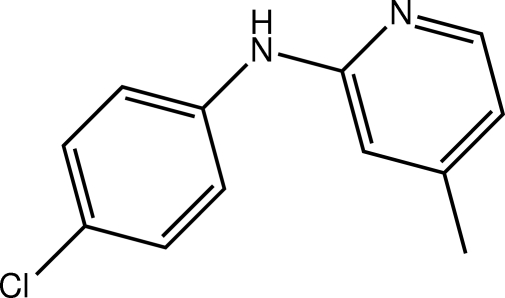
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H11ClN2
M r = 218.68
Monoclinic,
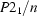
a = 15.9335 (15) Å
b = 4.0651 (4) Å
c = 17.0153 (16) Å
β = 98.755 (1)°
V = 1089.26 (18) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.32 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.30 × 0.30 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.776, T max = 0.862
9785 measured reflections
2509 independent reflections
1886 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.030
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.132
S = 1.04
2509 reflections
141 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810030138/hb5582sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810030138/hb5582Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2n⋯N1i | 0.86 (1) | 2.19 (1) | 3.029 (2) | 167 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
AZ thanks the Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia, for research grants (RG027/09AFR and PS374/2009B). The authors are also grateful to the University of Malaya for support of the crystallographic facility.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
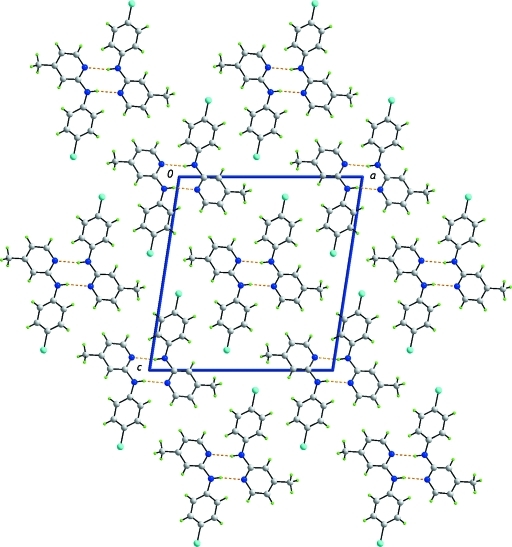
The title compound, (I), was investigated in the context of potential fluorescence properties (Kawai et al. 2001; Abdullah, 2005). The molecular structure of (I), Fig. 1, shows that the molecule is non-planar as seen in the dihedral angle of 48.03 (8) ° formed between the benzene and pyridyl rings, and in the twists about the central N–C bonds, i.e. the C7–N2–C1–N1 and C1–N2–C7–C8 torsion angles are -167.92 (17) and -144.79 (18) °, respectively. The amine-H and pyridine-N atoms are orientated in the same direction, an arrangement that facilitates the formation of N–H···N hydrogen bonds. Thus, centrosymmetrically related molecules are linked via N–H···N hydrogen bonds that lead to eight-membered {···NCNH}2 synthons, Table 1. The dimeric aggregates stack along the b axis, Fig. 2.
Experimental
2-Chloro-4-methylpyridine (1.0 ml, 1.14 mmol) was added to 4-chloroaniline (1.4543 g, 1.14 mmol) and heated for 2 h. The mixture was cooled and dissolved water (15 ml), extracted with diethyl ether (3 × 10 ml), washed with water (3 × 10 ml), and then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Evaporation of the solvent gave a gray solid. Recrystallization from ethanol yielded colourless blocks of (I).
Refinement
Carbon-bound H-atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H 0.93 to 0.96 Å) and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with Uiso(H) set to 1.2 to 1.5Uequiv(C). The N-bound H-atom was located in a difference Fourier map, and was refined with a distance restraint of N–H 0.86±0.01 Å; the Uiso value was freely refined.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing displacement ellipsoids at the 35% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Unit-cell contents shown in projection down the b axis in (I). The N–H···N hydrogen bonding is shown as orange dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C12H11ClN2 | F(000) = 456 |
| Mr = 218.68 | Dx = 1.333 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 2763 reflections |
| a = 15.9335 (15) Å | θ = 2.4–25.7° |
| b = 4.0651 (4) Å | µ = 0.32 mm−1 |
| c = 17.0153 (16) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 98.755 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1089.26 (18) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.30 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 2509 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1886 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.030 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −20→19 |
| Tmin = 0.776, Tmax = 0.862 | k = −5→5 |
| 9785 measured reflections | l = −22→20 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.132 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0689P)2 + 0.1992P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2509 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 141 parameters | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.59502 (4) | 1.02913 (16) | 0.10424 (3) | 0.0834 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.60831 (9) | 0.5290 (4) | 0.56614 (8) | 0.0495 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.57324 (9) | 0.6997 (4) | 0.43820 (9) | 0.0552 (4) | |
| H2n | 0.5222 (7) | 0.653 (5) | 0.4444 (11) | 0.061 (6)* | |
| C1 | 0.63451 (10) | 0.6751 (4) | 0.50365 (9) | 0.0439 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.66466 (12) | 0.5088 (5) | 0.63260 (11) | 0.0578 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.6472 | 0.4101 | 0.6767 | 0.069* | |
| C3 | 0.74612 (12) | 0.6230 (5) | 0.64035 (10) | 0.0570 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.7827 | 0.5985 | 0.6881 | 0.068* | |
| C4 | 0.77369 (11) | 0.7769 (4) | 0.57556 (10) | 0.0498 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.71648 (10) | 0.8019 (4) | 0.50667 (10) | 0.0461 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.7323 | 0.9030 | 0.4621 | 0.055* | |
| C6 | 0.86175 (12) | 0.9137 (6) | 0.58031 (13) | 0.0661 (5) | |
| H6A | 0.8620 | 1.0847 | 0.5414 | 0.099* | |
| H6B | 0.8999 | 0.7416 | 0.5701 | 0.099* | |
| H6C | 0.8797 | 1.0023 | 0.6325 | 0.099* | |
| C7 | 0.58319 (10) | 0.7850 (4) | 0.36041 (9) | 0.0428 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.51945 (11) | 0.9664 (4) | 0.31600 (11) | 0.0496 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.4740 | 1.0406 | 0.3396 | 0.059* | |
| C9 | 0.52239 (12) | 1.0389 (4) | 0.23723 (11) | 0.0544 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.4789 | 1.1588 | 0.2077 | 0.065* | |
| C10 | 0.59014 (12) | 0.9323 (4) | 0.20290 (10) | 0.0493 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.65418 (11) | 0.7545 (4) | 0.24569 (10) | 0.0481 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.6998 | 0.6843 | 0.2219 | 0.058* | |
| C12 | 0.65108 (10) | 0.6791 (4) | 0.32428 (10) | 0.0462 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.6946 | 0.5570 | 0.3532 | 0.055* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.1035 (5) | 0.0997 (5) | 0.0472 (3) | −0.0123 (3) | 0.0123 (3) | 0.0172 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0440 (8) | 0.0626 (9) | 0.0425 (8) | 0.0058 (6) | 0.0082 (6) | 0.0026 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0364 (8) | 0.0858 (12) | 0.0428 (8) | −0.0052 (7) | 0.0048 (6) | 0.0083 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0414 (8) | 0.0494 (9) | 0.0409 (8) | 0.0059 (7) | 0.0061 (6) | −0.0034 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0582 (11) | 0.0722 (13) | 0.0430 (9) | 0.0070 (9) | 0.0072 (8) | 0.0058 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0574 (11) | 0.0673 (11) | 0.0424 (9) | 0.0083 (9) | −0.0051 (8) | −0.0042 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0481 (9) | 0.0476 (9) | 0.0515 (10) | 0.0039 (7) | 0.0006 (7) | −0.0127 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0452 (9) | 0.0486 (9) | 0.0439 (9) | −0.0008 (7) | 0.0049 (7) | −0.0019 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0535 (11) | 0.0693 (12) | 0.0705 (13) | −0.0074 (9) | −0.0066 (9) | −0.0119 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0379 (8) | 0.0485 (9) | 0.0409 (8) | −0.0039 (7) | 0.0027 (6) | −0.0004 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0436 (9) | 0.0535 (10) | 0.0512 (10) | 0.0057 (7) | 0.0059 (7) | −0.0012 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0539 (10) | 0.0521 (10) | 0.0541 (10) | 0.0051 (8) | −0.0019 (8) | 0.0089 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0572 (10) | 0.0488 (9) | 0.0411 (8) | −0.0110 (8) | 0.0052 (7) | 0.0025 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0440 (9) | 0.0518 (10) | 0.0495 (9) | −0.0053 (7) | 0.0101 (7) | −0.0027 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0373 (8) | 0.0517 (9) | 0.0486 (9) | 0.0024 (7) | 0.0032 (7) | 0.0034 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C10 | 1.7376 (18) | C6—H6A | 0.9600 |
| N1—C2 | 1.335 (2) | C6—H6B | 0.9600 |
| N1—C1 | 1.339 (2) | C6—H6C | 0.9600 |
| N2—C1 | 1.368 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.383 (2) |
| N2—C7 | 1.400 (2) | C7—C12 | 1.391 (2) |
| N2—H2n | 0.857 (9) | C8—C9 | 1.380 (2) |
| C1—C5 | 1.398 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.366 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.373 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.396 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.367 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C11—C12 | 1.380 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.375 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C6 | 1.500 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | ||
| C2—N1—C1 | 116.69 (15) | C4—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C1—N2—C7 | 128.17 (14) | H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C1—N2—H2n | 117.2 (13) | H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C7—N2—H2n | 114.6 (13) | C8—C7—C12 | 118.64 (15) |
| N1—C1—N2 | 114.12 (15) | C8—C7—N2 | 117.97 (15) |
| N1—C1—C5 | 122.47 (15) | C12—C7—N2 | 123.27 (15) |
| N2—C1—C5 | 123.36 (15) | C9—C8—C7 | 120.91 (16) |
| N1—C2—C3 | 124.59 (18) | C9—C8—H8 | 119.5 |
| N1—C2—H2 | 117.7 | C7—C8—H8 | 119.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 117.7 | C10—C9—C8 | 119.40 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.00 (16) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.3 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.5 | C8—C9—H9 | 120.3 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.5 | C11—C10—C9 | 120.77 (16) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 117.32 (16) | C11—C10—Cl1 | 119.67 (14) |
| C5—C4—C6 | 120.81 (17) | C9—C10—Cl1 | 119.55 (14) |
| C3—C4—C6 | 121.87 (16) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.99 (16) |
| C4—C5—C1 | 119.92 (16) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.0 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.0 |
| C1—C5—H5 | 120.0 | C11—C12—C7 | 120.28 (15) |
| C4—C6—H6A | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C4—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C7—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 | ||
| C2—N1—C1—N2 | −177.70 (15) | C1—N2—C7—C8 | −144.79 (18) |
| C2—N1—C1—C5 | 0.0 (2) | C1—N2—C7—C12 | 39.4 (3) |
| C7—N2—C1—N1 | −167.92 (17) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | 0.6 (3) |
| C7—N2—C1—C5 | 14.4 (3) | N2—C7—C8—C9 | −175.42 (16) |
| C1—N1—C2—C3 | −0.7 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.8 (3) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.0 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.3 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.6 (3) | C8—C9—C10—Cl1 | −178.88 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—C6 | 178.85 (18) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.2 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C1 | −0.1 (2) | Cl1—C10—C11—C12 | 179.44 (13) |
| C6—C4—C5—C1 | −179.50 (17) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −0.4 (3) |
| N1—C1—C5—C4 | 0.4 (3) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | −0.1 (2) |
| N2—C1—C5—C4 | 177.85 (16) | N2—C7—C12—C11 | 175.77 (15) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2n···N1i | 0.86 (1) | 2.19 (1) | 3.029 (2) | 167 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB5582).
References
- Abdullah, Z. (2005). Int. J. Chem. Sci 3, 9–15.
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2009). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Kawai, M., Lee, M. J., Evans, K. O. & Norlund, T. (2001). J. Fluoresc.11, 23–32.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst.43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810030138/hb5582sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810030138/hb5582Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report