Abstract
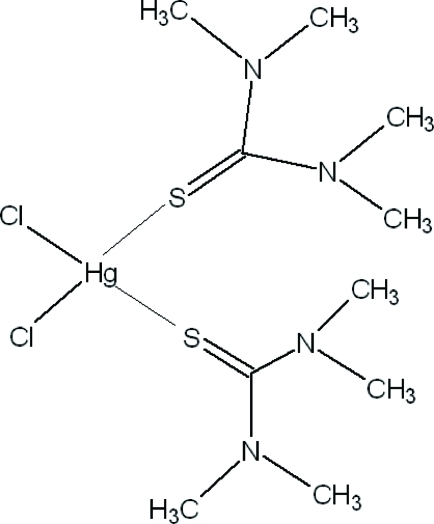
In the title compound, [HgCl2(C5H12N2S)2], the HgII atom is located on a twofold rotation axis and is bonded in a distorted tetrahedral coordination mode to two chloride ions and to two tetramethylthiourea (tmtu) molecules through their S atoms. The crystal structure is stabilized by C—H⋯N and C—H⋯S hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For background to Hg(II) complexes with thiourea ligands, see: Ahmad et al. (2009 ▶); Chieh (1977 ▶); Lobana et al. (2008 ▶); Popovic et al. (2000 ▶, 2002 ▶). The structure of the title compound is isotypic with [Cd(tmtu)2Br2] (Nawaz et al., 2010a
▶) and [Cd(tmtu)2I2] (Nawaz et al., 2010b
▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
[HgCl2(C5H12N2S)2]
M r = 535.94
Monoclinic,
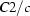
a = 18.7418 (12) Å
b = 9.5920 (6) Å
c = 13.5177 (9) Å
β = 130.834 (1)°
V = 1838.6 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 8.88 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.29 × 0.24 × 0.11 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX area detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.183, T max = 0.442
12167 measured reflections
2281 independent reflections
2103 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.031
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.020
wR(F 2) = 0.040
S = 1.07
2281 reflections
92 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.72 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.79 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2008 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810028138/wm2376sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810028138/wm2376Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Hg1—Cl1 | 2.5028 (8) |
| Hg1—S1 | 2.5329 (7) |
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2A⋯N2 | 0.96 | 2.52 | 2.849 (6) | 100 |
| C3—H3A⋯S1 | 0.96 | 2.68 | 2.996 (6) | 100 |
| C5—H5A⋯S1 | 0.96 | 2.62 | 3.024 (5) | 105 |
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, for providing the X-ray facility.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The coordination chemistry of mercury(II) complexes with thiourea type ligands has been the subject of several recent studies because of the importance of such systems as structural models in biology (Popovic et al., 2000; 2002). Mercury(II) is known form a wide variety of 1:1 and 1:2 complexes of the types LHgX2 (Popovic et al., 2002) and L2HgX2 (Ahmad et al., 2009; Chieh, 1977: Lobana et al., 2008), where X is a halide or pseudohalide, having structural arrangements entirely based on tetrahedral or pseudo-tetrahedral environments. We have recently reported the crystal structure of a Hg(CN)2 complex of N,N'-dibutylthiourea (dbtu) (Ahmad et al., 2009). Herein we report on the crystal structure of a mercury(II) chloride complex of tetramethylthiourea (tmtu), [Hg(C5H12N2S2)2Cl2], (I) .
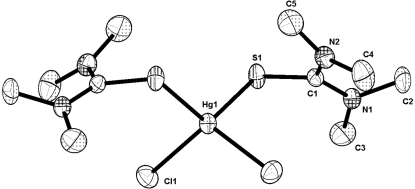
The crystal structure of (I) consists of discrete molecular species in which the mercury atom is located on a twofold rotation axis (Fig. 1) and is bonded in a distorted tetrahedral coordination mode to two chloride ions and to two tetramethylthiourea (tmtu) molecules. The Hg—S and Hg—Cl bond lengths are 2.5329 (7) and 2.5028 (8) Å, respectively. The bond angles around Hg are in the range expected for a tetrahedral coordination, with the S—Hg—S angle (120.75 (4)°) having the largest deviation from the ideal value. The main cause of this deviation is the steric interaction between the —CH3 groups. The SCN2— moiety of Tmtu is essentially planar with the C—N and C—S bond lengths corresponding to the values intermediate between single and double bonds.
The structure of the title compound is isotypic with [Cd(tmtu)2Br2] (Nawaz et al., 2010a) and [Cd(tmtu)2I2] (Nawaz et al., 2010b).
For a more detailed description of the structure, see: Nawaz et al. (2010a).
Experimental
To 0.27 g (1.0 mmol) mercury(II) chloride in 10 ml methanol was added two equivalents of tetramethylthiourea in 15 ml methanol. A clear solution was obtained that was stirred for 30 minutes. The colorless solution was filtered and the filtrate was kept at room temperature for crystallization. As a result, a white crystalline product was obtained, that was finally washed with methanol and dried.
Refinement
H atoms were placed in calculated positions with a C—H distance of 0.96 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of title compound with atomic numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. H-atoms were omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| [HgCl2(C5H12N2S)2] | F(000) = 1032 |
| Mr = 535.94 | Dx = 1.936 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 12167 reflections |
| a = 18.7418 (12) Å | θ = 2.6–28.3° |
| b = 9.5920 (6) Å | µ = 8.88 mm−1 |
| c = 13.5177 (9) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 130.834 (1)° | Colourless, plate |
| V = 1838.6 (2) Å3 | 0.29 × 0.24 × 0.11 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX area detector diffractometer | 2281 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: normal-focus sealed tube | 2103 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.031 |
| ω scans | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −24→24 |
| Tmin = 0.183, Tmax = 0.442 | k = −12→12 |
| 12167 measured reflections | l = −18→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.020 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.040 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0109P)2 + 2.5249P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.07 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 2281 reflections | Δρmax = 0.72 e Å−3 |
| 92 parameters | Δρmin = −0.79 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.00244 (8) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Hg1 | 1.0000 | 0.703186 (17) | 0.2500 | 0.04539 (7) | |
| Cl1 | 1.14323 (5) | 0.55933 (9) | 0.34397 (8) | 0.0591 (2) | |
| S1 | 1.02994 (5) | 0.83371 (9) | 0.43697 (7) | 0.04983 (18) | |
| N1 | 0.91286 (18) | 0.7622 (3) | 0.4747 (3) | 0.0482 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.84430 (16) | 0.8798 (3) | 0.2830 (2) | 0.0488 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.92029 (18) | 0.8240 (3) | 0.3933 (3) | 0.0367 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.8466 (3) | 0.8103 (4) | 0.4900 (4) | 0.0704 (10) | |
| H2A | 0.8192 | 0.8971 | 0.4446 | 0.106* | |
| H2B | 0.8793 | 0.8232 | 0.5812 | 0.106* | |
| H2C | 0.7977 | 0.7421 | 0.4542 | 0.106* | |
| C3 | 0.9842 (3) | 0.6647 (4) | 0.5756 (4) | 0.0769 (11) | |
| H3A | 1.0131 | 0.6182 | 0.5468 | 0.115* | |
| H3B | 0.9549 | 0.5970 | 0.5914 | 0.115* | |
| H3C | 1.0313 | 0.7149 | 0.6548 | 0.115* | |
| C4 | 0.7491 (2) | 0.8240 (5) | 0.2114 (4) | 0.0802 (12) | |
| H4A | 0.7531 | 0.7329 | 0.2441 | 0.120* | |
| H4B | 0.7174 | 0.8179 | 0.1200 | 0.120* | |
| H4C | 0.7144 | 0.8847 | 0.2231 | 0.120* | |
| C5 | 0.8518 (3) | 0.9798 (4) | 0.2094 (4) | 0.0774 (11) | |
| H5A | 0.9121 | 1.0250 | 0.2669 | 0.116* | |
| H5B | 0.8027 | 1.0483 | 0.1711 | 0.116* | |
| H5C | 0.8454 | 0.9323 | 0.1414 | 0.116* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Hg1 | 0.05014 (10) | 0.04849 (10) | 0.05259 (11) | 0.000 | 0.04018 (9) | 0.000 |
| Cl1 | 0.0519 (4) | 0.0599 (5) | 0.0652 (5) | 0.0126 (3) | 0.0381 (4) | 0.0065 (4) |
| S1 | 0.0386 (3) | 0.0716 (5) | 0.0453 (4) | −0.0091 (3) | 0.0300 (3) | −0.0142 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0611 (15) | 0.0488 (13) | 0.0566 (14) | 0.0005 (11) | 0.0480 (13) | 0.0002 (11) |
| N2 | 0.0439 (13) | 0.0560 (15) | 0.0465 (13) | 0.0051 (11) | 0.0295 (11) | 0.0020 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0415 (13) | 0.0364 (13) | 0.0415 (13) | −0.0023 (10) | 0.0312 (12) | −0.0061 (10) |
| C2 | 0.085 (2) | 0.081 (3) | 0.092 (3) | −0.011 (2) | 0.078 (2) | −0.014 (2) |
| C3 | 0.098 (3) | 0.070 (2) | 0.076 (2) | 0.015 (2) | 0.063 (2) | 0.024 (2) |
| C4 | 0.0387 (17) | 0.116 (3) | 0.070 (2) | −0.0013 (18) | 0.0292 (17) | −0.015 (2) |
| C5 | 0.088 (3) | 0.081 (3) | 0.069 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.054 (2) | 0.029 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Hg1—Cl1i | 2.5028 (8) | C2—H2B | 0.9600 |
| Hg1—Cl1 | 2.5028 (8) | C2—H2C | 0.9600 |
| Hg1—S1 | 2.5329 (7) | C3—H3A | 0.9600 |
| Hg1—S1i | 2.5329 (7) | C3—H3B | 0.9600 |
| S1—C1 | 1.730 (3) | C3—H3C | 0.9600 |
| N1—C1 | 1.336 (3) | C4—H4A | 0.9600 |
| N1—C2 | 1.460 (4) | C4—H4B | 0.9600 |
| N1—C3 | 1.461 (4) | C4—H4C | 0.9600 |
| N2—C1 | 1.327 (3) | C5—H5A | 0.9600 |
| N2—C5 | 1.453 (4) | C5—H5B | 0.9600 |
| N2—C4 | 1.466 (4) | C5—H5C | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9600 | ||
| Cl1i—Hg1—Cl1 | 113.08 (4) | H2A—C2—H2C | 109.5 |
| Cl1i—Hg1—S1 | 104.08 (3) | H2B—C2—H2C | 109.5 |
| Cl1—Hg1—S1 | 107.56 (3) | N1—C3—H3A | 109.5 |
| Cl1i—Hg1—S1i | 107.56 (3) | N1—C3—H3B | 109.5 |
| Cl1—Hg1—S1i | 104.08 (3) | H3A—C3—H3B | 109.5 |
| S1—Hg1—S1i | 120.75 (4) | N1—C3—H3C | 109.5 |
| C1—S1—Hg1 | 101.20 (9) | H3A—C3—H3C | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—C2 | 122.2 (3) | H3B—C3—H3C | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—C3 | 121.9 (3) | N2—C4—H4A | 109.5 |
| C2—N1—C3 | 114.4 (3) | N2—C4—H4B | 109.5 |
| C1—N2—C5 | 121.5 (3) | H4A—C4—H4B | 109.5 |
| C1—N2—C4 | 122.9 (3) | N2—C4—H4C | 109.5 |
| C5—N2—C4 | 114.2 (3) | H4A—C4—H4C | 109.5 |
| N2—C1—N1 | 119.5 (2) | H4B—C4—H4C | 109.5 |
| N2—C1—S1 | 121.6 (2) | N2—C5—H5A | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—S1 | 118.9 (2) | N2—C5—H5B | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—H2A | 109.5 | H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—H2B | 109.5 | N2—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 109.5 | H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—H2C | 109.5 | H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, y, −z+1/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2A···N2 | 0.96 | 2.52 | 2.849 (6) | 100 |
| C3—H3A···S1 | 0.96 | 2.68 | 2.996 (6) | 100 |
| C5—H5A···S1 | 0.96 | 2.62 | 3.024 (5) | 105 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: WM2376).
References
- Ahmad, S., Sadaf, H., Akkurt, M., Sharif, S. & Khan, I. U. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, m1191–m1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2008). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chieh, C. (1977). Can. J. Chem.55, 1583-1587.
- Lobana, T. S., Sharma, R., Sharma, R., Sultana, R. & Butcher, R. J. (2008). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem.634, 718–723.
- Nawaz, S., Sadaf, S., Fettouhi, M., Fazal, A. & Ahmad, S. (2010a). Acta Cryst. E66, m950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, S., Sadaf, S., Fettouhi, M., Fazal, A. & Ahmad, S. (2010b). Acta Cryst. E66, m951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Popovic, Z., Pavlovic, G., Matkovic-Calogovic, D., Soldin, Z., Rajic, M., Vikic-Topic, D. & Kovacek, D. (2000). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 306, 142–152.
- Popovic, Z., Soldin, Z. G., Pavlovic, G., Matkovic-Calogovic, D., Mrvos-Sermek, D. & Rajic, M. (2002). Struct. Chem.13, 425–436.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810028138/wm2376sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810028138/wm2376Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report