Abstract
In the title compound, C12H14O4, the dihedral angle between the benzene ring and the cyclopropyl ring is 60.3 (4)°. In the crystal structure, molecules are linked by intermolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds into chains running parallel to [101].
Related literature
For bond-length and angle data for related structures, see: Bradley et al. (1992 ▶); Fifer & White (2005 ▶). During the development of PDE4 (phosphodiesterase-4) inhibitors, roflumilast was synthesized as the positive control in the bioactivity screening and the title compound was prepared as an intermediate. For the synthesis of roflumilast, see: Bose et al. (2005 ▶).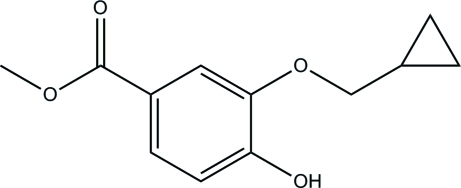
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H14O4
M r = 222.23
Monoclinic,
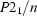
a = 9.2326 (18) Å
b = 7.4747 (15) Å
c = 16.105 (3) Å
β = 102.22 (3)°
V = 1086.3 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 113 K
0.24 × 0.22 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Saturn CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.976, T max = 0.988
7033 measured reflections
1904 independent reflections
1614 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.031
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.036
wR(F 2) = 0.100
S = 1.06
1904 reflections
148 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810026826/rz2473sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810026826/rz2473Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H3⋯O1i | 0.84 | 2.00 | 2.7808 (14) | 153 |
Symmetry code: (i) 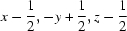 .
.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20972112), the Key Program of Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (09JCZDJC21600), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20091202110010) and the Tianjin Medical University Science Foundation (2009ky16).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Roflumilast is an effective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor (PDE4 inhibitor), which can be used in the treatment of asthma, inflammation, bronchitis, allergy and other disorders related to immune system, heart and kidney. During the development of our own PDE4 inhibitors, roflumilast was synthesized as the positive control in the bioactivity screening, and the title compound, methyl 3-(cyclopropylmethoxy)-4-hydroxybenzoate, was prepared as an intermediate. The crystallographic analysis of the title compound described herein further confirms the phenolic hydroxyl substituted position of the title compound.
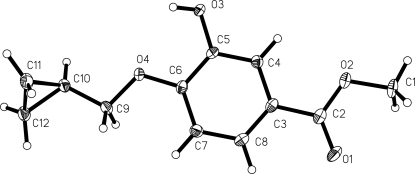
In title compound (Fig. 1), bond lengths and angles are normal and in a good agreement with those reported previously (Bradley et al., 1992; Fifer & White, 2005). Atoms O1—O4/C1—C8 are coplanar, with a maximum displacement of 0.028 (3) Å for atom O4. The dihedral angle between the benzene ring (C3—C8) and cyclopropyl ring (C10—C12) is 60.3 (4)°. In the crystal structure, molecules interact through intermolecular O—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) to form chains running parallel to the [101] direction.
Experimental
A solution of 3,4-dihydroxymethyl benzoate (1.68 g, 10 mmol) and potassium carbonate (2.76 g, 20 mmol) in acetone (50 ml) was added to a solution of cyclopropylmethyl bromide (1.35 g, 10 mmol) in acetone (50 ml). The reaction mixture was stirred at 40 ° C for 18 h, and then was filtered. The filtrate was evaporated in a rotary evaporator to get the dried crude product. Pure title compound (0.43 g, 18% yield) was obtained by flash column chromatography (Bose et al., 2005). Crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained through slow evaporation of a solution of the pure title compound in ethyl acetate/n-hexane (1:10 v/v).
Refinement
All H atoms were found on difference maps and included in the final cycles of refinement using a riding model, with C—H = 0.95–1.00 Å, O—H = 0.84 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for aryl and methylene H atoms and 1.5Ueq(C, O) for the methyl and hydroxy H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 40% probability level.
Crystal data
| C12H14O4 | F(000) = 472 |
| Mr = 222.23 | Dx = 1.359 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 3285 reflections |
| a = 9.2326 (18) Å | θ = 2.4–27.9° |
| b = 7.4747 (15) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 16.105 (3) Å | T = 113 K |
| β = 102.22 (3)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1086.3 (4) Å3 | 0.24 × 0.22 × 0.12 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn CCD area-detector diffractometer | 1904 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: rotating anode | 1614 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| confocal | Rint = 0.031 |
| Detector resolution: 7.31 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.4° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −10→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2005) | k = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.976, Tmax = 0.988 | l = −14→19 |
| 7033 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.100 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.070P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 1904 reflections | Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3 |
| 148 parameters | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.137 (12) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 1.20469 (11) | 0.31399 (12) | 0.41048 (5) | 0.0325 (3) | |
| O2 | 1.30178 (9) | 0.17490 (11) | 0.31110 (5) | 0.0271 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.89725 (9) | 0.09184 (11) | 0.06138 (5) | 0.0239 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.8217 | 0.1289 | 0.0271 | 0.036* | |
| O4 | 0.65026 (9) | 0.22515 (10) | 0.10058 (5) | 0.0201 (3) | |
| C1 | 1.44532 (14) | 0.17415 (17) | 0.36957 (8) | 0.0298 (3) | |
| H1A | 1.4785 | 0.2976 | 0.3822 | 0.045* | |
| H1B | 1.5174 | 0.1108 | 0.3436 | 0.045* | |
| H1C | 1.4368 | 0.1136 | 0.4223 | 0.045* | |
| C2 | 1.19019 (14) | 0.24965 (14) | 0.33996 (8) | 0.0216 (3) | |
| C3 | 1.04746 (14) | 0.24370 (13) | 0.27724 (7) | 0.0192 (3) | |
| C4 | 1.03704 (13) | 0.16800 (14) | 0.19666 (7) | 0.0186 (3) | |
| H4 | 1.1222 | 0.1169 | 0.1817 | 0.022* | |
| C5 | 0.90327 (13) | 0.16755 (13) | 0.13899 (7) | 0.0170 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.77661 (13) | 0.23945 (13) | 0.16152 (7) | 0.0175 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.78714 (14) | 0.31575 (15) | 0.24153 (7) | 0.0211 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.7020 | 0.3661 | 0.2568 | 0.025* | |
| C8 | 0.92302 (14) | 0.31775 (15) | 0.29883 (8) | 0.0217 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.9305 | 0.3704 | 0.3533 | 0.026* | |
| C9 | 0.51186 (13) | 0.27000 (15) | 0.12305 (7) | 0.0215 (3) | |
| H9A | 0.5102 | 0.3987 | 0.1374 | 0.026* | |
| H9B | 0.4996 | 0.1998 | 0.1732 | 0.026* | |
| C10 | 0.38989 (13) | 0.22846 (15) | 0.04938 (7) | 0.0213 (3) | |
| H10 | 0.3932 | 0.1075 | 0.0233 | 0.026* | |
| C11 | 0.32129 (13) | 0.37525 (17) | −0.00999 (8) | 0.0274 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.3624 | 0.4974 | 0.0009 | 0.033* | |
| H11B | 0.2860 | 0.3447 | −0.0707 | 0.033* | |
| C12 | 0.23882 (13) | 0.29816 (16) | 0.05244 (8) | 0.0241 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.1526 | 0.2203 | 0.0301 | 0.029* | |
| H12B | 0.2291 | 0.3730 | 0.1017 | 0.029* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0332 (6) | 0.0402 (5) | 0.0194 (5) | −0.0017 (4) | −0.0049 (4) | −0.0076 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0191 (5) | 0.0353 (5) | 0.0232 (5) | −0.0006 (3) | −0.0039 (4) | −0.0021 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0193 (5) | 0.0356 (5) | 0.0146 (4) | 0.0066 (3) | −0.0014 (3) | −0.0044 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0138 (5) | 0.0270 (5) | 0.0183 (4) | 0.0017 (3) | 0.0006 (3) | −0.0009 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0184 (7) | 0.0340 (7) | 0.0312 (7) | −0.0028 (5) | −0.0080 (6) | 0.0015 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0234 (7) | 0.0186 (6) | 0.0203 (6) | −0.0035 (4) | −0.0006 (5) | 0.0027 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0224 (7) | 0.0165 (6) | 0.0166 (6) | −0.0030 (4) | −0.0003 (5) | 0.0020 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0177 (6) | 0.0190 (6) | 0.0189 (6) | 0.0004 (4) | 0.0034 (5) | 0.0012 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0205 (6) | 0.0164 (6) | 0.0132 (6) | −0.0008 (4) | 0.0016 (5) | 0.0002 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0178 (6) | 0.0163 (6) | 0.0172 (6) | −0.0011 (4) | 0.0008 (5) | 0.0031 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0208 (7) | 0.0206 (6) | 0.0223 (6) | 0.0002 (5) | 0.0058 (5) | −0.0016 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0272 (7) | 0.0204 (6) | 0.0168 (6) | −0.0031 (5) | 0.0029 (5) | −0.0024 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0172 (7) | 0.0242 (6) | 0.0235 (6) | 0.0031 (4) | 0.0054 (5) | 0.0004 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0163 (7) | 0.0237 (6) | 0.0233 (6) | 0.0012 (4) | 0.0031 (5) | −0.0016 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0205 (7) | 0.0353 (7) | 0.0259 (7) | 0.0040 (5) | 0.0041 (5) | 0.0060 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0165 (7) | 0.0284 (6) | 0.0271 (7) | 0.0005 (5) | 0.0041 (5) | 0.0007 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C2 | 1.2144 (14) | C6—C7 | 1.3936 (17) |
| O2—C2 | 1.3389 (15) | C7—C8 | 1.3913 (18) |
| O2—C1 | 1.4541 (14) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| O3—C5 | 1.3625 (13) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O3—H3 | 0.8400 | C9—C10 | 1.4855 (16) |
| O4—C6 | 1.3604 (14) | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| O4—C9 | 1.4394 (15) | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9800 | C10—C12 | 1.4993 (17) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9800 | C10—C11 | 1.5043 (16) |
| C1—H1C | 0.9800 | C10—H10 | 1.0000 |
| C2—C3 | 1.4816 (16) | C11—C12 | 1.4988 (17) |
| C3—C8 | 1.3845 (18) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.4002 (16) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3792 (16) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.4028 (17) | ||
| C2—O2—C1 | 116.08 (9) | C3—C8—C7 | 120.58 (11) |
| C5—O3—H3 | 109.5 | C3—C8—H8 | 119.7 |
| C6—O4—C9 | 118.13 (9) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.7 |
| O2—C1—H1A | 109.5 | O4—C9—C10 | 108.28 (9) |
| O2—C1—H1B | 109.5 | O4—C9—H9A | 110.0 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C10—C9—H9A | 110.0 |
| O2—C1—H1C | 109.5 | O4—C9—H9B | 110.0 |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C10—C9—H9B | 110.0 |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.4 |
| O1—C2—O2 | 123.32 (11) | C9—C10—C12 | 117.02 (10) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 123.75 (12) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.08 (10) |
| O2—C2—C3 | 112.92 (10) | C12—C10—C11 | 59.87 (8) |
| C8—C3—C4 | 119.77 (11) | C9—C10—H10 | 116.0 |
| C8—C3—C2 | 118.84 (10) | C12—C10—H10 | 116.0 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.38 (12) | C11—C10—H10 | 116.0 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.08 (12) | C12—C11—C10 | 59.90 (8) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C12—C11—H11A | 117.8 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C10—C11—H11A | 117.8 |
| O3—C5—C4 | 118.40 (11) | C12—C11—H11B | 117.8 |
| O3—C5—C6 | 121.48 (10) | C10—C11—H11B | 117.8 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.10 (10) | H11A—C11—H11B | 114.9 |
| O4—C6—C7 | 125.49 (11) | C11—C12—C10 | 60.23 (8) |
| O4—C6—C5 | 114.69 (10) | C11—C12—H12A | 117.7 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.81 (11) | C10—C12—H12A | 117.7 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 119.63 (12) | C11—C12—H12B | 117.7 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.2 | C10—C12—H12B | 117.7 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.2 | H12A—C12—H12B | 114.9 |
| C1—O2—C2—O1 | −0.02 (15) | C4—C5—C6—O4 | −177.57 (9) |
| C1—O2—C2—C3 | −179.41 (9) | O3—C5—C6—C7 | 179.98 (10) |
| O1—C2—C3—C8 | 1.07 (16) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 1.75 (15) |
| O2—C2—C3—C8 | −179.54 (9) | O4—C6—C7—C8 | 178.38 (9) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | 179.92 (10) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.86 (16) |
| O2—C2—C3—C4 | −0.69 (14) | C4—C3—C8—C7 | 0.76 (16) |
| C8—C3—C4—C5 | 0.13 (16) | C2—C3—C8—C7 | 179.63 (10) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −178.71 (9) | C6—C7—C8—C3 | −0.39 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—O3 | −179.66 (9) | C6—O4—C9—C10 | −174.90 (9) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.38 (15) | O4—C9—C10—C12 | −168.23 (9) |
| C9—O4—C6—C7 | −8.73 (15) | O4—C9—C10—C11 | −99.07 (12) |
| C9—O4—C6—C5 | 170.55 (9) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −105.72 (12) |
| O3—C5—C6—O4 | 0.66 (14) | C9—C10—C12—C11 | 110.76 (12) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H3···O1i | 0.84 | 2.00 | 2.7808 (14) | 153 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: RZ2473).
References
- Bose, P., Sachdeva, Y. P., Rathore, R. S. & Kumar, Y. (2005). Patent WO 2005/026095 A1.
- Bradley, G., Ward, T. J., White, J. C., Coleman, J., Taylor, A. & Rhodes, K. F. (1992). J. Med. Chem.35, 1515–1520. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Fifer, N. L. & White, J. M. (2005). Org. Biomol. Chem.3, 1776–1780. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku. (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810026826/rz2473sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810026826/rz2473Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report